
Basic notions of morphology

The morpheme The grammatical form The grammatical meaning The grammatical category The functional semantic category

The criteria of morphemes According to the position of the morpheme in the word – central/ peripheral According to the significance of e morpheme for the word structure – root/affixational According to the degree of self-sufficiency – bound/loose According to the function of the morpheme – notional/functional According to the meaning the morpheme expresses – lexical/grammatical According to the material expression – positive (marked)/zero (unmarked) According to the structure of the morpheme – continuous/discontinuous

Synthetical types of form-building include affixation (books), sound interchange (toothteeth), suppletivity (good – better). Analytical forms present the expression of gram. meanings by means of combining a notional verb and an auxiliary element. Aglutinative type (boy’s) – aglutinative element has only one meaning but affixes have several meanings.

The grammatical category is a system of forms expressing a generalized grammatical meaning. The forms united into a grammatical category share a general meaning which gives a name to the category and differ the more specific meanings within the found meaning.

The features of grammatical categories: Each gram. Category is of a generalized character. A grammatical form exists if there is a special form for its expression. Grammatical categories manifest themselves when different forms of the same word are opposed and contrasted Gram. categories are divided into morphological and syntactical ones. Parts of speech with gram. categories which are displayed in the forms of a word are morphological ones. Syntactical categories are those which use combinations of words and sentences. The system of gram. categories is historical in its nature. In the process of the development of language some gram. categories may disappear. For example, in old English there were 4 cases: nominative, genitive, dative, accusative merged into one inflected form, the common case. The old genitive case is represented in Modern English by the inflected possessive case of nouns (bird’s) and some pronouns (one’s).
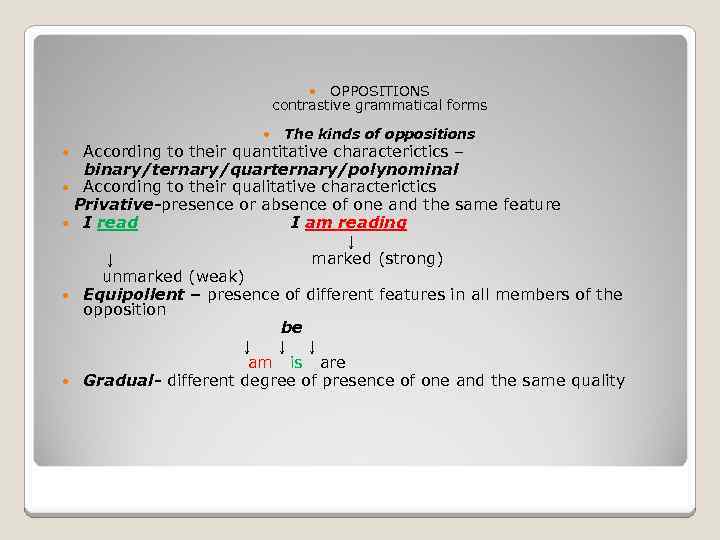
OPPOSITIONS contrastive grammatical forms The kinds of oppositions According to their quantitative characterictics – binary/ternary/quarternary/polynominal According to their qualitative characterictics Privative-presence or absence of one and the same feature I read I am reading ↓ marked (strong) unmarked (weak) Equipollent – presence of different features in all members of the opposition be ↓ ↓ ↓ am is are Gradual- different degree of presence of one and the same quality