cd888f44add7c70661e56b5b17d89121.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53

Bab 7 -8 Pengembangan Produk

Strategi Proses ü ü Pendekatan secara keseluruhan untuk memproduksi barang dan jasa Mendefinisikan: ü intensitas modal ü fleksibilitas proses ü integrasi vertikal ü keterlibatan Pelanggan
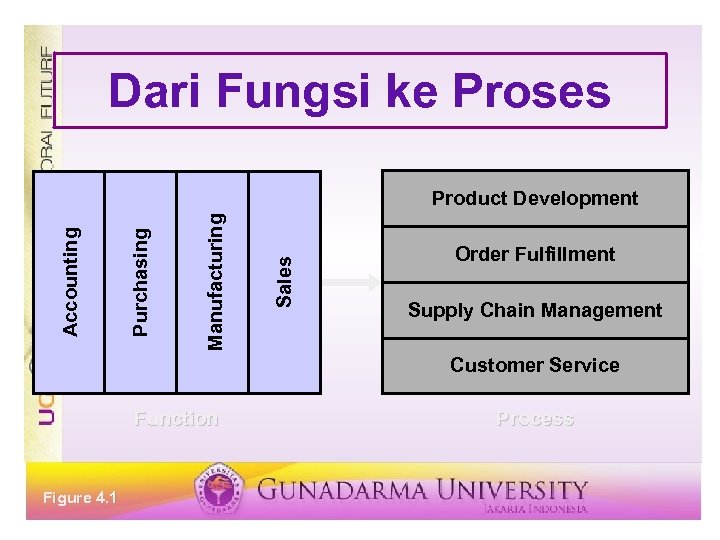
Dari Fungsi ke Proses Sales Manufacturing Purchasing Accounting Product Development Order Fulfillment Supply Chain Management Customer Service Function Figure 4. 1 Process

Tipe Proses ü Proyek ü produksi batch ü Produksi masal ü Produksi berkesinambungan

Tipe Proses PROJECT BATCH MASS CONTINUOUS Product Unique Made to order Made to stock Commodity Customer One-at-a-time Few individuals Mass market Demand Infrequent Fluctuates Stable Very stable Volume Very low Low to med High Very high No. of different Infinite Many, varied Few Very low Long-term Discrete, job Repetitive, Process industry products System assembly lines Equipment Varied General-purpose Special-purpose Highly automated Type of work Contracts Fabrication Assembly Mix, treat, refine Skills Experts, Wide range Limited range Equipment Table 4. 1 craftspeople of skills monitors

Proses Seleksi dengan Break-Even Analysis Total cost = fixed cost + total variable cost TC = cf + vcv Total revenue = volume x price TR = vp Profit = total revenue - total cost Z = TR - TC = vp - (cf + vcv)

Proses Seleksi dengan Break-Even Analysis Total cost = fixed cost + total variable cost TC = cf + vcv Total revenue = volume x price TR = vp Profit = total revenue - total cost Z = TR - TC = vp - (cf + vcv) cf v cv p = fixed cost = volume (i. e. , number of units produced and sold) = variable cost per unit = price per unit

Pemecahan masalah untuk volume Break-Even TR = TC vp = cf + vcv vp - vcv = cf v (p - c v ) = c f cf v= p-c v

Analisis Break-Even Fixed cost = cf = $2, 000 Variable cost = cv = $5 per raft Price = p = $10 per raft Example 4. 1
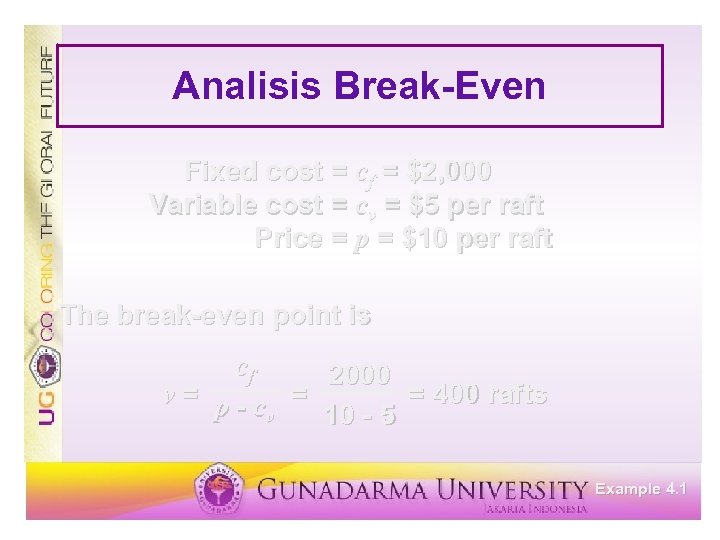
Analisis Break-Even Fixed cost = cf = $2, 000 Variable cost = cv = $5 per raft Price = p = $10 per raft The break-even point is cf 2000 v= p-c = = 400 rafts v 10 - 5 Example 4. 1
Analisis Break-Even Fixed cost = cf = $2, 000 Variable cost = cv = $5 per raft Price = p = $10 per raft $3, 000 — The $2, 000 — break-even point is cf 2000 v= p-c = = 400 rafts v 10 - 5 $1, 000 — Units Example 4. 1
Analisis Break-Even Fixed cost = cf = $2, 000 Variable cost = cv = $5 per raft Price = p = $10 per raft $3, 000 — The $2, 000 — break-even point is cf Total v = p - revenue cv = $1, 000 — line 2000 = 400 rafts 10 - 5 Units Example 4. 1
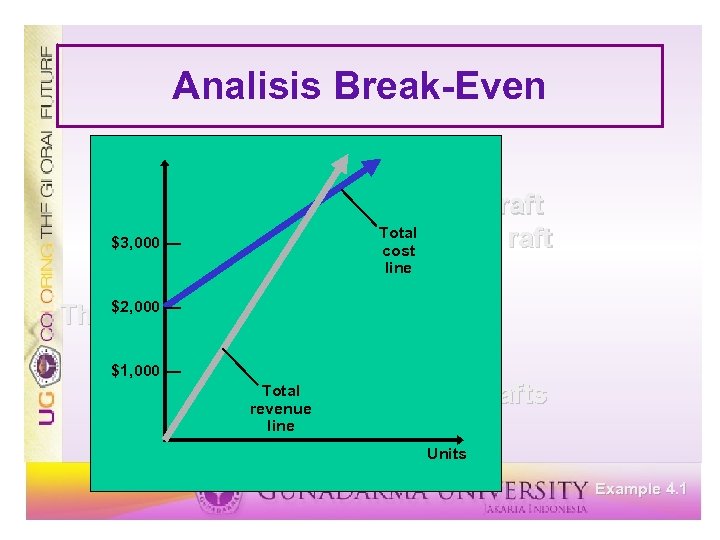
Analisis Break-Even Fixed cost = cf = $2, 000 Variable cost = cv = $5 per raft Total Price = p = $10 per raft $3, 000 — cost line The $2, 000 — break-even point is cf Total v = p - revenue cv = $1, 000 — line 2000 = 400 rafts 10 - 5 Units Example 4. 1

Analisis Break-Even Fixed cost = cf = $2, 000 Variable cost = cv = $5 per raft Total Price = p = $10 per raft $3, 000 — cost line The $2, 000 — break-even point is cf Total v = p - revenue cv = $1, 000 — line 2000 = 400 rafts 10 - 5 400 Break-even point Units Example 4. 1

Pemilihan diantara dua Proses Process A Process B $2, 000 + $5 v = $10, 000 + $2 v $3 v = $8, 000 v = 2, 667 rafts Below 2, 667, choose A Above 2, 667, choose B Example 4. 2
Pemilihan diantara dua Proses $20, 000 — $15, 000 — $10, 000 — $5, 000 — | 1000 | 2000 | 3000 | 4000 Units Example 4. 2
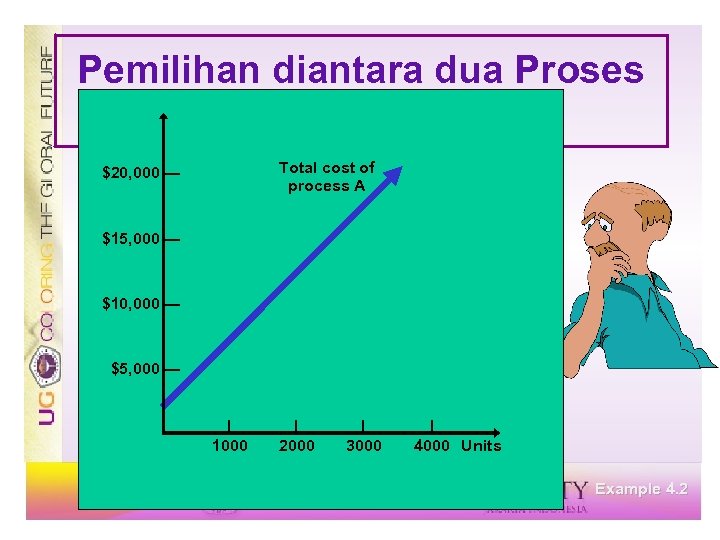
Pemilihan diantara dua Proses Processes Total cost of process A $20, 000 — $15, 000 — $10, 000 — $5, 000 — | 1000 | 2000 | 3000 | 4000 Units Example 4. 2
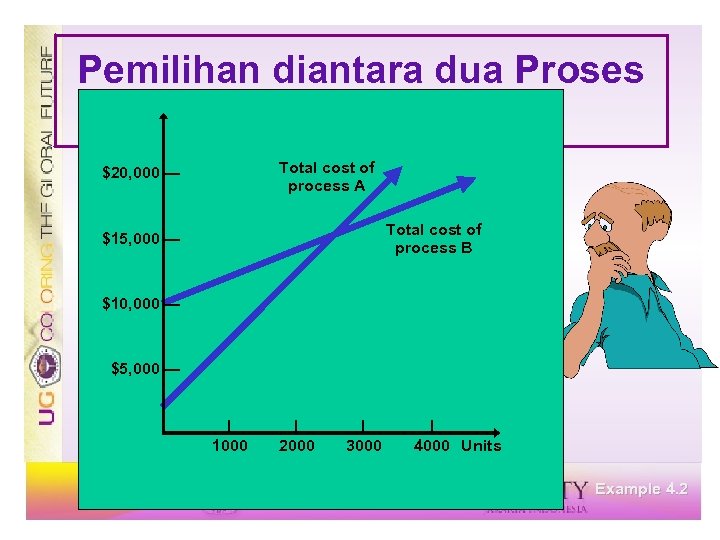
Pemilihan diantara dua Proses Processes Total cost of process A $20, 000 — Total cost of process B $15, 000 — $10, 000 — $5, 000 — | 1000 | 2000 | 3000 | 4000 Units Example 4. 2
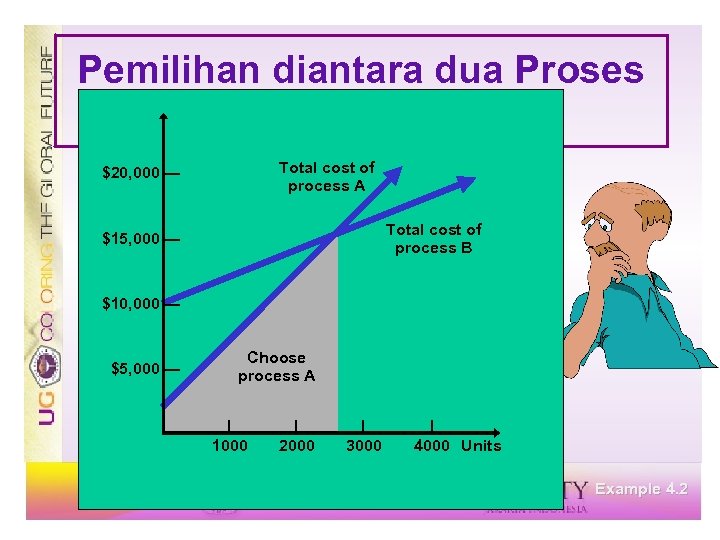
Pemilihan diantara dua Proses Processes Total cost of process A $20, 000 — Total cost of process B $15, 000 — $10, 000 — $5, 000 — Choose process A | 1000 | 2000 | 3000 | 4000 Units Example 4. 2
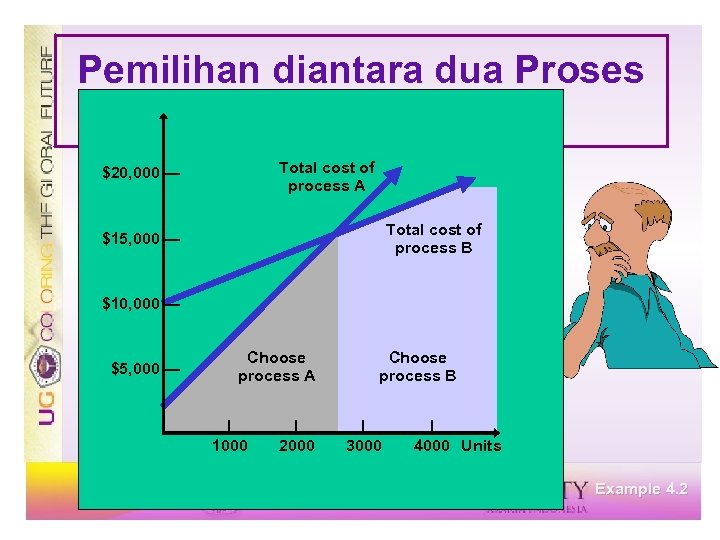
Pemilihan diantara dua Proses Processes Total cost of process A $20, 000 — Total cost of process B $15, 000 — $10, 000 — $5, 000 — Choose process A | 1000 | 2000 Choose process B | 3000 | 4000 Units Example 4. 2
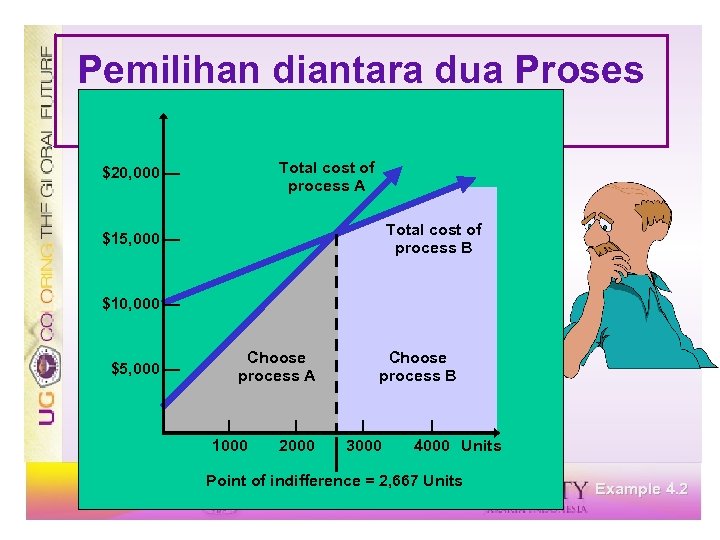
Pemilihan diantara dua Proses Processes Total cost of process A $20, 000 — Total cost of process B $15, 000 — $10, 000 — $5, 000 — Choose process A | 1000 | 2000 Choose process B | 3000 | 4000 Units Point of indifference = 2, 667 Units Example 4. 2

Point of Indifference ü Volume dimana biaya A = biaya B ü Aturan untuk memilih proses: ü Di atas titik indifference memilih proses dengan biaya variabel terendah ü Di bawah titik indifference memilih proses dengan biaya tetap terendah

Perencanaan Proses ü Keputusan membuat atau membeli ü Proses seleksi ü Pemilihan peralatan khusus ü Proses perencanaan ü Proses analisis

Keputusan Membuat atau Membeli 1. Biaya 2. Kapasitas 3. Kualitas 4. Kecepatan 5. Reliabilitas 6. Keahlian Make? Buy?

Seleksi Peralatan spesifik 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. biaya pembelian biaya operasional penghematan tahunan peningkatan pendapatan Analisis Replacement Risiko dan ketidakpastian Analisis Piecemeal

Proses Perencanaan ü ü ü Blueprints Bill bahan Bagan perakitan / diagram struktur produk Bagan proses operasi sheet Routing
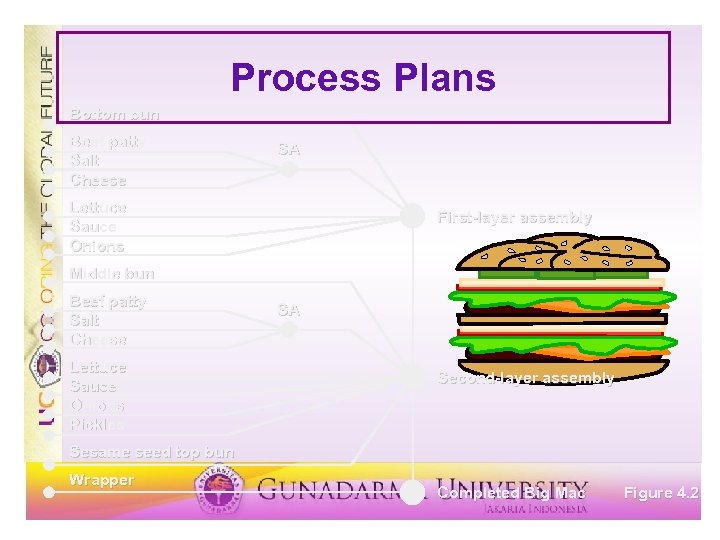
Process Plans Bottom bun Beef patty Salt Cheese SA Lettuce Sauce Onions First-layer assembly Middle bun Beef patty Salt Cheese Lettuce Sauce Onions Pickles SA Second-layer assembly Sesame seed top bun Wrapper Completed Big Mac Figure 4. 2

Bagan Proses Operasi Part name Crevice Tool Part No. 52074 Usage Hand-Vac Assembly No. 520 Oper. No. Description Dept. Machine/Tools Time 10 Pour in plastic bits 041 Injection molding 2 min 20 Insert mold 041 #076 2 min 30 Check settings & start machine 041 113, 67, 650 20 min 40 Collect parts & lay flat 051 Plastics finishing 10 min 50 Remove & clean mold 042 Parts washer 15 min 60 Break off rough edges 051 Plastics finishing 10 min Figure 4. 3

Analisis Proses ü Pemeriksaan sistematis semua aspek dari proses untuk meningkatkan operasi Lebih Cepat lebih hemat lebih murah Lebih responsif ü alat dasar proses flowchart proses diagram peta proses

Process Flowchart Description of process 1 Unload apples from truck 2 Move to inspection station 3 Weigh, inspect, sort 4 Move to storage 5 Wait until needed 6 Move to peeler 7 Apples peeled and cored 15 8 Soak in water until needed 20 9 Place in conveyor 5 10 Move to mixing area 11 Weigh, inspect, sort Distance (feet) Location: Graves Mountain Process: Apple Sauce Time (min) Operation Transport Inspect Delay Storage Step Date: 9 -30 -02 Analyst: TLR Page 1 0 f 3 Total 20 100 ft 30 50 ft 360 20 ft 30 480 190 ft Figure 4. 4

Process Diagram UPS Active Bins Receiving Reserve Storage Quality Assurance Picking Packing Monogramming Shipping Parcel Post Next-Day UPS Embroidering Back to Vendor Hemming Gift Boxing Figure 4. 5
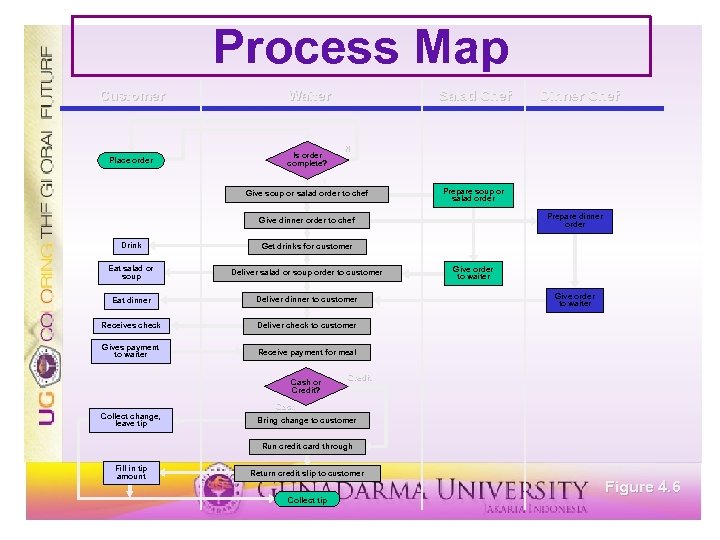
Process Map Customer Waiter Place order Is order complete? Salad Chef Dinner Chef N Y Give soup or salad order to chef Prepare soup or salad order Prepare dinner order Give dinner order to chef Drink Get drinks for customer Eat salad or soup Deliver salad or soup order to customer Eat dinner Deliver dinner to customer Receives check Deliver check to customer Gives payment to waiter Receive payment for meal Cash or Credit? Give order to waiter Credit Cash Collect change, leave tip Bring change to customer Run credit card through Fill in tip amount Return credit slip to customer Figure 4. 6 Collect tip

Extend’s Fast Food Simulation Model Figure 4. 7

SAP Solution for Apparel Figure 4. 8

Continuous Improvement and Breakthroughs

Continuous Improvement and Breakthroughs Figure 4. 9

Continuous Improvement and Breakthroughs Continuous improvement refines the breakthrough Breakthrough Improvement Continuous improvement activities peak; time to reengineer process Figure 4. 9
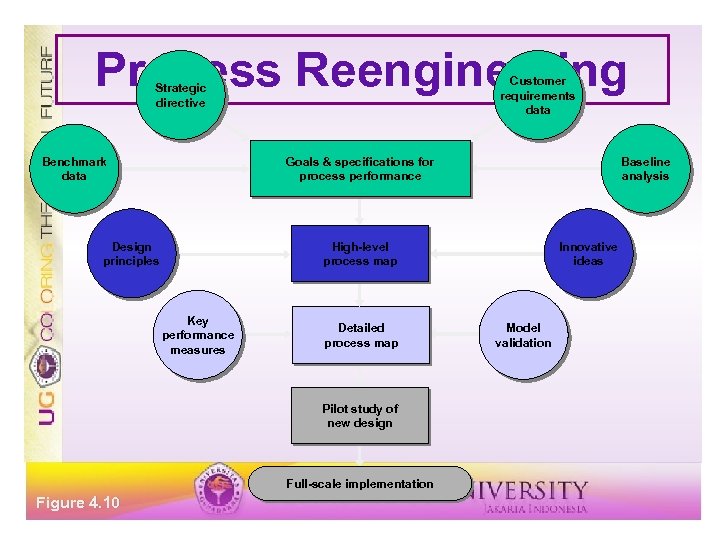
Process Reengineering Customer requirements data Strategic directive Benchmark data Goals & specifications for process performance Design principles High-level process map Key performance measures Detailed process map Pilot study of new design Full-scale implementation Figure 4. 10 Baseline analysis Innovative ideas Model validation

High-Level Process Map Subprocess Input Output Subprocess Figure 4. 11 Subprocess Performance Goal

Prinsip Proses Mendesain ulang Proses 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Membuang limbah , menyederhanakan , mengkonsolidasikan Proses Link untuk menciptakan nilai Yang tercepat dan paling mampu mengeksekusi Proses Flex Menangkap dan menyebarkan informasi secara digital Table 4. 2

Prinsip untuk Mendesain ulang Proses 6. Memberikan visibilitas melalui informasi mengenai status proses 7. Mencocokan proses dengan sensor dan umpan balik 8. Menambah kemampuan analitik 9. 10. Hubungkan , mengumpulkan dan menciptakan pengetahuan mengenai proses Personalisasi Table 4. 2

Teknik untuk Membangkitkan ide Inovatif ü ü ü variasi entry point untuk sebuah masalah Gambarkan analogi ubah perspektif Anda Coba sumbang terbalik Chain forward as sejauh mungkin Gunakan atribut Brainstorming ü Table 4. 3

Information Technology ü ü ü Management Information Systems (MIS) ü Memindahkan data dalam jumlah besar Decision Support Systems (DSS) ü Tambahkan dukungan pengambilan keputusan Expert System ü Rekomendasi dasar keputusan pada pengetahuan expert
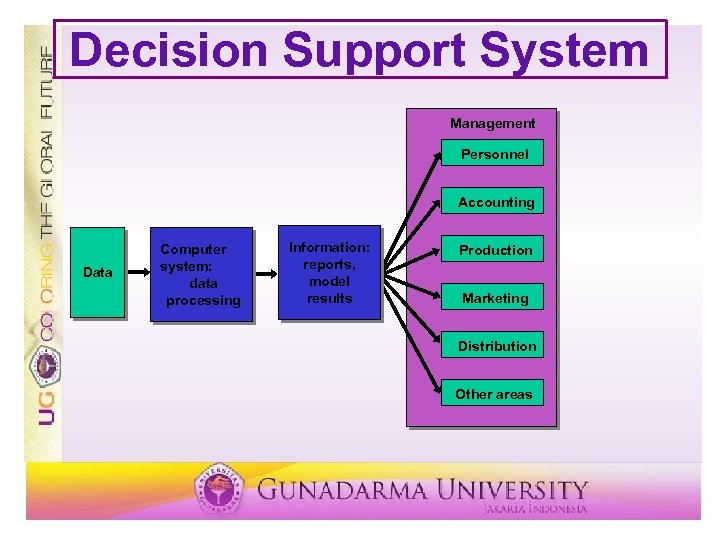
Decision Support System Management Personnel Accounting Data Computer system: data processing Information: reports, model results Production Marketing Distribution Other areas

Decision Support System Management Information System Personnel Accounting Data Computer system: data processing Information: reports, model results Production Marketing Distribution Other areas
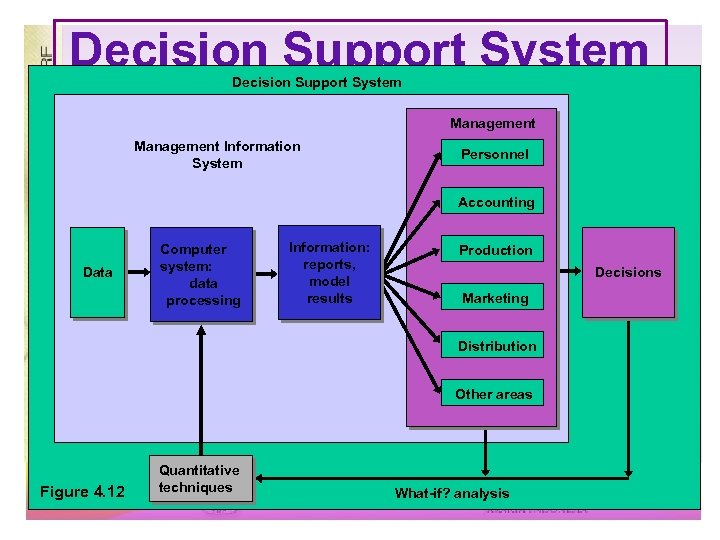
Decision Support System Management Information System Personnel Accounting Data Computer system: data processing Information: reports, model results Production Decisions Marketing Distribution Other areas Figure 4. 12 Quantitative techniques What-if? analysis

Artificial Intelligence ü Neural networks ü Meniru interkoneksi di otak ü Genetic algorithms ü Berdasarkan kemampuan adaptif di alam ü Fuzzy logic ü Mensimulasikan kemampuan manusia untuk menangani ambiguitas

Enterprise Software ü Mengumpulkan, menganalisis , dan membuat keputusan berdasarkan data ü ERP - Enterprise Resource Planning ü Mengelola berbagai proses ü ü Sumber daya manusia , manajemen material , rantai pasokan , akuntansi, keuangan , manufaktur , otomasi tenaga penjualan , layanan pelanggan , entri pesanan pelanggan Menemukan pola tersembunyi melalui data mining

Advanced Communications ü Electronic data interchange (EDI) ü Internet, extranets ü Wireless communications ü Teleconferencing & telecommuting ü Bar coding, RFT ü Virtual reality

Manufacturing Technology ü Numerically controlled (NC) machines ü ü Computer numerical controlled (CNC) ü ü Controlled by attached computer Direct numerical control (DNC) ü ü Controlled by punched tape Several NC machines controlled by single computer Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) ü Includes automated material handling

Automated Material Handling ü ü ü Conveyors Automated guided vehicle (AGV) Automated storage & retrieval system (ASRS)

Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) ü Programmable machine tools ü Controlled by common computer network ü Combines flexibility with efficiency ü Reduces setup & queue times

Components of e-Manufacturing CAD GT CAE CPC PDM Product life cycle Product Definition B 2 B, B 2 C Products Bar codes, RFT, EDI STEP CAD/CAM ERP Information Technology e. M Processes SCM, CRM CAPP DSS/ES/AI Sourcing & e-procurement Manufacture Internet, Intranet, extranet, satellites CNC machines Figure 4. 14 FMS Robotics AGV, ASRS Process control Cells Multiple factory and centers sites & suppliers
cd888f44add7c70661e56b5b17d89121.ppt