3c89435da867019ddbc594845babc73f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

Bell Ringer o What is significant about December 7, 1941? n If you don’t know, make your best educated guess.

Bell Ringer o o On a scale of 0 -4 how much do you know about WWII? What is one thing you would like to know about America’s involvement in WWII?

A World in Flames Chapter 16

America and the World o Wilson intended for democracy to be spread throughout the world n There are four major anti-democracies that arise during this time: Mussolini and Fascism in Italy, Stalin and Communism in the USSR, Hitler and Nazism in Germany, and Militarists in Japan

America and the World o Benito Mussolini returned from WWI convinced that Italy needed a stronger leader n n o In 1919 he founded the Fascist Party Fascists say that the nation is more important than the individual, that individualism makes a country weak Vladimir Lenin lead the Bolshevik Party by uniting the Russian Empire (USSR) and spreading communism throughout n When Lenin died, Joseph Stalin became dictator and killed 8 to 10 million peasants who resisted the Communist policies

America and the World o o Adolf Hitler was an anticommunist and an admirer of Mussolini Hitler fought for Germany in WWI n o The Versailles Treaty left him with hatred for the Allies and the German government who accepted the treaty The political and economic chaos lead to new political parties such as the National Socialist German Workers’ Party, or Nazi Party—which did not represent workers but rather focused on nationalism and anticommunism

America and the World o The Nazis tried to march on Munich and then try to take Germany by marching on Berlin, the capital—Hitler was arrested n o o Mein Kampf After his release from prison, Hitler changed tactics When the Great Depression struck, many Germans began voting for radical parties such as Nazis and Communists, by `32 the Nazis were the largest party in the Reichstag Many German leaders felt that if they helped Hitler into leadership, they could control him In 1933, Hitler was appointed chancellor, or prime minister

America and the World o The rise of dictatorships made Americans discouraged about the sacrifices they had made to get involved in WWI n n o o o Isolationism Nye Committee Congress passed the Neutrality Act of 1935 During the Spanish Civil War Fancisco Franco lead the Fascists against other groups such as the Communists Russia supported the communists, Hitler and Mussolini supported Franco Hitler and Mussolini signed an agreement pledging to cooperate, creating the Rome-Berlin Axis Shortly after this Japan allied itself with Germany by signing the Anti. Comintern Pact, requiring the two countries exchange info about Communist groups Together Germany, Japan and Italy became known as the Axis Powers, although they did not become allies until Sept. 1940

America and the World o With the situation in Europe getting worse, the US passed the Neutrality Act of 1937 n n Still trying to fix the depression FDR was not an isolationist He did believed that the US should try to preserve world peace FDR warned that the neutrality acts may cause us to go to war instead of keeping us out, but he did not veto them, since the public supported neutrality

America and the World o Economic hardship helped undermine the political system of Japan as well n n o Japan launched a full attack on China n n o Manchuria Military Rule FDR sent help American people wanted to stay out of it Germany- once Hitler raised his army, he was bent on conquest and many European leaders gave into his demands, hoping for peace, rather than trying to stop him

World War II Begins o o o Hitler first turned his attention to Austria and Czechoslovakia People accepted Hitler taking Austria, since the two countries had so much in common When Hitler went after Czechoslovakia, it was a democracy backed by France and the Soviet Union n To prevent war Czechoslovakia had to give up the Sudetenland

World War II Begins o Supporters of appeasement assumed that Hitler would be satisfied n o Chamberlain was buying time for the British army, since they were not prepared yet After the Munich Conference, Hitler turned his sights on Poland n n The Danzig Convinced Britain and France appeasement did not work

World War II Begins o o Germany proposed a nonaggression treaty with the Soviets, who agreed On Sept. 1, 1939 Germany invaded Poland, on Sept. 3, Britain and France declared war on Germany, officially starting WWII blitzkrieg or lightening On September 27 the Polish capital of Warsaw fell and by October 5 the Polish army was defeated

World War II Begins o o After Poland, Hitler attacked Norway and Denmark before invading France (which only took one month for Germany to control) Hitler decided to go around the Maginot Line- wall built by France after WWI- by attacking the Netherlands, Luxembourg and Belgium The Germans drove the surviving French and British troops toward the English Channel The Allies knew they needed to escape by sea, but Germany controlled all northern French ports except Dunkirk

World War II Begins o o o The evacuation left a large amount of the British’s supplies at Dunkirk On June 22, 1940 France surrendered in the same railway car in which the Germans surrendered in WWI, giving Germany most of northern France and it’s Atlantic coastline Hitler then set up a puppet government to run France

World War II Begins o o Winston Churchill took Neville Chamberlain’s place as prime minister He declared that Britain would never surrender, so Hitler ordered an attack The challenge for Germany was getting to Britain, the waters of the channel were choppy and Germany had few ships, the British air force would sink them Germany knew they had to defeat the air force to attack Britain

World War II Begins o o o In June 1940, the Luftwaffe, or German air force, attacked British shipping, then they launched an air battle to take out the British Royal Air Force The air battle lasted into the fall, became known as the Battle of Britain On Aug. 23 German bombers accidentally bombed London, causing rage by the British, who bombed Berlin the next night (the first time bombs were dropped in Berlin) The British endured the bombing by using newly developed radar and hiding in subways when they saw German planes coming The British fighters inflicted more losses than they suffered, leading to Hitler canceling the invasion of Britain

View of a V-1 rocket in flight, ca. 1944. Aircraft spotter on the roof of a building in London. St. Paul's Cathedral is in the background. "Children of an eastern suburb of London, who have been made homeless by the random bombs of the Nazi night raiders, waiting outside the wreckage of what was their home. "

Self-Reflection o o It’s quite possible that you already know a lot about the Holocaust. Rate yourself 0 -4 on how well you think you know it (0 being I’ve never heard it, 2 being I know some key terms and main ideas, 4 being you could teach it) If you are a 0 -2 write what you do know about the Holocaust and then say what you would like to know. If you are a 3 -4 what can you do to expand your understanding beyond just memorizing facts

The Holocaust o o o The Holocaust occurred when Nazis killed nearly 6 million Jews and millions of other people they considered inferior Shoah is the Hebrew word for catastrophe, is now used specifically for The Nazi campaign to exterminate Jews Once the Nazis took over, they put Hitler’s radical ideas in place, persecuted anyone who opposed them, were disabled, Gypsies, homosexuals, Slavic people and Jews

The Holocaust o o o In Sept. 1935 the Nazis put the Nuremberg Laws in place which took citizenship away from Jewish Germans and banned marriage between Jews and other Germans Two months later, they defined Jews as anyone with at least one Jewish grandparent, and denied them from voting or holding office Jews with German-sounding names had to take Jewish names, and “J” was marked on their passports Jews found it very hard to live since they were not allowed to work anywhere Many Jews refused to move during early Nazi rule, not wanting to give up the life they had made, also they thought it had to get better soon

With a partner… o Discuss the following: Why did people go along with things like the Nuremburg Laws?

The Holocaust o A young Jew killed a German diplomat in Paris as retaliation for the treatment of Jews n o o o Hitler ordered a staged attacks that made it look like a spontaneous reaction to the news The killing spree became known as Kristallnacht or “night of broken glass”—where 90 Jews died, thousands of businesses were destroyed and nearly 200 synagogues were wreaked The Gestapo, German secret police, arrested 20, 000 wealthy Jews releasing them only if they would emigrate and surrender all their possessions The Nazis also ordered that the Jewish community pay for the damage done during Kristallnacht

The Holocaust o o o Many Jews began trying to escape, including Albert Einstein and Otto Frank In 1938 the American consulate in Stuttgart, Germany received 100, 000 applications for visas Many would not receive visas to the US or any other country, leaving them stuck in Nazi territories
With a partner… o o Discuss the following: knowing what they knew then, did the United States have a moral obligation to allow German Jews to immigrate here? Why do you think they refused?

The Holocaust o o o Ships still departed with Jews crammed on them even though Mexico, Paraguay, Argentina and Costa Rica refused to allow Jews with fake documents The SS St. Louis entered Havana, Cuba with 930 refugees which Cuba refused to take; They circled off the coast of Florida trying to get the US to take them, but the US also refused They returned to Europe where most died in the Nazi’s “final solution”

The Holocaust o o o In Jan. of 1942 Nazi leaders met at the Wannsee Conference to determine the “final solution of the Jewish question” Some solutions had included shooting them and piling them in mass graves while others said to pile them in trucks and pump exhaust fumes to kill them At Wannsee the Nazis planned to put healthy people to work in concentration camps until they dropped dead and put old, young and infirm in extermination camps, where they would be gassed to death

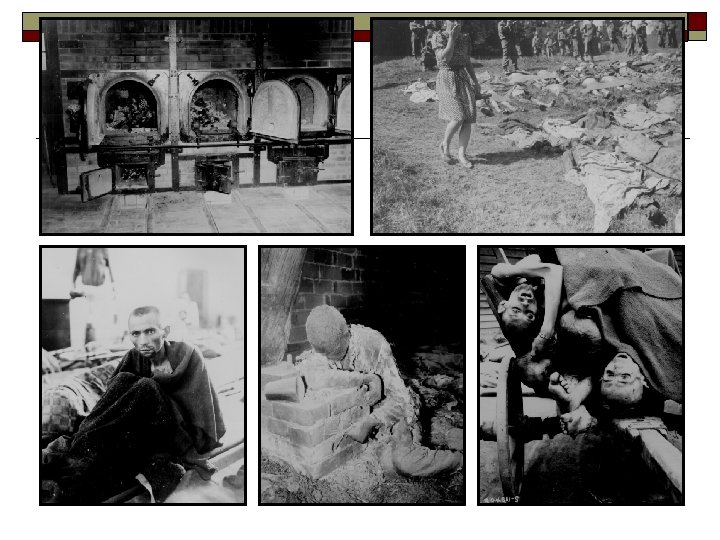
The Holocaust o o o The Nazis established their first concentration camp in 1933 Buchenwald was the first and largest but had no gas chambers, but hundreds died as a result of exhaustion and living conditions Most extermination camps were built in Poland, including Treblinka and Auschwitz alone housed 100, 000 people in 300 prison barracks; the gas chamber killed 2, 000 people at a time and killed 12, 000 people in a day An estimated 1. 6 million died there, 1. 3 million were Jews


America Enters the War o o Shortly after the war started, FDR asked Congress to revise the neutrality laws FDR gave Britain 50 old destroyers in exchange for bases, since there was no “sale” the neutrality acts didn’t apply

America Enters the War o o o The public supported FDR in his deal, showing a change in the public who now supported limited aid to the Allies Opinion was not unified though; at one extreme was Fight for Freedom Committee who urged the repeal of the Neutrality Acts and stronger action against Germany, on the other side was the America First Committee who was strict isolationists The election of 1940 showed that the public wanted to keep a president they knew

America Enters the War o o o After the election FDR stated that Britain fought for democracy and we had to help He said that the US and Britain stood for the four basic freedoms: Freedom of speech, freedom of worship, freedom from want and freedom from fear FDR came up with the Lend-Lease Act which allowed the US to lend or lease arms to any country “vital to the defense of the US”—this opened the door to send weapons to Britain By the end, the US had contributed more than 40 B in supplies to Allies This aide would help the SU as well after Hitler violated the Nazi-Soviet pact and Churchill and FDR said anyone who fights Nazism will have their support

America Enters the War o o o FDR still had to figure out how to get the arms to Britain, since the US was still neutral He declared the Western part of the Atlantic part of the Western Hemisphere, thus neutral allowing the US Navy to patrol it and reveal German sub locations In Aug. 1941 Churchill and FDR met on warships and agreed on the Atlantic Charter which said the two leaders would enforce a post war democracy for the world, nonaggression, free trade, economic advancement and freedom of the seas

America Enters the War o o o Churchill had said that FDR was going to force an incident to open hostilities with Germany He didn’t have to though; in Sept. German U-boat fired on the American destroyer Greer which lead to FDR ordering “shoot-on-sight” policy toward Germany subs Germans retaliated by sinking the Reuben James killing 115 sailors and creating a tense standoff in the North Atlantic

America Enters the War o o o FDR’s policies toward helping Britain lead to Japan’s attack on the US When WWII started, Britain had much of their Navy in the Pacific protecting its empire FDR started putting economic pressure on Japan to keep them from attacking Britain Congress passed the Export Control Act which allowed the president to restrict the sale of strategic materials (used for fighting a war) FDR blocked the sale of airplane fuel and scrap iron to Japan, who retaliated by signing a formal alliance with the Axis Powers

America Enters the War o o o FDR thought that his aid to China would have stopped Japan’s threat to Britain, but it failed so FDR froze all Japanese assets in the US and sent Mac. Arthur to the Philippines to build defense there FDR said he would lift the embargo if Japan withdrew from Indochina and made peace with China Japan decided to attack British and Dutch colonies as well as the Philippines and Pearl Harbor

America Enters the War o o o The thing that finally drew America into the war was the attack on Pearl Harbor Japan pretended to go along with negotiations, however, US Intelligence recovered Japanese communications that made it clear Japan was preparing to go to war with the US Commanders at Pearl Harbor received notice that Japan was going to attack, but Pearl Harbor was not mentioned Lack of communication lead to the devastating attack, on December 7, 1941 Japan sank or damaged 21 ships, 188 airplanes and killed 2, 403 Americans The next day FDR asked Congress for a declaration of war which the Senate voted 82 -0 and the House 388 -1 in favor of war on Japan

USS SHAW exploding during the Japanese raid on Pearl Harbor, December 7, 1941

America Enters the War o o Hitler did not have to declare war on America because of the alliance (that was only if Japan was attacked first) but he grew tired of American attacks on German subs He assumed the Japanese would easily take out the US in the Pacific He hoped that by helping Japan now, he could count on them to help with the Soviets after the US was defeated On Dec. 11, 1941 Italy and Germany declared war on the US
3c89435da867019ddbc594845babc73f.ppt