c005eaf99cb6f071e7fffd65f0f587ee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
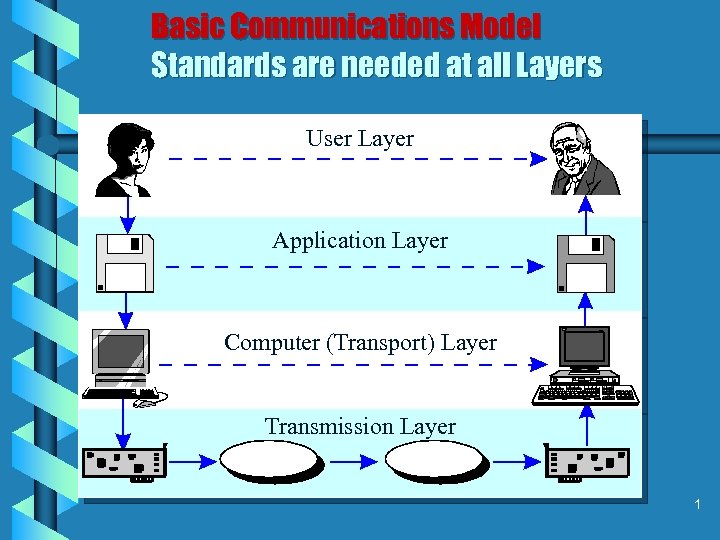
Basic Communications Model Standards are needed at all Layers User Layer Application Layer Computer (Transport) Layer Transmission Layer 1
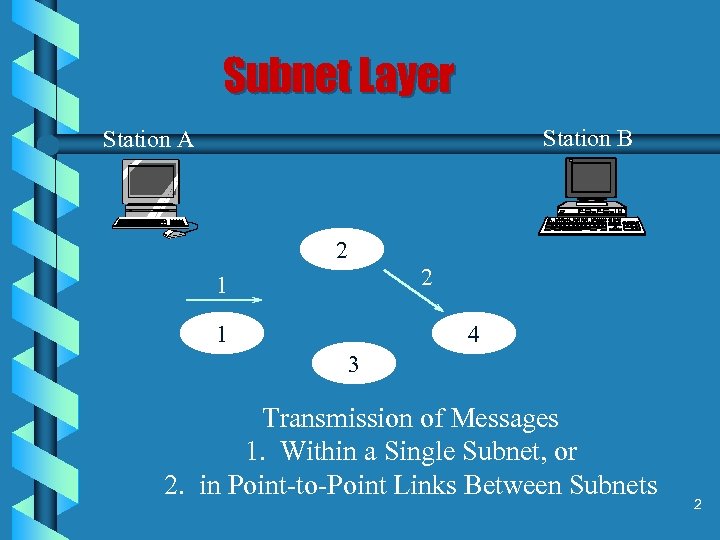
Subnet Layer Station B Station A 2 2 1 1 4 3 Transmission of Messages 1. Within a Single Subnet, or 2. in Point-to-Point Links Between Subnets 2
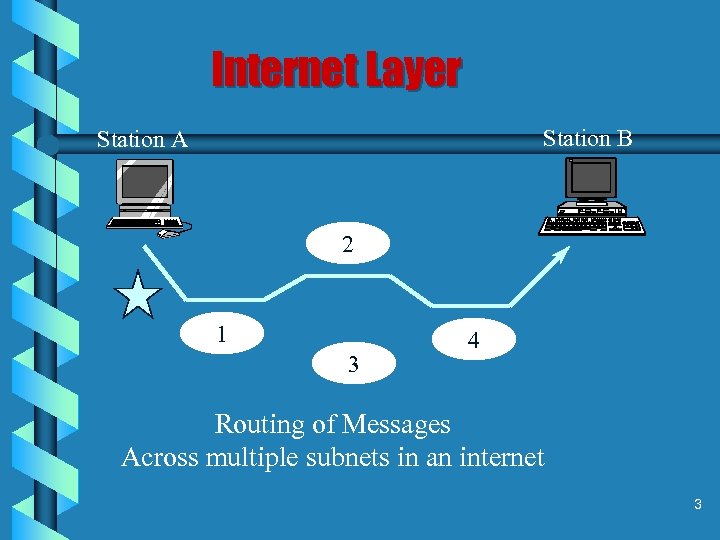
Internet Layer Station B Station A 2 1 3 4 Routing of Messages Across multiple subnets in an internet 3
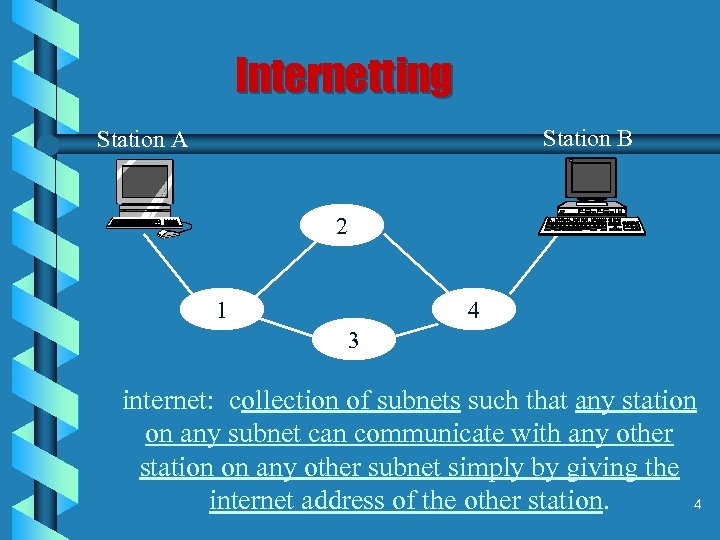
Internetting Station B Station A 2 1 4 3 internet: collection of subnets such that any station on any subnet can communicate with any other station on any other subnet simply by giving the 4 internet address of the other station.
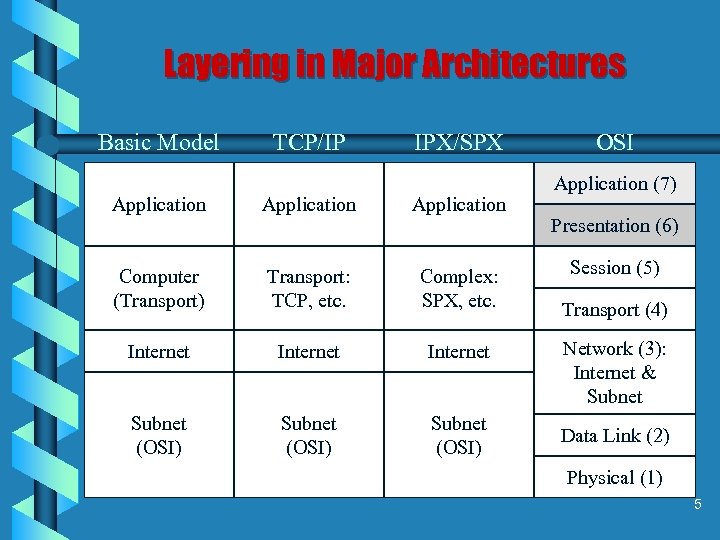
Layering in Major Architectures Basic Model TCP/IP IPX/SPX Application Computer (Transport) Transport: TCP, etc. Complex: SPX, etc. Internet Subnet (OSI) OSI Application (7) Presentation (6) Session (5) Transport (4) Network (3): Internet & Subnet Data Link (2) Physical (1) 5

OSI Architecture b Reference Model for Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) b Standards Agencies • • • ISO (computers) Don’t confuse OSI and ISO! ITU-T (telecommunications) b De jure standards (official/open) 6
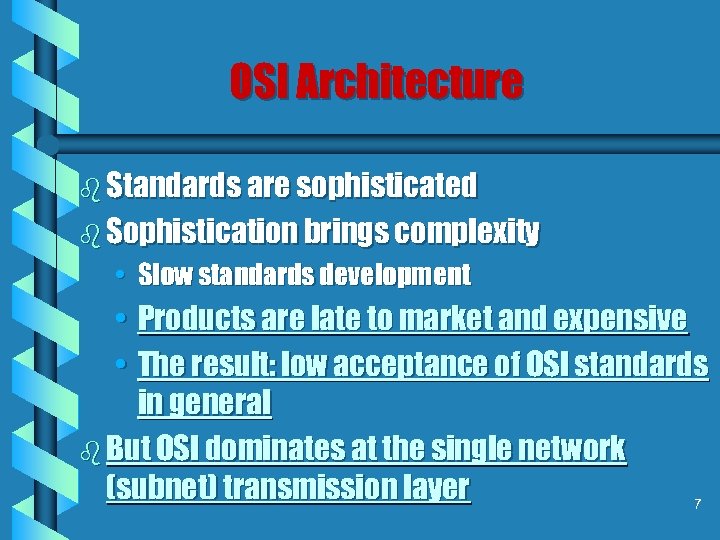
OSI Architecture b Standards are sophisticated b Sophistication brings complexity • Slow standards development • Products are late to market and expensive • The result: low acceptance of OSI standards in general b But OSI dominates at the single network (subnet) transmission layer 7

Physical Layer (OSI Layer 1) b Physical transmission standards b Physical • • Connector Transmission media b Electrical • Voltage levels • Meanings of various voltage levels 8

The Data Link Layer (OSI Layer 2) 9
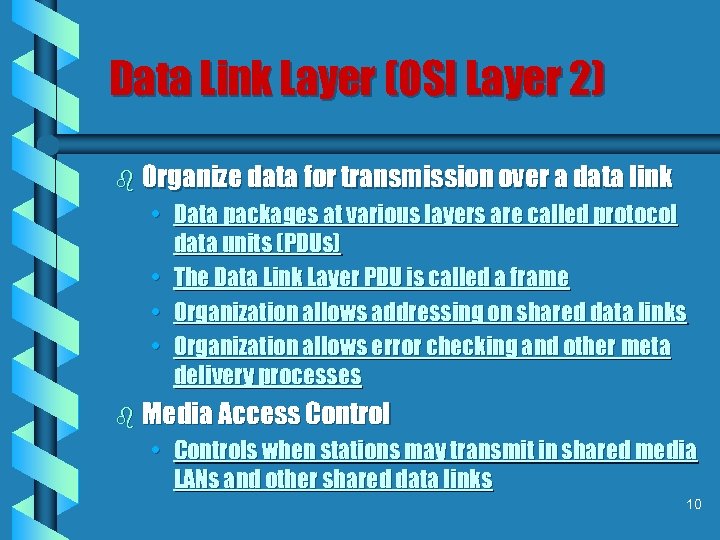
Data Link Layer (OSI Layer 2) b Organize data for transmission over a data link • Data packages at various layers are called protocol data units (PDUs) • The Data Link Layer PDU is called a frame • Organization allows addressing on shared data links • Organization allows error checking and other meta delivery processes b Media Access Control • Controls when stations may transmit in shared media LANs and other shared data links 10

TCP/IP Architecture b Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) • Of the Internet Society b De jure (official/open) 11

TCP/IP Architecture b Standards are simple • Often have “Simple” in the name • Standards and products are fast to market • Products are inexpensive and fast to market b Widely Used • On the Internet • In many corporate networks • Dominates at internet and transport layers 12

IPX/SPX b Novell Corporation b De facto (proprietary/closed) b Used only in Novell Net. Ware PC networks • But Net. Ware dominates PC networking • Second most widely used architecture at transport layer 13

SNA b Systems Network Architecture b IBM Corporation b De facto (proprietary/closed) b Dominates in mainframe communication • On IBM mainframe systems • On mainframe systems of other vendors 14
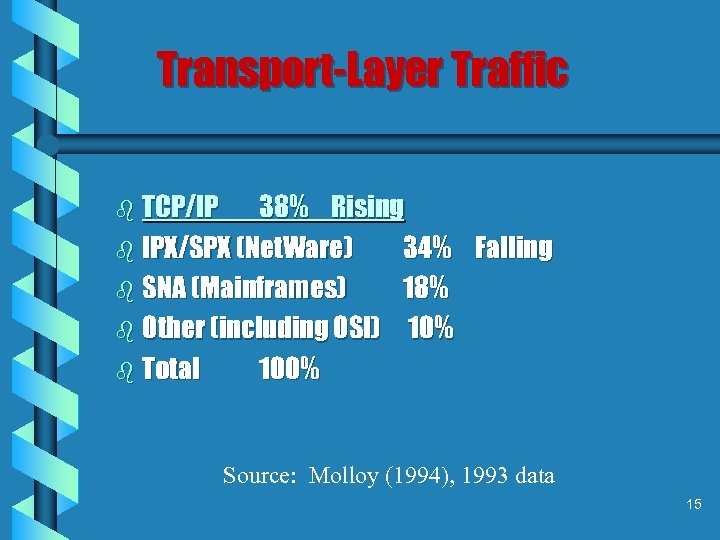
Transport-Layer Traffic b TCP/IP 38% Rising b IPX/SPX (Net. Ware) 34% Falling b SNA (Mainframes) 18% b Other (including OSI) 10% b Total 100% Source: Molloy (1994), 1993 data 15
Transmission Speeds b Bit: single 1 or 0 b Transmission speed is measured in bits per second (bps) • Duration of a single bit • Not velocity of propagation 10110100001110100101111010101 16
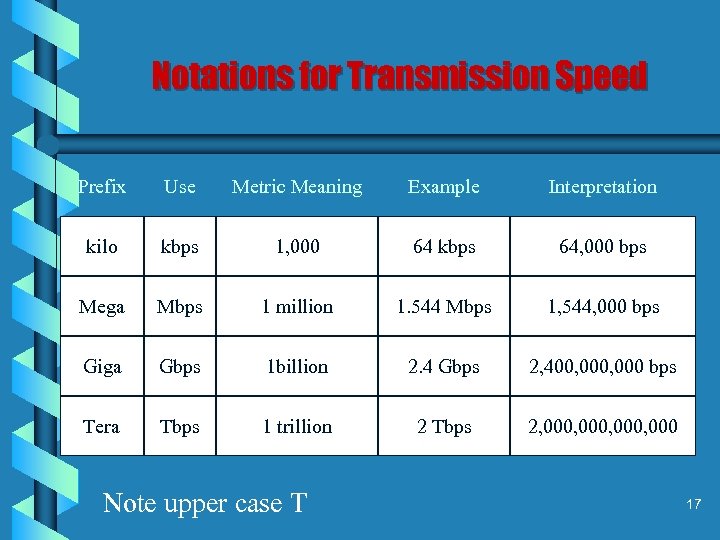
Notations for Transmission Speed Prefix Use Metric Meaning Example Interpretation kilo kbps 1, 000 64 kbps 64, 000 bps Mega Mbps 1 million 1. 544 Mbps 1, 544, 000 bps Giga Gbps 1 billion 2. 4 Gbps 2, 400, 000 bps Tera Tbps 1 trillion 2 Tbps 2, 000, 000 Note upper case T 17

LANs, MANs, & WANs b LAN • • Local area network Single office, building, campus 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps to the desktop common 1 Gbps coming b Will carry most traffic, because most traffic is local 18
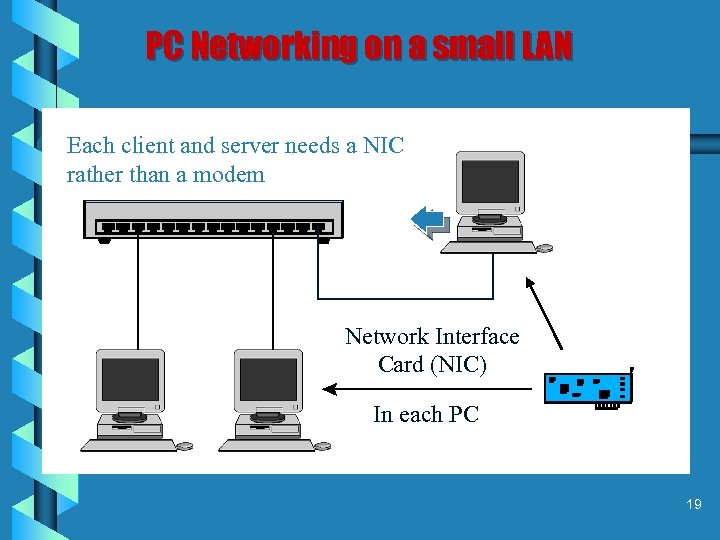
PC Networking on a small LAN Each client and server needs a NIC rather than a modem Network Interface Card (NIC) In each PC 19
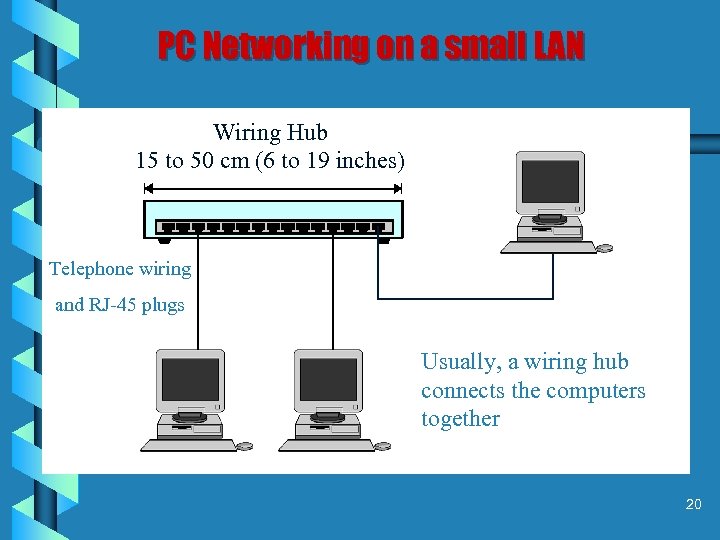
PC Networking on a small LAN Wiring Hub 15 to 50 cm (6 to 19 inches) Telephone wiring and RJ-45 plugs Usually, a wiring hub connects the computers together 20

LANs, MANs, & WANs b WAN • • Wide area network Intercity, international 9, 600 bps to 1 Mbps common to the desktop Links with higher speed are usually shared (multiplexed) by several desktops b Emerged before LANs, due to high cost of long-distance telephone charges 21
c005eaf99cb6f071e7fffd65f0f587ee.ppt