Bank+regulation.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Bank regulation

Need for banking regulation? • Banks’ fragility • Systemic risk • Protection of depositors
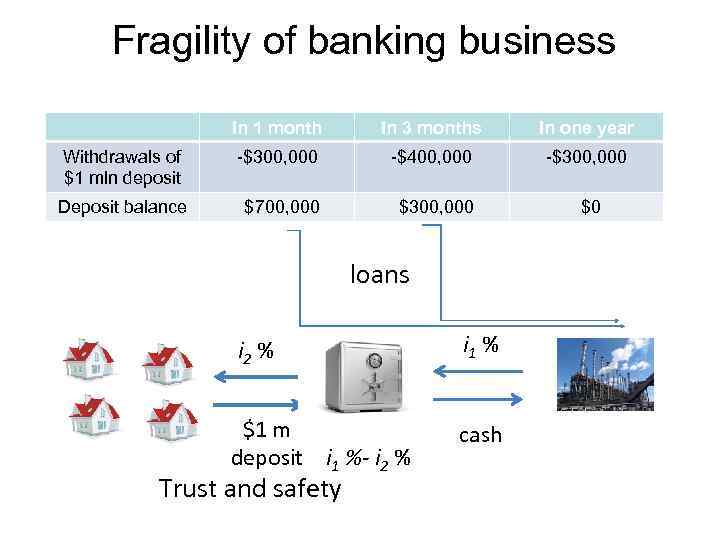
Fragility of banking business In 1 month In 3 months In one year Withdrawals of $1 mln deposit -$300, 000 -$400, 000 -$300, 000 Deposit balance $700, 000 $300, 000 $0 loans i 2 % i 1 % $1 m deposit i 1 %- i 2 % cash Trust and safety
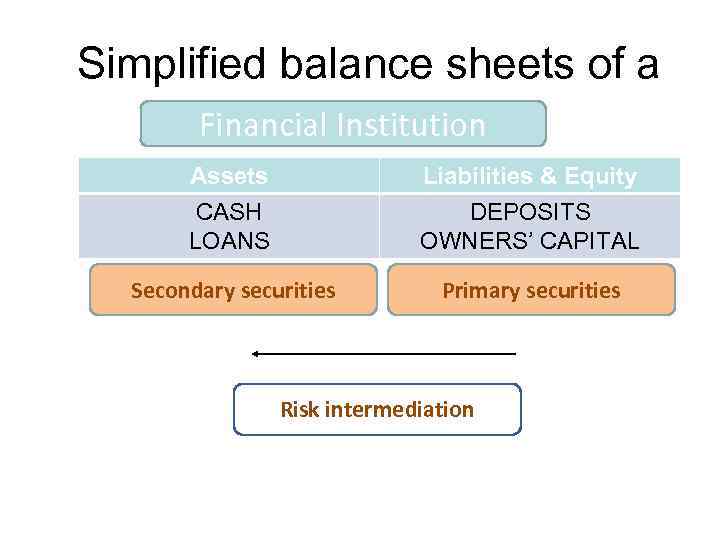
Simplified balance sheets of a Financial Institution Assets CASH LOANS Liabilities & Equity DEPOSITS OWNERS’ CAPITAL Secondary securities Primary securities Risk intermediation

E. g. 1. Deposits’ Withdrawals and Systemic Risk
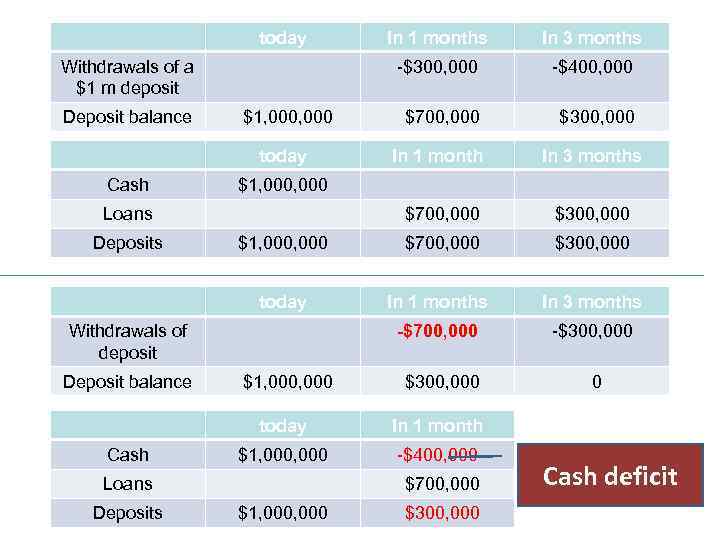
today In 1 months In 3 months -$300, 000 -$400, 000 $1, 000 $700, 000 $300, 000 today In 1 month In 3 months $700, 000 $300, 000 $1, 000 $700, 000 $300, 000 today In 1 months In 3 months -$700, 000 -$300, 000 $1, 000 $300, 000 0 today In 1 month $1, 000 -$400, 000 Withdrawals of a $1 m deposit Deposit balance Cash $1, 000 Loans Deposits Withdrawals of deposit Deposit balance Cash Loans Deposits $700, 000 $1, 000 $300, 000 Cash deficit
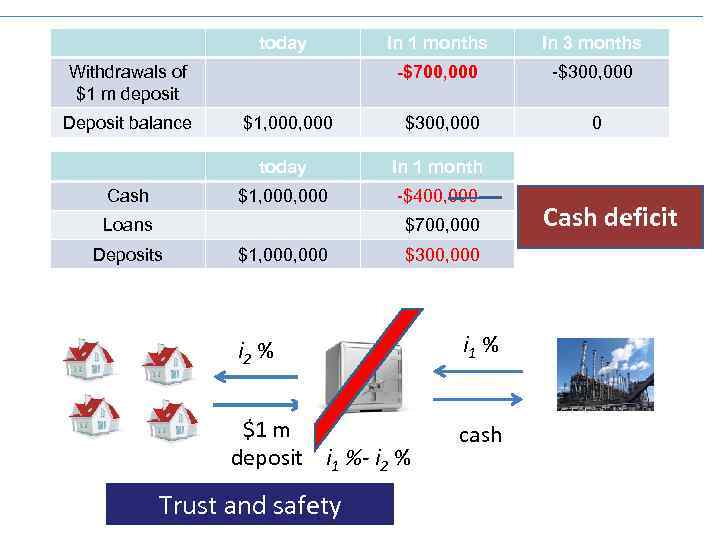
today In 1 months In 3 months -$700, 000 -$300, 000 $1, 000 $300, 000 0 today In 1 month $1, 000 -$400, 000 Withdrawals of $1 m deposit Deposit balance Cash Loans $700, 000 Deposits $1, 000 $300, 000 i 2 % i 1 % $1 m deposit i 1 %- i 2 % cash Trust and safety Cash deficit
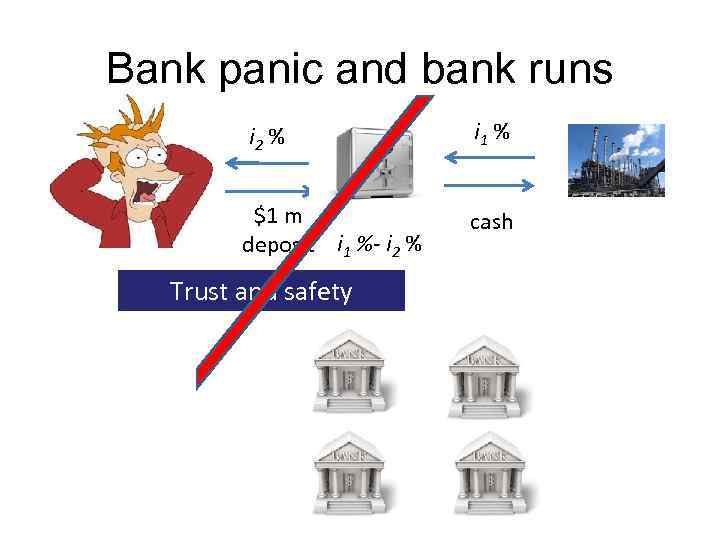
Bank panic and bank runs i 2 % i 1 % $1 m deposit i 1 %- i 2 % cash Trust and safety

E. g. 2. Deterioration of loans quality

Deterioration of loan quality today Loans Deposits In 1 month $1, 000 $800, 000 $1, 000 Net loss $1, 000 $-200, 000 today Loans Loan quality deteriorates In 1 month $1, 000 $800, 000 Deposits $ 700, 000 Capital $ 300, 000 $700, 000 $100, 000 Bank capital as a cusion against losses
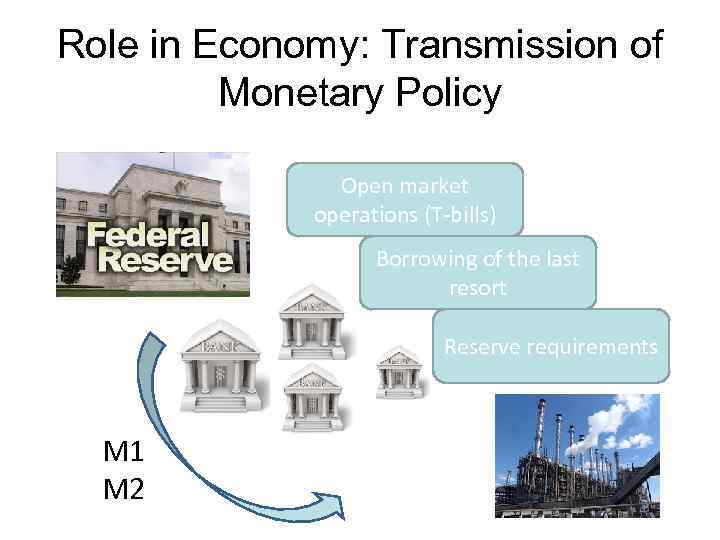
Role in Economy: Transmission of Monetary Policy Open market operations (T-bills) Borrowing of the last resort Reserve requirements M 1 M 2

Summary • FIs are a delegated monitor over the borrowers when there is: – Economies of scale in information costs – Benefits of economies of scale > cost of delegation • FIs are risky because of: – Assets transformation – Maturity intermediation – Denomination intermediation • FI are important in economy since they – facilitate payment transactions – allocate investments – are transmitters of central banks’ monetary policy

Central Banks 1991 1913 1864 1998
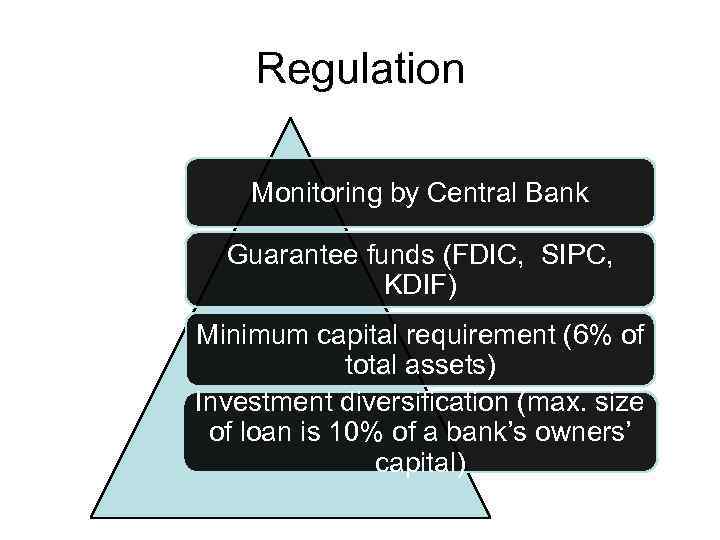
Regulation Monitoring by Central Bank Guarantee funds (FDIC, SIPC, KDIF) Minimum capital requirement (6% of total assets) Investment diversification (max. size of loan is 10% of a bank’s owners’ capital)
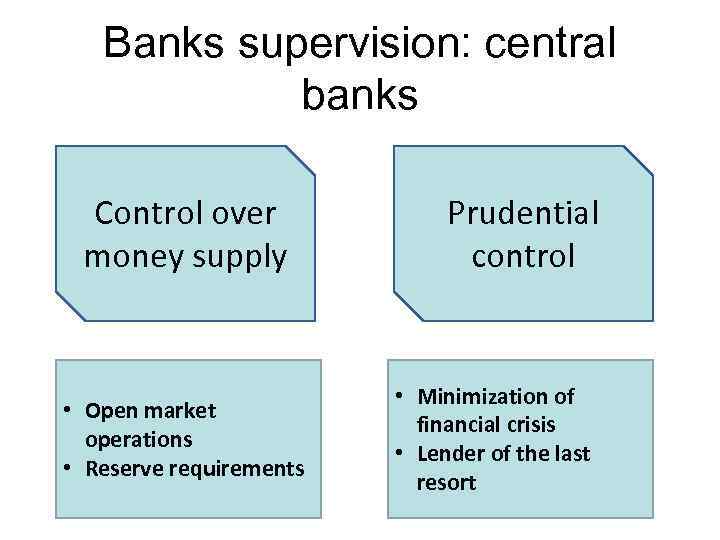
Banks supervision: central banks Control over money supply • Open market operations • Reserve requirements Prudential control • Minimization of financial crisis • Lender of the last resort

Deposits insurance • Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) – Established in 1934 – Resulted in decline of bank failure rate from 28. 16% in 1933 to 0. 27% in 1934 • Insurance size: – $250, 000 in the USA – £ 75, 000 in the UK – € 100, 000 in the most of EU

Banks supervision: restriction on entry • Chartering and licenses • Minimum capital requirements: – UK: £ 5 mln. – KZ: KZT 10 bn. – EU: € 5 mln. • Basel I, Basel III capital requirements: Equity to Total assets ratios
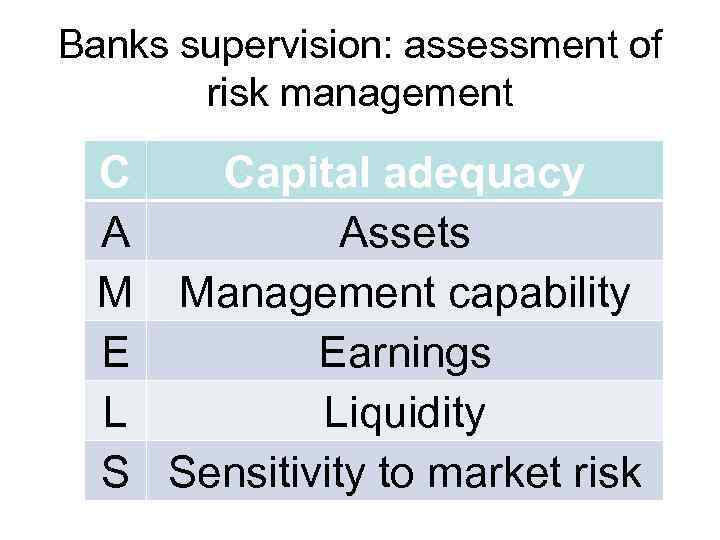
Banks supervision: assessment of risk management C Capital adequacy A Assets M Management capability E Earnings L Liquidity S Sensitivity to market risk

Regulations • Consumer protection: – Community Reinvestment Act (CRA): banks must serve local communities – Home Mortgage Disclosure Act (HMDA): prohibited discrimination on the basis of age, race, sex, or income
Regulation NOT TO REGULATE

Calculate risk asset ratio • Under Basel I bank capital requirement: Risk-asset ratio = Asset Cash Government bills Risk rate 0% 0% Mortgages Commercial loans 50% 100% amount $1, 600 $1, 500 $14, 000 $12, 000
Bank+regulation.ppt