Topic 4.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 30

Basic Framework of Planning and Budgeting Planning: Principles, types of plans, content of development plans 2. Budgeting: Functions, types of budgets, budget system 3. Methodology. 1. 1

1. PLANNING: Principles, Types of Plans, Content of Development Plans 2

Planning & Budgeting 3

Planning - a basic management function that (1) identifies the goals or objectives to be achieved, (2) formulates strategies to achieve them, (3) arranges or creates the means required, and (4) implements, directs, and monitors all steps in their proper sequence. Budgeting – a basic and essential process that allows businesses to attain many goals in one course of action. These goals include control and evaluation, planning, communication, and motivation. 4

Forecasting a planning tool that helps management in its attempts to cope with the uncertainty of the future, relying mainly on data from the past and present and analysis of trends. 5
![Planning Cycle - “Well plan is half done”. [1] Review what was done in Planning Cycle - “Well plan is half done”. [1] Review what was done in](https://present5.com/presentation/22816583_156586829/image-6.jpg)
Planning Cycle - “Well plan is half done”. [1] Review what was done in the past, in terms of impact, effectiveness and efficiency [6] Implement plans, monitor impact and income and expenditure – adjust where necessary. [2] Review and clarify vision, mission, strategy and objectives [5] Draw up a budget to cover the work. [3] Prepare operational plans [4] estimate costs needed to meet needs of the plan 6

Planning Functions A main policy method on enterprise and in branches Agreed-on development of enterprise Systematic predicted management Base for controllability Condition for optimal output (finance & production) 7

Principles of Planning Hierarchy, Material and moral interest Scientific character continuousness optimality validity Stability, flexibility directivity 8

Kinds of Planning Strategic Planning Tactic Planning Operational Planning 9

Strategic planning is a systematic, formally documented process for deciding what is the handful of key decisions that an organization, viewed as a corporate whole must get right in order to thrive over the next few years. The process results is the production of a corporate strategic plan. 10

Operational Planning: § Time schedule – operational production plans and figures (graphs). Dispatching – continuous operational monitoring, control and regulation of production processes and plans’ realization. 11

Main tasks of Operational Planning Rhythmical production of all units 100% plan Operating mode of enterprise Cut down the production lead time & goods in progress Control and regulation of production. 12

Types of Plans Feature 1. Obligation of plan tasks 2. Term of planning 3. Level of coverage 4. Object of Planning Types of Plans directive indicatice Long-term (5 and more years) Medium term (2 -5 year) Short-term (1 year) Scheduled (quarter, month, decade, week, day) General plan Part Plan operational (development plan) strategic Business plan Program 13

Strategy The art and science of planning and marshalling resources for their most efficient and effective use. 14

Structure of Strategic Plan 1. Main strategic plan (directions & goals) 2. Strategic Development Plan for Competitive Strengths (product strategies, resource strategies, and functional strategies of enterprise) 3. Plans of strategy's implementation 4. Schedule of strategic accounting, controlling and analyzing 15
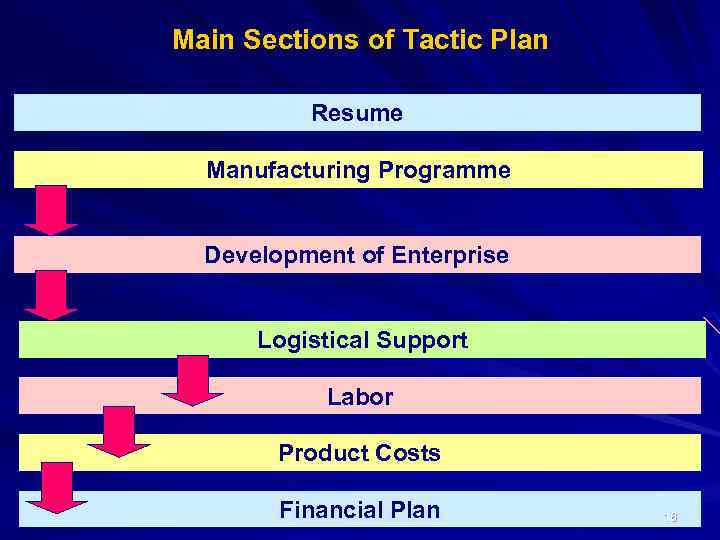
Main Sections of Tactic Plan Resume Manufacturing Programme Development of Enterprise Logistical Support Labor Product Costs Financial Plan 16

Other Sections of Tactical Plan Capital Investment Social Development of Personal Environment protection and natural resources usage Secondary Raw Materials usage Foreign Trade Activity etc 17

Business Plan -Set of documents prepared by a firm's management to summarize its operational and financial objectives for the near future (usually one to three years) and to show they will be achieved. 18

Structure of Business Plan 1. Resume 2. Sector research, characteristics of enterprise, and product description 3. Estimation of commodity market 4. Estimation of competitiveness 5. Marketing Plan 6. Production Plan 7. Managerial Plan 8. Risk estimation and Hedging 9. Financing Strategy 10. Financial Plan 19

2. Budgeting: Functions, Budgets Types, Budget System 20

Budgeting Establishing a planned level of expenditures, usually at a fairly detailed level. A company may plan and maintain a budget on either an accrual or a cash basis Entrepreneur's small business encyclopedia 21

Budget A budget is a document that translates plans into money - money that will need to be spent to get the planned activities done (expenditure) and money that will need to be generated to cover the costs of getting the work done (income). It is an estimate, or informed guess, about what one will need in monetary terms to do his/her work. 22

Budget is not Written in stone record of last year’s expenditure, with an extra 15% added on to cover inflation administrative and financial requirement An optimistic and unrealistic picture of what things actually cost 23

Main Budgets Types Sales budget – an estimate of future sales, often broken down into both units and dollars. It is used to create company sales goals. Production budget – an estimate of the number of units that must be manufactured to meet the sales goals. The production budget also estimates the various costs involved with manufacturing those units, including labor and material. Created by product oriented companies. Cash flow budget – a prediction of future cash receipts and expenditures for a particular time period. It usually covers a period in the short term future. The cash flow budget helps the business determine when income will be sufficient to cover expenses and when the company will need to seek outside financing. 24

Some Other Budget Types Marketing budget – an estimate of the funds needed for promotion, advertising, and public relations in order to market the product or service. Project budget – a prediction of the costs associated with a particular company project. These costs include labor, materials, and other related expenses. The project budget is often broken down into specific tasks, with task budgets assigned to each. A cost estimate is used to establish a project budget. Revenue budget – consists of revenue receipts of government and the expenditure met from these revenues. Tax revenues are made up of taxes and other duties that the government levies. Expenditure budget – includes spending data items. 25

3. Methodology 26

Classification of planning methods Features Main plan point Approach to definition of plan indicators Planning methods ● Resource (according to possibilities) ● objective (according to needs) ● Extrapolated ● Interpolated ● Econometric (method of averages) Method of calculation ● Normative Balance of resources and needs ● Balanced ● Matrix ● Monovariant (intuitive) ● Polyvariant ● Econometric ● Manual ● Mechanized ● Automation ● Table ● Graph ● network Alternativeness of plans Mode of plan’s calculations Presentation mode 27

Forecast methods Qualitative methods Analysis of time series Casual methods Modeling (econometric) 28

Approaches to Budgeting Traditional Zero-Base Budgeting Activity-Based Budgeting Performance-based Budgeting Beyond Budgeting 29

Budgeting Technique 30
Topic 4.pptx