b6b41141842ba202865dbd61efa6a9c3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
Back to Basic chromosome 임상세포유전학 CLINICAL CYTOGENETICS cell DNA

염색체검사 대상자는 누구인가? Back to Basic 출생전 진단 : 34세 이상 임산부, 염색체 이상아 가족력 출생후 소아기 : 다발성 기형 설명하기 어려운 정신박약, 성장지연 성염색체질환이 의심되는 경우 성장기 이후 : 외성기 이상(ambiguous genitalia), 무월경, 습관성 유산, 불임 (배우자와 같이 검사) 혈액종양, 고형종양
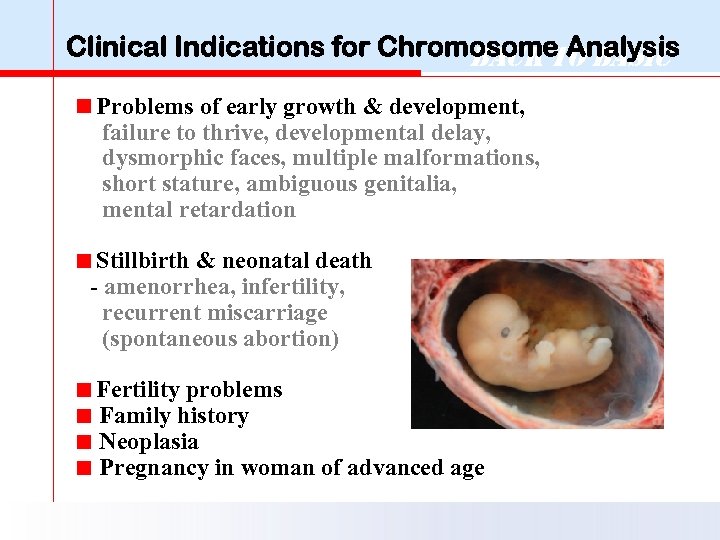
Clinical Indications for Chromosome Analysis Back to Basic Problems of early growth & development, failure to thrive, developmental delay, dysmorphic faces, multiple malformations, short stature, ambiguous genitalia, mental retardation Stillbirth & neonatal death - amenorrhea, infertility, recurrent miscarriage (spontaneous abortion) Fertility problems < Family history < Neoplasia < Pregnancy in woman of advanced age
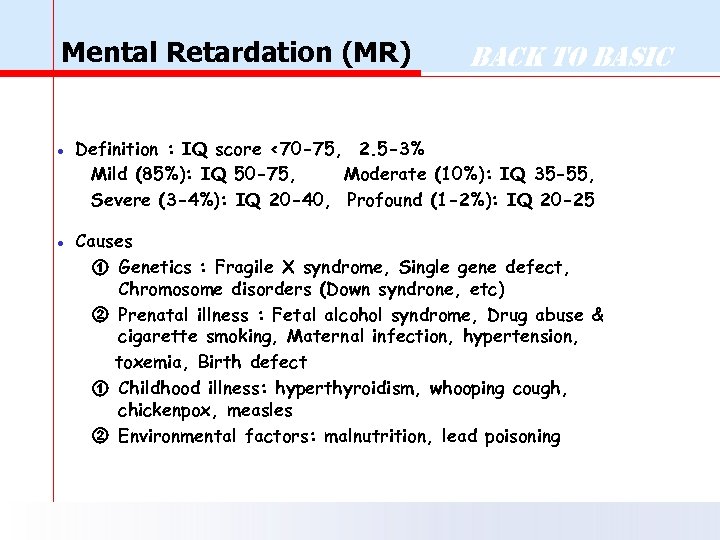
Mental Retardation (MR) Back to Basic ● Definition : IQ score <70 -75, 2. 5 -3% Mild (85%): IQ 50 -75, Moderate (10%): IQ 35 -55, Severe (3 -4%): IQ 20 -40, Profound (1 -2%): IQ 20 -25 ● Causes ① Genetics : Fragile X syndrome, Single gene defect, Chromosome disorders (Down syndrone, etc) ② Prenatal illness : Fetal alcohol syndrome, Drug abuse & cigarette smoking, Maternal infection, hypertension, toxemia, Birth defect ① Childhood illness: hyperthyroidism, whooping cough, chickenpox, measles ② Environmental factors: malnutrition, lead poisoning
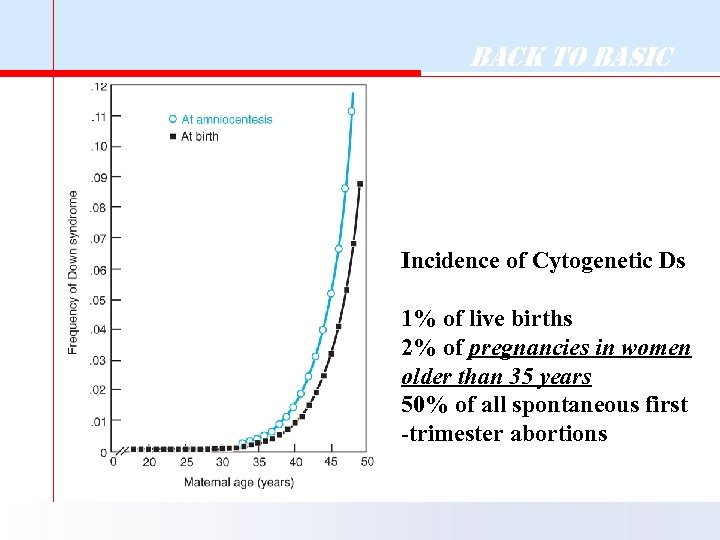
Back to Basic Incidence of Cytogenetic Ds 1% of live births 2% of pregnancies in women older than 35 years 50% of all spontaneous first -trimester abortions
염색체검사 검체 선택 Back to Basic v Peripheral Blood (PB); Congenital anomaly, Fragile X syndrome v Bone marrow (BM); Hematologic malignancies (leukemia, MDS, MPN) v Lymph node; Malignant lymphoma v Soft tissue; Solid tumor v Amniotic fluid (AF), CVS; Prenatal diagnosis v Skin biopsy- fibroblast

Giemsa Banding (G-Banding) Technique Back to Basic 1) PB/BM Culture RPMI 1640 FBS (15%) Pen-Strep L-Glutamine PHA PB/BM cells 3 -5 hrs High-resolution Banding Technique Using Methotrexate Cell Synchronization MTX(10 -7 M) 72 hrs 17 hrs Thymidine (10 -5 M) 2) Harvest 1) Colcemid (50 g/ml) treatment 2) Hypotonic Solution (KCl; 0. 075 M) treatment 3) Fixation (methanol: Acetic acid=3: 1) 5 hrs 3) Slide preparation & Staining (Giemsa-Trypsin) 4) Microscopy and Karyotyping 5) Printing (Photography) and Reporting * PHA, Phytohemagglutinin (T cell mitogen) **MTX , Methotrexate

염색체검사 장비 및 재료 CO 2 incubator at 37 o. C, 5%CO 2 clean bench Back to Basic Inverted Microscope Slide preparation

Back to Basic Conventional Cytogenetics in Hematologic Malignancies l 검사자 숙련도에 따라 슬라이드의 질적 차이가 많다 l 분열세포 적고, 염색체 길이 짧고, quality는 불량하다. l 복잡하고 다양한 핵형을 보이는 경우가 많다

Back to Basic CCD camera Microscope Main Program Monitor PC Printer Computerized Image Analyzer Cytovision®
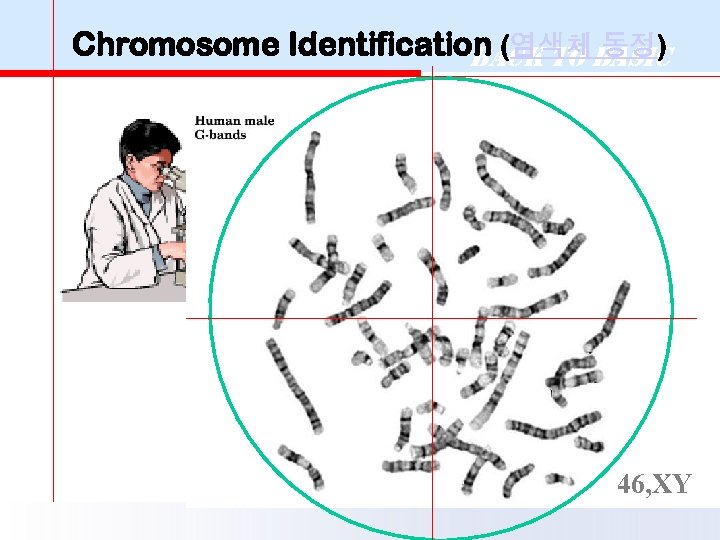
Chromosome Identification (염색체Basic Back to 동정) 46, XY
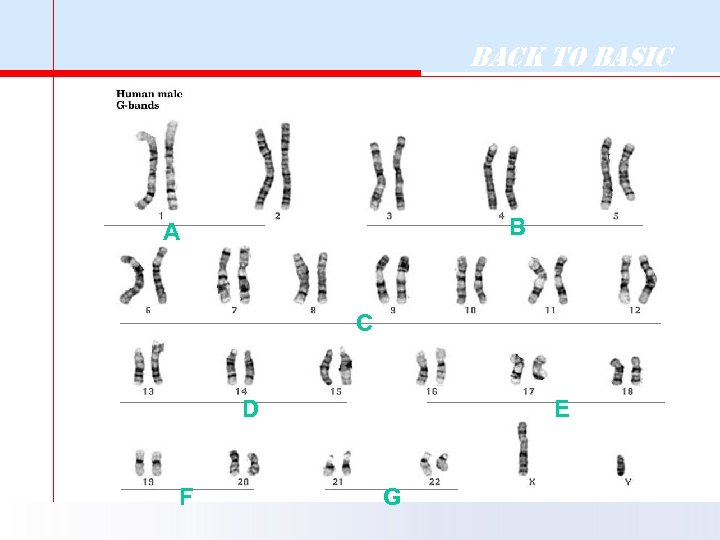
Back to Basic B A C D F E G
Back to Basic
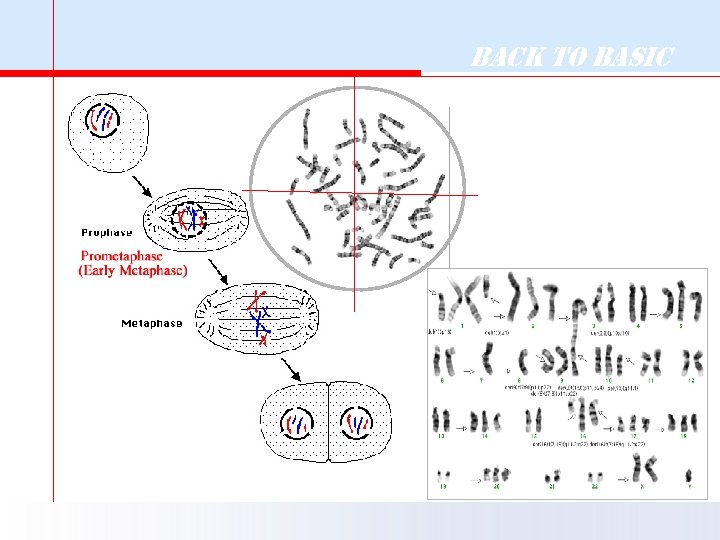
Back to Basic
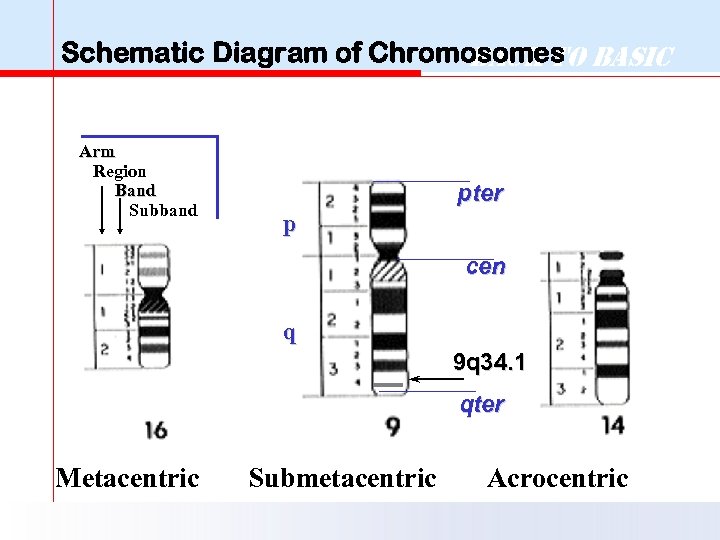
Schematic Diagram of Chromosomes Basic Back to Arm Region Band Subband pter p cen q 9 q 34. 1 qter Metacentric Submetacentric Acrocentric
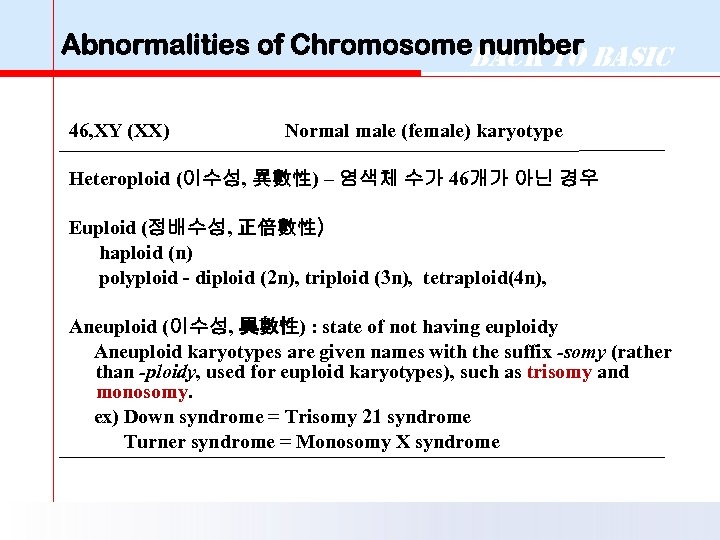
Abnormalities of Chromosome. Back to Basic number 46, XY (XX) Normal male (female) karyotype Heteroploid (이수성, 異數性) – 염색체 수가 46개가 아닌 경우 Euploid (정배수성, 正倍數性) haploid (n) polyploid - diploid (2 n), triploid (3 n), tetraploid(4 n), Aneuploid (이수성, 異數性) : state of not having euploidy Aneuploid karyotypes are given names with the suffix -somy (rather than -ploidy, used for euploid karyotypes), such as trisomy and monosomy. ex) Down syndrome = Trisomy 21 syndrome Turner syndrome = Monosomy X syndrome
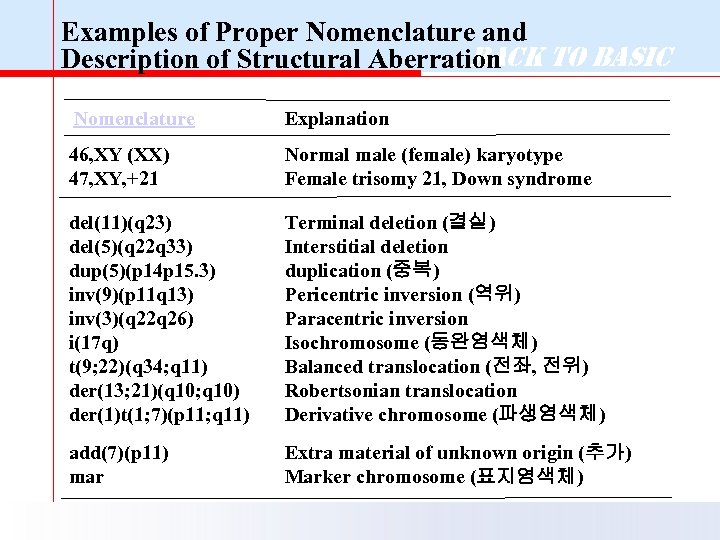
Examples of Proper Nomenclature and Back to Basic Description of Structural Aberration Nomenclature Explanation 46, XY (XX) 47, XY, +21 Normal male (female) karyotype Female trisomy 21, Down syndrome del(11)(q 23) del(5)(q 22 q 33) dup(5)(p 14 p 15. 3) inv(9)(p 11 q 13) inv(3)(q 22 q 26) i(17 q) t(9; 22)(q 34; q 11) der(13; 21)(q 10; q 10) der(1)t(1; 7)(p 11; q 11) Terminal deletion (결실) Interstitial deletion duplication (중복) Pericentric inversion (역위) Paracentric inversion Isochromosome (동완염색체) Balanced translocation (전좌, 전위) Robertsonian translocation Derivative chromosome (파생염색체) add(7)(p 11) mar Extra material of unknown origin (추가) Marker chromosome (표지염색체)
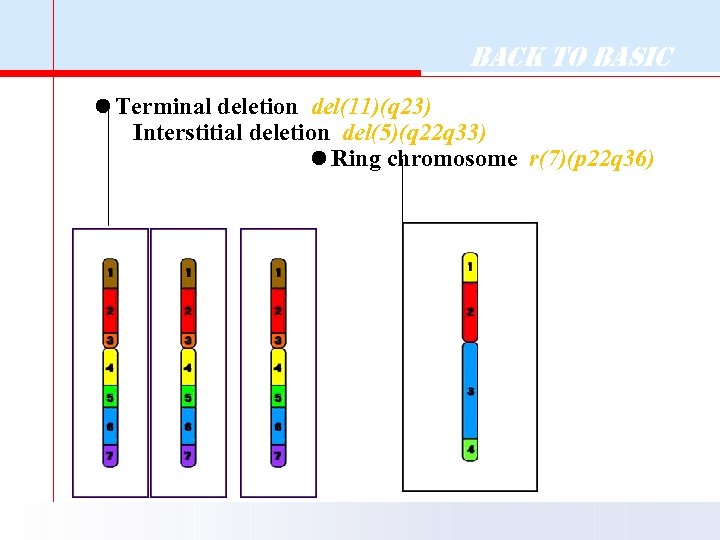
Back to Basic Terminal deletion del(11)(q 23) Interstitial deletion del(5)(q 22 q 33) Ring chromosome r(7)(p 22 q 36)
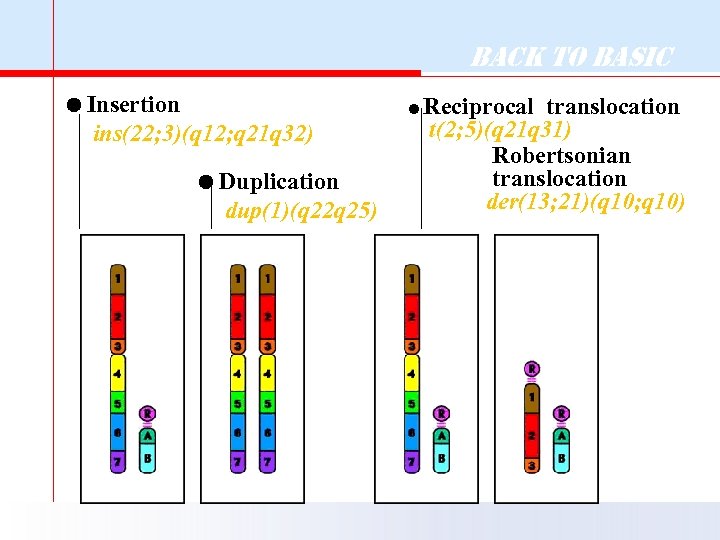
Back to Basic Insertion ins(22; 3)(q 12; q 21 q 32) Duplication dup(1)(q 22 q 25) =Reciprocal translocation t(2; 5)(q 21 q 31) Robertsonian translocation der(13; 21)(q 10; q 10)

Robertsonian translocation der(13; 15) 45, XX, der(13; 15)(q 10; q 10) Back to Basic
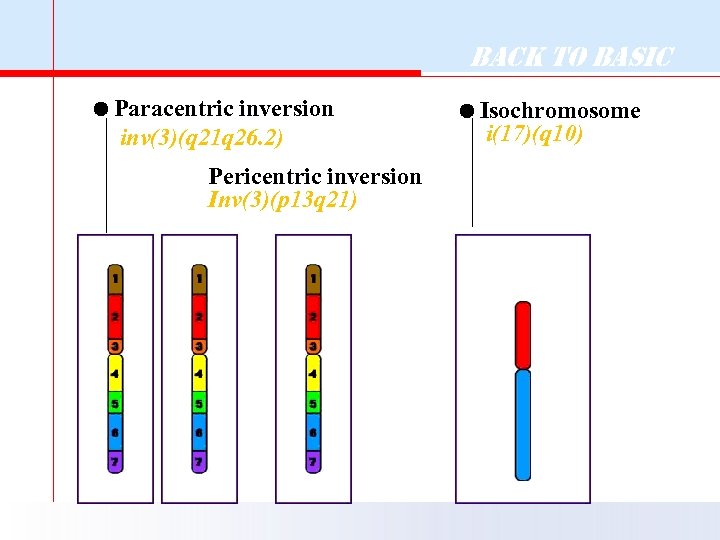
Back to Basic Paracentric inversion inv(3)(q 21 q 26. 2) Pericentric inversion Inv(3)(p 13 q 21) Isochromosome i(17)(q 10)

ISCN 2009 Back to Basic An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2009) The complete citation for reference lists is: ISCN (2009): An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature, Schaffer L. G. , Tommerup N. (eds); S. Karger, Basel, 2009 ISCN (1985, 1991, 1995, 2005)
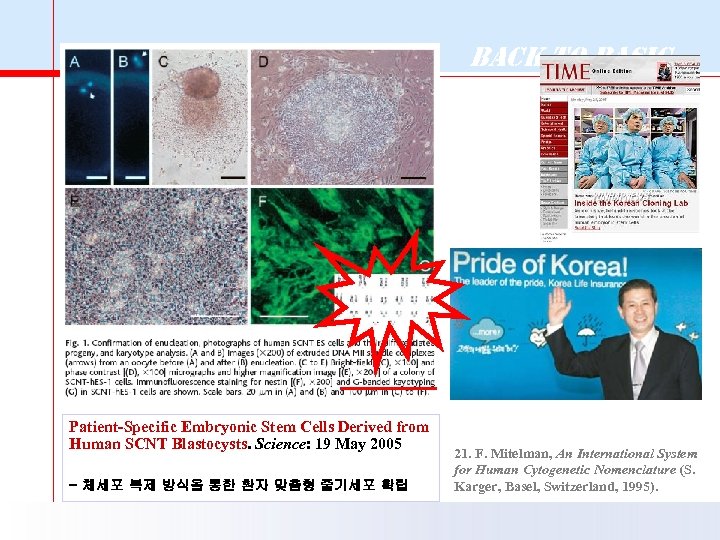
Back to Basic Patient-Specific Embryonic Stem Cells Derived from Human SCNT Blastocysts. Science: 19 May 2005 - 체세포 복제 방식을 통한 환자 맞춤형 줄기세포 확립 21. F. Mitelman, An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (S. Karger, Basel, Switzerland, 1995).

Back to Basic Morphology (A) and karyotyping (B) of interspecies blastocysts derived from a human cord fibroblast transfer into enucleated bovine oocyte. An interspecies blastocyst at hatching were obtained 144 hours after culture and subsequently provided for chromosome analysis using a cytovision. Karyotyping shows 46 pairs of autosome and sex chromosome of XY. A. K. Tarkowski and J. Rossant, Haploid mouse blastocysts developed from bisected zygotes. Nature 259 (1976), pp. 663– 665
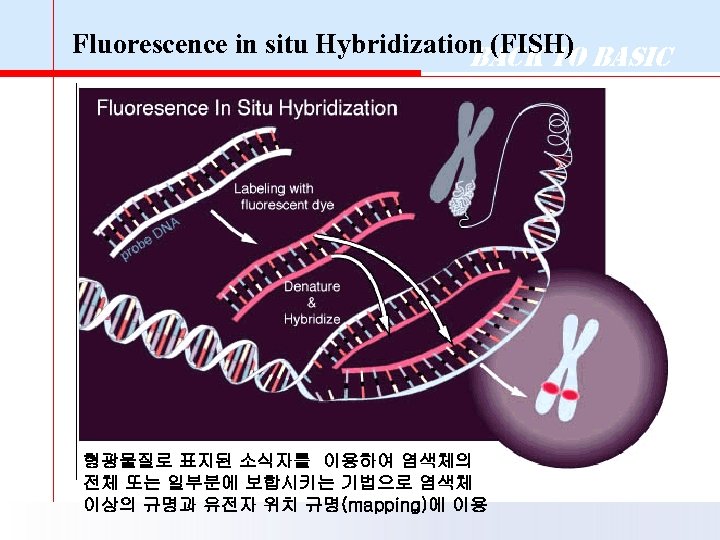
Fluorescence in situ Hybridization (FISH) Basic Back to 형광물질로 표지된 소식자를 이용하여 염색체의 전체 또는 일부분에 보합시키는 기법으로 염색체 이상의 규명과 유전자 위치 규명(mapping)에 이용
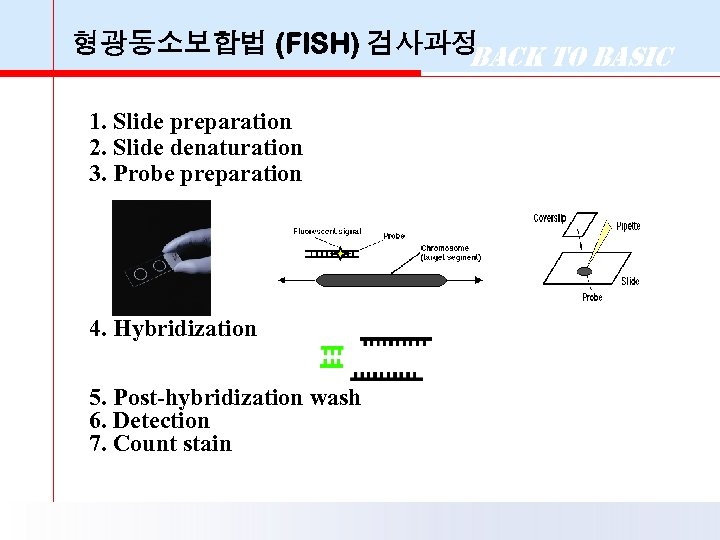
형광동소보합법 (FISH) 검사과정 Back to Basic 1. Slide preparation 2. Slide denaturation 3. Probe preparation 4. Hybridization 5. Post-hybridization wash 6. Detection 7. Count stain
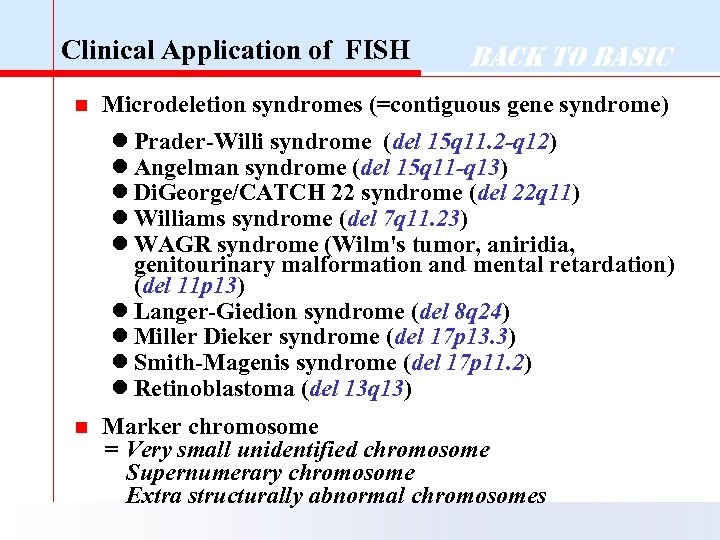
Clinical Application of FISH n Back to Basic Microdeletion syndromes (=contiguous gene syndrome) l Prader-Willi syndrome (del 15 q 11. 2 -q 12) l Angelman syndrome (del 15 q 11 -q 13) l Di. George/CATCH 22 syndrome (del 22 q 11) l Williams syndrome (del 7 q 11. 23) l WAGR syndrome (Wilm's tumor, aniridia, genitourinary malformation and mental retardation) (del 11 p 13) l Langer-Giedion syndrome (del 8 q 24) l Miller Dieker syndrome (del 17 p 13. 3) l Smith-Magenis syndrome (del 17 p 11. 2) l Retinoblastoma (del 13 q 13) n Marker chromosome = Very small unidentified chromosome Supernumerary chromosome Extra structurally abnormal chromosomes
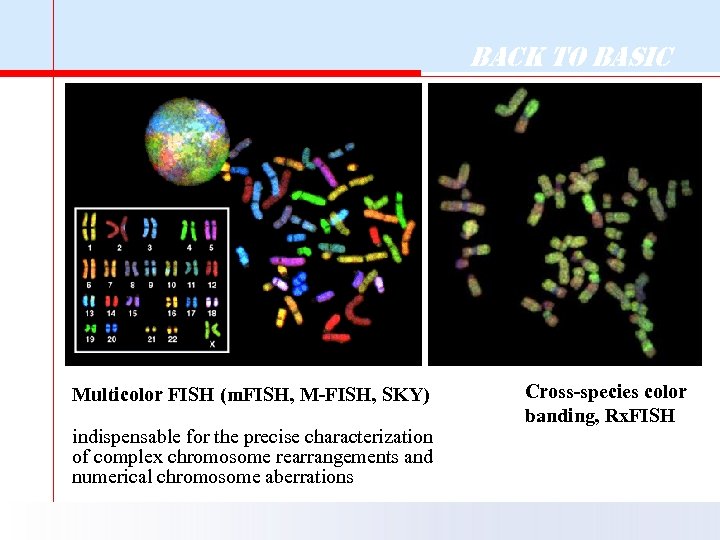
Back to Basic Multicolor FISH (m. FISH, M-FISH, SKY) indispensable for the precise characterization of complex chromosome rearrangements and numerical chromosome aberrations Cross-species color banding, Rx. FISH
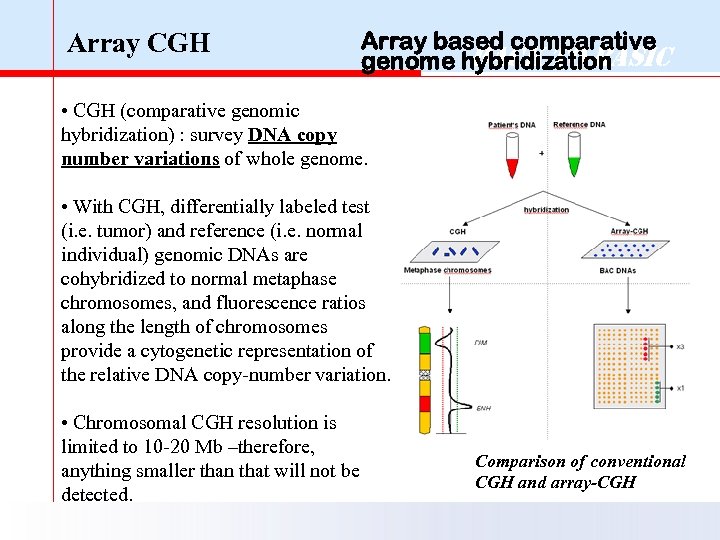
Array CGH Array based comparative Back to Basic genome hybridization • CGH (comparative genomic hybridization) : survey DNA copy number variations of whole genome. • With CGH, differentially labeled test (i. e. tumor) and reference (i. e. normal individual) genomic DNAs are cohybridized to normal metaphase chromosomes, and fluorescence ratios along the length of chromosomes provide a cytogenetic representation of the relative DNA copy-number variation. • Chromosomal CGH resolution is limited to 10 -20 Mb –therefore, anything smaller than that will not be detected. Comparison of conventional CGH and array-CGH

Back to Basic 한림의대 청해 강동성심병원 진단검사의학과 http: //labmed. hallym. ac. kr 세포유전학 검사정보

Back to Basic Genetics, Genomics, Proteomics Regenerative Medicine
b6b41141842ba202865dbd61efa6a9c3.ppt