92f437265d72ce0c1629e116de21619f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Basic Business Law (BPP 432/80) 2006 Fall Quarter Instructor: David Oliveiri Week 11: Facilitating Exchange Through Business Association; Corporations – Governance, Sarbanes-Oxley, Fundamental Changes

Agenda Role of Shareholders Role of Directors Role of Officers Duties of Directors and Officers Sarbanes-Oxley Impacts Fundamental Changes of Corporations

Learning Objectives Understand Shareholder, Director, and Officer Relationships, and How Corporate Risk/Control Bargaining Orders These Relationships Understand the Elements of the Shareholder’s Role Understand the Elements of the Director’s and Officer’s Roles and Pertinent Distinctions Between These Roles Understand the Legal Standards of Director and Officer Performance Understand What Sarbanes-Oxley Act Provides and How the Act Affects Director and Officer Roles Understand What are Fundamental Corporate Changes, Requiring Special Approval

Corporate Governance, Generally “New” Participants – Shareholders, Directors, Officers Primary Theme: – Separation of Ownership and Control – Broad Delegation (Shareholders Directors Officers) of Day-to. Day Operations Agency Principles Interwoven Deal Point of Risk vs. Control Foremost in Defining Relationships Among Participants Institutional Shareholder Services, Inc. – Service Providing Corporate Governance Ratings That Correlate Various Governance Variables and Financial Performance

Shareholders Owners of Corporation Residual or Equity Interest Similar to Sole Proprietors, Partners? Role of Shareholders = f (VD, VFC, P)

Shareholders’ Voting Rights – “One Share/One Vote” Primary “Forum” – Annual (By-Laws) and Special Shareholder Meetings Meeting Requirements -- Quorum (Majority Outstanding Stock “Represented”) + Majority Vote -- Exception: Articles Election of Directors – Annual (Unless 9 or More), Straight Voting v. Cumulative Voting Approval of Fundamental Changes Concentrations of Voting Power – Proxies, Voting Trusts, Shareholder Voting Agreements Restrictions on Transfers of Shares – Note on Stock Certificate [S&R 36 – Problem 8]
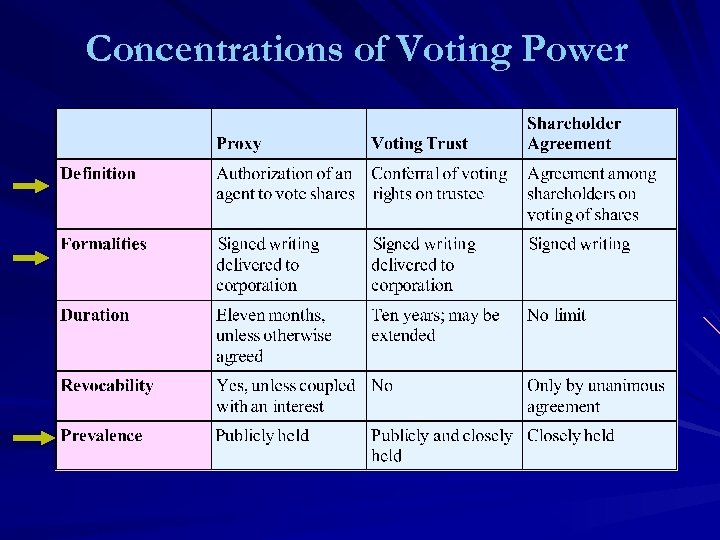
Concentrations of Voting Power

Shareholders’ Policing Rights Right to Inspect Books and Records = f (Good Faith, Proper Purpose) Compaq Case (S&R p. 707) v. Honeywell Case Right to Sue to Enforce Shareholder Rights – Direct Suits – Derivative Suits Right to Dissent to Fundamental Changes; Appraisal and “Cash Out” Steve Case, co-founder of AOL and architect of the ill-fated AOL-Time Warner merger, res from. TW’s Board in the face of the opposition of shareholders angered by the deal, which led write-downs, shareholder lawsuits, regulatory scrutiny, and a management purge – Roches 11/1/05
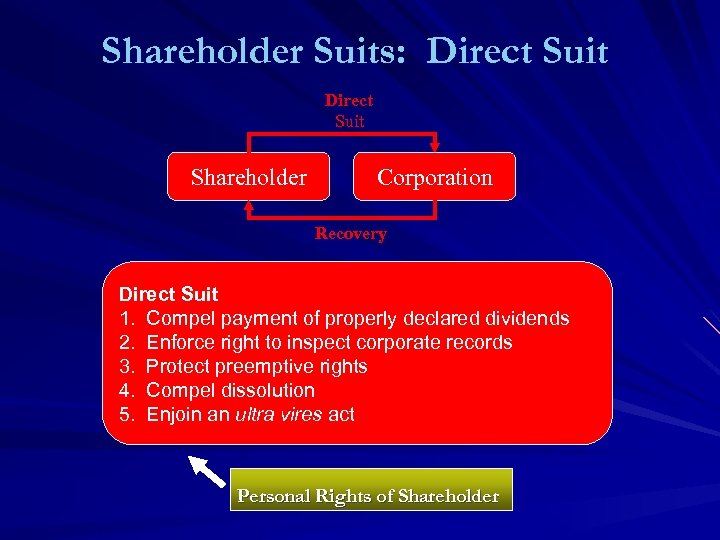
Shareholder Suits: Direct Suit Shareholder Corporation Recovery Direct Suit 1. Compel payment of properly declared dividends 2. Enforce right to inspect corporate records 3. Protect preemptive rights 4. Compel dissolution 5. Enjoin an ultra vires act Personal Rights of Shareholder

Shareholder Suits: Derivative Suit Shareholder Third Party Recovery Corporation Derivative Suit 1. Recover damages from management for breach of duty 2. Recover improper dividend 3. Enjoin wrongful issuance of shares 4. Recover damages from third party 5. Recover damages from management for ultra vires act. “On Behalf Of” Corp. ; All SH Benefit

Directors Basic Function: Delegated Power and Duty to Manage the Corporation Not Strictly Agents of Shareholders or Corporation But … Trustee-Like (Agent-Like) Fiduciary Duties Basic Directors’ Duties: – – – – Determine By-Laws Select and Remove Officers Determine Capital Structure Initiate Fundamental Changes Declare Dividends Determine Management Compensation +SOX Enhancements

Directors 101 Who Are They? – Insiders – Friends/Associates – Outsiders How Do People Become Directors? – Number (NY -- 3 or More Unless…) – Election (Articles 1 st SH Meeting Annually Unless Staggered) How Do Directors Do Their Job? – Collectively – In Meetings!! Quorum and Voting Action Taken Without Meeting – – – Delegation of Powers Directors’ Inspection Rights Compensation [S&R 36 – Problem 2, 3]

Officers Selection and Removal (“Exception”: Employment Contract) Role /Agents of the Corporation Authority Set and Delegated by Directors (Via By-Law or Board Resolution) Authority Impacts = f (Actual Express Authority [Articles, By-Laws, Board Resolution], Implied Authority, Apparent Authority, Ratification)

Fiduciary Duties of Directors and Officers ― Standards of Performance!! Obedience Diligence -- Review Quality of Decision Process – Ordinary Care – Reliance Upon Others Permitted – Business Judgment Rule – Immunizes Good Faith Decisions in Face of Uncertainty [S&R 36 – Problem 1] Loyalty – Review Fairness and Reasonableness of Specific Activities – – – Conflict of Interest [S&R 36 – Problems 5 a, b] Loans to Directors Corporate Opportunity [Broz] Transactions in Shares Duty Not to Compete +SEC Standards – The SEC notified 3 high-profile current and former directors of H International Inc. that they may be sued for failing to spot fraud that senior execs of newspaper company are suspected of committing – NY Times 12/15/05
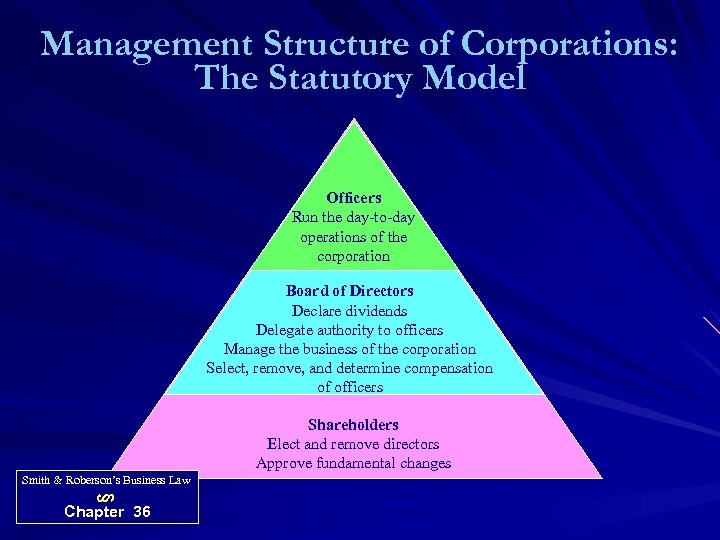
Management Structure of Corporations: The Statutory Model Officers Run the day-to-day operations of the corporation Board of Directors Declare dividends Delegate authority to officers Manage the business of the corporation Select, remove, and determine compensation of officers Shareholders Elect and remove directors Approve fundamental changes Smith & Roberson’s Business Law § Chapter 36

Management Structure of Typical Closely Held Corporation Shareholders = Directors = Officers Relative Problems – Boards of Family Businesses Grapple With How to Sack Executives Who Are Kin – WSJ 7/24/06
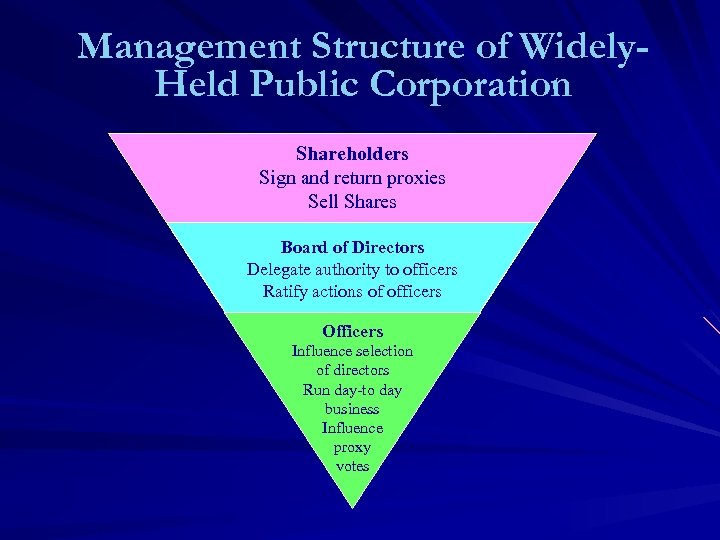
Management Structure of Widely. Held Public Corporation Shareholders Sign and return proxies Sell Shares Board of Directors Delegate authority to officers Ratify actions of officers Officers Influence selection of directors Run day-to day business Influence proxy votes

Sarbanes-Oxley Act An Act to protect investors by improving the accuracy and reliability of corporate disclosures made pursuant to the securities laws, and for other purposes 1/23/02 –

Sarbanes-Oxley Act (a. k. a. Public Company Accounting Reform and Investor Protection Act of 2002, SOX, Sarb. Ox) Legislative Reaction to Corporate and Accounting Scandals (Enron, Tyco, World. Com, …) New and Enhanced Standards for U. S. Public Companies, Boards, Management, and Public Accounting Firms Requires the SEC to Implement Regulations Specific Provisions: – – – Public Company Accounting Oversight Board Auditor Independence Corporate Responsibility Enhanced Financial Disclosures Enhanced White Collar Crime Penalties • Restatements of financial results by public companies soared in 2005, in part due to SOX – WSJ 3/3/ • Make SOX Fit – WSJ Editorial (Harvey L. Pitt, Former SEC Chairman) 4/13/06

Fundamental Changes of Corporations Economic Good Sense to Facilitate Fundamental Changes But … Fundamental Changes Materially Impact Interests of Shareholders, Officers, and Directors So, …Legal Rules for Approval Balance Economic Good Sense and Interests of Stakeholders What Are Fundamental Changes? – Charter Amendments – Combinations – Dissolution/Going Private Rights of Dissenting Shareholders
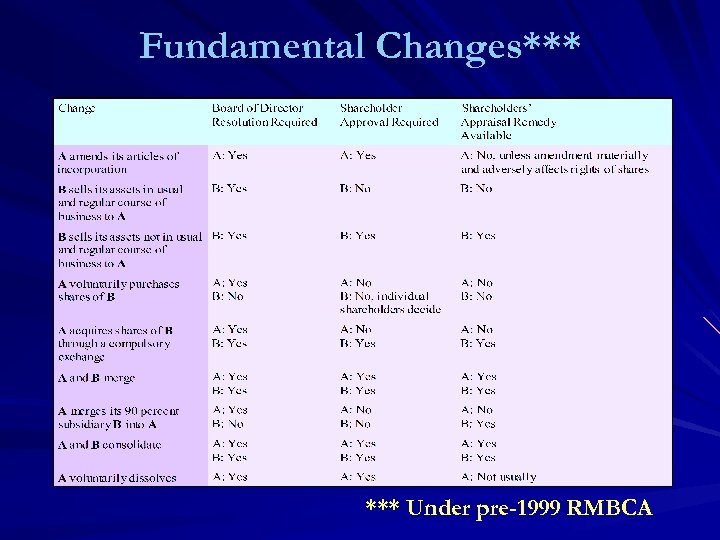
Fundamental Changes*** Under pre-1999 RMBCA

Bottom Lines; Q&A Separation Of Ownership And Management Characterizes Corporations – And Minimizes Shareholder Transactions Costs Shareholders Have No Duties, Generally! Broad Director and Officer Authority Is Bounded By Shareholder (+ Regulatory) Oversight/Legal Standards Of Performance The Business Judgment Rule Immunizes Good Faith Decisions; Application Is Fact-Based (i. e. Local) Sarbanes-Oxley Enhances Legal Standards Of Performance For Public Company Officers, Directors, Auditors, Lawyers
92f437265d72ce0c1629e116de21619f.ppt