f2a1deabe3b2c0eaeaadf53a77920d98.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52

BEA WEBLOGIC COMMUNICATIONS PLATFORM™ - WLSS Overview Michael Chang – BEA Systems Inc. Global Account Architect, Technical Manager mchang@bea. com 908 -692 -5286 12/03/05

AGENDA Corporate Overview BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper BEA Web. Logic SIP Server BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform and IMS Application Use Cases Summary Appendix 2

BEA CORPORATE OVERVIEW § Leading Application Infrastructure Company § One of ten largest software companies in the world § Over 16, 500 blue-chip customers worldwide § Majority of Fortune Global 500 companies rely on BEA § Demonstrated Strength and Stability § $1 B in Sales, >$1. 7 B in cash § 22 consecutive quarters of positive cash flow § Global presence § 81 offices in 34 countries § Over 3, 000 employees § Strategic Industry Influence § More than 2100 systems integrators, independent software vendors, and application service providers § Driving innovation into standards—J 2 EE, XML, Web Services, SIP 3
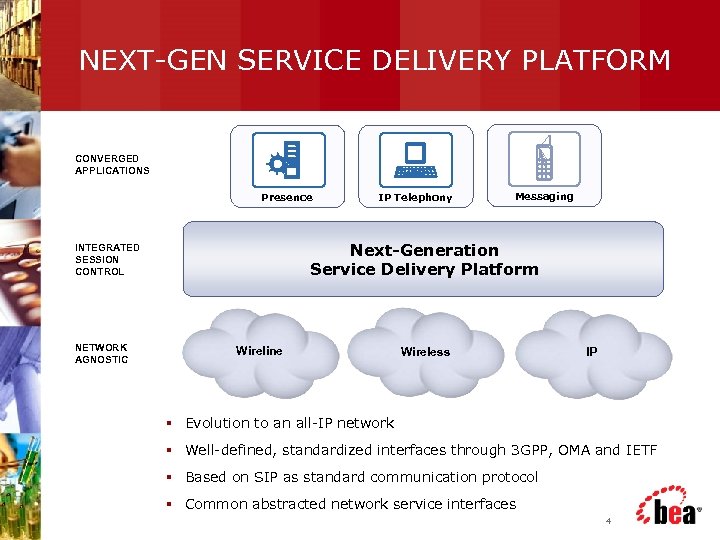
NEXT-GEN SERVICE DELIVERY PLATFORM CONVERGED APPLICATIONS Presence Messaging Next-Generation Service Delivery Platform INTEGRATED SESSION CONTROL NETWORK AGNOSTIC IP Telephony Wireline Wireless IP § Evolution to an all-IP network § Well-defined, standardized interfaces through 3 GPP, OMA and IETF § Based on SIP as standard communication protocol § Common abstracted network service interfaces 4
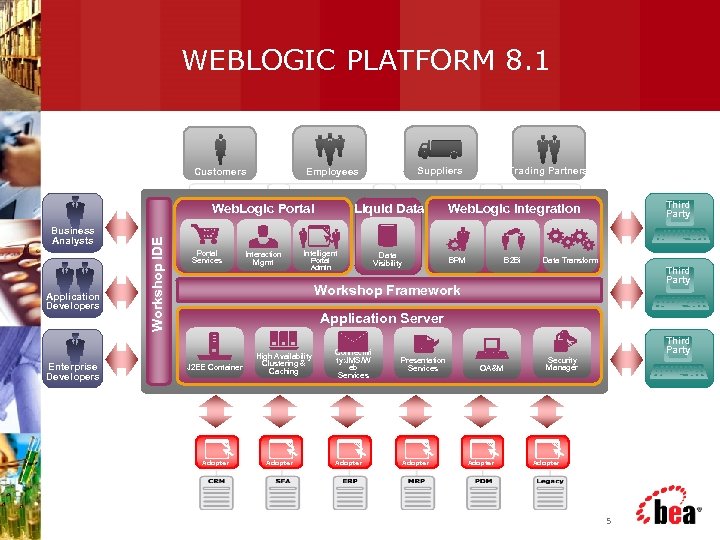
WEBLOGIC PLATFORM 8. 1 Customers Application Developers Enterprise Developers Workshop IDE Web. Logic Portal Business Analysts Portal Services Suppliers Employees Interaction Mgmt Liquid Data Intelligent Portal Admin Data Visibility Trading Partners Third Party Web. Logic Integration BPM B 2 Bi Data Transform Third Party Workshop Framework Application Server J 2 EE Container Adapter High Availability Clustering & Caching Adapter Connectivi ty: JMS/W eb Services Adapter Third Party Presentation Services Adapter OA&M Adapter Security Manager Adapter 5

AGENDA Corporate Overview BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper BEA Web. Logic SIP Server BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform and IMS Application Use Cases Summary Appendix 6

BEA IN COMMUNICATIONS § 50 of the top 50 global service providers use BEA Tuxedo or BEA Web. Logic to run their operations and services § BEA is, by far, the predominant application server vendor to telecom service providers (over 50%) § The majority of billing, provisioning, customer care, and Inventory management application providers operate within the BEA environment § The majority of leading network equipment providers utilise BEA solutions in their product suites and/or network deployments 7
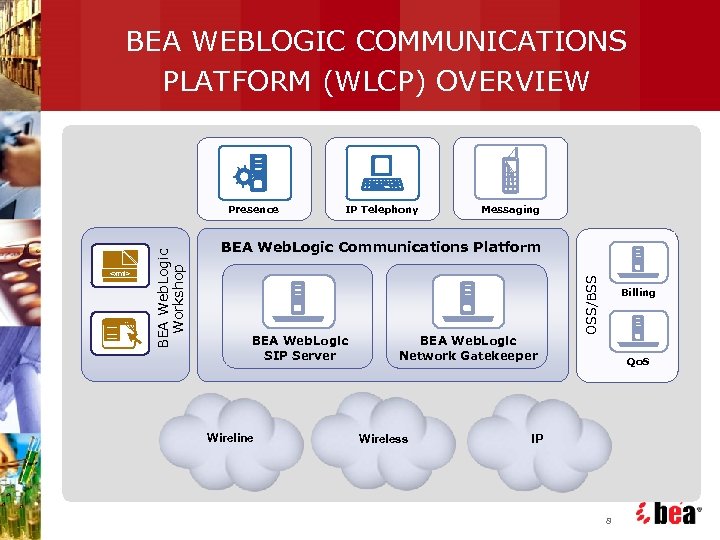
BEA WEBLOGIC COMMUNICATIONS PLATFORM (WLCP) OVERVIEW IP Telephony Messaging BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform BEA Web. Logic SIP Server Wireline BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper Wireless OSS/BSS <xml> BEA Web. Logic Workshop Presence Billing Qo. S IP 8
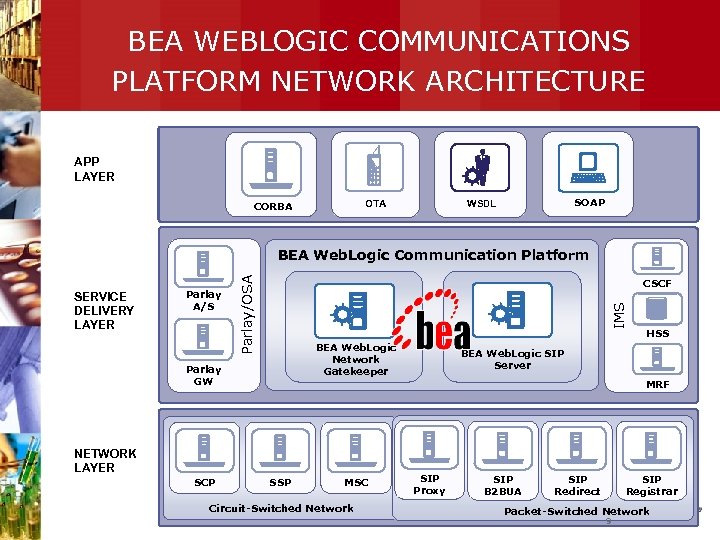
BEA WEBLOGIC COMMUNICATIONS PLATFORM NETWORK ARCHITECTURE APP LAYER OTA CORBA SOAP WSDL CSCF IMS SERVICE DELIVERY LAYER Parlay A/S Parlay/OSA BEA Web. Logic Communication Platform BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper Parlay GW BEA Web. Logic SIP Server MRF NETWORK LAYER SCP HSS SSP MSC Circuit-Switched Network SIP Proxy SIP B 2 BUA SIP Redirect SIP Registrar Packet-Switched Network 9
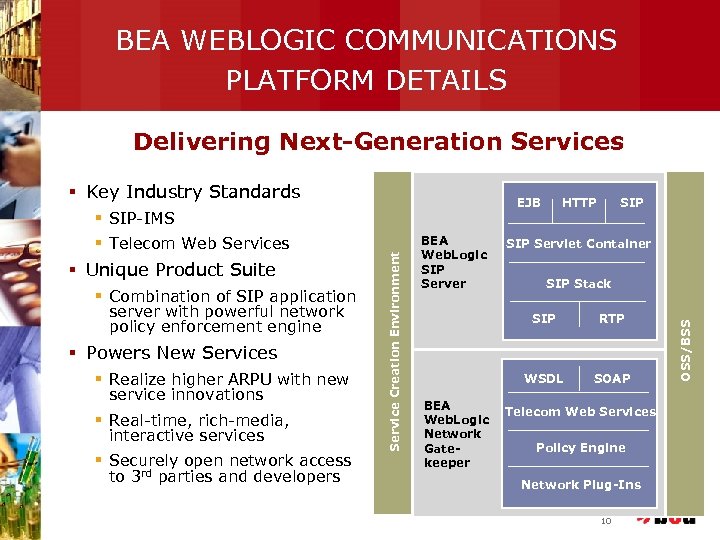
BEA WEBLOGIC COMMUNICATIONS PLATFORM DETAILS Delivering Next-Generation Services EJB § Telecom Web Services § Unique Product Suite § Combination of SIP application server with powerful network policy enforcement engine § Powers New Services § Realize higher ARPU with new service innovations § Real-time, rich-media, interactive services § Securely open network access to 3 rd parties and developers Service Creation Environment § SIP-IMS BEA Web. Logic SIP Server HTTP SIP Servlet Container SIP Stack SIP WSDL BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper RTP SOAP Telecom Web Services Policy Engine Network Plug-Ins 10 OSS/BSS § Key Industry Standards
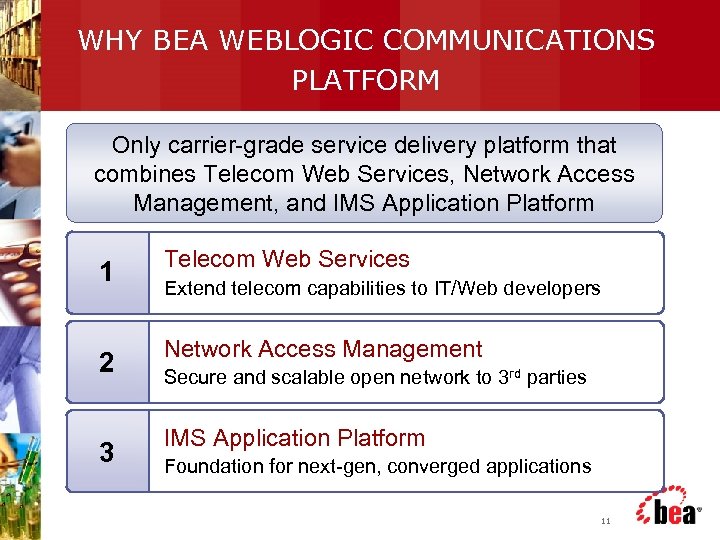
WHY BEA WEBLOGIC COMMUNICATIONS PLATFORM Only carrier-grade service delivery platform that combines Telecom Web Services, Network Access Management, and IMS Application Platform 1 2 3 Telecom Web Services Extend telecom capabilities to IT/Web developers Network Access Management Secure and scalable open network to 3 rd parties IMS Application Platform Foundation for next-gen, converged applications 11

AGENDA Corporate Overview BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper BEA Web. Logic SIP Server BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform and IMS Application Use Cases Summary Appendix 12
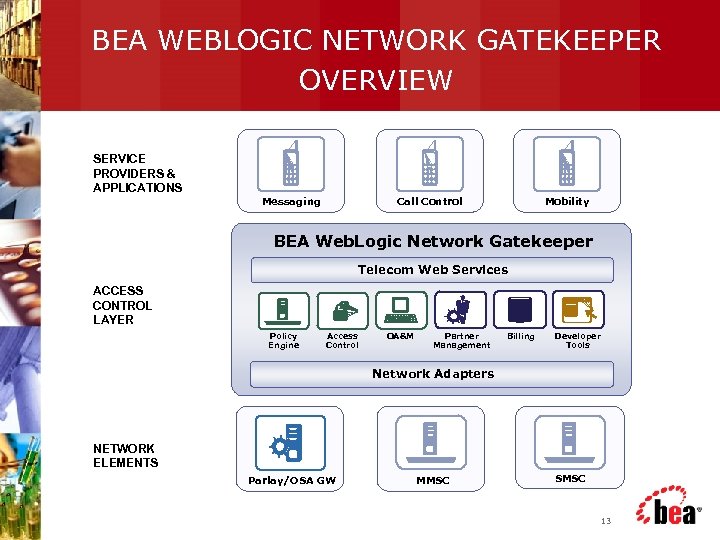
BEA WEBLOGIC NETWORK GATEKEEPER OVERVIEW SERVICE PROVIDERS & APPLICATIONS Messaging Call Control Mobility BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper Telecom Web Services ACCESS CONTROL LAYER Policy Engine Access Control OA&M Partner Management Billing Developer Tools Network Adapters NETWORK ELEMENTS Parlay/OSA GW MMSC SMSC 13

BEA WEBLOGIC NETWORK GATEKEEPER (WLNG) Enhance Partner/Customer Satisfaction with Network Service Quality and Security § What It Is § Java/Telecom Web Services-based platform to control & manage enterprise/carrier network quality § Policy enforcement engine controlling access to operator’s network from 3 rd party apps BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper Telecom Web Services § What It Does § Telecom-enable business applications § Guarantee customer/partner Qualityof-Service (Qo. S) with Service Level Agreements (SLA) enforcement Policy Engine Access Control OA&M Partner Management Network Adapters § Increase network quality by controlling network access, usage and traffic § Network traffic routing and throttling 14 Billing
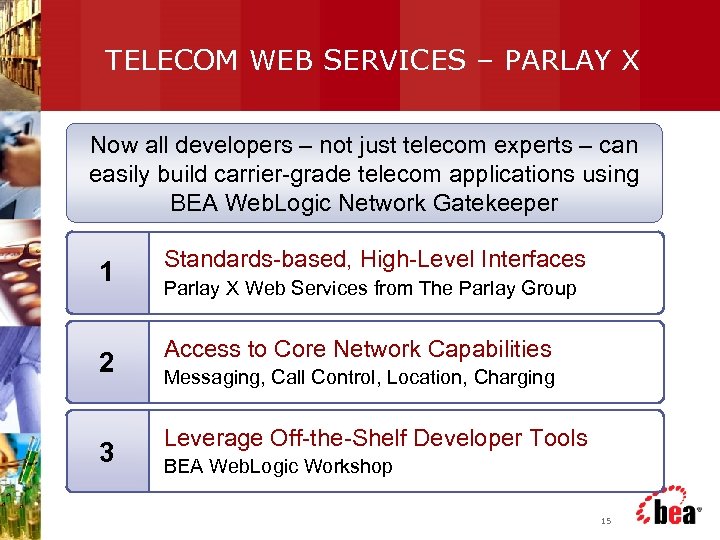
TELECOM WEB SERVICES – PARLAY X Now all developers – not just telecom experts – can easily build carrier-grade telecom applications using BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper 1 2 3 Standards-based, High-Level Interfaces Parlay X Web Services from The Parlay Group Access to Core Network Capabilities Messaging, Call Control, Location, Charging Leverage Off-the-Shelf Developer Tools BEA Web. Logic Workshop 15

AGENDA Corporate Overview BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper BEA Web. Logic SIP Server BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform and IMS Application Use Cases Summary Appendix 16

BEA WEBLOGIC SIP SERVER SERVICE PROVIDERS & APPLICATIONS Voice/Video Real-time Collaboration Real-time Voice/Video Messaging Voice/Video Over IP Push-to-Talkover-Cellular BEA Web. Logic SIP Server SERVICE DELIVERY LAYER SIP Servlet Container HTTP Servlet Container SIP HTTP BEA Web. Logic Server NETWORK ELEMENTS SIP User Agent SIP Proxy SIP Redirect SIP B 2 BUA 17
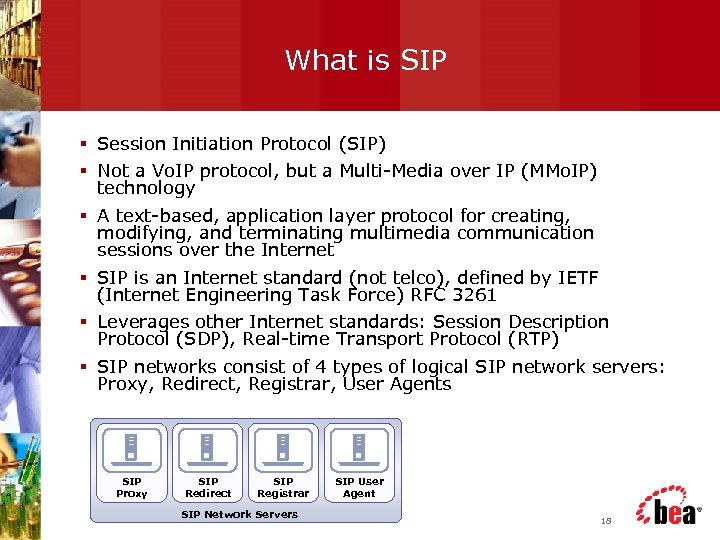
What is SIP § Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) § Not a Vo. IP protocol, but a Multi-Media over IP (MMo. IP) technology § A text-based, application layer protocol for creating, modifying, and terminating multimedia communication sessions over the Internet § SIP is an Internet standard (not telco), defined by IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) RFC 3261 § Leverages other Internet standards: Session Description Protocol (SDP), Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) § SIP networks consist of 4 types of logical SIP network servers: Proxy, Redirect, Registrar, User Agents SIP Proxy SIP Redirect SIP Registrar SIP Network Servers SIP User Agent 18

SIP Services § Realtime Multi-Media over IP (MMo. IP) Services § SIP is more than just Vo. IP. The real value is real-time, interactive multimedia services over IP. § Interactive file sharing § Multimedia messaging § Multimedia instant messaging § Multimedia conferencing § Realtime video sharing § Push-to-Talk over Cellular (Po. C) § Multimedia services over IP § Interactive multimedia gaming § Multiparty groups and communities 19

Why Session Initiation Protocol For Operators § Gain competitive advantages from new converged IT-telecom services § Standards-based open interface for multi-vendor service interoperability & integration § Leverage a wider IT developer pool § New business models with new service types § Reduces costs of creating and launching new services For End Users § Enriched peer-to-peer communications and collaboration § Real-time, interactive multimedia experiences § More productive and effective communications 20
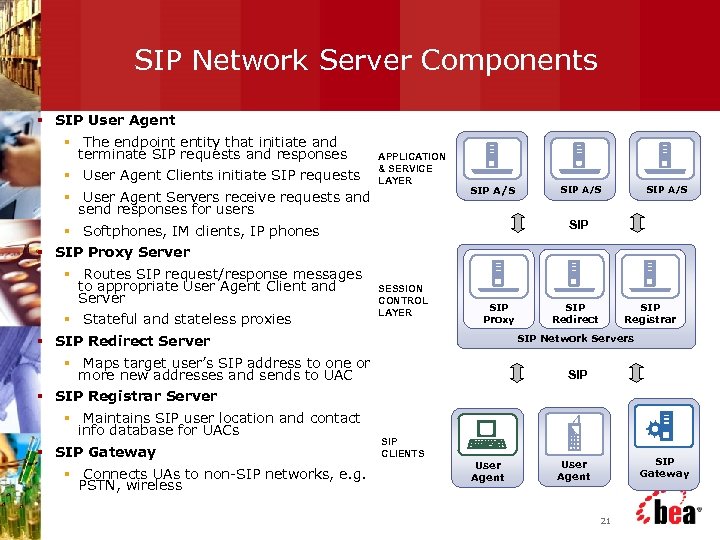
SIP Network Server Components § SIP User Agent § The endpoint entity that initiate and terminate SIP requests and responses § User Agent Clients initiate SIP requests APPLICATION & SERVICE LAYER § User Agent Servers receive requests and send responses for users SIP A/S SIP § Softphones, IM clients, IP phones § SIP Proxy Server § Routes SIP request/response messages to appropriate User Agent Client and Server § Stateful and stateless proxies SESSION CONTROL LAYER SIP Proxy SIP Redirect SIP Registrar SIP Network Servers § SIP Redirect Server § Maps target user’s SIP address to one or more new addresses and sends to UAC SIP § SIP Registrar Server § Maintains SIP user location and contact info database for UACs § SIP Gateway § Connects UAs to non-SIP networks, e. g. PSTN, wireless SIP CLIENTS User Agent SIP Gateway User Agent 21

BEA WEBLOGIC SIP SERVER (WLSS) Transform existing applications into real-time (“live”), peerto-peer, multiparty, multimedia end-user experiences § What It Is § Application server for SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) applications § Built on BEA Web. Logic Server § SIP is an Internet standard (IETF) BEA Web. Logic SIP Server § What It Does § Turns internet into “Live” communications and collaboration application § Converges IT with multimedia telephony technologies § Enables simultaneous voice, video, web, content, images, games, instant messaging, conferencing services § Why BEA SIP Servlet Container HTTP Servlet Container SIP HTTP BEA Web. Logic Server § Proven telecom industry success: Top 50 global carriers using BEA § Industry-leading, carrier-grade J 2 EE platform § Proven Servlet product & technology leadership 22
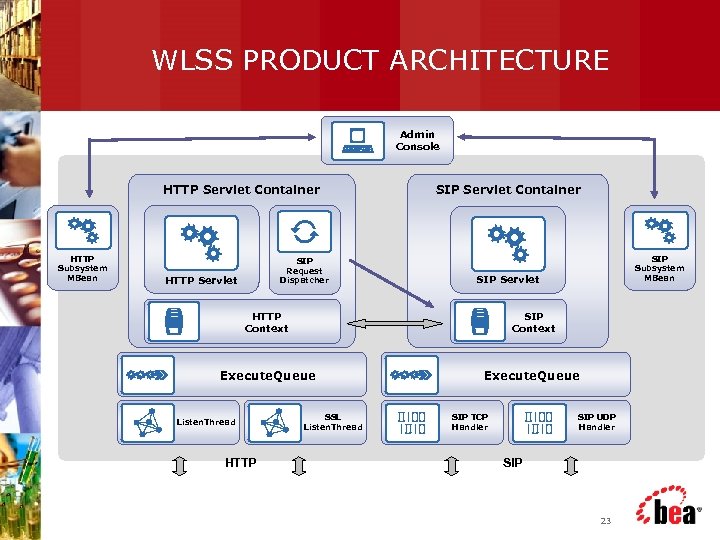
WLSS PRODUCT ARCHITECTURE Admin Console HTTP Servlet Container HTTP Subsystem MBean SIP Request Dispatcher HTTP Servlet SIP Servlet Container SIP Subsystem MBean SIP Servlet HTTP Context SIP Context Execute. Queue Listen. Thread HTTP SSL Listen. Thread SIP TCP Handler SIP UDP Handler SIP 23

Converged J 2 EE-SIP Application Server § Develop, deploy, and manage co-located SIP/HTTP servlet applications § Ease development of converged SIP-HTTP Servlet applications § HTTP events trigger SIP requests and vice versa § SIP applications have native interface to J 2 EE services without the need to use RMI or SOAP § SIP and HTTP Servlet Containers are managed as a single entity § Enhanced scalability, security, performance and manageability 24
SIP Application vs. Network Servers SIP Network Servers § Network element provided by network equipment providers (NEP) § Perform SIP session management § Not designed to be deployment and execution platforms for SIP application logic § Main use case is SIP proxy SIP Application Servers § Application element provided by ISVs § Designed to host complex, converged application logic which rely on SIP network servers for session control § Main use case is Back-to-Back User Agents (B 2 BUA) doing 3 rd Party Call Control (3 PCC) 25
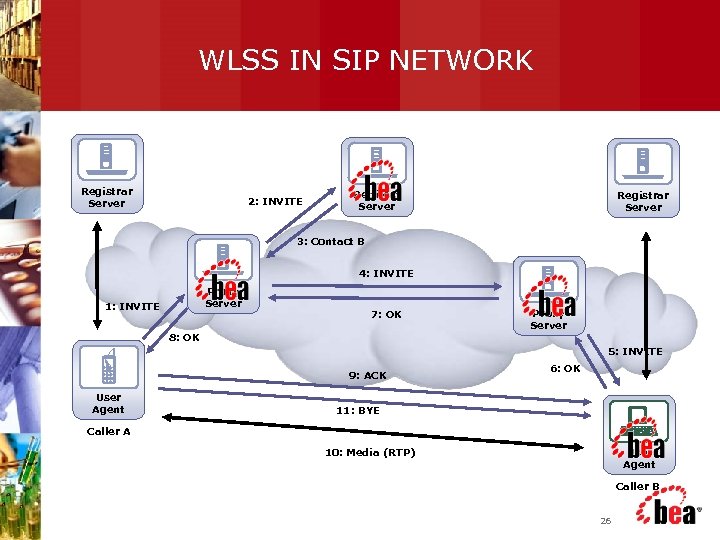
WLSS IN SIP NETWORK Registrar Server 2: INVITE Redirect Server Registrar Server 3: Contact B 4: INVITE Proxy Server 1: INVITE 7: OK Proxy Server 8: OK 5: INVITE 9: ACK User Agent 6: OK 11: BYE Caller A User Agent 10: Media (RTP) Caller B 26
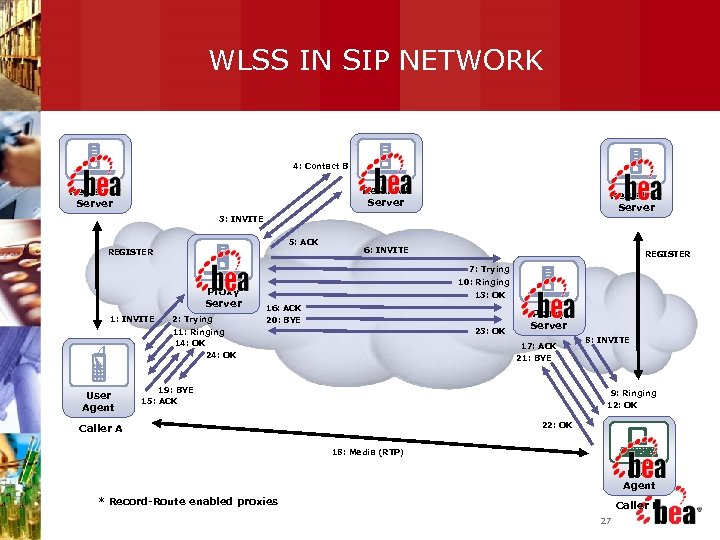
WLSS IN SIP NETWORK 4: Contact B Redirect Server Registrar Server 3: INVITE 5: ACK REGISTER 6: INVITE REGISTER 7: Trying Proxy Server 1: INVITE 2: Trying 10: Ringing 13: OK 16: ACK 20: BYE 23: OK 11: Ringing 14: OK 24: OK User Agent Proxy Server 17: ACK 21: BYE 19: BYE 15: ACK 8: INVITE 9: Ringing 12: OK 22: OK Caller A 18: Media (RTP) User Agent * Record-Route enabled proxies Caller B 27

SESSION INITIATION PROTOCOL (SIP) § Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) § Originated in mid-90 s from Columbia University by co-author of Realtime Transport Protocol (RTP) and Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP), to define a standard for Multiparty Multimedia Session Control (MMUSIC) § Developed, and standardized by the SIP Working Group of Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), published initially as RFC 2543 § IETF is the primary standards body for most Internet protocols, such as HTTP (RFC 2616), RTP, etc. § Application-level signaling protocol for initiating, modifying and terminating multimedia communication sessions over IP networks § SIP messags use text-based encoding like HTTP § Session Description Protocol (SDP) – describes media capabilities and characteristics of SIP devices § Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) – used for real-time multimedia data transport over UDP/IP § Resource Reservation Setup Protocol (RSVP) – used to establish voice quality of service § SIP Network Entities § § SIP protocol specifies 4 types of logical SIP network entities: User Agent, Proxy Server, Redirect Server, Registrar Server 3 GPP IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) § 3 GPP has chosen SIP as the standard signaling protocol for establishing multimedia communications sessions in 3 G, all-IP networks based on UMTS 28

SIP SERVLETS (JSR-116) § SIP Servlet API § Standardized thru JCP as JSR-116 (spec lead: Cisco/dynamicsoft) § Specifies execution environment for network -based SIP applications § Implemented on SIP-enabled J 2 EE app servers § Builds on J 2 EE HTTP Servlet APIs § Enables Servlets to do SIP signaling, either as a User Agent or Proxy § Specifies “converged” SIP-HTTP Servlet containers § Declarative and programmatic security § SIP Protocol Support § RFC 3261 – SIP protocol § RFC 3265 – Event Notification § RFC 3428 – SIP MESSAGE Method 29

What’s New in WLSS 2. 1 § Enhanced High Availability § Clustering support § Separation of WLSS Data Tier vs. WLSS Engine Tier § New Security Features § IETF RFC 3325: P-Asserted-Identity SIP header support § Adds support for Client-Cert authentication § Adds support for JDBC Digest Identity Assertion provider § Enhanced Configuration Flexibility § Changes to configuring load balancers, network configurations, access logging, and data tier § Enhanced Performance § Industry-leading SIP message processing and call set-up latency § Additional RFCs 30

WLSS SIP Servlet Container Overview § JSR-116 SIP Servlet API § SIP protocol stack § Implements key RFCs § SIP transaction management § SIP session management § SIP servlet lifecycle management § Shared container startup/shutdown with WLS HTTP servlet container § Concurrent execution of SIP and HTTP applications § Links HTTP/SIP servlet contexts § Management via WLS Admin Console § JMX/MBean-based § JAAS-based security via WLS § SIP/HTTP apps can share same user ID and password 31

AGENDA Corporate Overview BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper BEA Web. Logic SIP Server BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform and IMS Application Use Cases Summary Appendix 32
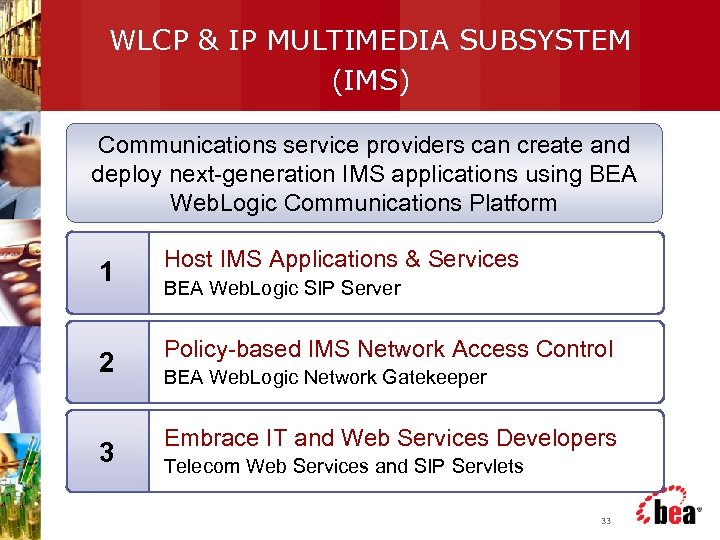
WLCP & IP MULTIMEDIA SUBSYSTEM (IMS) Communications service providers can create and deploy next-generation IMS applications using BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform 1 2 3 Host IMS Applications & Services BEA Web. Logic SIP Server Policy-based IMS Network Access Control BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper Embrace IT and Web Services Developers Telecom Web Services and SIP Servlets 33
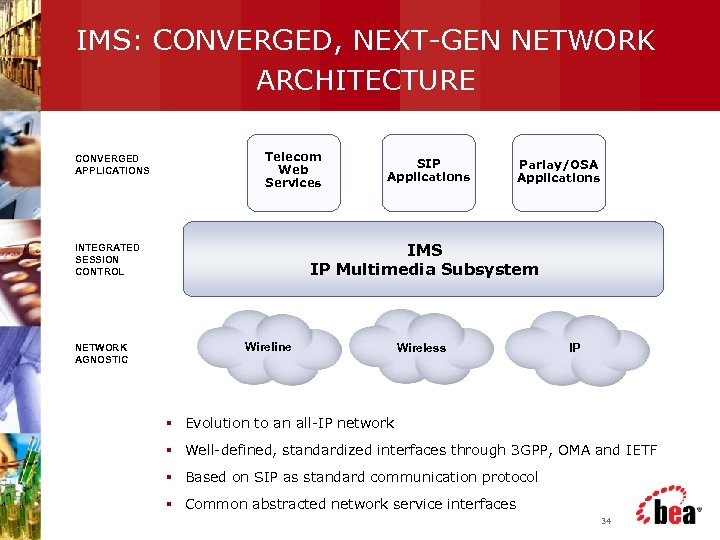
IMS: CONVERGED, NEXT-GEN NETWORK ARCHITECTURE CONVERGED APPLICATIONS Telecom Web Services Parlay/OSA Applications IMS IP Multimedia Subsystem INTEGRATED SESSION CONTROL NETWORK AGNOSTIC SIP Applications Wireline Wireless IP § Evolution to an all-IP network § Well-defined, standardized interfaces through 3 GPP, OMA and IETF § Based on SIP as standard communication protocol § Common abstracted network service interfaces 34
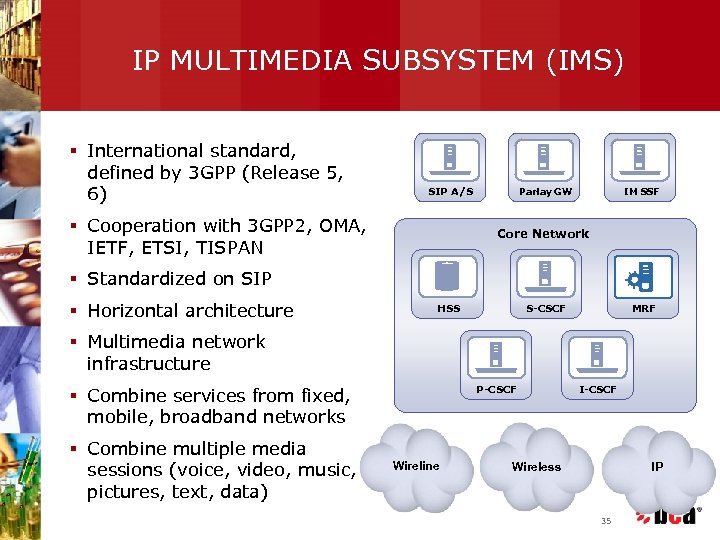
IP MULTIMEDIA SUBSYSTEM (IMS) § International standard, defined by 3 GPP (Release 5, 6) SIP A/S § Cooperation with 3 GPP 2, OMA, IETF, ETSI, TISPAN Parlay GW IM SSF Core Network § Standardized on SIP § Horizontal architecture HSS S-CSCF MRF § Multimedia network infrastructure P-CSCF § Combine services from fixed, mobile, broadband networks § Combine multiple media sessions (voice, video, music, pictures, text, data) Wireline I-CSCF Wireless IP 35

AGENDA Corporate Overview BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper BEA Web. Logic SIP Server BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform and IMS Application Use Cases Summary Appendix 36
IMS: IP Multimedia Subsystem What is IMS § Telecom industry standard for next-gen, 3 G IP-based network architecture by the 3 rd Generation Partnership Project § SIP network architecture for the telecom industry Why IMS § Supported by all major telco standards groups: wireless, wireline, cable § Levels the playing field across fixed, mobile, broadband, IP service providers § Accelerates path to increase revenue and decreased costs Key IMS Players § NEPs (Ericsson chairs IMS) § ISVs (IT and telecom) § SIs (global and regional) 37

Application Use Cases § CLICK-TO-CALL/DIAL § REAL-TIME VIDEO SHARING § INSTANT MESSAGING § VOICE-VIDEO TELEPHONY § VIDEO CONFERENCING § MULTI-CHANNEL TELEVOTING § AUTO-INITIATED CONFERENCE CALLS § RICH-MEDIA ENTERPRISE COLLABORATION § INTELLIGENT ROADSIDE ASSISTANCE § PUSH-TO-TALK OVER CELLULAR 38

AGENDA Corporate Overview BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper BEA Web. Logic SIP Server BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform and IMS Application Use Cases Summary Appendix 39

SUMMARY 1 2 3 4 Leverage Mature Industry Standards Telecom Web Services, SIP, J 2 EE. Benefit from Unique WLCP Strengths Combined value of Telecom Web Services, Network Access Management & IMS Application Platform. Launch New Services Now! Use BEA Web. Logic SIP Server and BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper for next-gen service delivery. Monetize 3 rd Party Providers Now! Use BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper to securely, and scalably manage 3 rd party network access. 40

AGENDA Corporate Overview BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform BEA Web. Logic Network Gatekeeper BEA Web. Logic SIP Server BEA Web. Logic Communications Platform and IMS Application Use Cases Summary Appendix 41

CLICK-TO-CALL/DIAL § Ability to initiate a telephony session from a hyperlink from a Web browser or desktop application § Initiate calls from MS Outlook-like contact lists via click from a PC, PDA, mobile device § Calls are routed via SIP to other IP communication end-points, or routed from the IP network to circuit-switched network devices via PSTN-IP gateways § Enables addition of presence, availability and location data for higher value-add § Can be embedded into Instant Messaging and other Web-based portal applications to “call-enable” existing applications § Sample use cases: § Web-based directory service § Call sales/support reps directly from the corporate website § Call sales/marketing reps from direct marketing e-mails 42

REAL-TIME VIDEO SHARING § Peer-to-peer, real-time, multimedia video streaming service. § Can be offered over full packet-switched networks, or as “combo” service, combining both circuit and packet switched networks. § “Combinational” use case – Send video/pictures over packet network during a circuit-switched phone call. § Enriches the end-user experience by exchanging pictures, video clips, or live video streams during a phone call. § Operators can leverage PSTN infrastructure, investments, telephony performance, user familiarity, and expertise. § Video content is delivered, and consumed, in near real-time, with marginal latency. § Provides live end-user experiences of “being there” and “sharing the moment”. § Spirit of “Live” – Even when sharing stored video clips, “liveness” is maintained since an on-going voice conversation is maintained. 43

INSTANT MESSAGING § Allow end-users to send/receive messages instantly § Messages can contain any MIME-type media content § Text § Images § Audio/Video § Application data § SIP and IMS bring instant messaging to mobile devices without interoperability issues § Provides store & forward capabilities § Presence-based intelligent messaging forwarding § Support message delivery to non-SIP devices, such as MMS endpoints 44

VOICE INSTANT MESSAGING § Form of instant messaging, but instead of sending text, it’s using audio files to send voice messaging. § End-users can record voice messages instantly using applications in their phones, or use existing audio files stored on their devices. § Like IM, voice messages can be sent to one or more recipients. § Use-case scenarios § Impulse Messaging – Spontaneous urge to be verbal § Fast-n-Easy – Talking is faster and easier than typing in text using a phone/PDA keyboard § Individualism – Voice communication is more natural, personal, and individualistic, including singing 45

VOICE-VIDEO TELEPHONY § Enables users to add video to an existing voice call, depending on the multimedia capabilities of the other party’s communication device § SIP enables real-time, peer-to-peer, 1 -1, and multiparty voice and video telephony over the IP network § SIP-PSTN interoperability allows IP-based voice/video telephony sessions with circuit-switched video communication sessions 46

VIDEO CONFERENCING § Enables real-time addition of other video call participants into an existing 1 -1 video call session § Extends point-to-point video calls to multi-point video sessions § A video conference bridge links together multiple point-topoint video calls into a single video conference § Video telephony connections are established from the endpoint terminasl to the video conference bridge 47

MULTI-CHANNEL TELEVOTING § Extends televoting systems to end-users using different access networks, e. g. fixed, wireless, IP, cable, etc. § Allows existing televoting applications to tally votes from multiple voting mechanisms, such as IVR, SMS, WAP, MMS, etc. § Voting application can incorporate location-based network data to provide real-time, region-specific, voting results 48

AUTO-INITIATED CONFERENCE CALLS § Network initiates pre-scheduled conference call, based on the network availability presence data of each core participant for a scheduled conference call, and dials-in each user § Application can leverage plug-ins to enterprise calendaring systems (MS Outlook), and Parlay X Web Services network interfaces § Removes the end-user inconvenience of having to navigate through conference call announcement menus, and remembering meeting passwords § Encourages increased usage of auto-conferencing services § Provides Network Operators a branding opportunity on end-user desktops and devices 49

RICH-MEDIA ENTERPRISE COLLABORATION § Add voice, video, presence, location capabilities to existing enterprise collaboration applications and portals § Extends existing MS Outlook/Lotus Workplace-like enterprise collaboration applications with real-time “live”, voice-video-web-email-file sharing-IM-presence capabilities § Extends B 2 E-B 2 B-B 2 E, intranet/extranet/partnernet portals with new real-time, collaboration features enabling new business processes and dynamics 50

INTELLIGENT ROADSIDE ASSISTANCE § Enables end-users in emergency situations to dynamically find & communicate directly with the nearest, available Auto Service Provider § End-users interface into an Auto Service Finder application using voice/click/dial-initiated Emergency Assistance number § Leverages Parlay X-based Telecom Web Services § User Location Web Service - Determines end-user proximity to nearest Auto Service Provider § User Status Web Service – Determines availability of end-user and nearest Auto Service Vehicle § Call Routing Web Service – Establishes call between end-user with nearest, available Auto Service Vehicle operator 51

PUSH-TO-TALK OVER CELLULAR § Provides direct 1 -1/1 -many voice communication services over 2. 5 G/3 G cellular networks e. g. GPRS/EDGE, 1 x. RTT, 1 x. Ev. DO § Brings two-way communications to regular cellular phones § Enables end-users to communicate 1 -1, or 1 -many § Extremely short call set-up times (no need to dial; just push) § Enables new business opportunities using real-time, always-on, “walkie-talkie” voice communications § Efficient usage of cellular access and radio network resources § Network resources used only for one-way during talk spurt § Not use two-way network resources for entire call session § Leverage existing 2. 5 G/3 G cellular networks § Enable faster service rollout § Doesn’t require separate network infrastructure investments § Provide natural growth path to WCDMA 52
f2a1deabe3b2c0eaeaadf53a77920d98.ppt