1844004e9faf59d24cca28d933a7db4f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

BASROC/CONFORM OPEN DAY 2009 At STFC Cockroft Institute Daresbury Bleddyn Jones University of Oxford 1. Gray Institute for Radiation Oncology & Biology 2. 21 Century School Particle Therapy Cancer Research Institute, Oxford Physics.

CANCER…. . the threat to humanity 40% risk during lifetime…might even increase with global warming (thermodynamics) n Surgery, Radiotherapy, Chemotherapy can all be risky and permanently injurious……. . no cause for complacency. n R/T 12% of NHS cancer budget; its provision regarded as inadequate internationally n

Which form of technology would you like used to treat your cancer?
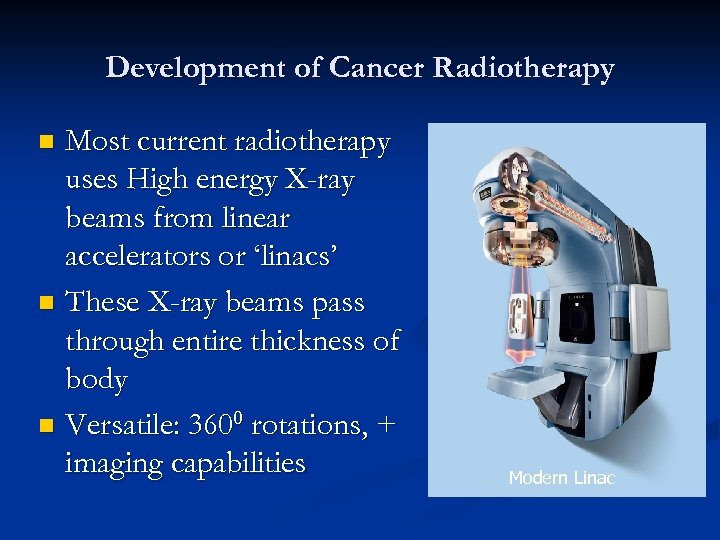
Development of Cancer Radiotherapy Most current radiotherapy uses High energy X-ray beams from linear accelerators or ‘linacs’ n These X-ray beams pass through entire thickness of body n Versatile: 3600 rotations, + imaging capabilities n Modern Linac
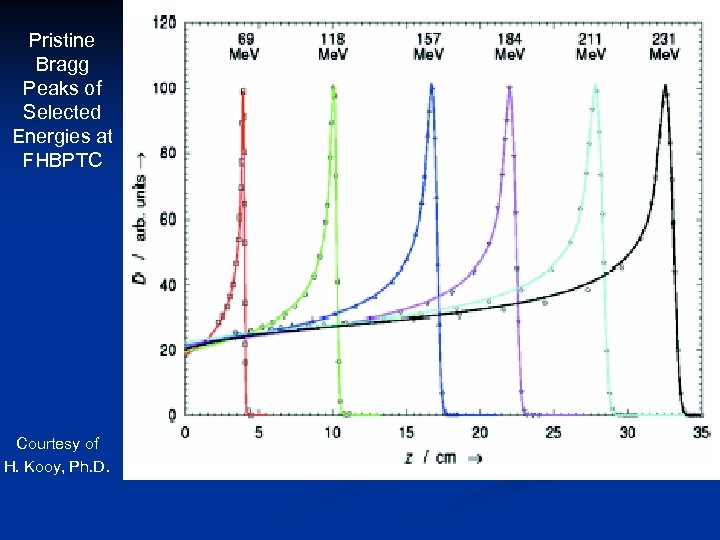
Pristine Bragg Peaks of Selected Energies at FHBPTC Courtesy of H. Kooy, Ph. D.
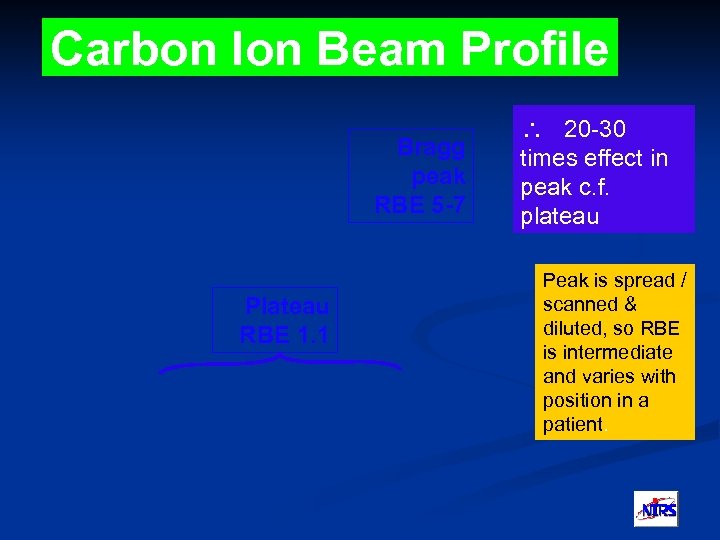
Carbon Ion Beam Profile Bragg peak RBE 5 -7 Plateau RBE 1. 1 20 -30 times effect in peak c. f. plateau Peak is spread / scanned & diluted, so RBE is intermediate and varies with position in a patient.
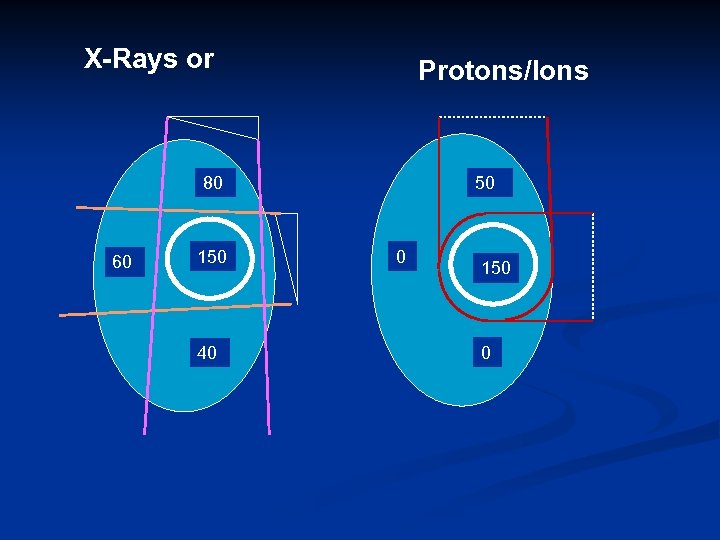
X-Rays or Protons/Ions 80 60 150 40 50 0 150 0
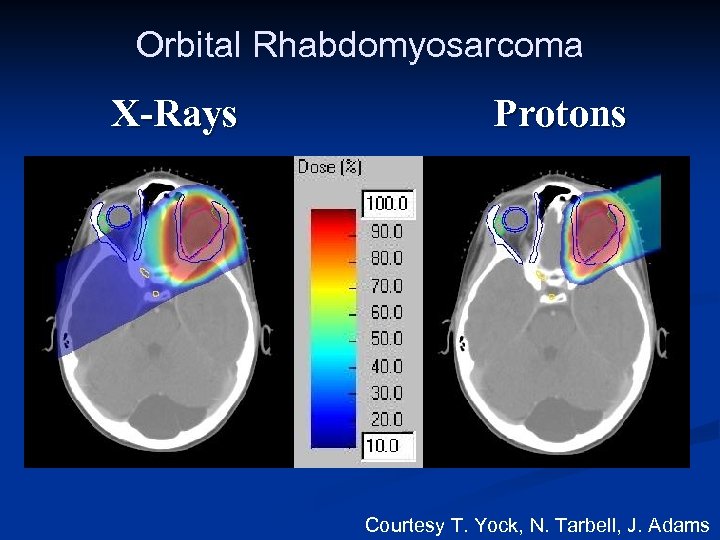
Orbital Rhabdomyosarcoma X-Rays Protons Courtesy T. Yock, N. Tarbell, J. Adams

International Scene n n n Japan: formed National Institute of Radiation Sciences 1957. 1986 Decision to have C ion therapy Commenced 1996 Japan Government Science Policy Review 20062010 noted favourable results and need for science to contribute directly to health of population. Emphasis on cancers that are difficult to treat and for a kinder form of radiotherapy Japan will soon have 10 facilities, all protons + 3 C ions. Tariff of ~ $ 30, 000 per course allowed.

Countries who used national Physics labs/projects to start Particle Therapy n n n Germany ……GSI…. . Heidelberg University Hospital Synchrotron built close to German Cancer Research Institute France…Orsay University Protons; GANIL (Caen) will host new IBA 400 Me. V C cyclotron Switzerland: large expansion at PSI (Villigen); development of spot scanning techniques. Austria…. . will use novel CERN cyclolinac system Italy …. Pavia, synchrotron system Stanford/USA. . plans for new high tech accelerator for C ions; twenty proton centres planned in USA.
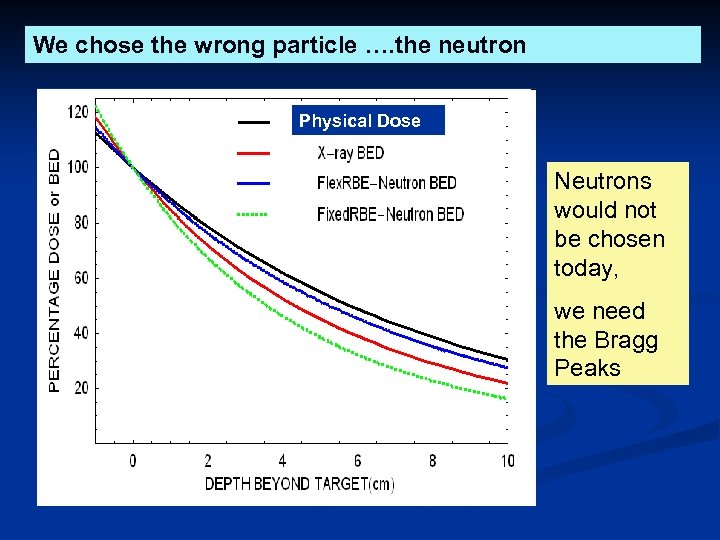
We chose the wrong particle …. the neutron Physical Dose Neutrons would not be chosen today, we need the Bragg Peaks
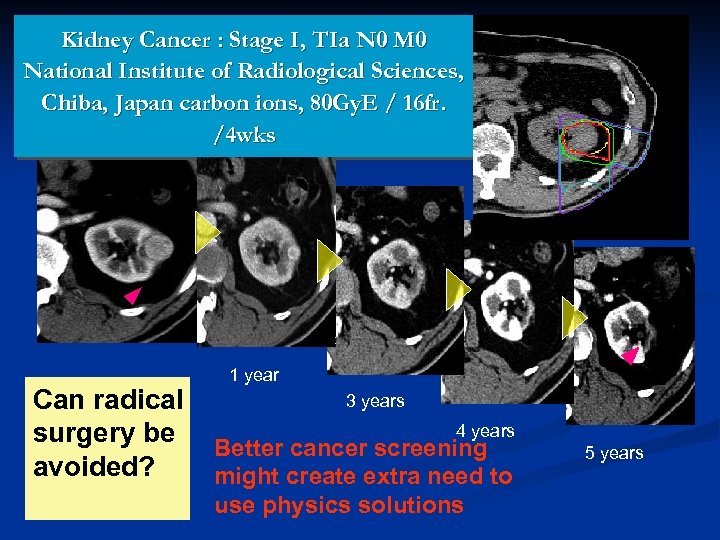
Kidney Cancer : Stage I, TIa N 0 M 0 National Institute of Radiological Sciences, Chiba, Japan carbon ions, 80 Gy. E / 16 fr. /4 wks 治療前 1 year 3 years Can radical 4 years surgery be Better cancer screening avoided? might create extra need to use physics solutions 5 years
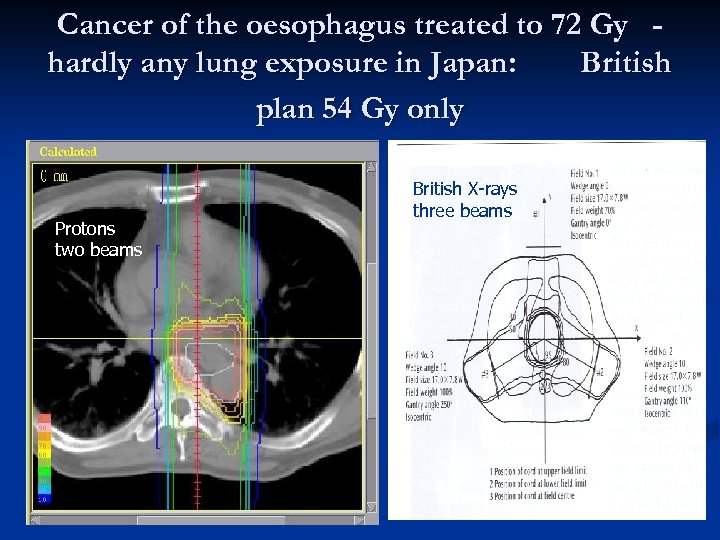
Cancer of the oesophagus treated to 72 Gy hardly any lung exposure in Japan: British plan 54 Gy only Protons two beams British X-rays three beams
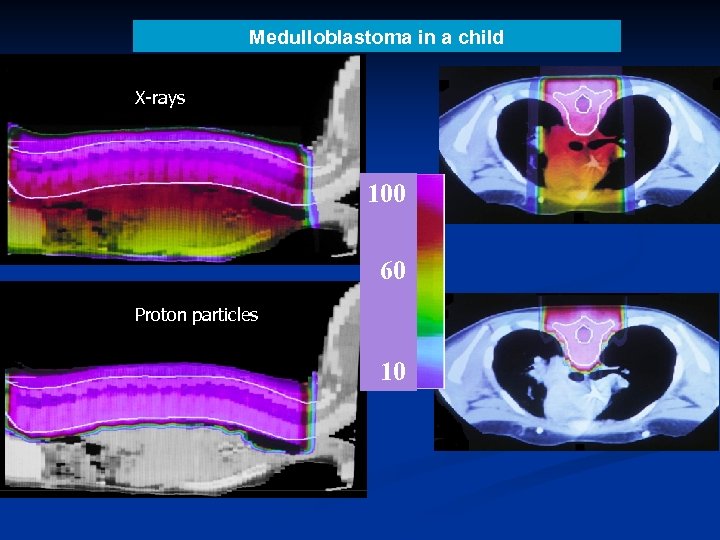
Medulloblastoma in a child X-rays 100 60 Proton particles 10

The only working model in UK (funded by NHS doctor working during his holiday)
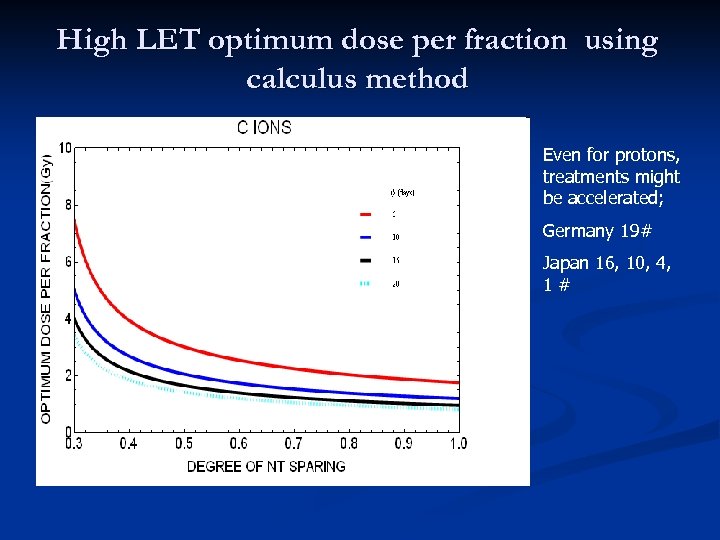
High LET optimum dose per fraction using calculus method Even for protons, treatments might be accelerated; Germany 19# Japan 16, 10, 4, 1#
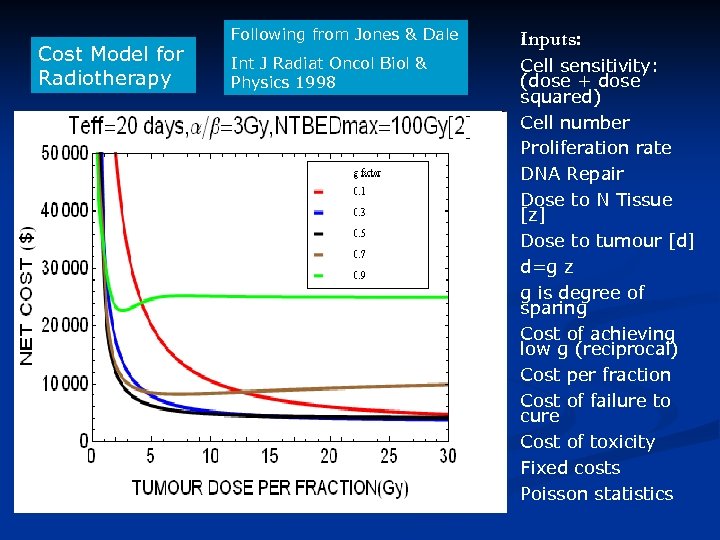
Cost Model for Radiotherapy Following from Jones & Dale Inputs: Int J Radiat Oncol Biol & Physics 1998 Cell sensitivity: (dose + dose squared) Cell number Proliferation rate DNA Repair Dose to N Tissue [z] Dose to tumour [d] d=g z g is degree of sparing Cost of achieving low g (reciprocal) Cost per fraction Cost of failure to cure Cost of toxicity Fixed costs Poisson statistics

Japanese Progress in Fractionation 1 treatment only for small lung cancer n 4 treatments for prostate cancer n Most treatments in 12 -16 treatments over 4 weeks n Cost applied regardless of fractionation n Germany 19 fractions in 19 days at GSI n Protons in USA 4 -8 (eye); to 38 fractions prostate/skull base. n

Expected and achievable benefits n n n Reduce fear of cancer treatment, improved patient experience Dose increase to cancer : 1% increase in cancer control per unit increase in dose …. . i. e. 15 Gy extra 15% extra control Dose reduction to organs e. g. lung, brain, eye, spine, bowel, bone: leading to reduced or absence of many side effects Chemotherapy better tolerated Better quality of life, ability to contribute to society etc.

UK Position Member of PARTNER, ULICE & ENVISION EU FP 7 grants……totalling ~24 M Euro n Occupying a peripheral role…data collection, instrumentation, leadership skills, modelling. n PAMELA – could transform our position to be leader in terms of new technology, clinical efficiency, clinical policies/research, and opportunity for comprehensive radiobiology programme under our own guidance. n

EMMA Ring See Smith: WE 4 PBI 01 PAMELA Particle Accelerator for MEdica. L Applications n n n Clinical Requirements PAMELA – status Summary Electrons – at relativistic velocities approaching speed of light Protons, helium to carbon range of ions – at non-relativistic velocities
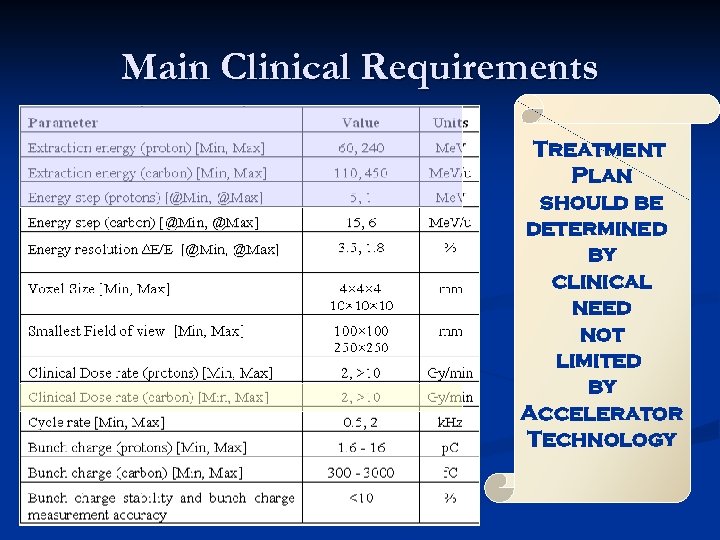
Main Clinical Requirements Treatment Plan should be determined by clinical need not limited by Accelerator Technology
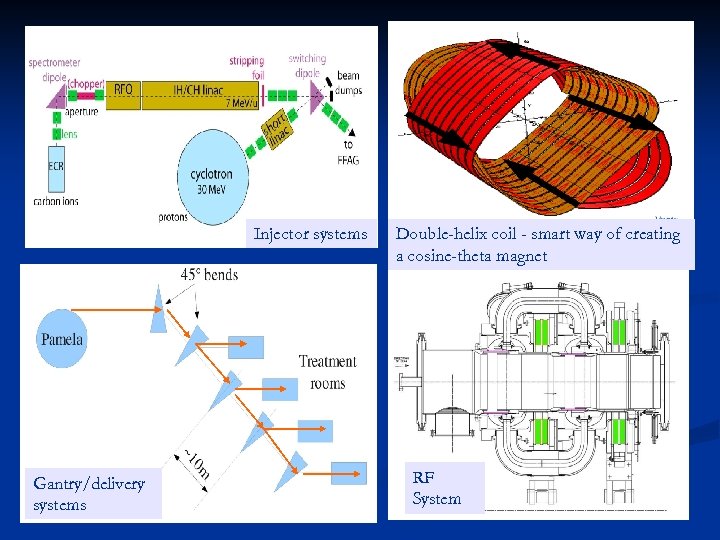
Injector systems Gantry/delivery systems Double-helix coil - smart way of creating a cosine-theta magnet RF System
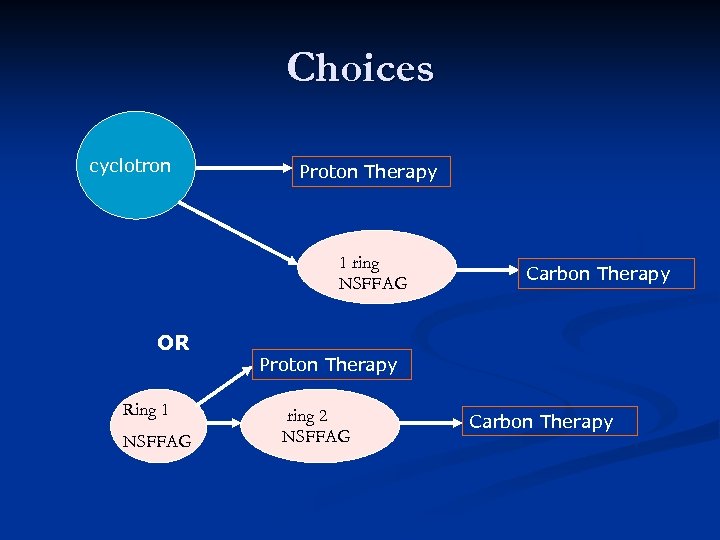
Choices cyclotron Proton Therapy 1 ring NSFFAG OR Ring 1 NSFFAG Carbon Therapy Proton Therapy 1 ring 2 NSFFAG Carbon Therapy

Next steps 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Complete the proton ring design Develop the carbon ring Develop beam transport & gantry Seek component prototype funding • Main ring magnets, RF, Kickers, Carbon RFQ Seek machine funding • UK Demonstrator for CPT
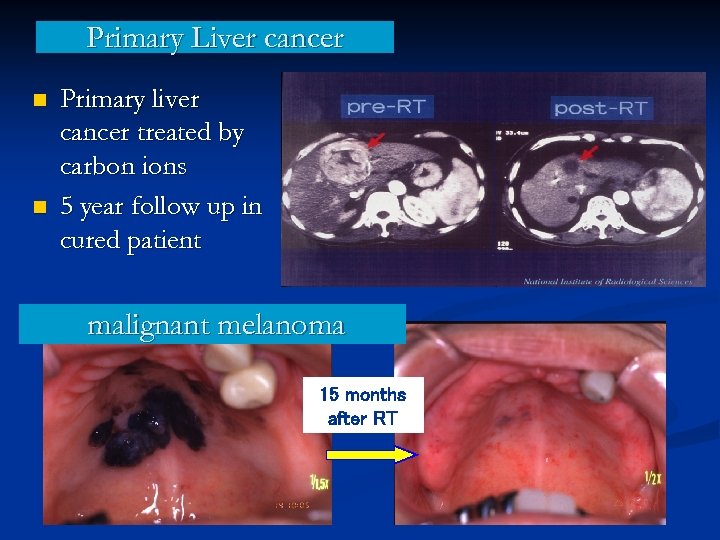
Primary Liver cancer n n Primary liver cancer treated by carbon ions 5 year follow up in cured patient malignant melanoma 15 months after RT
Some PAMELA work on radiobiology of n n Dose rate (and so dose duration) Ion species Throughput Dose painting …new features N C +

Gantries Heidelberg has huge 300+ ton gantry…… First in world n French seeking to use cryogenic s/c magnet to halve the weight n CONFORM system magnets within gantries offers best long term solution to gantry manufacture at lower tonnage, footprint and cost n

21 Century School Particle Therapy Cancer Research Institute, Oxford Since January 2009 our aims are to promote: - Education (Public, Professions and Policy Makers) n Research [Physics, Biology and Medicine] n Investment [NHS, Research Councils, Cancer Charities and Public] n Advanced Technology Ion Treatment Facility in UK and elsewhere - including third world with cost optimisation. n
1844004e9faf59d24cca28d933a7db4f.ppt