Lecture 6.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 10

Basic Translation Approaches Lecture 6

Overview • transformational approach; • denotative approach; • communicational approach;

Translation Theories Classification • Transformational • Denotative • Communicational

Transformation Theory SL translation = transformation TL objects structures Transformation (Syntactic level) Equivalence (Lexical level)

Transformation Theory Substitution: • morphological equivalencies • lexical equivalencies • syntac tic equivalencies and/or transformations

Transformational Theory Advantages Clearance (translation – a set of multi-level replacements) Analytical and synthetic languages Disadvantage Insufficiency (when the source text corresponds to one indivisible concept)

Denotative Theory Base – an idea of denotatum (actual object referred to by language sign) Mental operations: • translator reads (hears) a message in the source language; • translator finds a denotatum and concept that correspond to this message; • translator formulates a message in the target language relevant to the above denotatum and concept. Relationship between the source and target word forms is occasional rather than regular.

Example • Bulk-density method is the measurement of product volume (V) and density (ρ) Объемно -массовый метод сводится к измерению объема (V) и плотности (ρ) продукта. • Staff only Служебное помещение. • Формула изобретения ?
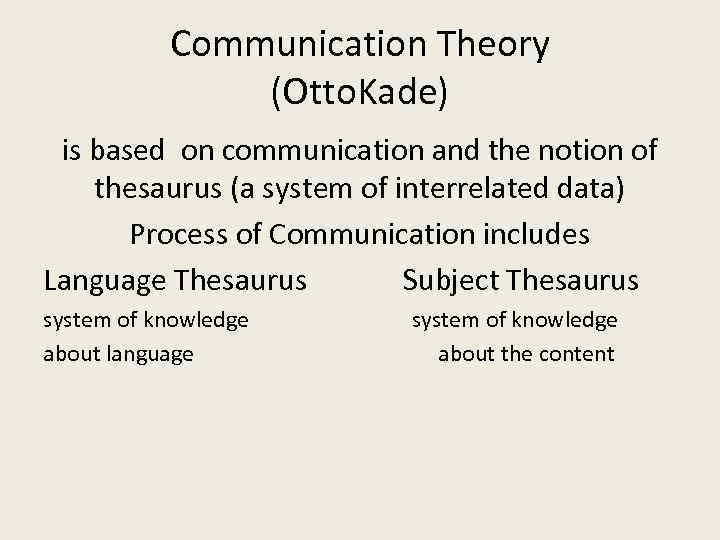
Communication Theory (Otto. Kade) is based on communication and the notion of thesaurus (a system of interrelated data) Process of Communication includes Language Thesaurus Subject Thesaurus system of knowledge about language system of knowledge about the content

Example Several new schools appeared in the area В районе появились новые школы В районе появились новые косяки рыбы Thus, translation is a message sent by a translator to a particular user and the adequacy of translation depends on similarity of their background information rather than only on linguistic correctness.
Lecture 6.pptx