c45e7faf76b96ec240bed93621043b65.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72

BASIC FALL PROTECTION OFFERED BY: CH BULL CO SOUTH SAN FRANCISCO, CA

Falls Kill • Unrestrained falls from 10’ kill or disable 4 out of 5 victims • Unrestrained falls from 11’ kill 4 out of 5
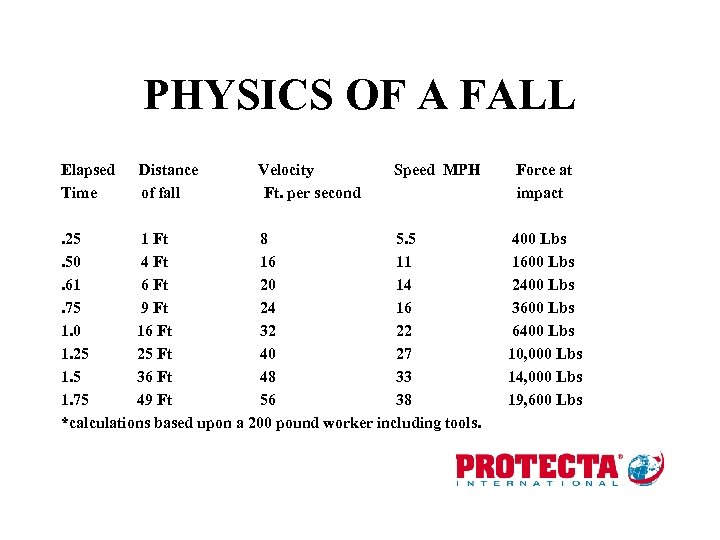
PHYSICS OF A FALL Elapsed Time Distance of fall Velocity Ft. per second Speed MPH . 25 1 Ft 8 5. 5. 50 4 Ft 16 11. 61 6 Ft 20 14. 75 9 Ft 24 16 1. 0 16 Ft 32 22 1. 25 25 Ft 40 27 1. 5 36 Ft 48 33 1. 75 49 Ft 56 38 *calculations based upon a 200 pound worker including tools. Force at impact 400 Lbs 1600 Lbs 2400 Lbs 3600 Lbs 6400 Lbs 10, 000 Lbs 14, 000 Lbs 19, 600 Lbs

Construction • In 1995 1, 048 people died on the job – 32% of fatal accidents involved falls

Key Areas of Concern • • Falls from heights Confined spaces Lift equipment Scaffolds

Eliminating the Risk • • Don’t go there Build a work platform Implement a personal fall arrest system Use alternative means

Fall Protection • A series of steps taken to reasonably lessen or eliminate the risk of falling in the work place

What Is Fall Protection? • • Equipment? Planning? A culture change? It is all of the above

Key Fall Exposures, Concerns • • At heights When positioned Confined spaces Lift devices

The Regulatory Environment • Employers have the GENERAL DUTY to provide a safe, healthy workplace

Hierarchy of Regulation • State or federal standards – Minimum acceptable • Manufacturer notices, warnings, instructions • Employer safety policy

Generally Speaking the Regs Require • • • Fed OSHA limits free falls to 6’ or less Cal/OSHA limits free fall to 30” or more Special criteria for confined space work Fall protection in lift devices Scaffold builders to be “tied off”

Specific Regulations • 29 CFR 1910 • 29 CFR 1926 • Multiple state regulations – CAL/OSHA of Regulations, Title 8 – Subchapter 7

Two Types of Personnel Are Described • Competent • Qualified

Competent Persons • • Know application limits Regulations Able to “solve and resolve” problems Have authority to take necessary actions

Qualified Persons • Degree or certificate of competency – PE • Vast experience • Skill necessary to “solve and resolve” technical problems

Personal Fall Arrest Systems • Must be in place when the risk is present • Must limit impact loads on the victim • Must ACTUALLY work in the environment in which they are used

When Positioned • A fall of NO MORE THAN 2 FEET • A minimum 3, 000# anchor • All other hardware must meet PFAS requirements
Powered Lift Equipment • Confusing Scenario – Scissor lift – Boom lift or other device

Scissors Lift • Working surface

Boom Lift • Must be “tied off” – 29 CFR 1910. 67(c)(2)(v) A full body harness shall be worn and a lanyard attached to the boom or basket when working from an aerial lift.

One More Look at Boom Lifts • Do you see any problems here? – Free fall potential? – Anchor strength? – Basket capacity?

Federal Regulatory Basis • OSHA – 29 CFR 1926 Sub R • Steel erection only – 29 CFR 1926 Sub M • Well documented • 6’ free fall

29 CFR 1926 Sub R • Significant changes – 1926. 760(a) sets 15’ “trigger height” with exceptions – Specific training

What if Conventional Fall Protection Will Not Work • Fall protection plans are acceptable alternative – Very restrictive – Very specific

Fall Protection Plans • Require clear statement that “conventional” fall protection “is impractical or creates a greater hazard. ” • Must clearly identify why conventional systems are not appropriate

Plans Must be Specific • Where it is to be implemented • Who is responsible for implementation • A qualified person must approve the plan and any changes • The plan must be maintained on site

Additional Actions May be Required for Compliance • Title 8§ 1671. 1(a)(9) requires controlled access zones and safety monitoring when “no other alternatives measure has been implemented…. ”

Controlled Access Zones • Control line set not less than 6’ nor more than 25’ from unprotected or leading edge • Set with lowest point no less than 39” nor more than 45” above the working level • Must be clearly marked at not more than 6’ intervals

Safety Monitoring • Safety monitor must be competent person • Must always be in communication with employees being monitored • Monitor should have no other responsibilities diverting attention

Safety at Heights: A Simple Proposition • • A - anchorage B - full body harness C - connectors D - devices

Anchor Points • Basic - most common alternative • Engineered - meets 2: 1 safety factor • Most common errors Assume anchor point is strong enough Somebody else tied off to this anchor point

Can You Recognize an Appropriate Anchor? • 5, 000 lbs • 3, 000 lbs • How about a rule of thumb?

Anchor Point Evaluation • Ford F-250 Extended Cab • 2 WD • 5, 058 lb.

Anchorage Selection • 5, 000 pound requirement • Set as high as possible – Cuts free fall • Use correct device – Cable or web sling – Carabiner, handgrip

Weight Limits • Most fall arrest equipment sold in the United States has a stated weight limit of 310 pounds. • Why? • Anchor quality

B: Body Harness • The only acceptable device for use in a fall arrest situation • Spreads load to minimize injuries – OSHA allows 1, 800 pound impact load – ANSI Z 359. 1 -1992 limits impact to 900 pounds • Positions victim for rescue

Harness Categories • General use • Specialized • Rescue, Climbing

Common Features • Ease of inspection • Improved labeling • Two-color design

Harness Fit • Legs closed tightly • Sub pelvic strap correctly positioned • D-ring positioned between shoulders

Harness Inspection • Webbing okay? – No burns, tears, discoloration • Hardware okay? – Properly positioned – No cracks

Connectors • Must be double locking • Must be compatible • Must be inspected prior to each use

Energy Absorbing Devices • Must absorb the energy built up during a fall • Must control energy imparted on both victim and anchor point • All get longer under load

Shock Absorber Types • • Rip stitch “Woof material” Tearing Self retracting lifelines

Inspection is Critical • Webbing undamaged? • Hardware functional? • Shock absorber okay?

Make Your Inspection COMPLETE! • Internal damage can be hard to detect • Tug on the lanyard legs to be sure they are attached

Falls Actually Don’t Kill…. The Stop Does the Damage • Contact with lower levels, dangerous equipment • Swings into structures

Fall Protection Math • Lanyard length + shock absorber length + victim height + elongation = REQUIRED CLEAR SPACE • 6’ + 42” + 1’ = >15’ • Do you have this much distance?

Fall Protection: • 10% equipment • 90% rigging

Rigging Is Critical • Anchor set as high as possible • Lanyard attached properly to harness – Shock absorber clipped to back d-ring

Self Retracting Lifelines • Must be positioned over work area – Minimize swing fall potential • Cuts anchor requirement – 3, 000 lbs. . Vs. 5, 000 lbs. .

Temporary Horizontal Lifelines • Ideal for steel, bridge, and decking • Anchored correctly • Check vertical clearance – Nearly 20’ may be needed

Engineered Fall Arrest/Protection Systems • Fall arrest – there may be fall from an exposed edge • Fall restraint – prevents personnel from reaching an exposed edge

Cell Tower

Light Tower

Arenas

Crane Runway

Ladder

Bridge

Roof Application

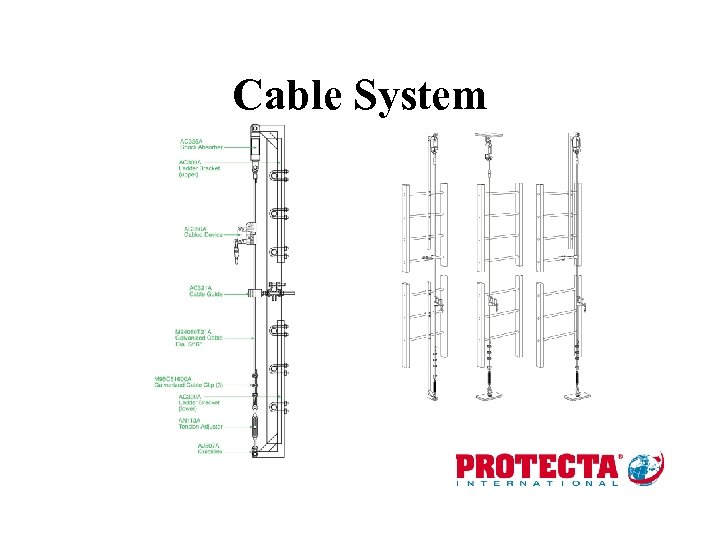
Horizontal systems • • Cable systems Rigid rail systems Embedded strut Beam trolley

Cable System

Embedded Strut

Beam Trolley

Vertical climbing systems • Cable systems • Rail systems
Cable System

Summary- Engineered Systems • • Definition Standards Hazards and Solutions What are the benefits of an Engineered System?

Benefits • • • Cost effective Versatile Low Maintenance Very easy to use COMPLIANT

Inspection Intervals • Title 8 Sec 1670 (19) requires that PFAS “shall be inspected not less than twice annually” by a competent person • Inspection date must be documented

Rescue: The Final Challenge • Most falls are self rescued • If rescue is required it – Must be timely, per OSHA – Must be within 15 minutes, per ANSI • Must be part of the plan

A Safety Reminder • Even if you were born to do a job, it doesn't necessarily mean that you're going to automatically do it safely. … You know what you're doing, its what you've been trained to do your whole life. Nothing could possibly go wrong, right? ? ? • Think again!

Thank You! It starts right now. Remember knowledge is not power, it is what you do with what you know that gives you power
c45e7faf76b96ec240bed93621043b65.ppt