733a6ef48a4994321f8c4d9a76a731ae.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Bellringer What is the difference between Tension, Compression and Shearing?

Objective: Describe how earthquakes waves are generated and how earthquakes waves move throughout the earth.
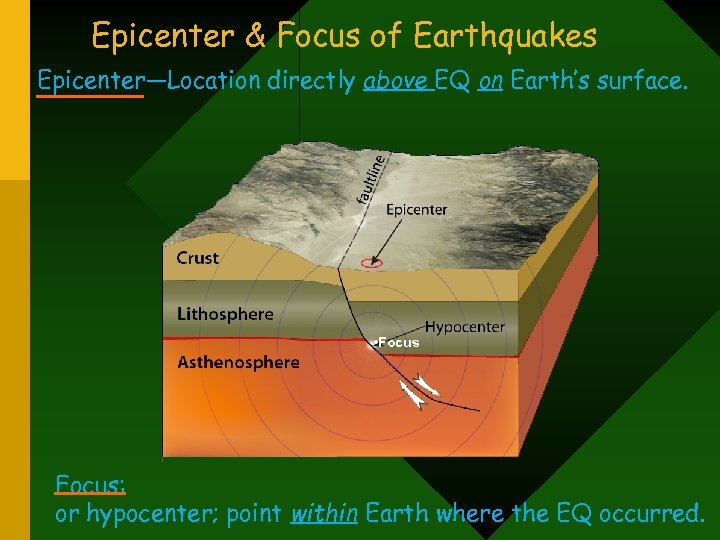
Epicenter & Focus of Earthquakes Epicenter—Location directly above EQ on Earth’s surface. • Focus: or hypocenter; point within Earth where the EQ occurred.
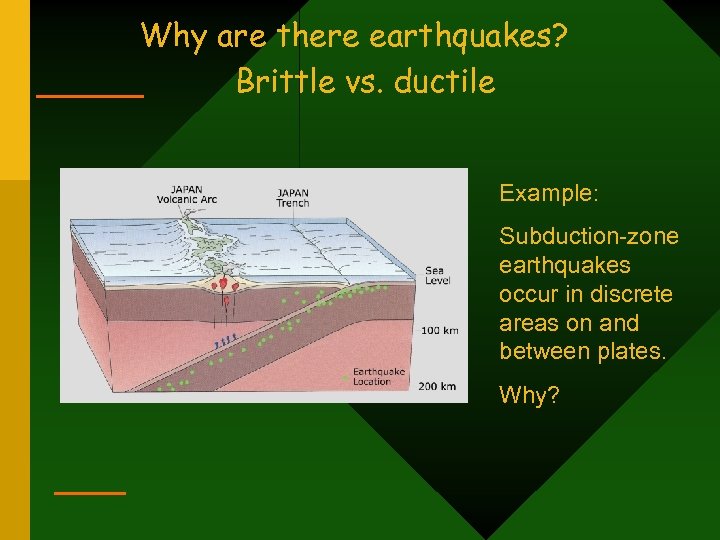
Why are there earthquakes? Brittle vs. ductile Example: Subduction-zone earthquakes occur in discrete areas on and between plates. Why?
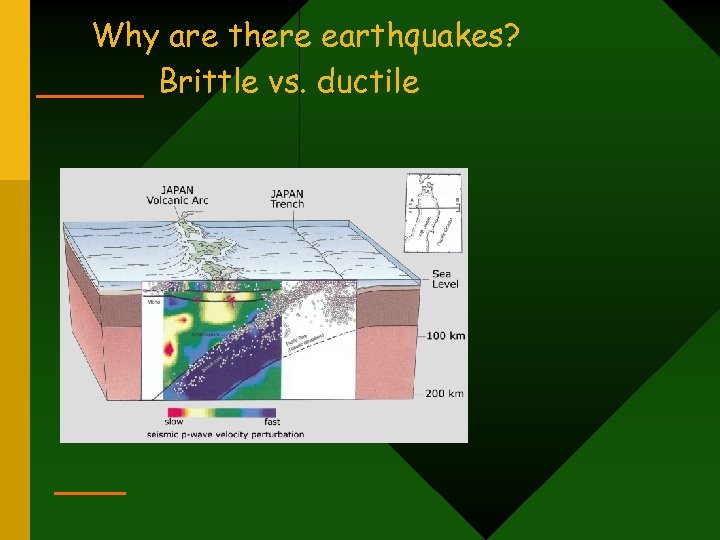
Why are there earthquakes? Brittle vs. ductile
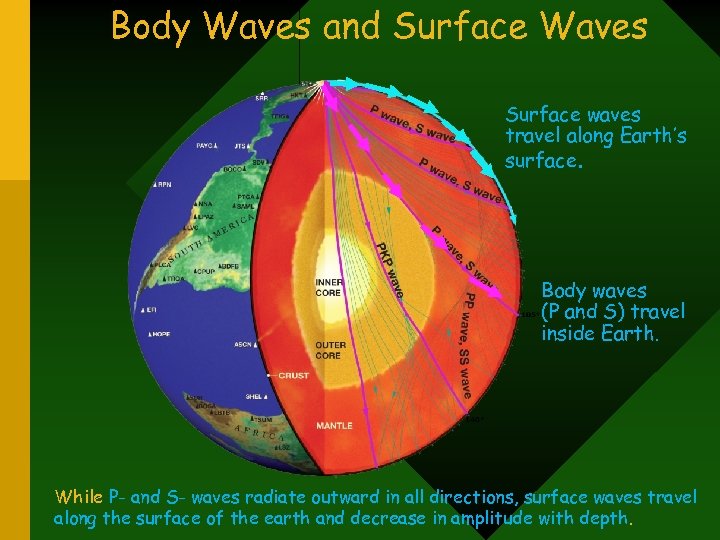
Body Waves and Surface Waves Surface waves travel along Earth’s surface. Body waves (P and S) travel inside Earth. While P- and S- waves radiate outward in all directions, surface waves travel along the surface of the earth and decrease in amplitude with depth.
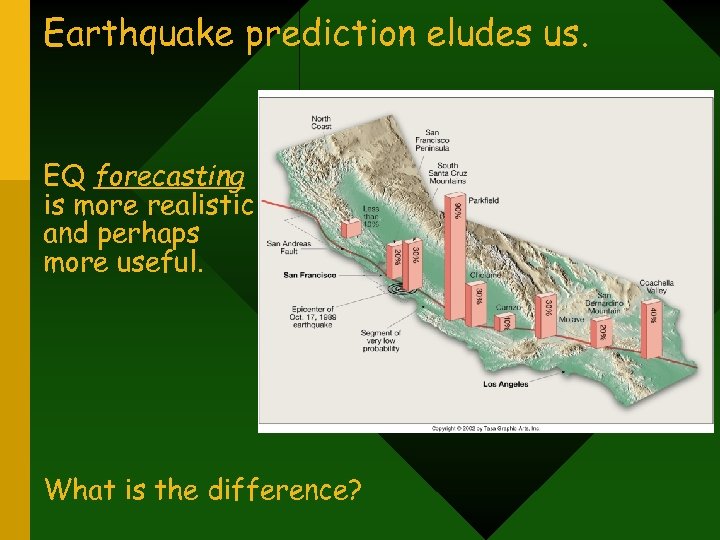
Earthquake prediction eludes us. EQ forecasting is more realistic and perhaps more useful. What is the difference?

Three Types of Stress • Tension- force that pulls on the crust resulting in the center becoming thinner • Compression- force that squeezes a rock until it folds or breaks • Shearing-force that pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions
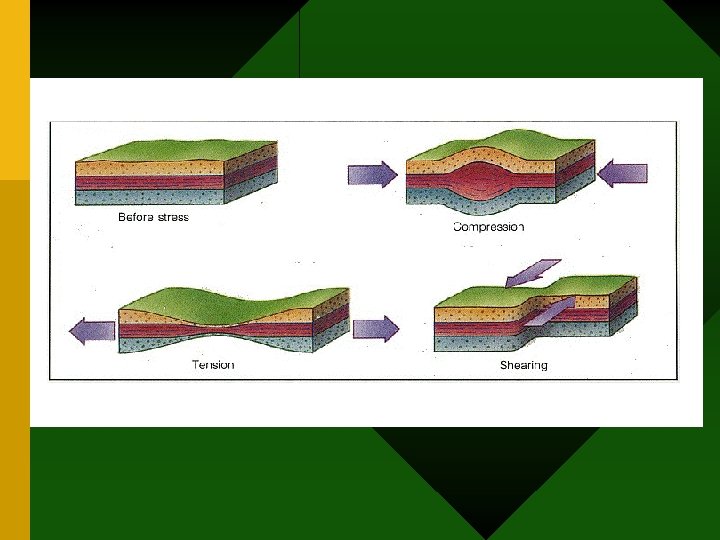

TOO Much Stress!!!! • Fault o break in the crust o slabs of crust slip past each other • Fault plane o surface that separates the two moving pieces

• Hanging Wall-rock above the fault • Footwallrock below the fault

Three Basic types of Faults • Normal o the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall • Reverse o the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall • Strike-Slip o the blocks of rock slip past each other sideways o little up or down motion o (no actual hanging wall or footwall)

Normal Fault • Caused by a tension force • Associated with diverging plates (rifts) • Example o Rio Grande rift valley in New Mexico o Jordan rift valley in Israel o The New Madrid Earthquake in Missouri
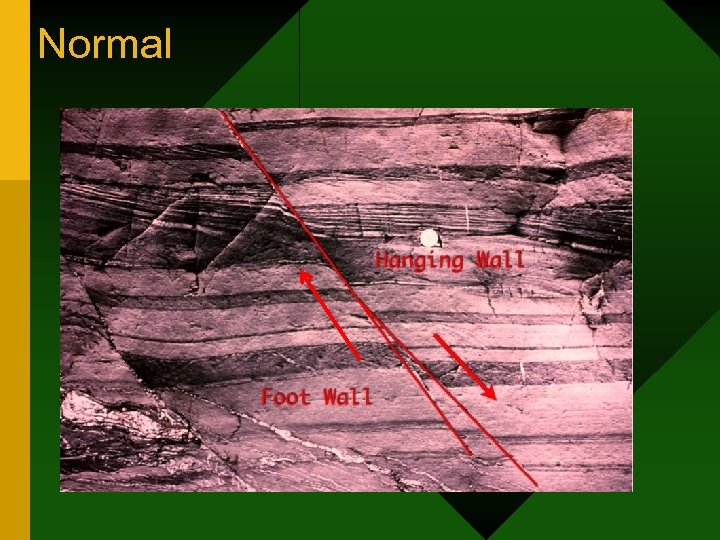
Normal

Reverse (AKA Thrust) Fault • Caused by compression forces • Allows for crustal shortening • Produced Wyoming Overthrust Belt, Glacier National Park & Appalachian Mountains • Great Alaskan Earthquake
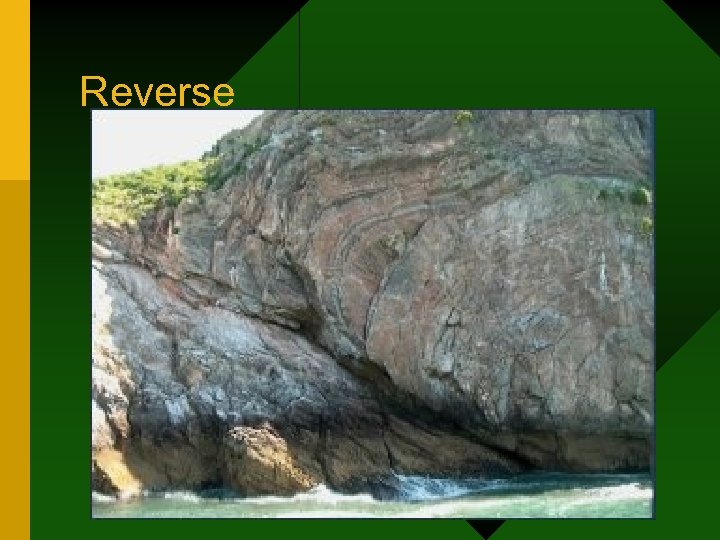

Reverse

Strike-Slip Fault • Caused by shearing motion • Associated with transform plate boundary • Example o San Andreas Fault o Produced Loma Preita Earthquake

Strike-slip

Quiz 1. What were the 3 things Wegner used to develop his theory of continental drift? 2. What did Wegner call his super continent? 3. Why wasn’t Wegner’s theory of continental drift accepted?

Quiz 4. What data did Harry Hess use that changed world opinion about Wegner’s theory? 5. What was Hess’ theory called? 6. What mechanism drives continental drift? 7. ______ refers to the deformation of the crust as a consequence of plate interaction.

Quiz 8. ____ is made of the crust and upper mantle. 9. What are the 3 types of plate boundaries? 10. What are the 3 types of faults? 11. What causes a fault? 12. What is the location directly above an earthquake on Earth’s surface?
733a6ef48a4994321f8c4d9a76a731ae.ppt