BASIC ECONOMIC TERMINOLOGY UNEMPLOYMENT & INFLATION. Unemployment Unemployment


BASIC ECONOMIC TERMINOLOGY UNEMPLOYMENT & INFLATION .

Unemployment Unemployment is a status in which individuals are without job and are seeking a job. It is one of the most pressing problems of any economy especially the underdeveloped ones.This has macroeconomic implications too some of which are discussed below. Reduction In The Output Reduction In Tax Revenue Rise In The Government Expenditure

Unemployment Types: Cyclical Unemployment Seasonal unemployment Frictional unemployment Structural Unemployment

Causes Of Unemployment Rapid changes in technology Recessions Inflation Disability Undulating business cycles Changes in tastes as well as alterations in the climatic conditions. This may in turn lead to decline in demand for certain services as well as products. Attitude towards employers Willingness to work Perception of employees Employee values Discriminating factors in the place of work (may include discrimination on the basis of age, class, ethnicity, color and race). Ability to look for employment

Effects Costs Individual Social Socio-political Benefits Unemployment is argued to be "beneficial" to the people who are not unemployed in the sense that it averts inflation, which itself has damaging effects, by providing a reserve army of labour, that keeps wages in check.
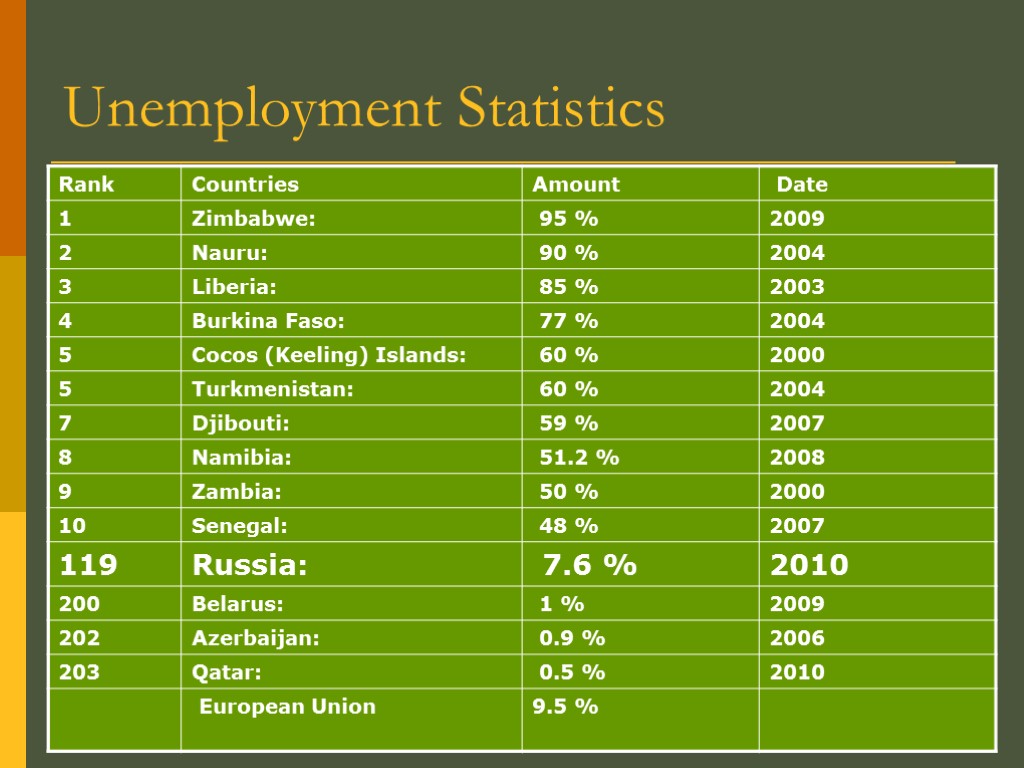
Unemployment Statistics

The Unemployment Rate in Russia The unemployment rate in Russia was last reported at 5.4 percent in July of 2012. Historically, from 1999 until 2012, Russia Unemployment Rate averaged 8.1 Percent reaching an all time high of 14.6 Percent in February of 1999 and a record low of 5.4 Percent in May of 2008. The unemployment rate can be defined as the number of people actively looking for a job as a percentage of the labour force.

The difinition of inflation In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.

Types of Inflation Hyperinflation is the most extreme inflation phenomenon, with yearly price increases of three-digits percentage points and an explosive acceleration. High inflation could range anywhere between 50% and 100%. High inflation is a situation of price increase of 30%-50% a year. Both kinds can be stable or dangerously accelerate to enter in an hyperinflation condition. Moderate inflation -. One could consider an inflation as moderate when it ranges from 5% to 25-30%. Low inflation can be characterized from 1-2% to 5%. Around zero there is no inflation (price stability). Below zero, a country faces deflation.

Causes OF Inflation Demand-pull inflation refers to the idea that the economy actual demands more goods and services than available. The cost-push theory , also known as "supply shock inflation", suggests that shortages or shocks to the available supply of a certain good or product will cause a ripple effect through the economy by raising prices through the supply chain from the producer to the consumer. Money supply plays a large role in inflationary pressure as well. Monetarist economists believe that if the Federal Reserve does not control the money supply adequately, it may actually grow at a rate faster than that of the potential output in the economy, or real GDP. Inflation can artificially be created through a circular increase in wage earners demands and then the subsequent increase in producer costs which will drive up the prices of their goods and services.

Effects OF Inflation The effects of inflation can be brutal for the elderly who are looking to retire on a fixed income. This can be readily tied to higher unemployment rates. When extremes arise in the supply/demand structure, imbalances are created. The mortgage crisis of 2007 is a great example of this. Home prices were increasing at a very rapid rate from 2002 to 2005 and got to the point where the prices became too high, forcing buyers to step aside. A similar example can be seen in the internet euphoria in the stock market back in 1998 to 2000. This rapid acceleration in stock prices eventually became unsustainable and led to a disastrous fall.
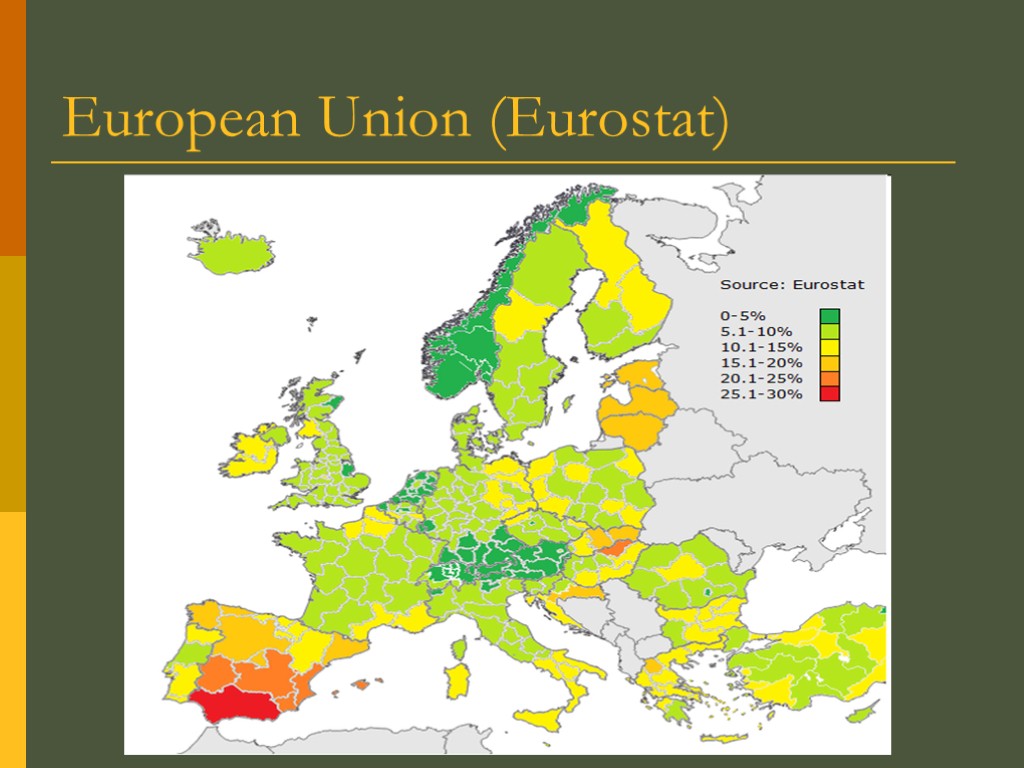
European Union (Eurostat)
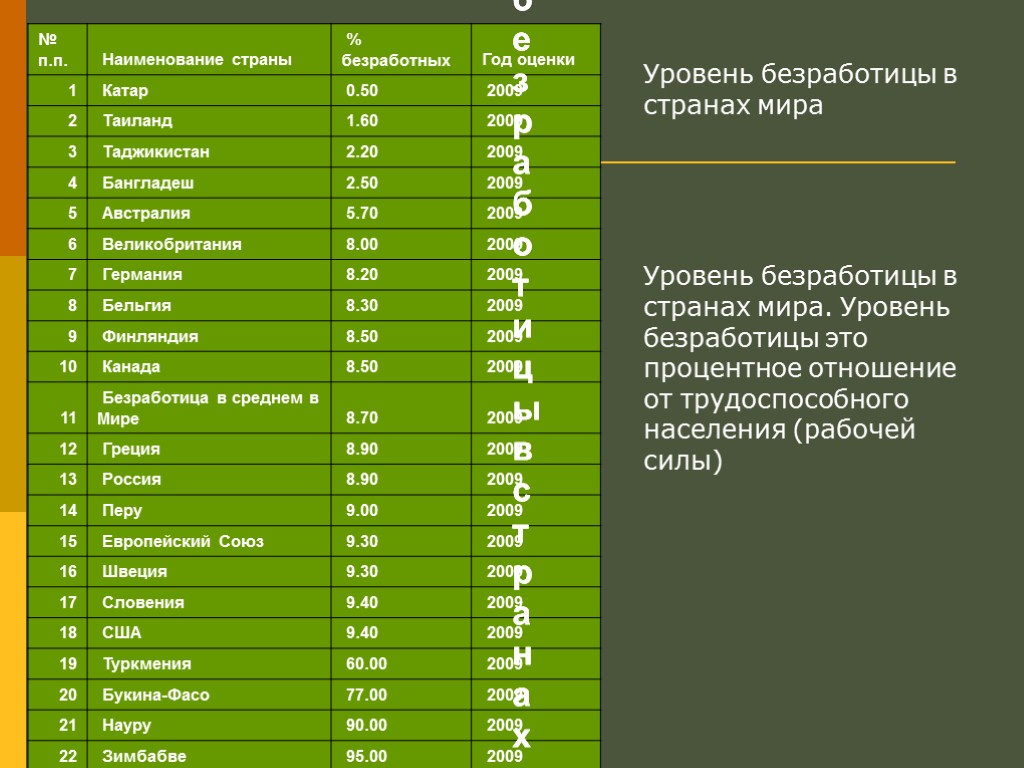
Уровень безработицы в странах мира. Уровень безработицы это процентное отношение от трудоспособного населения (рабочей силы) Уровень безработицы в странах мира
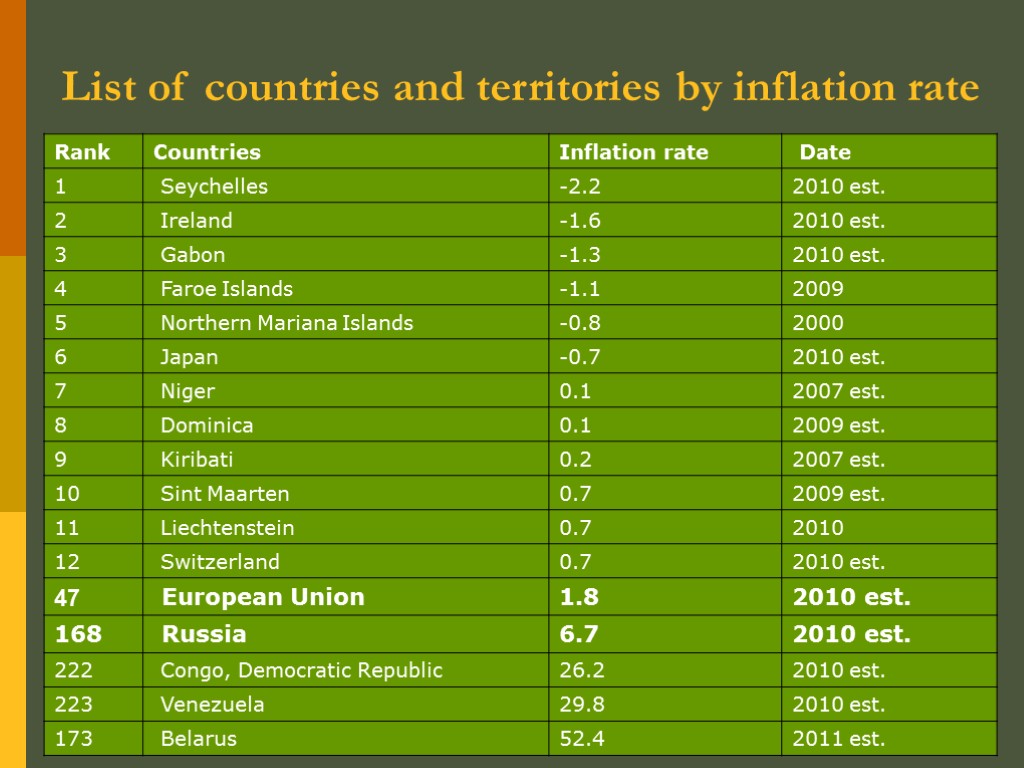
List of countries and territories by inflation rate
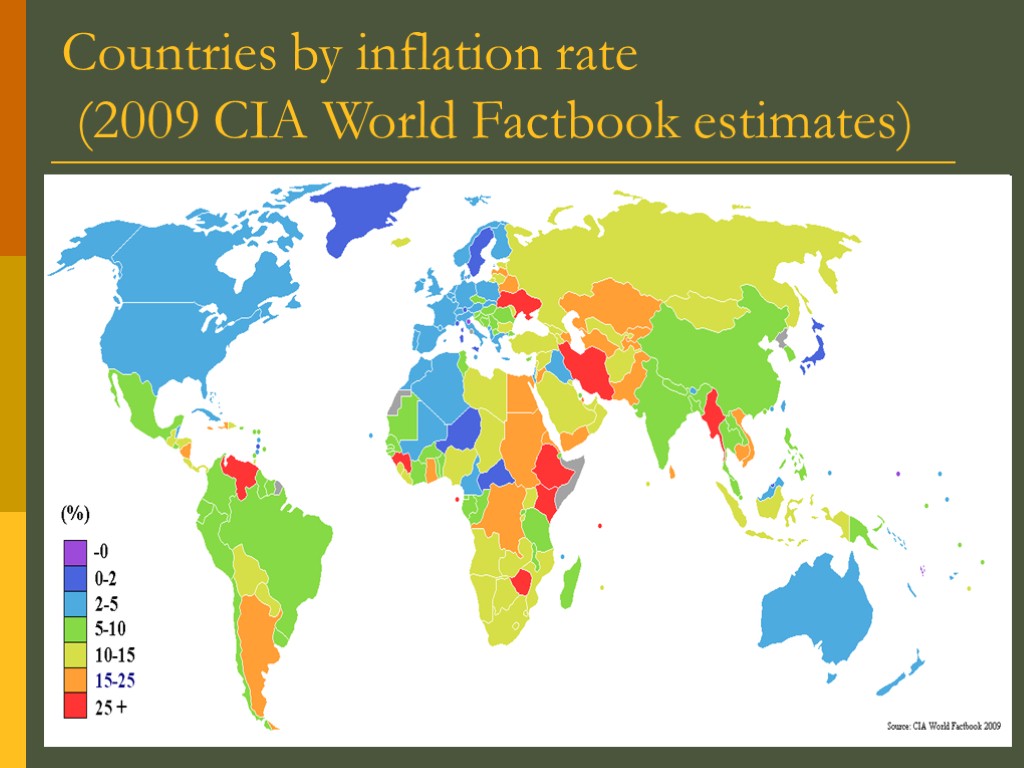

Countries by inflation rate (2009 CIA World Factbook estimates)
basic_economic_terminology-2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

