7c22f2a4ca8e04e89d18794474b4ea7f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52

Bell. Work l 1 What do you think of when you hear “Technology and Information Management” and how would you relate it to business?

Chapter 8 2 Technology and Information Management Chapter 8 Technology and © 2008 Thomson/South-Western Information Management

Lesson 8. 1 Electronic Technology Fundamentals Objectives l Describe the basic elements of computers. l Describe how the Internet provides information to users. 3

Information l l l 4 Discoveries and inventions have had major impact on society. New technologies have made dizzying changes in the way we live and work, and the pace of change is not likely to slow in the years ahead. With the invention of computers, World Wide Web, and wireless communication, simple business transactions that once took weeks of paper handling are now processed in minutes.

Information (continued) l l Whether an office is in a bank, factory, or daycare center, it must still collect, process, store, retrieve, and distribute data. The modern electronic office is an information center operated by knowledge workers – People who work with information l l 5 Ex: Clerks, supervisors, and managers at all levels are knowledge workers who handle data and information Data are the original facts and figures that businesses generate

Information (continued) l l 6 Information is data that have been processes in some meaningful way that is useful to decision makers. Technology has changed the way businesses handle data and information.

Computer Technology l l 7 The current electronic revolution started with the creation of the computer over 50 years ago The computer and the Internet plus additional electronic devices set the stage for reconstructing how businesses operate.
Computers l l 8 Computers are a machine that processes and stores data according to instructions stored in it. The machine parts and anything attached to it is called hardware. The instructions that tell the computer what to do are called software. As illustrated on the next slide, computers have three basic elements: a way to enter data, a central processing unit to act on the data, and a way to output the results.
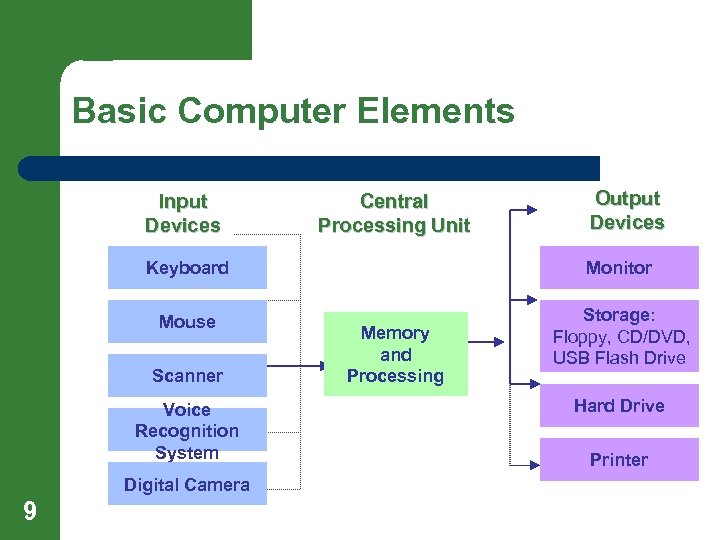
Basic Computer Elements Input Devices Central Processing Unit Output Devices Keyboard Monitor Mouse Storage: Floppy, CD/DVD, USB Flash Drive Scanner Voice Recognition System Digital Camera 9 Memory and Processing Hard Drive Printer
Computers (continued) l l l 10 Users can enter data through such devices as keyboards, voice recognition systems, and scanners. (All examples of input devices) The central processing unit receives and processes the data as directed by the software stored permanently or temporarily in the computer. Users can view data entered and processed on monitors or can print or store the data on disks, such as hard drives, floppy disks, CDs, and DVDs. (all examples of output devices)
Types of Computers l l Computers come in different sizes and serve different purposes. Types of computers – Mainframe: large computers l 11 Companies use large computers to store and retrieve vast amounts of data for the entire company

Types of Computers (continued) – Personal computer (PC) l – Personal digital assistant (PDA) l l 12 The typical office computer that most workers use is a desktop or personal computer Is a computer-like device that can be carried in a pocket and used, among other things, to send a receive messages wirelessly. PDAs usually contain calculators, an address book, a notepad for keeping ”to do” lists and a fax modem.

Types of Software l l All computer need two types of software Types of software – Operating system software is a master control program that manages the computer’s internal functions and file system. l – Application software refers to programs that perform specific tasks. l 13 Ex: Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X Ex: Word processing for creating written documents, spreadsheets for performing calculations on rows and columns of data, databases for storing related information for later retrieval, and software for creating graphics

Moore’s Law l Moore’s Law — amount of data a computer chip can process doubles about every 18 months – l According to Moore’s Law, a computer bought only one to two years ago will be obsolete this year. – 14 l This law was predicted by Gordon Moore and the law has proven to be rather accurate. As processing speed increases, high tech companies are constantly producing new and better software to take advantage of the technologies capabilities. Can be costly business expenditures

The Internet l Internet — worldwide network of linked computers that allows users to transfer data from one computer to another – l World Wide Web — access tool for the Internet; usually synonymous with Internet – 15 The internet permits businesses to work together electronically and for employees to communicate with other employees at any distance. The Web permits text plus photographs, videos and sounds to be transmitted over the Net, all with just a minimal amount of computer savvy.

Internet (continued l Hyperlink — Web page address embedded in a word, phrase, or graphic that, when clicked, transports users to that address. – – 16 Web pages usually contain hyperlinks to other sites on the Web that contain information of interest to site users. Hyperlinks often appear as colored, underscored words, but addresses can be embedded just about anywhere on the Web page.

Internet (continued) l l Much business is transacted on the Internet. The use of the letter “e” before a name means “electronic. ” – – – 17 – For example, “e-commerce” refers to a business that buy and sell to other businesses as well as businesses that sell to consumers “E-business” means businesses that buy and sell only to other businesses Retailers that sell to customers on the web are known as “e-retailers. ” Anyone who sends messages to others is using “e-mail”

Internet (continued) – 18 ”e-appliances” are consumer appliances, such as refrigerators and microwave ovens, that contain chips that allow people to use email to obtain data such as cooking, freezing, and maintenance information that can be stored in the e-appliance.

Using the Internet l l To get onto the Internet, you need a modem, an electronic device inside or outside the computer that enables it to send data over phone lines or cable. You also need an Internet Service Provider (ISP), a service that provides access to the Internet through its large computers. – 19 Ex: AOL, Net. Zero, and many regional telephone companies or cable TV companies

Using the Internet (continued) l To use the Web, you also need a browser. – – – l A search engine is a program that assists in locating information on the Net. – 20 This is a program that permits you to navigate and view Web pages. Most computers already come equipped with a browser. Ex: Microsoft Internet Explorer, Fire. Fox, Safari, Google Chrome Ex: Google

Question l An individual who wishes to access the WWW needs d) An ISP A browser A computing device All of the above – Answer: All of the above (d) a) b) c) 21

Question l The original facts and figures that business generate are called d) Data Information Figures Information points – Answer: Data (a) a) b) c) 22

Assignment Using the Internet, research information about a specific ergonomic problem related to working with electronic equipment, such as one related to radiation from computer equipment, uncomfortable chairs, or poorly designed desks. Prepare a report (1 page) of your findings. Please make sure that you have a works cited page and make sure that you are paraphrasing and not copying the information you find verbatim. 23 l If you finish early, please complete #’s 3 & 4 on l

Lesson 8. 1 Electronic Technology Fundamentals – Exit Ticket Objectives: l Describe the basic elements of computers. l Describe how the Internet provides information to users. 24

Lesson 8. 2 Managing Technology Objectives l Describe the basic technology infrastructure used by businesses. l Describe the information systems that managers use to aid in their decision making. 25

Managing Technology l l As computers became a dominant force throughout the world, organizations had to manage the computer systems as well as the computer specialists. In major organizations, the top computer executive is the chief information officer (CIO). – – 26 The CIO must posses not only knowledge about electronic equipment but also expert management skills. CIOs must keep up with new technologies and know what types of equipment to purchase to meet an organization’s specific needs.

Distributing Information l l l 27 Employees are constantly using their computers to record, process, send, store, and retrieve information. The company’s computer system must make these tasks easy and fast to perform Telecommunication (data communication) is the movement of information from one location to another electronically. – The means used for this movement may be telephone lines, cable, or satellite.

Distributing Information (continued) l l Workers need an electronic means for sharing information Local area network (LAN) — serves users in a single building or building complex. – l 28 In a LAN, a computer that stores data and application software for all PC workstations is called a file server (server) Firms with multiple locations have to send information to employees who are graphically dispersed. – Wide area network (WAN) is a network of linked computers that covers a wide geographic area.

Intranet and Extranets l Intranet — is a private company network that allows employees to share resources no matter where they are located – – – Usually the intranet even connects to the Internet, but it is sealed off from the general public to protect company information. Ex: Farm Bureau Bank Intranets enable employees to accomplish many electronic tasks. l 29 Ex: Groups of employees working on the same project can discuss, share, plan, and implement ideas without having to leave their desks.

Intranet and Extranets (continued) l Extranet — is a private network that companies use to share certain information with selected people outside the company, such as suppliers and major customers. – 30 Ex: A supplier of raw materials for a manufacturer or merchandise for a national retailer, for instance, could serve the company better by tracking the company’s daily inventory balance. When inventory get low, the supplier could deliver its goods just when the company needs them. An extranet enables the supplier to see the company’s inventory records without allowing access to other company data.

Information Security l l l 31 One of the major concerns of the CIO is information security. CIOs must do whatever is necessary to make certain that hackers cannot steal, destroy, or alter information When you buy goods on the Net, you must provide basic information, such as name, address, telephone number, and e-mail address

Information Security (continued) l l l The Federal Trade Commission and good business practice require the businesses notify buyers of their right and how personal information will be used. Companies must also take defensive strategies to protect electronic information. Firms often use firewall systems to protect information from outsiders who try to break into their network. – 32 Firewall — uses special software that screens users who enter and/or exit a network by requesting specific

Information Systems l Organizations are experiencing an information explosion. – – 33 Employees generate business data constantly. They record sales transactions, collect customer information, and track inventory. When employees key such data into their computers, the data becomes part of the company’s database. Database is a collection of data organized in a way that makes the data easy to find, update, and manage.
Information Systems (continued) l A computer system that processes data into meaningful information is called an information system. – 34 Three key types of information systems are management information systems, decision support system, and executive support systems.

Management Information System l A management information system (MIS) integrates data from various departments to make it available to help managers with day-today business operations. – – 35 An MIS deals with specific and highly structured data. For example, a sales report can show a manager where sales are slow. From this information, the manager might decide to do a special promotion for customers in this area.

Decision Support System l A decision support system (DSS) helps managers consider alternatives in making specific decisions. – – 36 For example, a DSS can help a manager determine the most efficient routes for the company’s delivery trucks. The ability to analyze “what if? ” scenarios is a key capability of a DSS.

Executive Information System l An executive information system (EIS) combines and summarizes ongoing transactions within the company to provide top-level executives with information needed to make decisions affecting the present and future goals and direction of an organization. – 37 For example, executives might use the EIS to collect outside information that affects the company, such as information regarding competitors, the state of the economy, and government policies.

Question l The movement of information from one location to another electronically is called d) A network The Internet Telecommunications Computer-based communications – Answer: Telecommunications (c) a) b) c) 38

Question l A computer that stores data and application software for all PC workstations is called a d) Mainframe Server Network Local area network – Answer: Server (b) a) b) c) 39

Assignment 40

Lesson 8. 2 Managing Technology – Exit Ticket Objectives l Describe the basic technology infrastructure used by businesses. l Describe the information systems that managers use to aid in their decision making. 41

Lesson 8. 3 The Effects of Technology on Work and Workers Objectives l Discuss types of problems that employees face in today’s high-technology organizations. l Describe technology’s present and future impact on businesses. 42

The Effects of Technology l l 43 Computers, the Internet, and other forms of electronic technology have affected our lives as consumers and as workers. Over the past several decades, computer have changed the ways individuals perform work tasks, which in turn has caused anxieties in people about job screening, about their ability to cope with new technology, and about electronic devices that may affect their health

Health Problems l l Certain complaints arise among workers who spend most of their work time using computers and other automated equipment. One type of injury that can occur from repetitive motion such as using a computer keyboard or playing video games is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). – 44 CTS occurs when the tunnel is a person’s wrist becomes too narrow for the nerves and tendons that support the hands.

Health Problems (continued) l l The science of adapting equipment to the work and health needs of people is called ergonomics. Ergonomics experts study the relationship between people and machines. – 45 For example, they work with engineers to design more comfortable chairs and produce lighting that reduces eye strain.

Changed Jobs l l 46 A major role of today’s managers id to manage change. The rapid rate at which changes occur can be disruptive. To survive, businesses must be adaptable and employees must change to meet the needs of employers. Nearly all jobs have been restructured and new jobs are evolving. – Often employees are retrained for new jobs

New Job Market l l Computerization has reduced the need for some skills and increased the need for others. Today’s employees must have technical skills as well as interpersonal skills. – 47 For example: employees who work at computer help desks assist workers who have computer problems.

The Future l l l Computer technology is now an indispensable part of business throughout the world. Businesses either move with the technology or fade away. The Internet is transforming how we work and live. – It has increased the intensity of world wide competition The cost of producing goods and services in this electronic age has led to increased competition that has lowered prices. 48 l

Question l Which of the following can be seen as health problems for knowledge workers? d) Eye strain Backaches Carpal tunnel syndrome All of the above – Answer: All of the above (d) a) b) c) 49

Question l Which of the following is not true about ergonomics? d) Ergonomics studies the relationship between people and machines Ergonomics engineers design systems that reduce strain Ergonomics includes the use of lighting. All of the above are true – Answer: All of the above are true (d) a) b) c) 50

Assingment 51

Lesson 8. 3 The Effects of Technology on Work and Workers – Exit Ticket Objectives l Discuss types of problems that employees face in today’s high-technology organizations. l Describe technology’s present and future impact on businesses. 52
7c22f2a4ca8e04e89d18794474b4ea7f.ppt