c2b0b83e035afaa33c243a4b84af3847.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43

BAB 2 PROCUREMENT AND PURCHASING 1

Sumber : 1. Business Logistics Management, Ronald H. Balou. 2. Physical Logistics Management, Grant M. Davis & John E. Dillard, Jr. 3. Strategic Logistics Management, Douglas M. Lambert & James R. Stock. 4. Principles of Marketing, Phillip Kotler. 2

SUPPOSE YOU ARE A CAR MANUFACTURER. . 3 You would buy materials, and distribute the final product.

DEFINISI LAMBERT Purchasing : Pembelian aktual dari material dan aktivitas-aktivitas yang berhubungan dengan proses pembelian. Procurement : Aktivitas yang meliputi proses dan strategis. 4

DEFINISI LEENDERS Purchasing : Proses pembelian (pembelajaran dari kebutuhan, lokasi dan pemilihan supplier, negosiasi harga, jaminan pengiriman). Procurement : Purchasing, stores, transport, receiving, pemeriksaan barang yang datang, storage). 5

PURCHASING AND MATERIALS MANAGEMENT A widely used organizational approach to purchasing management involves a concept known as materials management. This concept recognizes purchasing as one of several activities dealing with the planning for, acquisition of (pengadaan), and utilization of materials. In this approach, organization is structured so that all activities bringing materials into and through the plant (pabrik) are combined under one person known as the materials manager. (dikelola oleh seorang manajer material) 6

PURCHASING AND MATERIALS MANAGEMENT The basic rationale for this type of organization is that, taken alone, the functions of purchasing have conflicting objectives. For example, purchasing’s concern that supply be continuous may conflict with inventory control' s emphasis on minimizing inventory levels, or with traffic's objective of shipping in full loads. The expanded use of computers has made it possible for the materials manager to coordinate this increased level of operations. 7

PHYSICAL DISTRIBUTION Physical distribution takes the output-finished goods-from the end of the firm's production process to the customer. This transaction may involve packaging, finished goods warehousing, outbound transportation, delivery to customers, customer complaints, and accounting for all product costs since the product left the production line. 8

DELIVERY TO CUSTOMERS 9 Do we carry only the final products? What if our final product is a sub-material for another product?

MANAGING LOGISTICS Logistics contributes to both the materials management and the physical distribution functions. Logistics function manages the shipment of all incoming goods from suppliers and all outgoing goods to customers. The firm's traffic manager typically carries out these activities. 10

PURCHASING OBJECTIVES Purchasing’s responsibility is to buy materials of the right quality, in the right quantity, at the right time, at the right price, from the right source, with delivery at the right place. In most concerns continuity of operations is of critical importance. The purchasing function must not allow production to be disrupted by a lack of needed materials. 11

PURCHASING OBJECTIVES… Furthermore, this objective must be achieved with a minimum investment in inventories. Achieving this objective of security with a minimum investment demands a fine balancing of various factors: risk of shutdown, the cost inherent in forward buying, and the economies of quantity purchases. Weighing these factors calls for experience and a high order of professional judgment. 12

PURCHASING OBJECTIVES… Another objective is the maintenance of adequate quality. Quality refers primarily to the suitability of an item for its intended purpose. The objective is to procure the goods that are best suited rather than those of highest absolute quality. 13

PURCHASING OBJECTIVES… In addition to product quality, the services offered by the suppliers must be evaluated in the light of the organization's own needs. An initial low cost quoted by one supplier may legitimately be rejected in favor of a supplier with a higher initial cost balanced by valuable service factors. 14

PURCHASING OBJECTIVES… A further objective of purchasing is to avoid duplication, waste, and obsolescence of the various items purchased. The purchasing department can do much to eliminate these risks by considering each purchase in relation to long-range operating plans as well as the short-range considerations of the immediate purchase. 15

PURCHASING PROCEDURES AND TECHNIQUES… Some recent trends in procurement: Electronic Ordering Stockless Purchasing Standardization, and Just in Time Purchasing. 16

CURRENCY ISSUES IN INTERNATIONAL PURCHASING 17 Why do we have so many different currencies?

CURRENCY ISSUES IN INTERNATIONAL PURCHASING… Three methods to reduce the risk of buying in a foreign currency : Forward contracts Futures contracts Currency options 18

MANAGEMENT OF DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS Relationship management with channel members Trust, dependence and commitment Learning from successful relationships 19

TUJUAN PURCHASING Getting the right materials (meeting quality requirement), in the right quantity, for delivery at the right time and right place, from the right source (a vendor who reliable and will meet its commitments in a timely fashion), with right service (both before and after sales), and the right price. 20

PROCUREMENT (1) l l l Procurement is an important link in the Supply Chain. The objective of procurement is to ensure that there are sufficient supplies at the right price, of the required quality, in the right place and at the right time. Organisations have specific departments responsible for procurement. 21

PROCUREMENT (2) Organisations are in need of a number of items: l. Utilities air, listrik, telepon l. Fuel: bahan bakar l. Capital Assets: bangunan, kantor, mobil l. Computer hardware and software l. Stationary items : Alat tulis kantor. 22

PROCUREMENT (3) Organisations are in need of a number of items: l. Outsourced services: pihak ke tiga l. Transport and distribution services l. Security: keamanan

PROCUREMENT OBJECTIVES (1) According to Rushton et al, when setting procurement objectives, consideration should be given to the following: l Ensuring the supply of raw materials and other supplies l. The quality of supplies l. The price l. The origin of the supplies l. The method of supply 24

PROCUREMENT OBJECTIVES (2) l. The mode of transport used l. Deciding goods are to be acquired first l. Whether to make or buy 25

MAKE OR BUY? The decision whether to make or buy a good depends on the following: l. Cost l. Supply guarantees l. Production capacity l. Competitive advantage 26

SASARAN PURCHASING Menjamin kelancaran aliran material, supplies, dan pelayanan yang dibutuhkan untuk operasi organisasi. Menjaga agar tidak terjadi kekurangan persediaan. Memelihara dan meningkatkan kualitas. Menemukan atau mengembangkan supplier. 27

PEMBELIAN Ronald H. Ballou • • • Memilih dan menujuk supplier. Pengukuran performance supplier. Negoisasi kontrak. Mempertimbangkan harga, kualitas dan pelayanan. Sumber barang – barang dan pelayanan. Merencanakan waktu pembelian. Merencanakan waktu penjualan. Mengevaluasi nilai penerimaan. Memperkirakan harga, pelayanan dan perubahan demand. Merinci bentuk dari produk yang akan diterima. 28

LANGKAH – LANGKAH SIKLUS PEMBELIAN Dobbler 1994, 324 • Pengenalan, pendefinisian dan penggambaran kebutuhan. • Pengajuan daftar pembelian kedepartemen Pembelian dg form. • Investigasi dan pemilihan supplier. • Persiapan dan penerbitan purchasing order ( DO ). • Tindak lanjut pemesanan. • Penerimaan dan pemeriksaan matrial. • Pemeriksaan invoice. • Penutupan pesanan. Catatan bagi departemen pembelian: • Open Order • Close Order. • Commodity record. • Supplier record. • Special toll record. 29
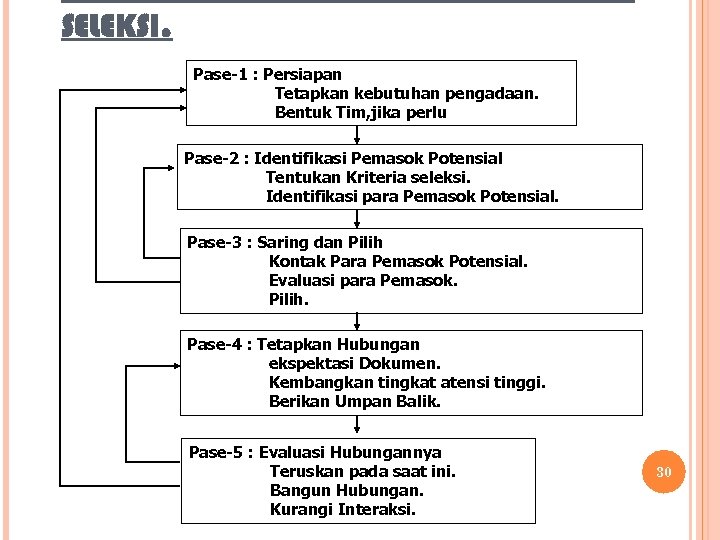
SELEKSI. Pase-1 : Persiapan Tetapkan kebutuhan pengadaan. Bentuk Tim, jika perlu Pase-2 : Identifikasi Pemasok Potensial Tentukan Kriteria seleksi. Identifikasi para Pemasok Potensial. Pase-3 : Saring dan Pilih Kontak Para Pemasok Potensial. Evaluasi para Pemasok. Pilih. Pase-4 : Tetapkan Hubungan ekspektasi Dokumen. Kembangkan tingkat atensi tinggi. Berikan Umpan Balik. Pase-5 : Evaluasi Hubungannya Teruskan pada saat ini. Bangun Hubungan. Kurangi Interaksi. 30
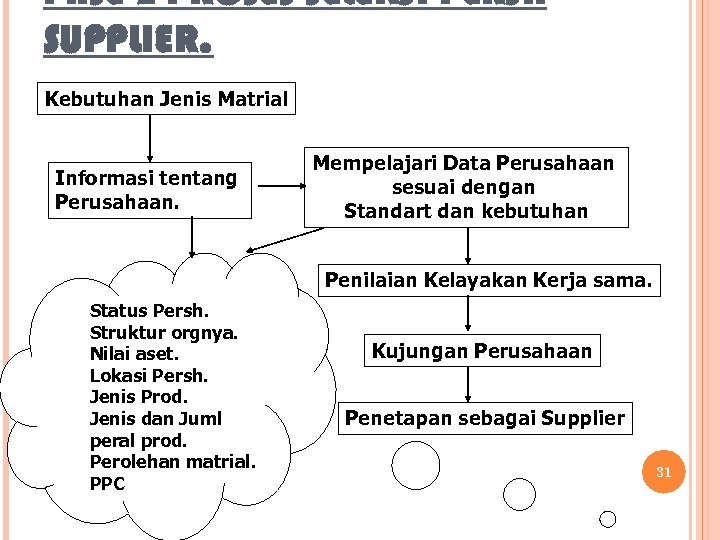
PASE-2 PROSES SELEKSI PERSH SUPPLIER. Kebutuhan Jenis Matrial Informasi tentang Perusahaan. Mempelajari Data Perusahaan sesuai dengan Standart dan kebutuhan Penilaian Kelayakan Kerja sama. Status Persh. Struktur orgnya. Nilai aset. Lokasi Persh. Jenis Prod. Jenis dan Juml peral prod. Perolehan matrial. PPC Kujungan Perusahaan Penetapan sebagai Supplier 31

SUPPLIER YANG POTENSIAL Supplier yg baik adalah ; ( Prof. Wilbur england, dr Harvard University ) Selalu jujur dan adil pd setiap transaksi. Mempunyai fasilitas pabrik yg memadai. Mampu menghasilkan produk sesuai dg spesifikasi konsumen. Kondisi keuangan baik. Harga yg realitis baik thp konsumen maupun thp persh sendiri. Senantiasa mengembangkan produk dan proses produksinya. Selalu mengutamakan pelayanan terbaik untuk konsumen. 32

POTENSIAL Company profile Penelitian Awal Siapa Pengelolahnya. Bgimana konditenya. Bank references. Credit references. Penjualan tahunan. Laba dlm 5 th. Daftar konsumen. Jumlah tenaga kerja. Luas pabrik. Develp suber dana. Tingkat rejek Jlm pengawas mutu. Peralatan /teknologi. Kondisi Keuangan Mngt baik. kwltas prod baik. Modalnya memadai utk mhdpi kalim. Dananya cukup u/ mempercepat proses prod bila diperlukan. harga yg ditawarkan realitis. Siap menghadapi goncanganekonomi u/menjamin kontinuitas pgiriman Kunjungan kepabrik Operasi & peralannya. Kmampuan mngt splier. Motiva spier u/ kerjasm. Kmapuan R&D splier. efektif PPC. Moral spier scr umum. Jml Pngrm pesan yg ditolak. PKS jk Panjang. aktivitas pengelolah Matrial. 33
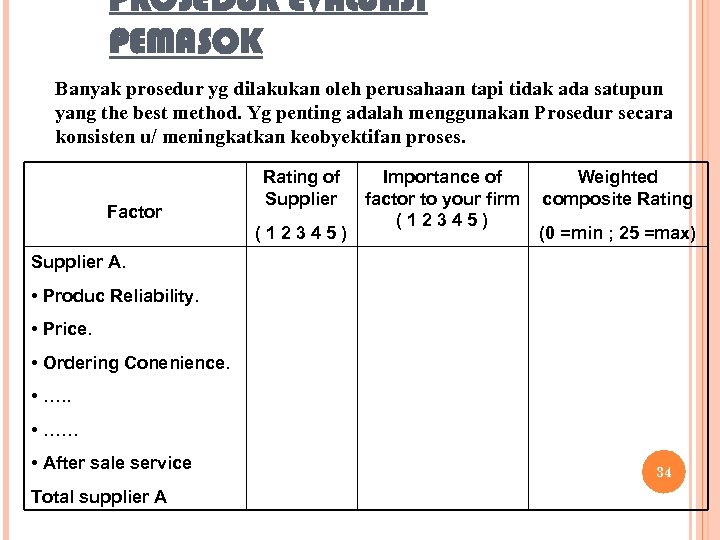
PROSEDUR EVALUASI PEMASOK Banyak prosedur yg dilakukan oleh perusahaan tapi tidak ada satupun yang the best method. Yg penting adalah menggunakan Prosedur secara konsisten u/ meningkatkan keobyektifan proses. Factor Rating of Supplier (12345) Importance of factor to your firm (12345) Weighted composite Rating (0 =min ; 25 =max) Supplier A. • Produc Reliability. • Price. • Ordering Conenience. • …… • After sale service Total supplier A 34

Menstandarisasi barang-barang yang dibeli. Membeli barang-barang yang dibutuhkan dan memberikan pelayanan pada tingkat ongkos yang murah. Meningkatkan posisi kompetitif organisasi. Mengharmoniskan hubungan antara pekerjaan yang produktif dengan fungsi lain pada organisasi. Mengupayakan pencapaian tujuan purchasing pada ongkos administrasi yang paling murah. 35

PERAN PURCHASING DALAM CUSTOMER SERVICE Produk dan jasa yang handal. Datang tepat waktu. Ongkos/biaya murah. 36

PERAN STRATEGIS PURCHASING Melalui hubungan dengan pihak pasar, pihak purchasing bisa memperoleh informasi penting tentang teknologi baru, potensi material dan jasa baru, sumber pasokan baru dan perubahan kondisi pasar. Dengan komunikasi, purchasing bisa membantu membentuk strategi organisasi untuk memperoleh keunggulan kesempatan pasar. 37

SELEKSI DAN EVALUASI PEMASOK Proses paling penting adalah pemilihan supplier. Proses pengambilan keputusan : decision makers dan decision influencers (Decision Making Unit). 38

JUST IN TIME Berdasarkan sistem tarik (pull system). Kesulitan dalam mengimplementasikan JIT : Dalam masalah pengendalian mutu, sulitnya melakukan perubahan dari inspeksi total. Dalam maslah persediaan, sulit mengubah sistem lotsize ke cara pengiriman yang sering dan pada saat yang pasti. Dalam sistem produksi, pemasok dan pembeli mengharapkan adanya akses kepada sistem persediaan. 39
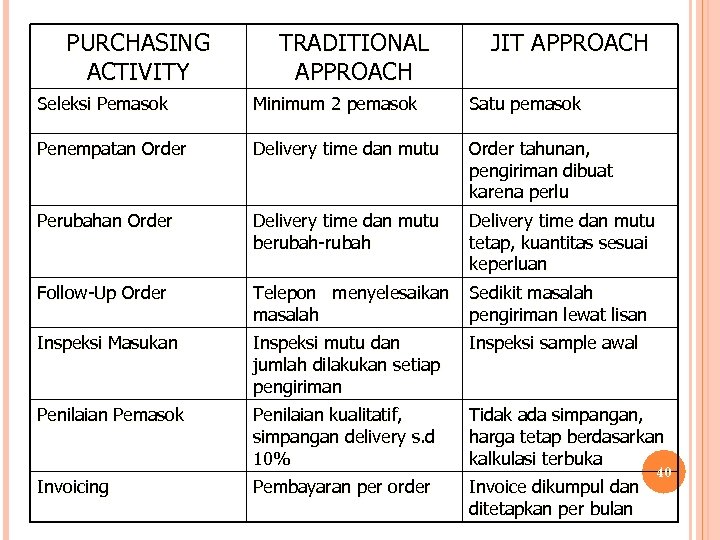
PURCHASING ACTIVITY TRADITIONAL APPROACH JIT APPROACH Seleksi Pemasok Minimum 2 pemasok Satu pemasok Penempatan Order Delivery time dan mutu Order tahunan, pengiriman dibuat karena perlu Perubahan Order Delivery time dan mutu berubah-rubah Delivery time dan mutu tetap, kuantitas sesuai keperluan Follow-Up Order Telepon menyelesaikan masalah Sedikit masalah pengiriman lewat lisan Inspeksi Masukan Inspeksi mutu dan jumlah dilakukan setiap pengiriman Inspeksi sample awal Penilaian Pemasok Penilaian kualitatif, simpangan delivery s. d 10% Tidak ada simpangan, harga tetap berdasarkan kalkulasi terbuka Pembayaran per order Invoice dikumpul dan ditetapkan per bulan Invoicing 40

PROGRAM PENGURANGAN ONGKOS Cost Reduction : Penurunan dalam harga pembelian, hal ini berarti hanya jika perusahaan membayar pada harga yang lebih rendah. Cost Avoidance : Sejumlah yang harus dibayar , kurang dari jumlah pembayaran sebenarnya. 41

LATIHAN : 1. 2. Jelaskan bagaimana peranan procurement/purchasing dalam bisnis logistik. Jelaskan dengan contoh proses pemilihan suplier. (Cari di internet atau observasi langsung ke perusahaan untuk mencari contoh proses pemilihan suplier di perusahaan). 42

ADA PERTANYAAN? 43
c2b0b83e035afaa33c243a4b84af3847.ppt