2016, May 27th, Evolution.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 102

Battle of Evolution vs Creationism

Jean-Baptiste Lamarck Philosophie Zoologique, 1809


1858. Darwin and Wallace produce a joint book called ‘On the Tendency of Species to form Varieties; and on the Perpetuation of Varieties and Species by Natural Means of Selection’,

1859. On the Origin of Species Darwin formulates the scientific theory of evolution by natural selection

1860 Oxford Huxley– Wilberforce evolution debate

Watchmaker analogy Used as a creationist argument, that every complicated mechanism has to have a designer


Evolution of Creationism

Henry M. Morris and Young Earth Creationism In 1961, Morris coauthored “The Genesis Flood”. The prominent difference is that YEC believes that God created the Earth in six 24 -hour days between 5, 700 and 10, 000 years ago

Gap creationism (19 th century) there was a gap of time (some billion years) between creation of Earth and creation of Adam and Eve

Day-age creationism Six days of creation are not ordinary 24 hour days, but some billion years each.
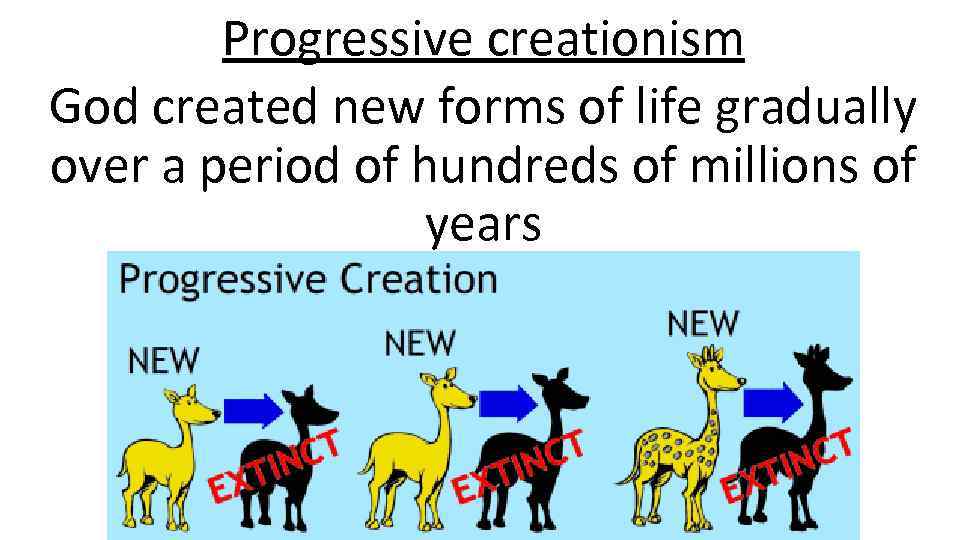
Progressive creationism God created new forms of life gradually over a period of hundreds of millions of years

Theistic evolution is real, but that it was set in motion by God

First used in “Of Pandas and People”, 1989 textbook for high school biology classes

1969 the USA: Susan Epperson vs. Arkansas

2005 Dover Panda Trial “intelligent design is not science, that it "cannot uncouple itself from its creationist, and thus religious, antecedents, "

October 4, 2007, the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe adopted its Resolution titled “The dangers of creationism in education”. Resolution observed: “The war on theory of evolution and on its supporters most often originates in forms of religious extremism, closely linked to extreme right-wing political movements, " hereby member states should "firmly oppose the teaching of creationism”

Right now in the world Australia – evolution, some creationism. Brazil – creationism forbidden in science. Europe – schools have right to pick curriculum. Iran – evolution preferred to creationism. Pakistan - evolution isn’t taught at school. Saudi Arabia – opposes evolution. Turkey – an open governmental conflict.
What controversial pages of Evolution do you know?
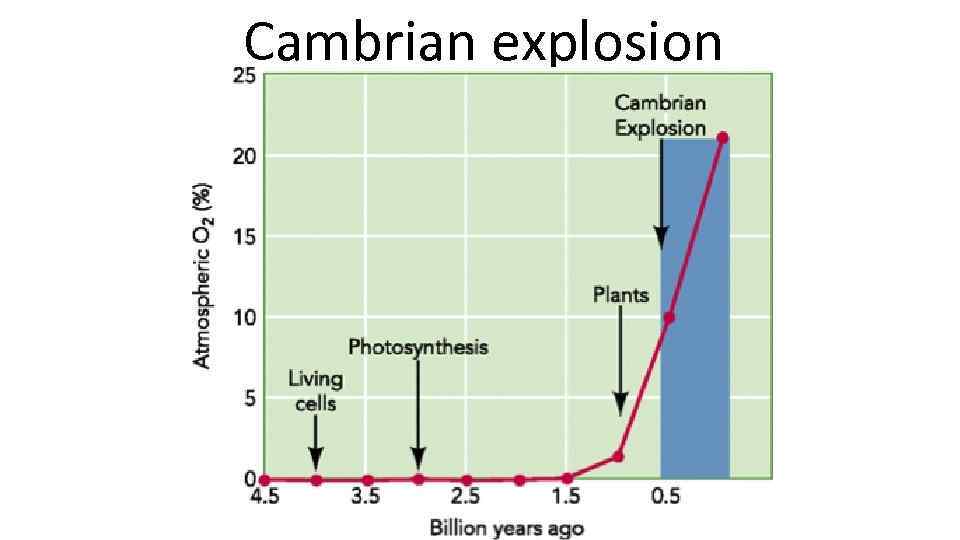
Cambrian explosion

Evolution is change in the heritable traits of biological populations over successive generations

Charles Darwin in his book On the Origin of Species (1859) defines three major principles of evolution: -Variation -Adaptation -Heredity

Why are creatures different?

Adaptation -How and why do animals adapt to environment?

Do the cubs retain all the traits of their parents? Why?

Why is Darwin’s Theory of Evolution discarded by so many religions?
What is natural selection? How is being ‘fittest’ regulated?
Why are people so sure about Evolution?

How old is life on Earth?

Many schools in the world teach creationism – what do you think of this?
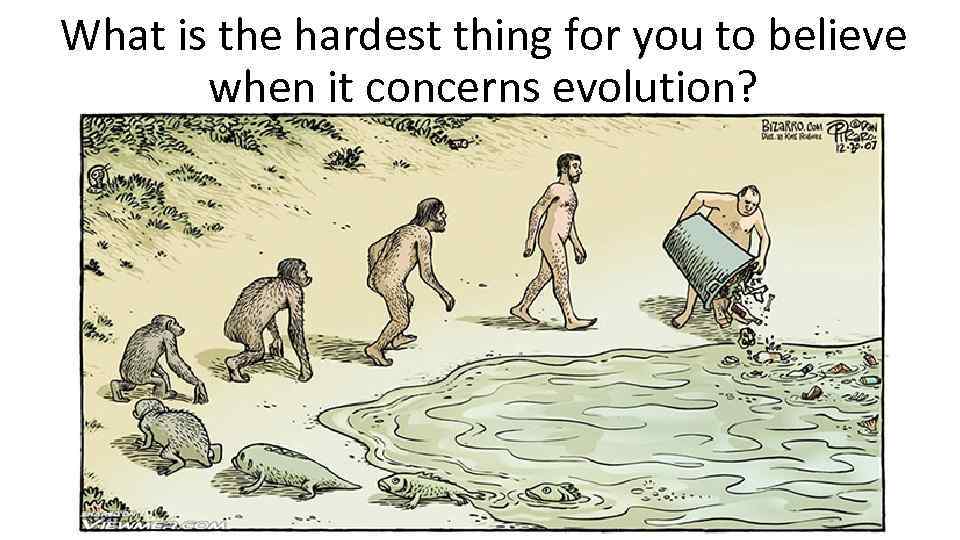

What is the hardest thing for you to believe when it concerns evolution?

Can you watch evolution happening? Is it a good or bad thing?

Do you think humans are set apart from the animal kingdom?

How long ago did human become human and what made us human?

What do you think we will look like millions of years from now?

Evolutionary Theories on Gender and Sexual Reproduction © 2003 Brad Harrub, Ph. D. and Bert Thompson, Ph. D.

Asexual reproduction vs sexual reproduction Gender vs sex Gametes

The origin and maintenance of sex and recombination is not easily explained by natural selection. Evolutionary biology is still unable to reveal why animals would abandon asexual reproduction in favor of more costly and inefficient sexual reproduction. Exactly how did we arrive at two separate genders - each with its own physiology? If, as evolutionists have argued, there is a materialistic answer for everything, then the question should be answered: “Why sex? ” Is sex the product of a historical accident or the product of an intelligent Creator?

Biology texts illustrate amoebas evolving into more complicated organisms, which then give rise to amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and, eventually, humans. Yet, we never learn exactly when or how independent male and female sexes originated. Somewhere along this evolutionary path, both males and females were required in order to ensure (обеспечить) the procreation (потомство) that was necessary to further the existence of a particular species.

But how do evolutionists explain this? When pressed to answer questions such as, “Where did males and females actually come from? , ” “What is the evolutionary origin of sex? , ” evolutionists become silent. How could nature evolve a female member of a species that produces eggs and is internally equipped to nourish a growing embryo, while at the same time evolving a male member doesn’t include such a process? And, further, how is it that these gametes conveniently “evolved” so that they each contain half the normal chromosome number of body cells?

In his book, The Masterpiece of Nature: The Evolution of Genetics and Sexuality, Graham Bell described the dilemma in the following manner: ‘Sex is the queen of problems in evolutionary biology. Perhaps no other natural phenomenon has aroused so much interest; certainly none has sowed as much confusion. The insights of Darwin and Mendel, which have illuminated so many mysteries, have so far failed to shed more than a dim and wavering light on the central mystery of sexuality, emphasizing its obscurity by its very isolation.

In an article in Bioscience on “How Did Sex Come About? , ” Julie Schecter remarked: ‘Sex is ubiquitous (вездесущий). . . Yet sex remains a mystery to researchers, to say nothing of the rest of the population. Why sex? At first blush, its disadvantages seem to outweigh its benefits. After all, a parent that reproduces sexually gives only one-half its genes to its offspring, whereas an organism that reproduces by dividing passes on all its genes. Sex also takes much longer and requires more energy than simple division. Why did a process so blatantly unprofitable to its earliest practitioners become so widespread? ’


The Lottery Principle was first suggested by American biologist George C. Williams in his monograph, Sex and Evolution. Williams’ idea was that reproduction introduced genetic variety in order to enable genes to survive in changing or novel environments. He used the lottery analogy to get across the concept that breeding asexually would be like buying a large number of tickets for a national lottery but giving them all the same number. Sexual reproduction, on the other hand, would be like purchasing a small number of tickets, but giving each of them a different number.

The essential idea behind the Lottery Principle is that since sex introduces variability, organisms would have a better chance of producing offspring that will survive if they reproduce a range of types rather than merely more of the same. As Carl Zimmer wrote under the title of “Evolution from Within” in his volume, Parasite Rex: “A line of clones might do well enough in a forest, but what if that forest changed over a few centuries to a prairie? ”

As Reichenbach and Anderson summarized the issue: ‘One theory is that sexual reproduction provides the best defense against the rapidly reproducing, infectious species that threaten the existence of organisms. The diversity in the species that results from combining different gene pools favors the survival of those that are sexually reproduced over those that by cloning inherit repetitive genetic similarity’

But the Lottery Principle has fallen on hard times of late. It suggests that sex would be favored by a variable environment, yet a close inspection of the global distribution of sex reveals that where environments are stable (such as in the tropics), sexual reproduction is most common. In contrast, in areas where the environment is unstable (such as at high altitudes or in small bodies or water), asexual reproduction is rife.


The Tangled Bank Hypothesis (Гипотеза Заселённого Берега) The “tangled bank” phraseology comes from the last paragraph of Darwin’s Origin of Species, in which he referred to a wide assortment of creatures all competing for light and food on a “tangled bank. ” According to this concept, in any environment where there exists intense competition for space, food, and other resources, a premium is placed on diversification.

As Zimmer described it: ‘In any environment—a tidal flat, a forest canopy, a deep-sea hydrothermal vent—the space is divided into different niches where different skills are needed for survival. A clone specialized for one niche can give birth only to offspring that can also handle the same niche. But sex shuffles the genetic deck and deals the offspring different hands. It’s basically spreading out progeny (потомство) so that they’re using different resources.

The Tangled Bank Hypothesis, however, also has fallen on hard times. In his book, Evolution and Human Behavior, John Cartwright concluded: ‘Although once popular, the tangled bank hypothesis now seems to face many problems, and former adherents (последователи) are falling away. The theory would predict a greater interest in sex among animals that produce lots of small offspring that compete with each other.

In fact, sex is invariably associated with organisms that produce a few large offspring, whereas organisms producing small offspring frequently engage in parthenogenesis [asexual reproduction]. In addition, the evidence from fossils suggests that species go for vast periods of geologic time without changing much’

According to Margulis and Sagan, bacteria “evolved” in such a fashion as to ultimately be responsible for sexual reproduction. Yet if that is the case, why, then, have the bacteria themselves remained virtually unchanged—from an evolutionary viewpoint—for billions of years of Earth history?


The Red Queen Hypothesis was first suggested by Leigh Van Valen in an article titled “A New Evolutionary Law” in Evolutionary Theory. His research suggested that the probability of organisms becoming extinct bears no relationship to how long they already may have survived. In other words, as Cartwright put it: “It is a sobering thought that the struggle for existence never gets any easier; however well adapted an animal may become, it still has the same chance of extinction as a newly formed species. ”

Biologists came to refer to the concept as the Red Queen Hypothesis, named after the character in Lewis Carroll’s Through the Looking Glass who took Alice on a lengthy run that actually went nowhere. As the queen said to poor Alice, “Now, here, you see, it takes all the running you can do, to keep in the same place. ”

Think of it as a “genetics arms race (гонка вооружений)” in which an animal constantly must run the genetic gauntlet (выдерживать) of being able to chase its prey, elude predators, and resist infection from disease-causing organisms. In the world of the Red Queen, organisms have to run fast -just to stay still! That is to say, they constantly have to “run to try to improve” (and the development of sex would be one way of accomplishing that).

Yet doing so provides no automatic guarantee of winning the struggle known as “survival of the fittest. ” “Nature, ” said the eminent British poet Lord Tennyson, is “red in tooth and claw. ” Currently, the Red Queen Hypothesis seems to be the favorite of evolutionists worldwide in attempting to explain the reason as to the “why” of sex.

The DNA Repair Hypothesis Think about this. Why are babies born young? Stupid question—with a self-evident answer, right? Evolutionists suggest otherwise. The point of the question is this. Our somatic (body) cells age. Yet cells of a newborn have had their clocks “set back. ” Somatic cells die, but the germ line (зародышевая линия) seems to be practically immortal. Why is the case? How can “old” people produce “young” babies?

In a landmark article published in 1989, Bernstein, Hopf, and Michod suggested that they had discovered the answer: ‘We argue that the lack of ageing of the germ line results mainly from repair of the genetic material by meiotic recombination during the formation of germ cells. Thus our basic hypothesis is that the primary function of sex is to repair the genetic material of the germ line. ’

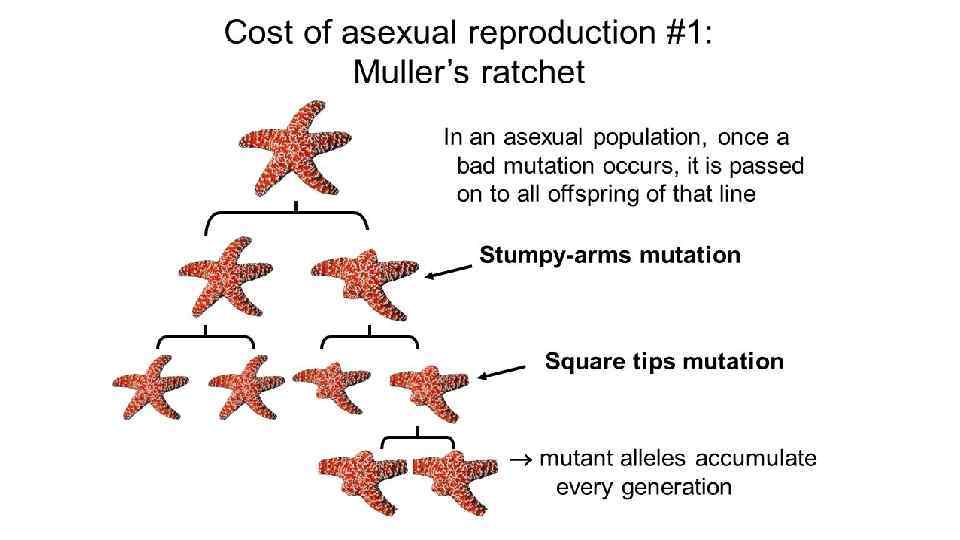
DNA can be damaged in at least two ways. First, ionizing radiation or mutagenic chemicals can alter the genetic code. Or, second, a mutation can occur via errors during the replication process itself. Most mutations are harmful. In an asexual organism, by definition, any mutation that occurs in one generation will be passed on automatically to the next.

In his book, The Red Queen, Matt Ridley compared it to what occurs when you photocopy a document, then photocopy the photocopy, and then photocopy that photocopy, etc. Eventually, the quality deteriorates severely. Asexual organisms, as they continue to accumulate mutations, face the unpleasant prospect of eventually becoming both unable to reproduce and unviable (нежизнеспособны) - neither of which would be at all helpful to evolution.

But sexual reproduction allows most plants and animals to create offspring with good copies of two genes via crossover and would thus, help eliminate this degradation since mutations, although they might still be passed on from one generation to the next, would not necessarily be expressed in the next generation (a mutation must appear in the genes of both parents before it is expressed in the offspring).



Biological Theories of Gender refers to the cultural differences expected (by society / culture) of men and women according to their sex. A person’s sex does not change from birth, but their gender can.

The psychological approach suggests there is a large distinction between sex and gender. Sex being a major hereditary factor, but it is gender roles that are defining the diversity and adaptation of the social species.

The biological approach suggests there is no distinction between sex & gender, thus biological sex predefines all variations of gendered behavior. If the requirement for the gender role changes, the evolution prefers biological alteration of the species.

Clown anemonefish all start out as male. If the female dies, the dominant male can change sex and become female. Another male will become the dominant male.

Parrotfish start out as male or female but have all set of sex organs of both sexes; they are hermaphrodites and they can change from female to male. Some females will become supermales: larger males with brilliant, lively coloring.

Gender is determined by two biological factors: hormones and chromosomes. Creatures can’t alter their chromosomes naturally, but they can change their hormones.
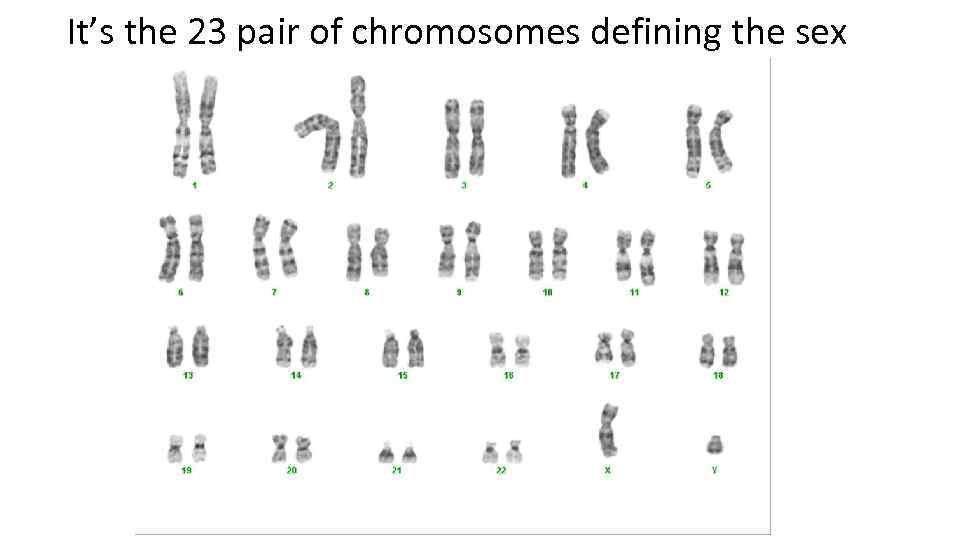
It’s the 23 pair of chromosomes defining the sex
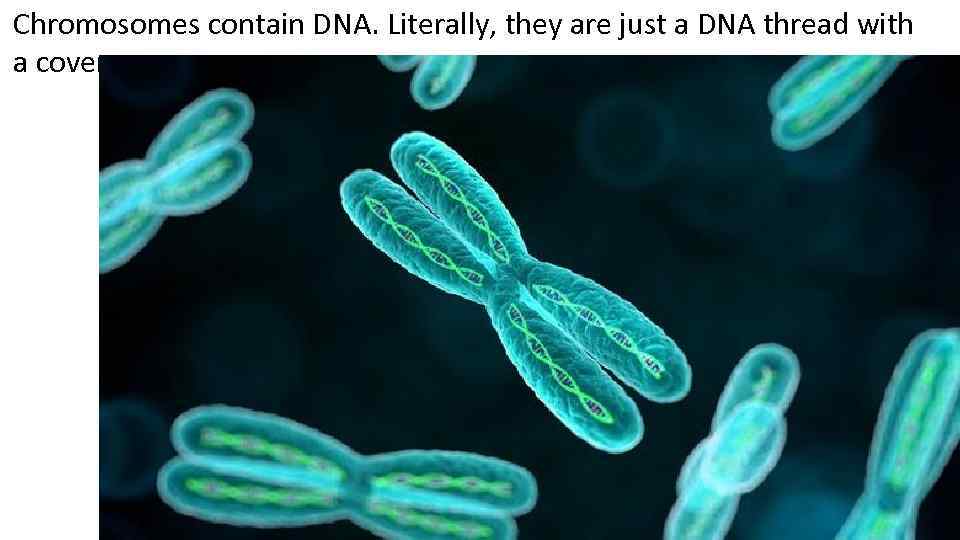

Chromosomes contain DNA. Literally, they are just a DNA thread with a cover
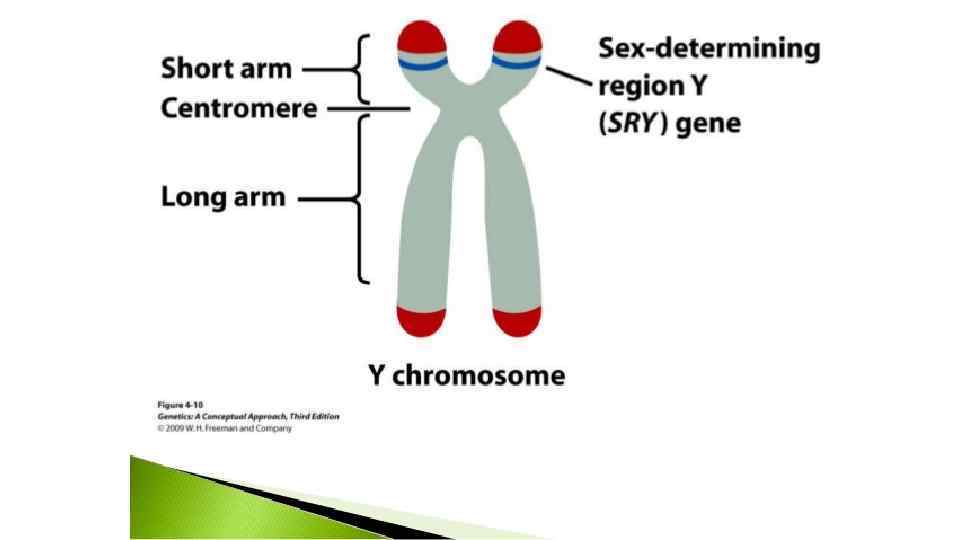

During the child development, the SRY gene “tells” the embryo to develop as a male. Even if it’s a normal male embryo which has Y chromosome, but SRY-gene is missing, it will develop as a normal female instead. Koopman in 1991 proved the following: If it’s a normal female embryo and has XX chromosomes and SRY-gene is implanted, the embryo develops as a normal male.

One of the most controversial uses of this discovery was as a means for gender verification at the Olympic Games, under a system implemented by the International Olympic Committee in 1992. Athletes with a SRY gene were not permitted to participate as females.
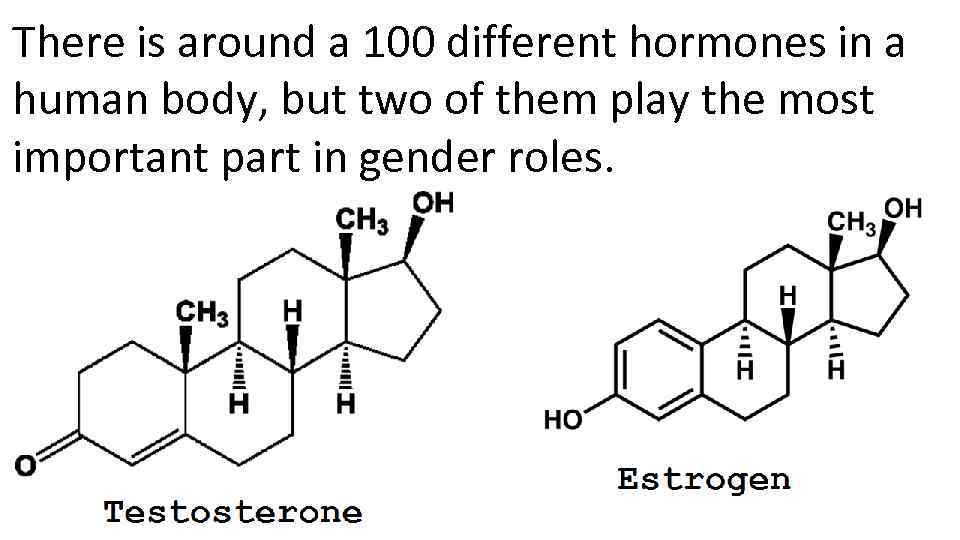
There is around a 100 different hormones in a human body, but two of them play the most important part in gender roles.

Testosterone levels in a male body are 7 -8 times bigger than in a female. Male produces and consumes 20 times more testosterone a day. Muscle growth, hair growth, bone development and ‘masculinization’ of brain (male brain hemispheres are much more independent)

Estrogen levels in female body are much higher than in a male’s. Estrogen takes care of the blood vessels, development of bones and plays the most important role in pregnancy.

What happens if you give the wrong guy the wrong ampoule? There was a series of experiments in 1966 that changed the sexual behavior of both male and female rats by manipulating the amount of male and female hormones that the rats received during their early development. They displayed “reversed” sexual behavior and the effects were unchangeable.

In 1977 they ran the similar tests with testosterone and monkeys – and found out that monkeys, that were given additional doses of testosterone during prenatal development later became more aggressive, than other females. Same results were achieved in 1982 studies, when human mothers were given testosterone during their pregnancy. Children grew more aggressive.

Genetic Expectations The research published in 2008 stated that there is equal amount of X and Y chromosomes and both male and female gametes in a human body. Any variations in amount of male and female children born happens between pregnancy and birth (woman body doesn’t control what gender her children will be)

Effects of climate change 1 °C increase in annual temperature predicts one more male than expected per every 1, 000 females born in a year. The colder it gets, the higher the mortality rate among boys (they are more fragile). The colder it gets, the longer adult males live (less testosterone).

Stress during pregnancy (especially malnutrition) also greatly increases boys mortality rate. In opposite, Hepatitis B virus increases girls mortality rate instead.

War As research by Finland scientists follows, they have analyzed all live births in Finland from 1751 to 1997. While there were some unexplainable peaks on the background of the general decrease of male births, two of them – the biggest ones – fall to the First and Second World War. In both cases the birth rate of males has greatly increased. Neither can be explained by environment changes, use of pesticides or other drugs or chemicals, or the differences in parent ages.

Father’s Age During two researches through the USA and Denmark, when over 2 million pregnancies were analyzed, such results were achieved: -Mother’s age doesn’t affect the child’s age -Young fathers have a higher rate of having a son

Why Different Roles? -Male gender is an avant-garde of changes, while female is a correcting conservative. Since woman bears the direct genetic material of her mother, male is one generation ahead of any genetic changes and are more prone to mutations

-Since in most species males have less parental role, than females, they are much more adaptable to the different gender roles to provide the survival of the species. Females, on other hand, have much less variability because it usually endangers their biological role


Do you see yourself as a typical man or woman? Why or why not? Who do you think has life easier, girls or guys? Why?
Are men and women equal in ability and intelligence?

What things can either men or women do that the other cannot do and why?
Should boys and girls be brought up differently?

Should boys and girls be treated differently on the part of the parents?

Can men wear women's clothing or can women wear men's clothing? Can women wear blue clothes? Can men wear pink clothes?
Is it OK for men to cry? Why? Is it OK for women to fight, swear and appear angry? Who do the children go to for emotional support? For financial support?

Who is regarded as the head of the family? What are the responsibilities of a father to his family? What are the responsibilities of a mother to her family?

If your mother had to leave for vacation, could your father take care of her responsibilities in her absence? And what if reversed happened – your father left for vacation?
2016, May 27th, Evolution.pptx