d3c94c7a00519f7527b9b2e76880d3d9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Benchmarking Logo here Paul G. Russell, CPP/Fellow Packaging Process Manager Hewlett-Packard Company March 2002

Overview • Process used to collect information • Analysis • Transferring into action
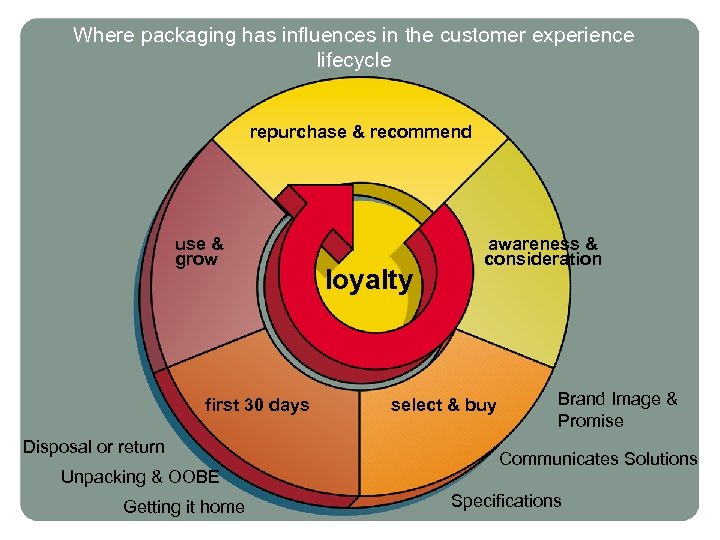
Where packaging has influences in the customer experience lifecycle repurchase & recommend use & grow first 30 days Disposal or return Unpacking & OOBE Getting it home loyalty awareness & consideration select & buy Brand Image & Promise Communicates Solutions Specifications
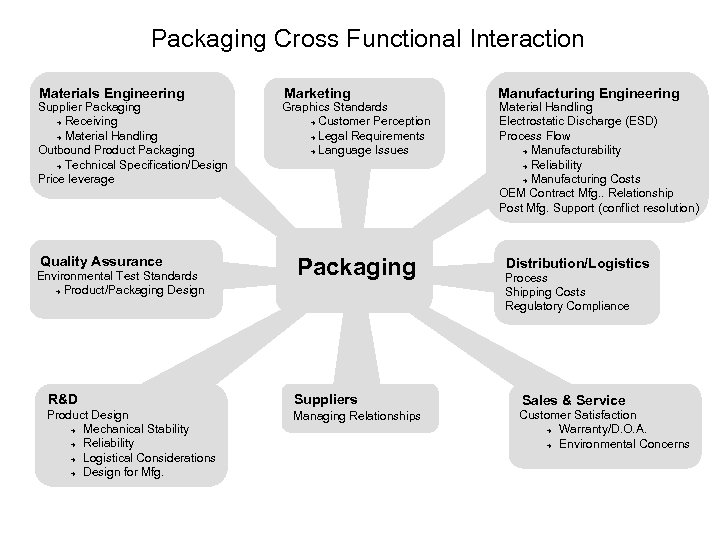
Packaging Cross Functional Interaction Materials Engineering Supplier Packaging è Receiving è Material Handling Outbound Product Packaging è Technical Specification/Design Price leverage Quality Assurance Environmental Test Standards è Product/Packaging Design Marketing Graphics Standards è Customer Perception è Legal Requirements è Language Issues Packaging R&D Suppliers Product Design è Mechanical Stability è Reliability è Logistical Considerations è Design for Mfg. Managing Relationships Manufacturing Engineering Material Handling Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Process Flow è Manufacturability è Reliability è Manufacturing Costs OEM Contract Mfg. . Relationship Post Mfg. Support (conflict resolution) Distribution/Logistics Process Shipping Costs Regulatory Compliance Sales & Service Customer Satisfaction è Warranty/D. O. A. è Environmental Concerns
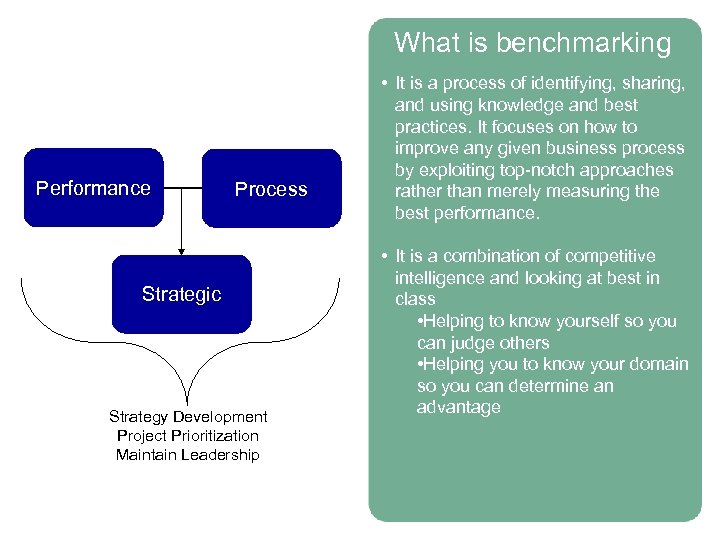
What is benchmarking Performance Process Strategic Strategy Development Project Prioritization Maintain Leadership • It is a process of identifying, sharing, and using knowledge and best practices. It focuses on how to improve any given business process by exploiting top-notch approaches rather than merely measuring the best performance. • It is a combination of competitive intelligence and looking at best in class • Helping to know yourself so you can judge others • Helping you to know your domain so you can determine an advantage
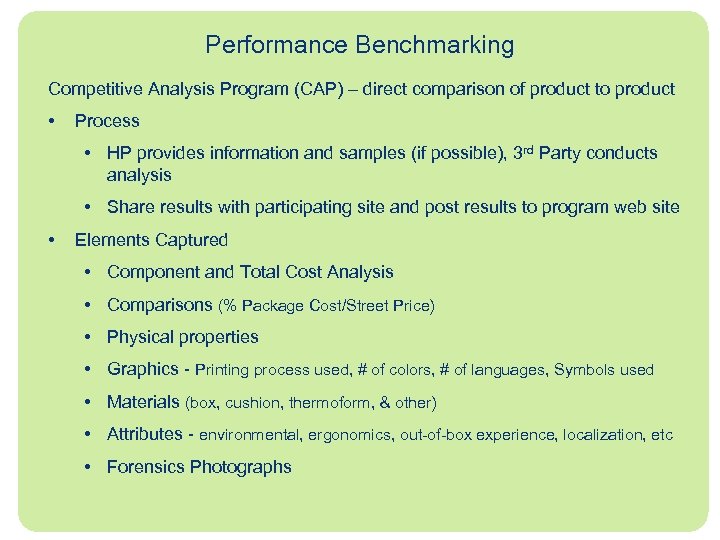
Performance Benchmarking Competitive Analysis Program (CAP) – direct comparison of product to product • Process • HP provides information and samples (if possible), 3 rd Party conducts analysis • Share results with participating site and post results to program web site • Elements Captured • Component and Total Cost Analysis • Comparisons (% Package Cost/Street Price) • Physical properties • Graphics - Printing process used, # of colors, # of languages, Symbols used • Materials (box, cushion, thermoform, & other) • Attributes - environmental, ergonomics, out-of-box experience, localization, etc • Forensics Photographs
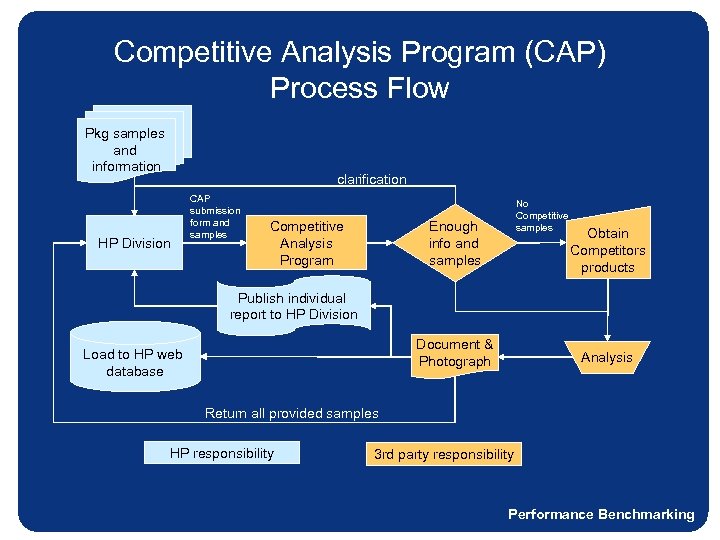
Competitive Analysis Program (CAP) Process Flow Pkg samples and information clarification HP Division CAP submission form and samples Competitive Analysis Program No Competitive samples Enough info and samples Obtain Competitors products Publish individual report to HP Division Document & Photograph Load to HP web database Analysis Return all provided samples HP responsibility 3 rd party responsibility Performance Benchmarking
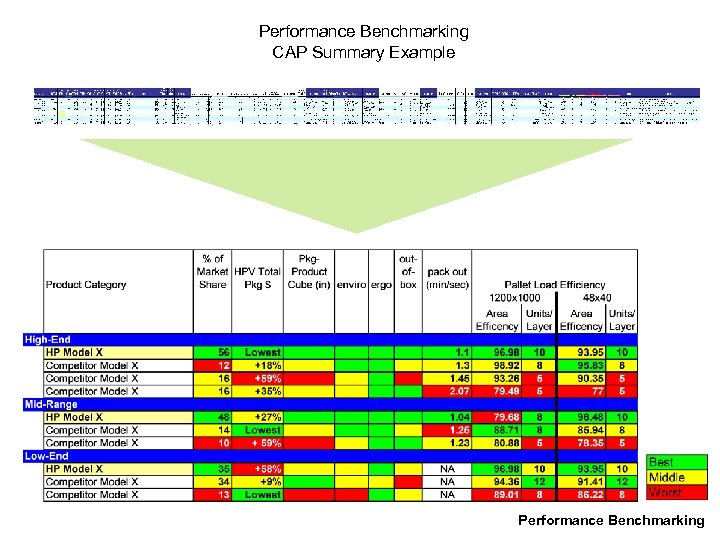
Performance Benchmarking CAP Summary Example Performance Benchmarking
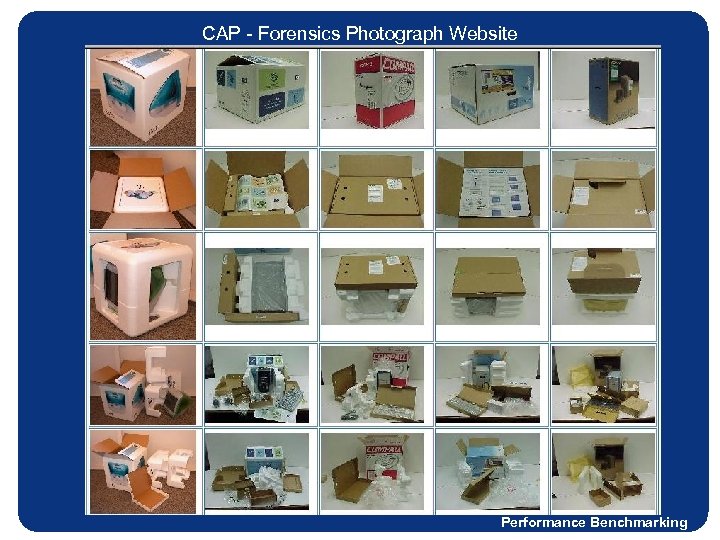

CAP - Forensics Photograph Website Performance Benchmarking

Critical Focus Areas • Product Selection • • Get agreement on how products will be selected for comparison (industrial design, price point, features, etc. ) Determining Quotable Volumes • Using generic on-going monthly volumes for costing (5 K, 10 K, 25 K) – Use "threshold volume" for generic numbers. This assumes in a competitive environment companies are all using technologies and processes that are cost effective at threshold volumes. – Map to your typical volume runs. • Highly People Dependent • • • Use product line representatives to determine what products (yours and the competition) should be benchmarked and volumes to quote. Poor upfront data leads to poor results. Check information obtained via 3 rd party with internal engineers to validate assumptions and findings. Sourcing Products • Develop clear budget expectations upfront for buying competitors products. Using a “buy & return” method is difficult and can exceed regional sourcing capabilities. • Leverage internal competitive test labs – they may already have what you want • Purchase products quickly, once products are identified, as they have a tendency to roll to the next generation Performance Benchmarking

Process Benchmarking using a survey instrument We used a questionnaire that addressed 4 major categories: • Procurement processes • Packaging processes and interactions • Marketing approach and customer value • Environmental focus For each area, subcategories of interest include: • Structure • Process • Metrics • Future (Packaging only) • Customer values (Marketing only) • E-commerce and total buy (Procurement only)
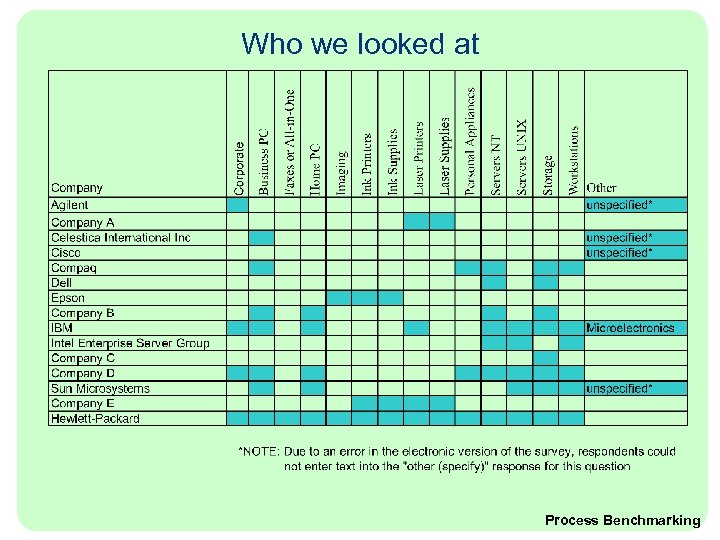
Who we looked at Process Benchmarking

Critical Focus Areas in using a Survey Instrument ? • Selecting right players and getting them to participate can be difficult • Use of a 3 rd Party is critical • Pre-established relationships are helpful (conferences and seminar) • Develop the right questions • Spend about half of your total project time designing/optimizing the questions • Sell the benefits/value to participants • Give them examples of what they’ll get for their effort (report) • Make them part of a team • Provide frequent updates • Get you hands on the raw data • Allows drill down and complete understanding of the details • Provides opportunity to validate 3 rd party analysis Process Benchmarking

Strategic Benchmarking through interviewing • Know your strategic opportunities • Identify companies, outside our sector, which are best in class in those areas • Engage companies • Why them and your intent • Non-disclosure agreements • Reciprocal • Agree on process and amount of time • Conduct interviews and document • Compile into recommended lists of projects or process modifications

Critical Focus Areas Interviewing In Teams Of Two • Each Interviewer takes a different role • Each is tracking and recording different types of information on different levels • Each can offer help when the other gets stuck • Having two interviewers is indispensable for reconstructing and interpreting later in the synthesis process Good information is: “Two people are 80% more effective in gathering information than by one person alone” • Specific attributes which are important to you • Useful for creating a clear understanding • Focused on key drivers for your business • Captures key issues/challenges • Identifies what isn’t known by the interviewee • Adds value in both directions Ask permission to follow up and/or come back Strategic Benchmarking
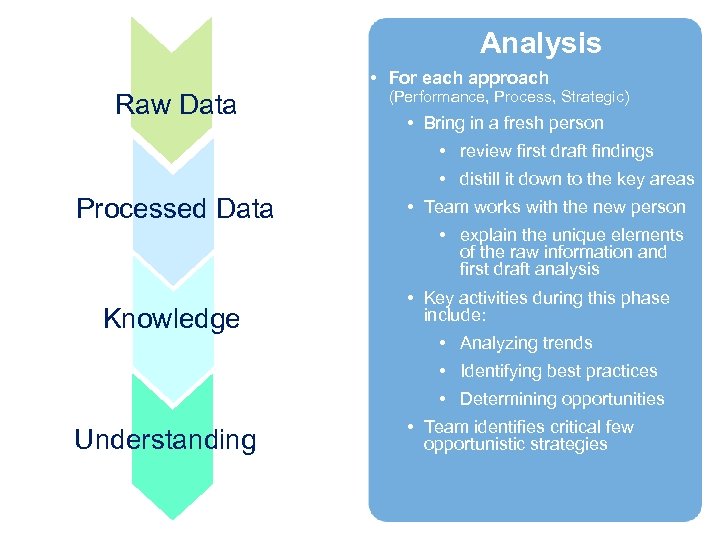
Analysis • For each approach Raw Data (Performance, Process, Strategic) • Bring in a fresh person • review first draft findings • distill it down to the key areas Processed Data • Team works with the new person • explain the unique elements of the raw information and first draft analysis Knowledge • Key activities during this phase include: • Analyzing trends • Identifying best practices • Determining opportunities Understanding • Team identifies critical few opportunistic strategies

Pulling it all together Used HP change management process • Developed a list of opportunistic strategies Tactical projects mapped into strategies • Identified key stakeholders to own each strategy Internal packaging council (control resources) Get their input and use their language • Gain acceptance and buy off • Use council meetings to track progress and keep everyone on the same page. • Develop/modify reward structure to drive the right behaviors.

Conclusion Benefits I hope came across: • Exposure to our benchmarking methodologies • How we identify key opportunities • How we transfer this knowledge into actionable strategies and projects

Thank You Any questions?
d3c94c7a00519f7527b9b2e76880d3d9.ppt