TB prevention.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 9


BCG Vaccination TB Prevention

BCG Vaccination in Children Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is a live attenuated vaccine derived from Mycobacterium bovis The WHO Expanded Programme on Immunization (EPI) recommends BCG vaccination as soon as possible after birth in countries with a high TB prevalence
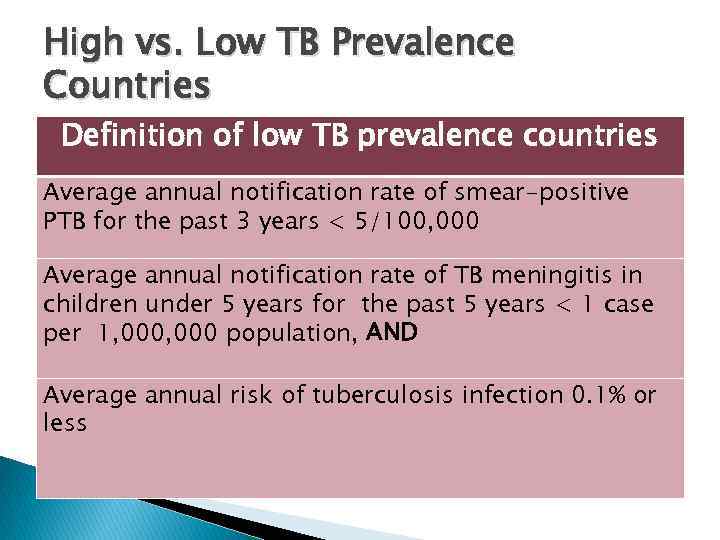
High vs. Low TB Prevalence Countries Definition of low TB prevalence countries Average annual notification rate of smear-positive PTB for the past 3 years < 5/100, 000 Average annual notification rate of TB meningitis in children under 5 years for the past 5 years < 1 case per 1, 000 population, AND Average annual risk of tuberculosis infection 0. 1% or less

BCG Vaccination in Children (2) Although there have been several reports of disseminated BCG infection in HIVinfected individuals, BCG appears to be safe in the vast majority of cases There is a wide range of reported BCG efficacy in published studies to date (080%) ◦ It is generally accepted that BCG vaccination provides protection against the more severe types of TB

BCG Vaccination: WHO Recommendations on BCG: In countries with a high TB prevalence (irrespective of the HIV prevalence), the benefits of BCG vaccination outweigh the risks Recommend a policy of routine BCG immunization (single dose) for all neonates unless there is known primary (e. g. , congenital) immunodeficiency

BCG Vaccination: WHO Recommendations on BCG: WHO does not recommend BCG vaccination for: ◦ Children with symptomatic HIV infection ◦ HIV-positive children who are at minimal risk for infection with M. tuberculosis ◦ Children with known primary (e. g. , congenital) immunodeficiency WHO does recommend BCG vaccination for: ◦ Asymptomatic children with HIV who are living in a country with a high prevalence of TB

BCG Vaccination: EPI The EPI Unit in the Caribbean recommendations differ from WHO regarding BCG and HIV infection. The recommendations are as follows: ◦ HIV exposed infant–should not receive BCG until their HIV status is known. If the baby tests HIVnegative, then the baby can receive BCG vaccine ◦ HIV infected infant – The child should not receive BCG vaccine regardless of the status of the baby (symptomatic or asymptomatic)

BCG: Policy Considerations There are several factors that must be considered when deciding on which of the various recommendations is most appropriate for country implementation: ◦ National PMTCT programmes are being scaled up and there are less infants being born with HIV infection ◦ The capacity for earlier infant diagnosis is increasing ◦ TB prevalence in the country
TB prevention.pptx