fb08156fc50805a23db3f6e49a5fb8b7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Basic Economic Concepts Scarcity, Opportunity Cost & PPC Capitalism Characteristics Supply and Demand

SCARCITY n n Economics is the study of limited resources and unlimited needs and wants Scarcity leads to making choices Opportunity Cost is what is sacrificed when one choice is made over the “next best alternative” Every decision has an opportunity cost

Opportunity Cost to every decision!
SCARCITY Marginal decision making = the result of an additional change n Marginal benefits vs. marginal costs is the basis for making the decision n Examples: 1 more hour of sleep vs. eating breakfast Part time job vs. goofing off College vs. full time job n
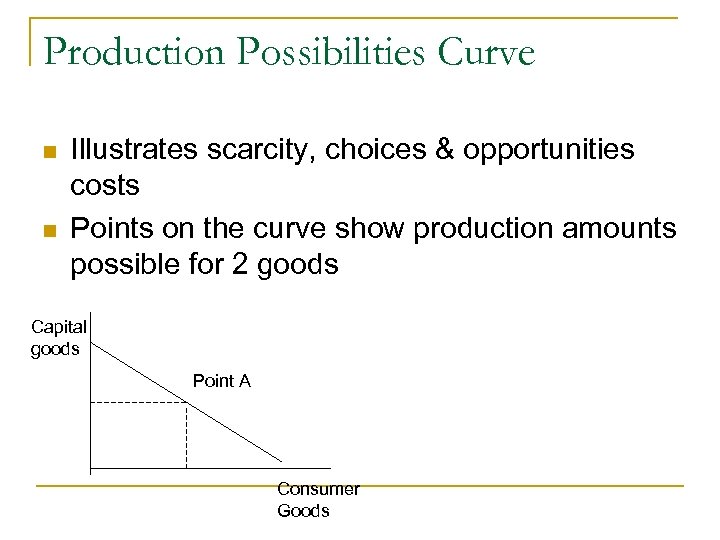
Production Possibilities Curve n n Illustrates scarcity, choices & opportunities costs Points on the curve show production amounts possible for 2 goods Capital goods Point A Consumer Goods
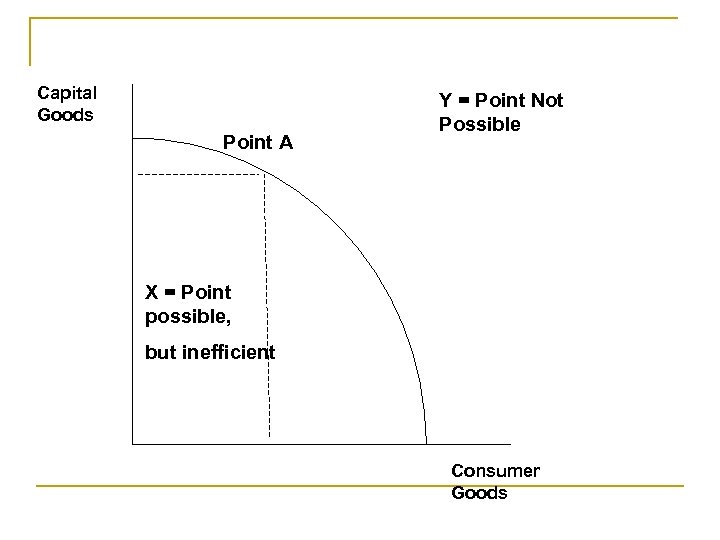
Capital Goods Point A Y = Point Not Possible X = Point possible, but inefficient Consumer Goods

CAPITALISM – MARKET ECONOMY n n n Ownership of all resources is in the hands of individuals Decision making is by individuals in the market Voluntary exchange of goods and services Self interest influences all decisions – to the benefit of society Competition is the regulating mechanism

CAPITALISM – MARKET ECONOMY n n Markets and Prices coordinate the millions of decisions System is facilitated by: q q Specialization Use of money Technology Active, but limited government involvement

CAPITALISM – MARKET ECONOMY n Basic Questions every society must ask: q q q What goods & services to produce? How much to produce? For whom to produce? How will changes be implemented?

Non Sequitur by Wiley Miller
CAPITALISM – MARKET ECONOMY n Lesson on property rights – Power point

Supply and Demand n Go to Power Point on S & D

Problem Areas in AP Economics n n Investment – term defined as business spending for capital equipment, machinery, factories, inventories, etc. Personal investment is NOT used in Macro Investment decisions are MB vs MC MB = rate of return business will receive (profit motive = revenue – cost = profit) n MC = interest rate that must be paid to borrow funds for Ig (gross private investment)

Problem Areas in AP Economics n n n Real Interest rate – cost of borrowing the money to buy the capital goods (machinery) If rate of return is greater than the cost of the interest, the investment will be profitable Ex: 10% rate of return is greater than 7% interest = profitable decision Even if capital is financed by savings, it gives up interest earned on $$$savings REAL interest is used – inflation adjusted $$ (nominal rate – inflation rate = real interest rate)

Problem Areas in AP Economics n Investment Demand Curve shows amount n of Ig at each real interest rate amount Ig Demand Curve shifts (left or right) when other factors change: q q q Costs of production Business taxes Technology changes Excessive inventories (no need for new production) Expectations for future business conditions
Problem Areas in AP Economics n Key Graphs to know and teach: q q q q Circular Flow PPC Supply and Demand Foreign Exchange Rates (S & D) Investment Demand Business Cycles AD/AS (Short Run and Long Run)
Problem Areas in AP Economics n Key Graphs to know and teach: q q q Loanable Funds (S & D) + AD/AS (Fiscal Policy) Money Market + Ig Demand + AD/AS (Monetary Policy) Phillips Curve (Long Run and Short Run) Laffer Curve Cost Curves (Micro)
fb08156fc50805a23db3f6e49a5fb8b7.ppt