28d2d54f3dc94b6e7de11933148d0893.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 108

BANK AUDIT A Practical Approach By CA Ajay Atolia 1

BANK AUDIT • Banking is a dynamic activity. Therefore Banks are different from most other commercial enterprises. Now a days banking has constantly been undergoing a change. 2

BANK AUDIT • Significant Segment of our Practice • To be completed in shortest possible time. 3

BANK AUDIT • Divergences observed by RBI. Over the period due to increase in NPAs in the banking system, RBI has been taking a stricter cognizance of the divergences. In the meeting of CSA, RBI has raised the following issues: 4

BANK AUDIT • Divergences observed by RBI. • NPA not properly identified whereas the same have been identified in normal course of audit. • Exact date of NPA not recorded. • Classification between secured and unsecured • Non implementation of Restructuring packages • Direct v/s indirect landing • Non fund based exposure 5

BANK AUDIT • Increased in Responsibility • Prudential Norms • Restructuring Norms • Anti Money Laundering Norms • Basel II and III • Increase in Certification • Information Technology and CBS • Auditing Standards 6

BANK AUDIT Expectation- Opinion on True and Fair View • Bank: With Time Line • Auditor: ICAI With Documentation • Regulator: With Compliance • Share Holder Fair -Without any window dressing 7

BANK AUDIT Role of Branch Auditor Role of Branch auditor is very important. All the advances and deposits of the bank are accounted at branches and being audited by branch auditors. Among the branches under audit only 20 branches being audited by CSA. Therefore Central Auditors are heavily relied on work of Branch Auditors. 8

Type of Work • Work to be done in Bank audit being divided into four parts. • Statutory Audit • Long Form Audit Report • Tax Audit • Certificate 9

BANK AUDIT Initial Consideration The matters to be considered by a proposed central auditor/branch auditor upon receiving intimation of appointment. 10
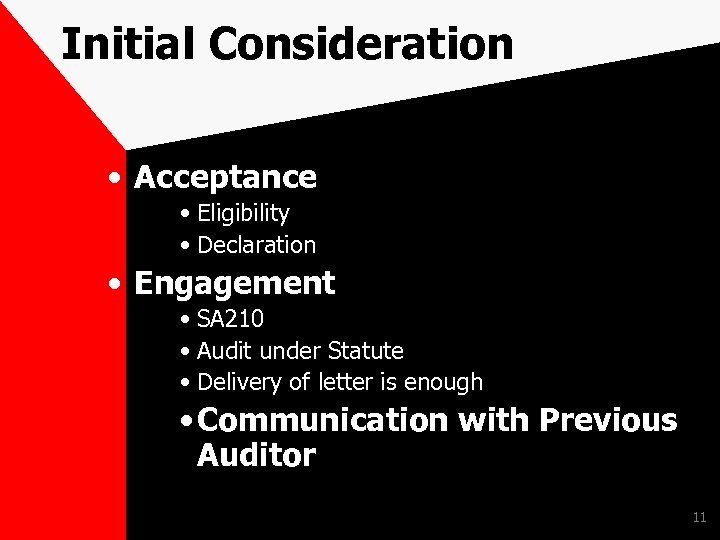
Initial Consideration • Acceptance • Eligibility • Declaration • Engagement • SA 210 • Audit under Statute • Delivery of letter is enough • Communication with Previous Auditor 11

AUDIT PLANNING We have to achieve what the Auditing Standards expect from us, with in the giving timeliness. Practically we have 10 to 12 working days to plan and equipped us to complete the audit. 12

Audit Planning • Hence it becomes imperative to plan the audit in systematic manner to enable completion of all the important area leaving no room for any material misstatement. • What is basically needed for effective execution of the job is, error free documentation and effective preparation of related working papers. 13

Audit Planning • Knowledge of branch business: The auditor must know the business composition of the branch, nature and size of the branch. This understanding will help to design the audit program. 14

Audit Planning • Audit Program • Define the Scope of Audit • Significant Audit Areas • Materiality Level • Over all time schedule • Sample Size • Set of instructions 15

Audit Planning • Communication with Branch • For smooth and timely completion • Inform time schedule • List of requirements • Used as Representation letter • Banks guidelines for Closing and Audit • Accounting Policy of The bank 16

Audit Planning • Access to System • Request for user id (view only) • Guidance Note on Bank Audit issued by ICAI • CA Journal Feb. 2017 • A Check list for Branch Overview and Internal Control is annexed as Annexure IV 17

Audit Planning • Adherences of SA ( Standard of Auditing) • SA- 260 and 265 SA 260 deals with the auditor’s responsibility to communicate with those charged with governance in relation to an audit of financial statements. In addition, SA 265 establishes specific requirements regarding the communication of significant deficiencies in internal control the auditor has identified during the audit to those charged with governance. 18

Audit Planning • SA- 600 Para 19 of SA state that there should be sufficient liaison between the principal auditor and the branch auditor. SA- 700, 705 and 706: These SA defines the manner of reporting in auditor’s report and inclusion of qualifications and matter of emphasis in auditor’s report. 19

AUDIT PROCEDURE 20

Accounting Software’s (System) 1. CBS Now all the bank branches are under CBS system. It is important to note that CBS system is used only for accounting of day to day transactions of the Bank. Closing Returns only in respect of Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss Account are generated from the CBS system. Therefore give the attention towards exception reports generated through CBS system. 21

Accounting Software’s (System) CBS- Key Points 1. Maker Checker concept 2. Password Controls 3. Day start/Day end activities 4. Master Creations 5. Exception Reports 6. Audit Trails 22

Accounting Software’s (System) CBS- MIS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Interest Flag Report- No Pending Insurance Limit Expiry Report Overdue Report of advances Limitation Expiry Report (Loan acknowledgement) 6. TOD Report 7. Overdue Deposit Report 8. Dormant Flag Report 23

Accounting Software’s (System) 2. Other Software's Returns related to asset classification as per RBI guidelines on Prudential Norms on Income Recognition and Asset Classification for advances, calculation of capital charge on credit risk as per BASEL II requirements, submission of CIBIL data and other various reports for financial reporting and regulatory compliance are being generated through other system 24

Accounting Software’s (System) 2. Other Software's • The data in this software is migrated from the CBS system with manual interventions. • Banks are heavily relying on the returns generated through this software, for various Policy decisions / MIS requirements. • Any deviation / error in the data of this software shall have serious implications, inclusive of attracting penal provisions by Regulators. 25

Statutory Audit • As per Banking Regulation Act, 1949 • Balance Sheet • Profit & Loss A/C • Other Annexure • True & Fair view 26

Balance Sheet As per Form ‘A’ of Third schedule of Banking Regulation Act. Assets Side • Cash and Balances with RBI, Balances with Bank and Money at call, Investments, , Fixed Assets and Other Assets. Advances Liabilities Side • Capital , Reserve and Surplus, Deposits, Borrowings, Other Liabilities and Provisions 27
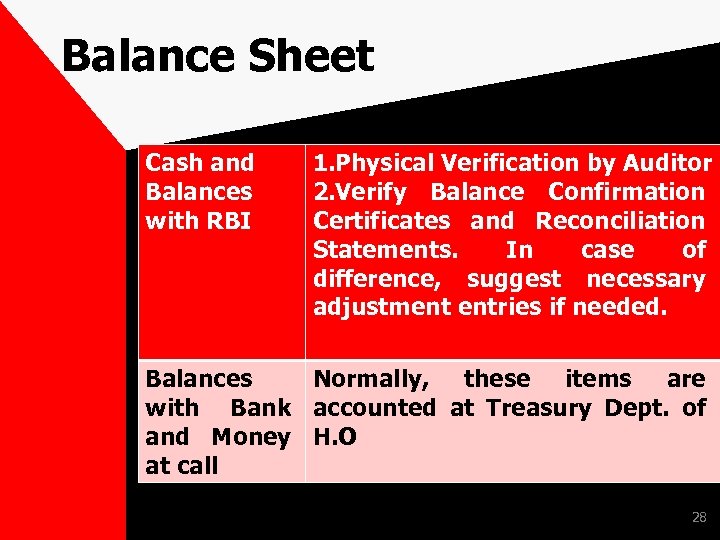
Balance Sheet Cash and Balances with RBI 1. Physical Verification by Auditor 2. Verify Balance Confirmation Certificates and Reconciliation Statements. In case of difference, suggest necessary adjustment entries if needed. Balances Normally, these items are with Bank accounted at Treasury Dept. of and Money H. O at call 28
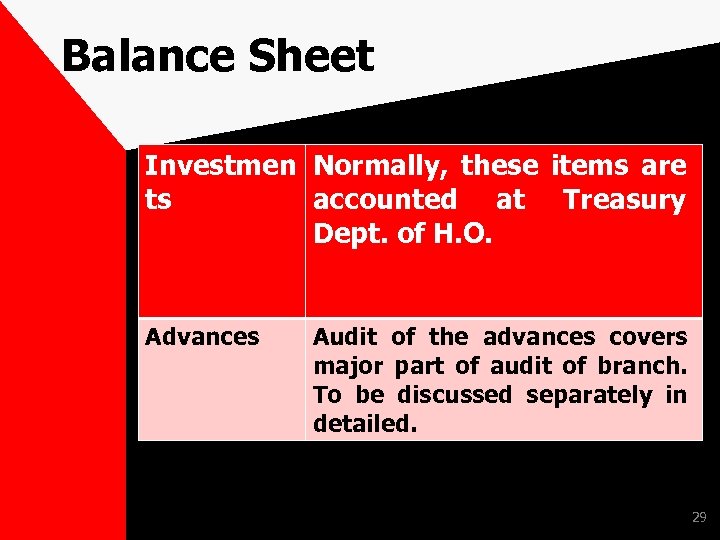
Balance Sheet Investmen Normally, these items are ts accounted at Dept. of H. O. Treasury Advances Audit of the advances covers major part of audit of branch. To be discussed separately in detailed. 29
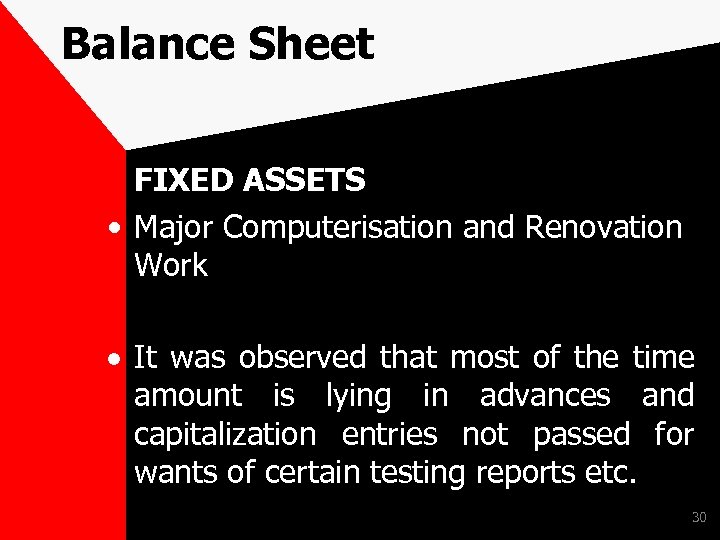
Balance Sheet FIXED ASSETS • Major Computerisation and Renovation Work It was observed that most of the time amount is lying in advances and capitalization entries not passed for wants of certain testing reports etc. 30
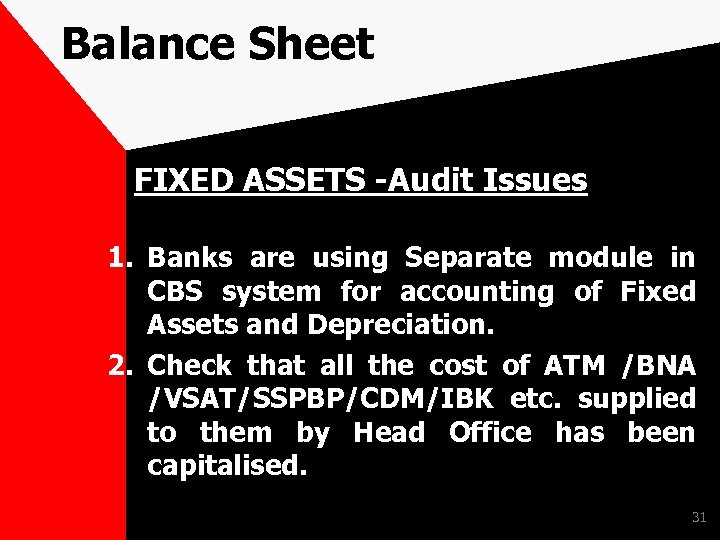
Balance Sheet FIXED ASSETS -Audit Issues 1. Banks are using Separate module in CBS system for accounting of Fixed Assets and Depreciation. 2. Check that all the cost of ATM /BNA /VSAT/SSPBP/CDM/IBK etc. supplied to them by Head Office has been capitalised. 31

Balance Sheet FIXED ASSETS -Audit Issues 3. No Entry should be pending in Region/Branch office Administrative/ Intermediary Account for responding in relation cost transfer of these Assets. 4. Inter Branch Transfers to be shown separately. 5. Sale of asset to be shown separately. 6. Date put to use to be captured 32 correctly.

Balance Sheet OTHER ASSETS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Sundry Asset and Suspense Accounts Inter Branch accounts Stationery and Stamps in Hands Interest Accrued TDS Receivables Prepaid Expenses 33

Balance Sheet Capital To be dealt at Head office. In same bank branches, Head Office account is considered as Capital of Branch. Reserve and Surplus To be dealt at Head office 34

Balance Sheet Deposits 1. Saving Bank Deposits 2. Current Account/Demand Deposits 3. Term Deposit – INR Deposits – Foreign Currency Deposits 35

Balance Sheet Deposits- Audit Issues • Unclaimed Deposits/ Inoperative Accounts • Depositor Education and Awareness Fund (DEAF) Scheme 2014 • Interest Accrued But Not Due • Overall Reconciliation • Translation/ Revaluation of Foreign Currency Deposit • Window-dressing • Know Your Customers Norms 36

Balance Sheet Borrowings To be dealt at Head office Other Liabilities and Provisions 1. Bills Payable 2. Inter-office Adjustments 3. Interest Accrued 4. Others (Including Provisions) 37

PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT As per Form ‘B’ of Third schedule of Banking Regulation Act. Verify the figures of Balance Sheet with General Ledger and figures of Profit and Loss account with Income and expenditure ledger. 38

INCOME & EXPENSES • Expenses • Interest Expended • Establishment Expenses ( Salary & Allowances) • Rent • Printing & Stationery Ensure the accrual concept of accounting. Separate note for non compliance of AS-5 Prior Period items. 39

INCOME & EXPENSES • Income • Interest Earned on Advances • Commission • Fee Based Income • Service Charges 40

INCOME & EXPENSES • Checking of Interest rates and its application on large advances. • Accrued and Outstanding items • Accounting Standard-5 AND 9 • RBI Guidelines • Comparative Analysis • Analytical Review 41
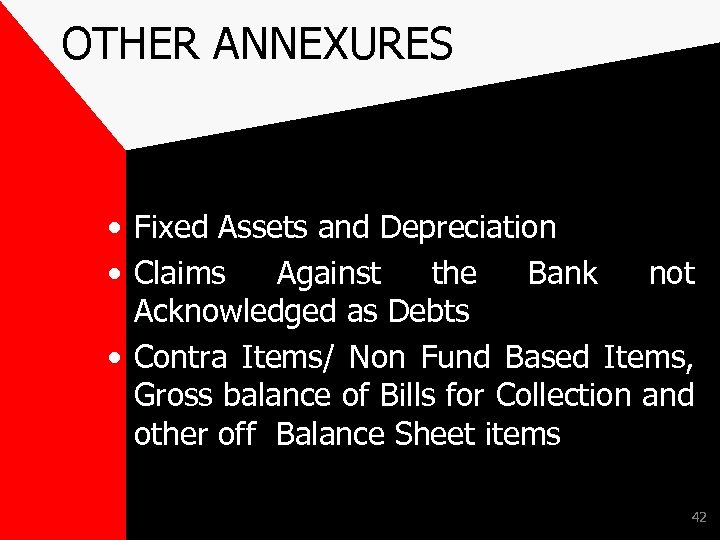
OTHER ANNEXURES • Fixed Assets and Depreciation • Claims Against the Bank not Acknowledged as Debts • Contra Items/ Non Fund Based Items, Gross balance of Bills for Collection and other off Balance Sheet items 42

OTHER ANNEXURES • Fixed Assets and Depreciation(already discussed) • Claims Against the Bank not Acknowledged as Debts This return includes the information of claims made and suit filed against the branches for instance- Rent Recovery, Consumer cases, Fraud, cases by employees etc. ) • Compare the return with the return of last year and last quarter. • Check that entry in the books has been passed for all claims against the Bank not acknowledged as debt and reversal of entry has been passed on settlement 43 / deletion of a claim.

OTHER ANNEXURES Contra Items/ Non Fund Based Items, Gross balance of Bills for Collection and other off Balance Sheet items. It is contra item so available from both asset and liability side. 44

OTHER ANNEXURES • Sensitive Accounts, Nostro accounts and Local Branch Office /Local Main office/ Service branch account. • Break up of outstanding entries in GL Suspense A/c • Bad Debts Written-off • Returns related to advances. 45
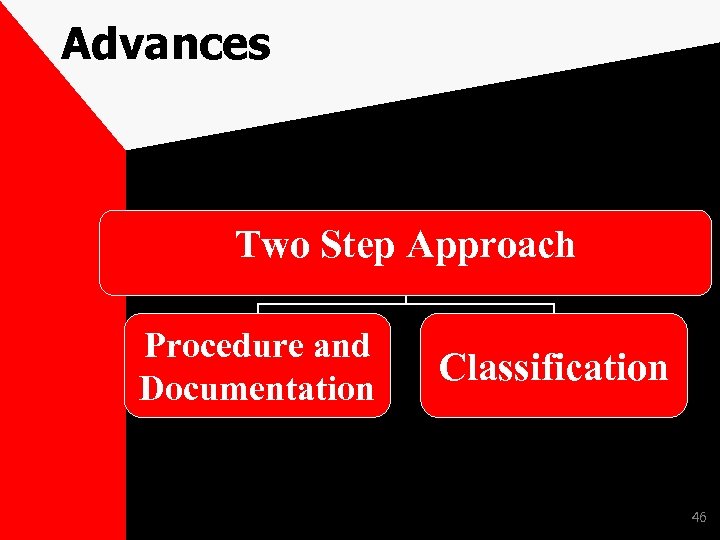
Advances Two Step Approach Procedure and Documentation Classification 46

Advances Procedure and Documentation – Nature of Borrowing arrangement ( Sole, Multiple or Consortium) – Whether sanction has been made as per the banks policies. – Credit appraisal reports contains adequate information’s – Check whether the terms of sanction have been complied with? 47

Advances Procedure and Documentation – Check whether all the documentation formalities have been complied with before release of facilities by the branch? – Check whether in the cases of corporate borrowers due charges have been registered with the Registrar of Companies? – Check whether Compliance of Companies Act 2013 such as borrowing power, special resolution has been complied with? 48

Advances Procedure and Documentation – Stock Audit Report – Rating by External Agencies – Disbursement Process – End use verification certificate – Renewals 49

Advances Classification • Facility Wise a Cask Credit/Over Draft b Term Loan/Demand Loan c Bills Purchased /Bill Discounting • Sector Wise a Priority Sector b SSI c Others 50

Advances Classification • Security Wise a Secured b Guaranteed c Unsecured • Health Wise a. Performing (Standard) b. Non Performing (NPAs) 51

Advances • Every year in the month of July, Reserve Bank of India is issuing master circular for IRAC Norms. This circular is available on RBI website www. rbi. org. in. The circular provides prudential norms applicable for the current year in great details. 52
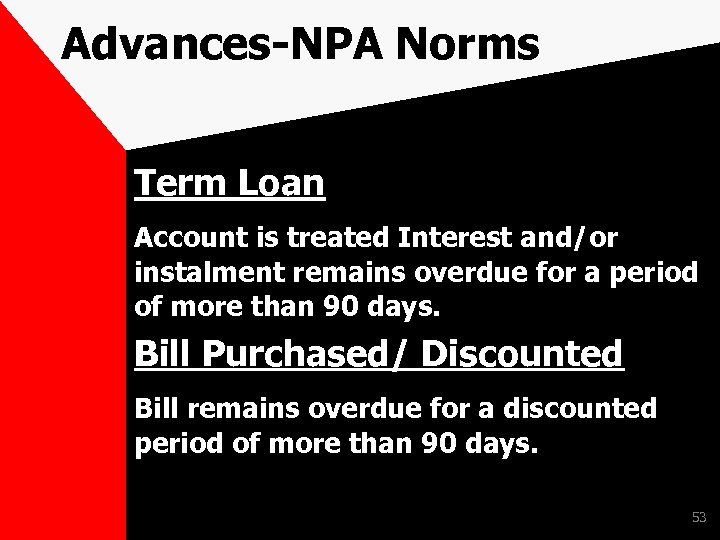
Advances-NPA Norms Term Loan Account is treated Interest and/or instalment remains overdue for a period of more than 90 days. Bill Purchased/ Discounted Bill remains overdue for a discounted period of more than 90 days. 53

Advances-NPA Norms Cash Credit & Overdraft • Account is treated as NPA if it remains out of order for a period of more than 90 days. An account is treated as out of order if, The outstanding balance remains continuously in excess of sanctioned / drawing power limit, 54
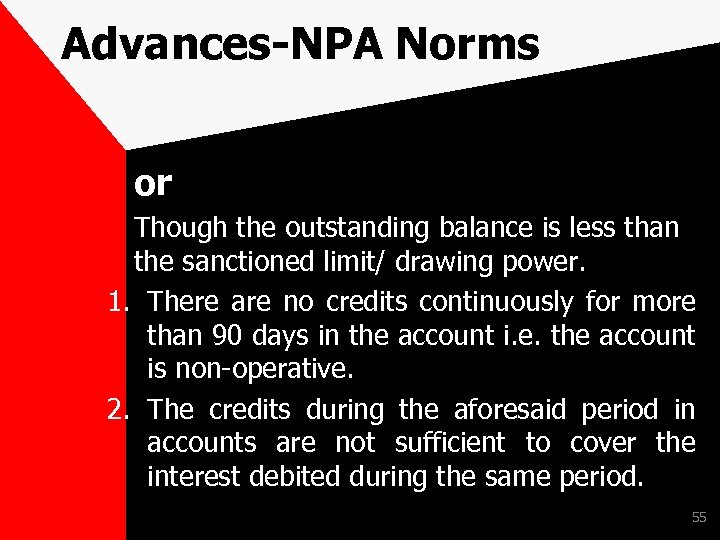
Advances-NPA Norms or Though the outstanding balance is less than the sanctioned limit/ drawing power. 1. There are no credits continuously for more than 90 days in the account i. e. the account is non-operative. 2. The credits during the aforesaid period in accounts are not sufficient to cover the interest debited during the same period. 55

Advances-Key Issues Major deficiencies observed 1. Realizable Value of Security 2. Review date 3. Balance of borrower 4. Repayment schedule and first installment date. 5. Change in Sanction Limit 56

Advances-Key Issues Major deficiencies observed 6. Continues excess date 7. Credits in CBS and Other System 8. Re schedulement date 9. Renewal date 10. Stock Statement date 57

Advances-Key Issues Stress Assets Mechanism In the backdrop of the slowdown of the economy, and resulting increase in NPAs and restructured accounts in the Banks, a need was felt to ensure that the banking system should recognise financial distress early, takes prompt steps to resolve it, and ensures fair recovery for lenders and investors. 58

Advances-Key Issues Stress Assets Mechanism Hence before a loan account turns into a NPA, banks are required to identify incipient stress in the account by creating three subcategories under the Special Mention Account (SMA) category as given in the table below: 59
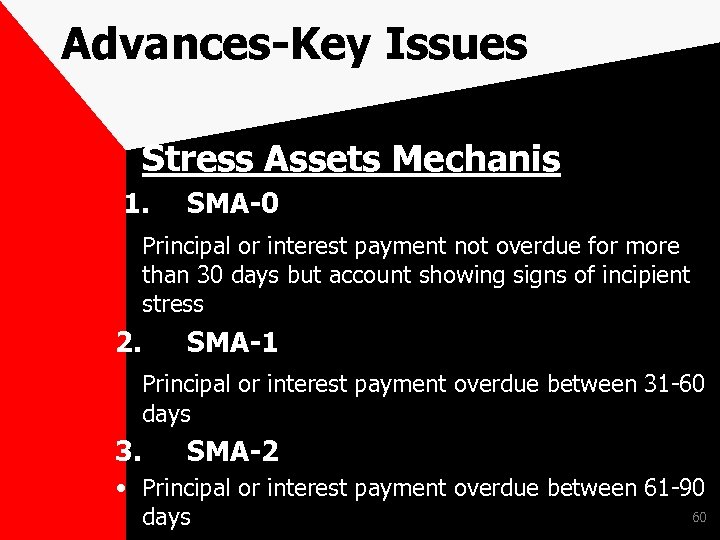
Advances-Key Issues Stress Assets Mechanis 1. SMA-0 Principal or interest payment not overdue for more than 30 days but account showing signs of incipient stress 2. SMA-1 Principal or interest payment overdue between 31 -60 days 3. SMA-2 • Principal or interest payment overdue between 61 -90 60 days

Advances-Key Issues RBI Circular dated 21 st Nov. 2016 and 28 th Dec. 2016 for Relaxation in Prudential Norms There are 2 circulars in which relief has been provided for certain advances having sanction limit of less than Rs. 100 lacs. 61
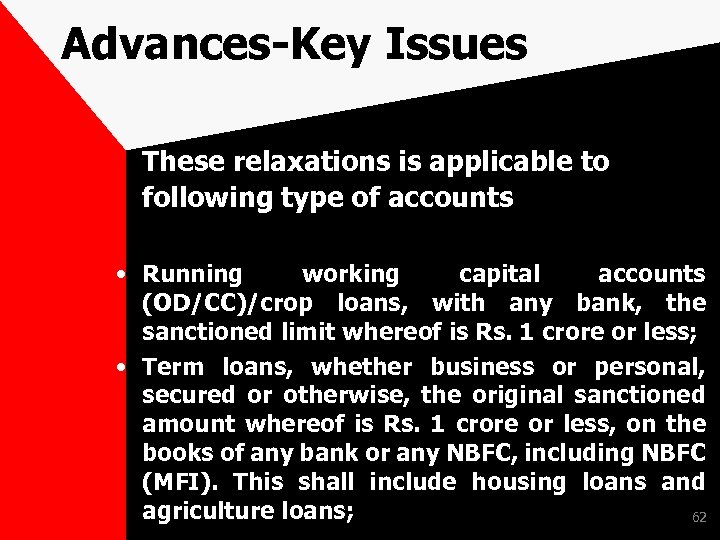
Advances-Key Issues These relaxations is applicable to following type of accounts • Running working capital accounts (OD/CC)/crop loans, with any bank, the sanctioned limit whereof is Rs. 1 crore or less; • Term loans, whether business or personal, secured or otherwise, the original sanctioned amount whereof is Rs. 1 crore or less, on the books of any bank or any NBFC, including NBFC (MFI). This shall include housing loans and agriculture loans; 62

Advances-Key Issues • Relaxation of 90 days (60+30) has been provided to the Small Borrowers • These Circulars covered only those borrowers whose dues is payable only between 1 st Nov. 2016 to 31 st Dec. 2016 63

Advances-Key Issues • The additional time given shall only apply to defer the classification of an existing standard asset as substandard and not for delaying the migration of an account across sub-categories of NPA • Dues payable before 1 st November 2016 & after 1 st January, 2017 will be covered by the extant instructions for the respective REs 64

Advances-Key Issues Conclusion of 2 circulars Accordingly the interpretation is that dues up to 31 st Oct. 2016 has to be recovered on 31 -03 -2017 to retain the account as Standard Assets. 65

Advances under consortium Asset classification of account under consortium should be based on the record of recovery of the individual member banks. There is no relevance of classification of account in lead bank or in other member bank. 66

Agriculture Advances • Classifications based on overdue crop season • The length of crop season is not defined in RBI circular • The length of crop season would be determined by SLBC in each state. • lot of misunderstanding at branch level, regarding commencement and closure of crop season 67

Agriculture Advances RBI Norms • a loan granted for short duration crops will be treated as NPA, if the installment of principal or interest thereon remains overdue for two crop seasons. • The term overdue means any amount due to the bank under any credit facility is overdue if it is not paid on the due date fixed by the bank. • Rabi season (planted October-November and harvested in March-April). • Kharif season (planted May- June and harvested in October- November). 68

Agriculture Advances RBI Norms Accordingly any disbursement in Agriculture loanKCC up to 30. 09. 2015 ( i. e. Rabi season 20142015 and Kharif Season 2015) is not realised, the account will be NPA as on 31. 03. 2017. 69

Accounts regularized near about balance sheet date The asset classification of accounts where few credits are recorded should be examined thoroughly without scope for subjectivity. Where the account indicates inherent weakness on the basis of data available, the account should be deemed as a NPA. 70

Advances • Asset classification to be borrowerwise not facility-wise • Temporary Deficiencies- Not NPA • Special Category Advances such as • Against banks own deposit • NSC KVP IVP Life Insurance Policies Are not be treated as NPA 71

Advances Erosion in value of security Asset should be straightaway classified as doubtful or loss asset as appropriate. Value of security erodes by 50% as compared to last valuation - Doubtful Value of security erodes up to 10% of current outstanding - Loss 72

Advances-Restructuring • Definition of Restructured Accounts- (Annex-5 of Master Circular) A restructured account is one where the bank, for economic or legal reasons relating to the borrower's financial difficulty, grants to the borrower concessions that the bank would not otherwise consider. Restructuring would normally involve modification of terms of the advances / securities, which would generally include, among others, alteration of repayment period / repayable amount/ the amount of instalments / rate of interest (due to reasons other than competitive reasons). 73

Advances-Restructuring New RBI Guidelines • General Principal • Accounts of Standard, SSA and DA category • No retrospective effect • Deterioration will continue • Only financial viable account • reasonable certainty of repayment from the borrower • BIFR cases are not eligible for restructuring without their express approval 74

Advances-Restructuring • CHANGE IN CLASSIFICATION • As per the circular the account classified as ‘standard’ should be immediately reclassified as ‘sub-standard asset’ upon restructuring. Other then covered under SRT 75
![Advances-Restructuring SPECIAL REGULATORY TREATMENT [SRT] 76 Advances-Restructuring SPECIAL REGULATORY TREATMENT [SRT] 76](https://present5.com/presentation/28d2d54f3dc94b6e7de11933148d0893/image-76.jpg)
Advances-Restructuring SPECIAL REGULATORY TREATMENT [SRT] 76
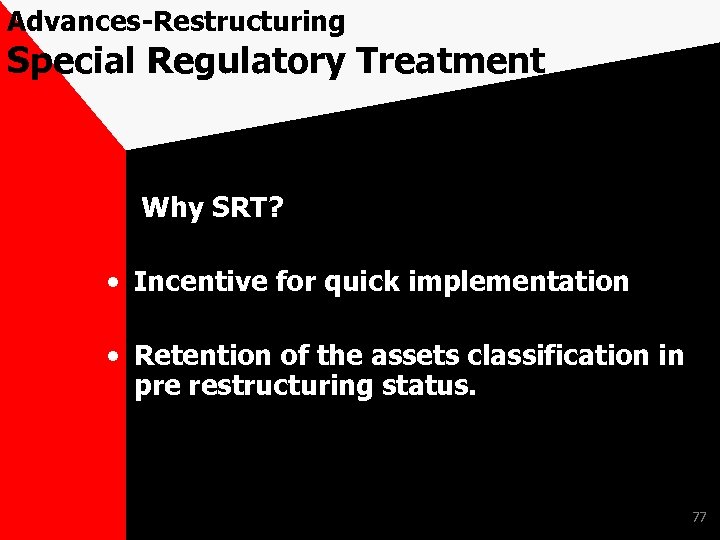
Advances-Restructuring Special Regulatory Treatment Why SRT? • Incentive for quick implementation • Retention of the assets classification in pre restructuring status. 77

Advances-Restructuring Special Regulatory Treatment Benefit available Long Term Project Loans to Infrastructure and Core Industries Popularly Known as S 4 A cases, 5/25 case and SDR cases 78

Advances-Restructuring Special Regulatory Treatment • Asset classification benefit is available (Stand Still Clause) for 18 months • It is clarified that ‘stand-still’ clause only applies to asset classification and banks shall not recognise income on accrual basis if the interest is not serviced within 90 days from the due date. (RBI circular dated 10 th Nov. , 2016) 79

Advances-Restructuring Agriculture Advances 1. 2. 3. 4. Due to Natural Calamity These restructuring as per the RBI circular on Guidelines For Relief Measures By Banks In Areas Affected By Natural Calamities. SLBC of concerned state decide about natural calamity and terms and conditions of relief Terms and Conditions of the scheme to be followed for Restructuring Application to be obtained from Borrower for Restructuring without which restructuring cannot be made 80

Advances-Restructuring Agriculture Advances • Instances- – Restructuring in areas where draught not declared – Full amount of Loan restructured instead of dues for the year to be restructured as per restructuring scheme Check whether benefit given to only eligible accounts and not to ineligible accounts to prevent them 81 to become NPA.

Unhedged foreign currency exposures of the entities A high level of unhedged foreign currency exposures of the entities can increase the probability of default in times of high currency volatility. Hence, banks are required to estimate the riskiness of unhedged position of their borrowers and required to make incremental provisions on their exposures to such entities with exposure of over Rs 25 crores in Banking System. 82

Demonetization It Primary responsibility of concurrent auditor. Not much for branch auditors. Statutory Auditors have to Review the reports of concurrent auditors. ICAI guidance note on Bank Audit prescribed that if the Statutory Auditors come across for any shortcomings, they may report the same appropriately either in LFAR or in main audit report. 83
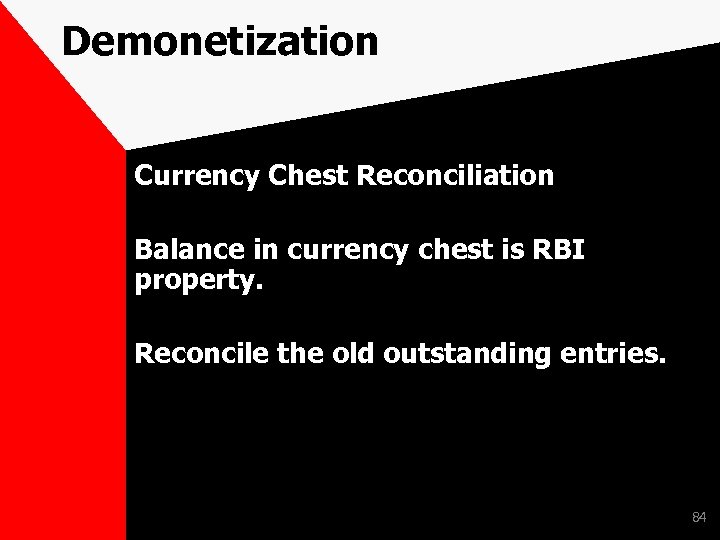
Demonetization Currency Chest Reconciliation Balance in currency chest is RBI property. Reconcile the old outstanding entries. 84

Compliance with Accounting Standards • Segregate the AS to be complied at Branch and HO • Check the compliance and report non compliance • AS-5 Net Profit or Loss for the period, Prior Period items and Changes in Accounting Policies. • AS-9 Revenue recognition • AS-11 The effects of change in foreign exchange Rates. • Disclosure for AS to be complied at HO • AS-3 Cash Flow statement • • AS-15 Employee Benefits AS-17 Segment Reporting AS-18 Related party Disclosure AS-22 Accounting for taxes on Income 85

Other Important items • Sundry Liability, Sundry Asset of Suspense Account. • Transaction in dormant account • Large Value transaction in newly opened account • Debit balance in savings account • Reversal of Misc. Charges • Credit Card Transactions 86

Other Important items • • • Overdue term deposits System Testing Bank Guarantee Letter of Credits Frauds Claims not acknowledge as debts 87
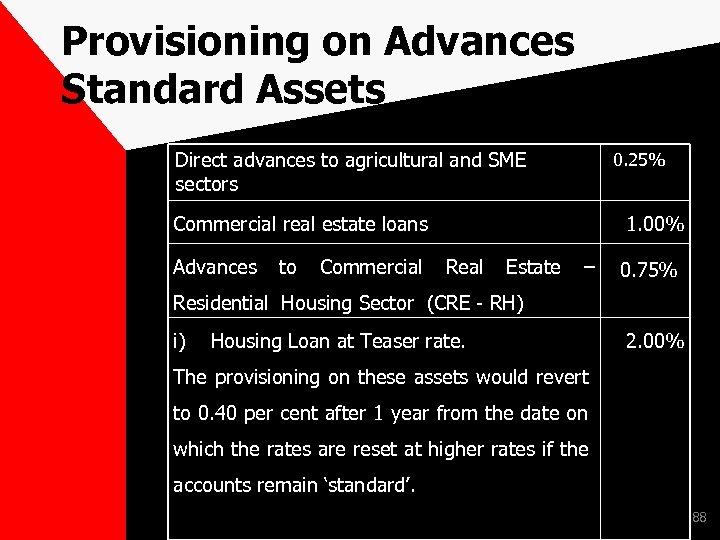
Provisioning on Advances Standard Assets Direct advances to agricultural and SME 0. 25% sectors Commercial real estate loans 1. 00% Advances to Commercial Real Estate – 0. 75% Residential Housing Sector (CRE - RH) i) Housing Loan at Teaser rate. 2. 00% The provisioning on these assets would revert to 0. 40 per cent after 1 year from the date on which the rates are reset at higher rates if the accounts remain ‘standard’. 88
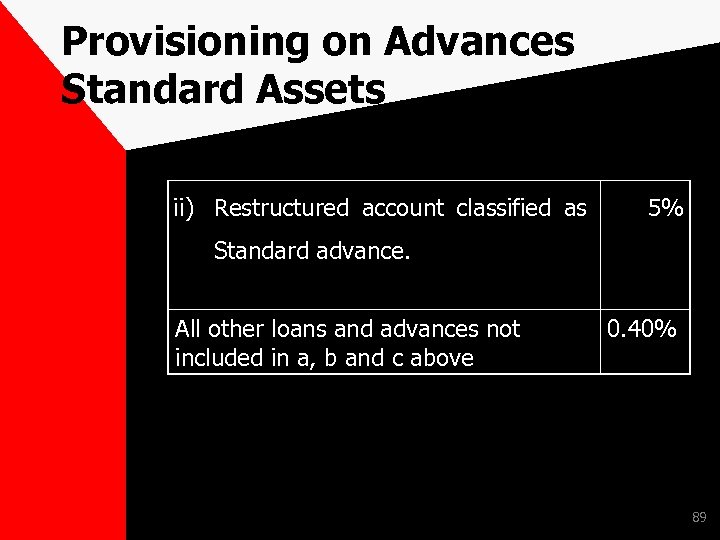
Provisioning on Advances Standard Assets ii) Restructured account classified as 5% Standard advance. All other loans and advances not included in a, b and c above 0. 40% 89

Provisioning on Advances Sub Standard Assets For Secured Portion without 15% making any allowance for DICGC/ECGC guarantee cover and securities For Unsecured Exposure 25% 90
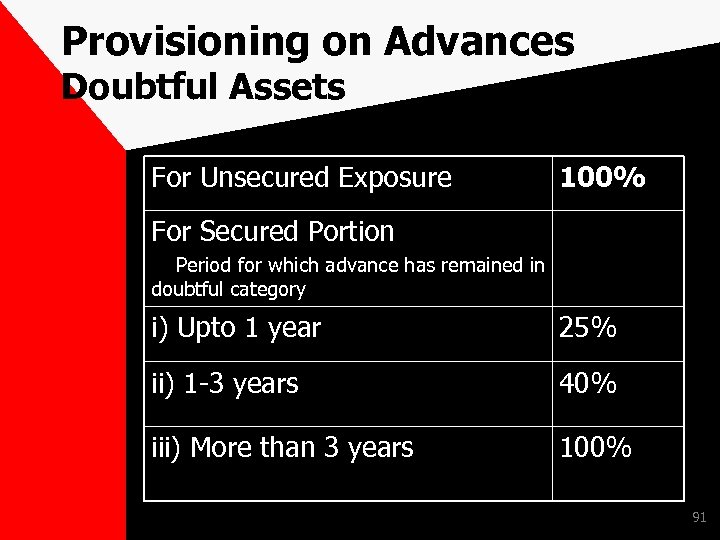
Provisioning on Advances Doubtful Assets For Unsecured Exposure 100% For Secured Portion Period for which advance has remained in doubtful category i) Upto 1 year 25% ii) 1 -3 years 40% iii) More than 3 years 100% 91

Provisioning on Advances Loss Assets • For entire outstanding, whether secured or not 100% • In most of the banks, provisions on advances been made at Zonal or Head office level. Branch Auditors are required to verify the classification only. 92

Reporting • Auditors Report – Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Account have been drawn up in the forms ‘A’ and ‘B’ respectively of the third schedule of banking regulation act. – He had called for the informations and explanations and same have been given and considered satisfactory. – Transactions of the bank, which have came to his notice, have been within the powers of the bank. – The returns received from the offices and branches of the banks have been found adequate for the purpose of his audit. – Illustrative format given in Guidance Note on Audit of Banks issued by ICAI also suggest that auditor should comment that financial statements comply with the applicable Accounting Standards. – Branch Auditors also report on the above matters in his report. 93

Reporting • Adherences of SA ( Standard of Auditing) • Emphasis of matter paragraph. SA- 700, 705 and 706: These SA defines the manner of reporting in auditor’s report and inclusion of qualifications and matter of emphasis in auditor’s report. It has been observed that qualifications are not quantified. Further all weakness are made subject to. ( Such as non deduction of TDS etc. ) Please segregate the qualification which have impact on true and fair view considering the materiality and other having weak internal control. Report all other significant items in the Emphasis of matter paragraph. 94

Reporting • Adherences of SA ( Standard of Auditing) • SA- 260 and 265 • SA 260 deals with the auditor’s responsibility to communicate with those charged with governance in relation to an audit of financial statements. In addition, SA 265 establishes specific requirements regarding the communication of significant deficiencies in internal control the auditor has identified during the audit to those charged with governance. • • Every CSA are reported these matters to ACB and Board, Therefore branch Auditors must send these issues to respective CSA through separate letter. 95

Reporting • Memorandum Of Changes • Banks have unique system for recording the changes suggested by the auditors during the course of the audit. • No correction or revision permitted • Counter signed by Branch Managers • Disagreement 96

Long Form Audit Report • Reporting to RBI • Questionnaire • Systems & Procedures • Tool for internal control • A detailed checklist for LFAR is Annexed as Annexure VI. 97

Long Form Audit Report Major Clauses in LFAR • A. Assets : 1. Cash 2. Balances with RBI, SBI and Other Banks. 3. Money at Call and Short Notice. 4. Investments 5. Advances 6. Other Assets 98

Long Form Audit Report • B. Liabilities: 1. Deposits 2. Other Liabilities 3. Contingent Liabilities • C. Profit and Loss Account. 99

Long Form Audit Report • D. General: 1. Books & Records 2. Reconciliation of Control & Subsidiary Records. 3. Inter Branch Accounts 4. Audits/ Inspections 5. Frauds 6. Other Miscellaneous Matters 100

Long Form Audit Report E. Annexure attached to the LFAR – For Large Advances having exposure with more than 5% of Total Advances or Rs. 2. 00 Crores whichever is less. F. Questionnaires applicable to Specialized Branches like : • Branches dealing in Foreign Exchange Transactions. • Branches dealing in Very Large Advances in excess of Rs. 100 Crores. • Branches dealing in NPA Recovery (Asset Recovery Management Branch) • Branches dealing in Clearing House Operations 101 (Service Branches)
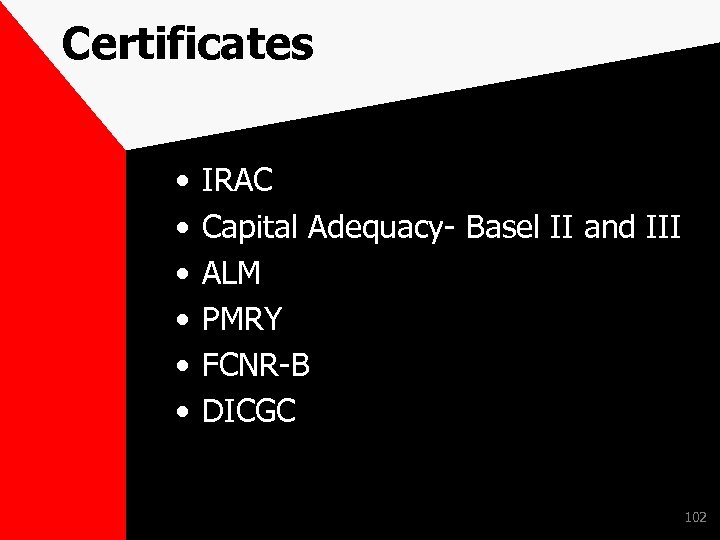
Certificates • • • IRAC Capital Adequacy- Basel II and III ALM PMRY FCNR-B DICGC 102
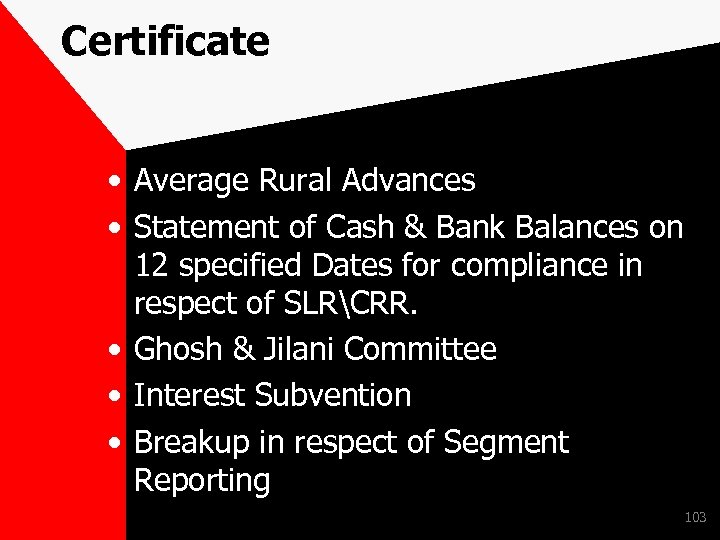
Certificate • Average Rural Advances • Statement of Cash & Bank Balances on 12 specified Dates for compliance in respect of SLRCRR. • Ghosh & Jilani Committee • Interest Subvention • Breakup in respect of Segment Reporting 103

Certificate • Certificate of 2% Interest Subsidy claim of Agricultural Advances • Certification in respect of bank’s claim relating to interest subvention in respect of rupee export credit. • Interest subvention on Housing Loans • Central sector subsidy for Education Loan 104

Tax Audit • Form 3 CA • Form 3 CD • TDS 105

Audit Evidence • The Auditor should document matters, which are important in providing evidences that audit were carried out in accordance with the basic principles. Working papers will come to the rescue, whenever, at a later date if there is query about any matter or issue relating to the work performed by the auditor. • On completion of audit, all working papers must be organized in a file in a proper sequence and must be reviewed by a partner other than the one who conducted the audit of the branch. 106

Bank Audit • Please feel free to call on any issue on following • CA Ajay Atolia, Partner S. R. Goyal & Co. Chartered Accountants • “SRG HOUSE” 2, M. I. Road, Opp. Ganpati Plaza Jaipur 302 001, India Tel : +91 -141 -2362363, 2362365 Fax : +91 -141 -2362487 Email : ajay@srgoyal. com Cell No. + 91 - 9829169260 107

Bank Audit • THANKS 108
28d2d54f3dc94b6e7de11933148d0893.ppt