3c8a25dc4015fc2f7286decf03031aba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

B. Information Technology (IS) CISB 454: Introduction to Knowledge Management Knowledge Creation & KM Architecture

Learning Objectives l At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: u u define knowledge creation and sharing discuss the knowledge infrastructure elaborate on the knowledge management architecture decide on building versus buying a KM softwaresystem 3 -2

Knowledge Creation & KM Architecture Knowledge Creation and Sharing

Knowledge Creation Definition l Dynamic activity that can enhance organization success and economic well-being l Driver of innovation l Involves knowledge acquisition, selection, generation and sharing l Maturation u translates experience into knowledge 3 -4
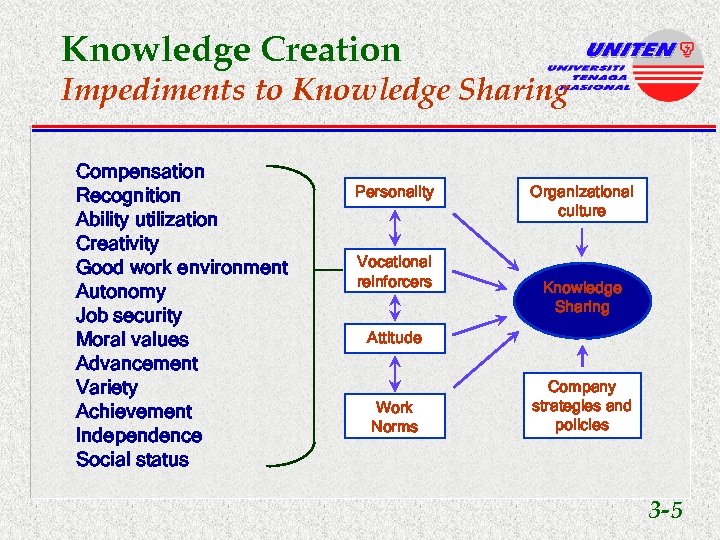
Knowledge Creation Impediments to Knowledge Sharing Compensation Recognition Ability utilization Creativity Good work environment Autonomy Job security Moral values Advancement Variety Achievement Independence Social status Personality Vocational reinforcers Organizational culture Knowledge Sharing Attitude Work Norms Company strategies and policies 3 -5
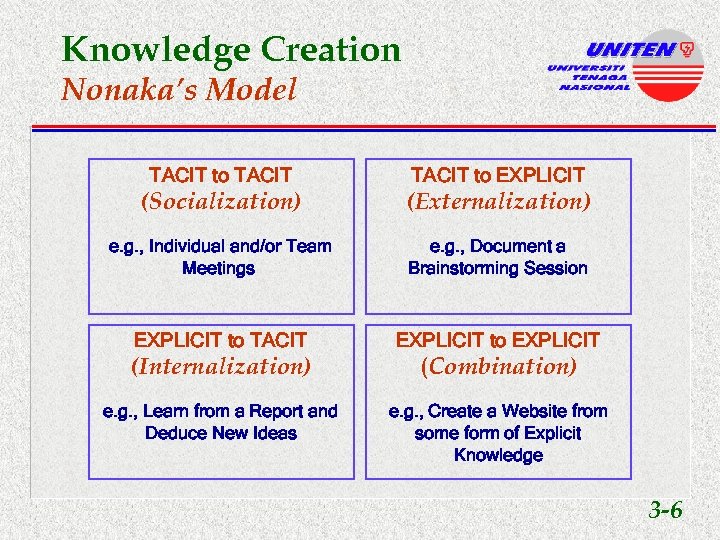
Knowledge Creation Nonaka’s Model TACIT to EXPLICIT (Socialization) (Externalization) e. g. , Individual and/or Team Meetings e. g. , Document a Brainstorming Session EXPLICIT to TACIT EXPLICIT to EXPLICIT (Internalization) (Combination) e. g. , Learn from a Report and Deduce New Ideas e. g. , Create a Website from some form of Explicit Knowledge 3 -6
Knowledge Creation & KM Architecture Knowledge Infrastructure
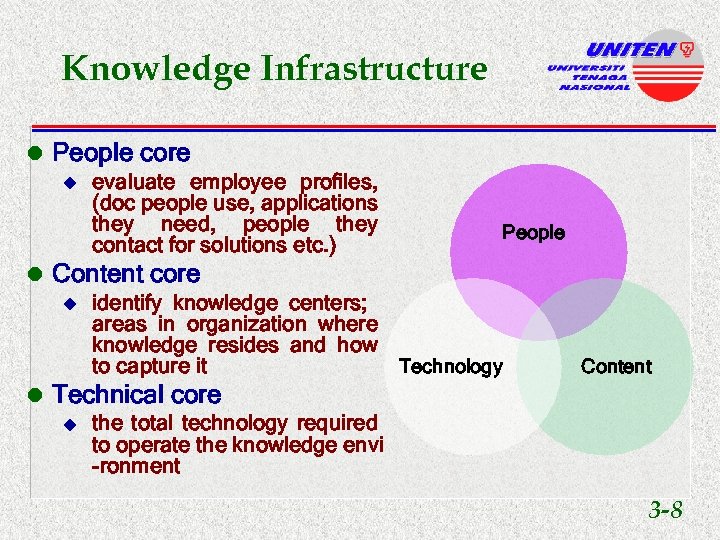
Knowledge Infrastructure l People core u evaluate employee profiles, (doc people use, applications they need, people they contact for solutions etc. ) People l Content core u identify knowledge centers; areas in organization where knowledge resides and how Technology to capture it Content l Technical core u the total technology required to operate the knowledge envi -ronment 3 -8
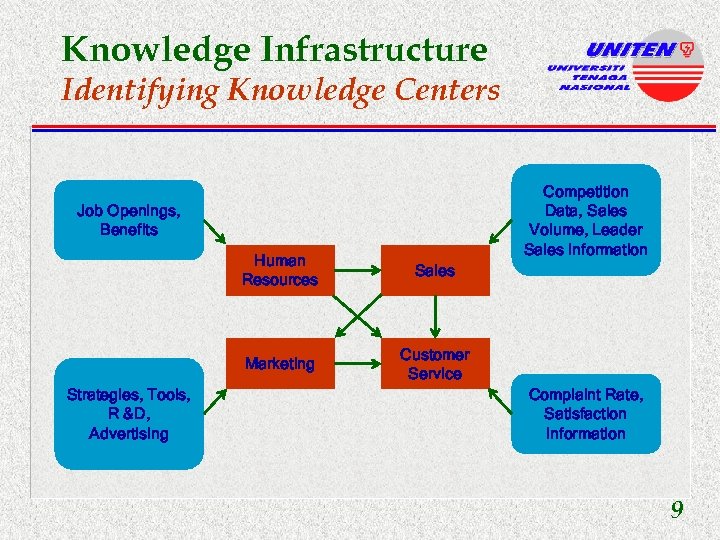
Knowledge Infrastructure Identifying Knowledge Centers Competition Data, Sales Volume, Leader Sales Information Job Openings, Benefits Human Resources Marketing Strategies, Tools, R &D, Advertising Sales Customer Service Complaint Rate, Satisfaction Information 9

Knowledge Creation & KM Architecture Knowledge Management Architecture
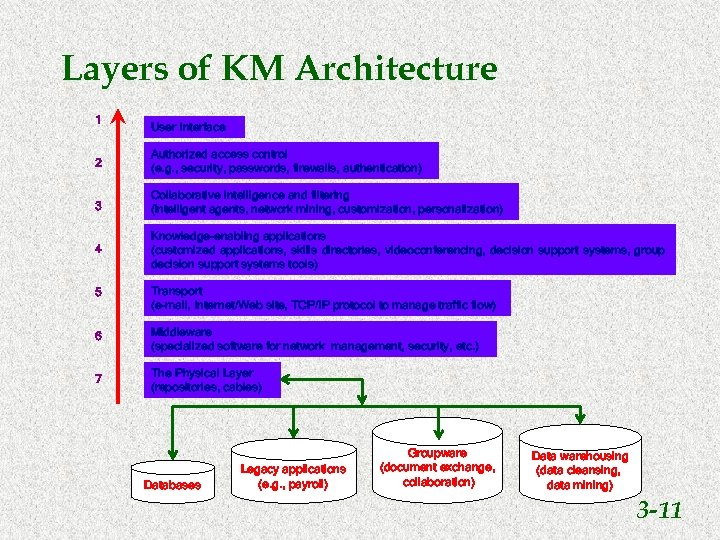
Layers of KM Architecture 1 User Interface 2 Authorized access control (e. g. , security, passwords, firewalls, authentication) 3 Collaborative intelligence and filtering (intelligent agents, network mining, customization, personalization) 4 Knowledge-enabling applications (customized applications, skills directories, videoconferencing, decision support systems, group decision support systems tools) 5 Transport (e-mail, Internet/Web site, TCP/IP protocol to manage traffic flow) 6 Middleware (specialized software for network management, security, etc. ) 7 The Physical Layer (repositories, cables) Databases Legacy applications (e. g. , payroll) Groupware (document exchange, collaboration) Data warehousing (data cleansing, data mining) 3 -11
The User Interface (Layer 1) l User interface design focuses on u u u consistency relevancy visual clarity navigation usability 3 -12
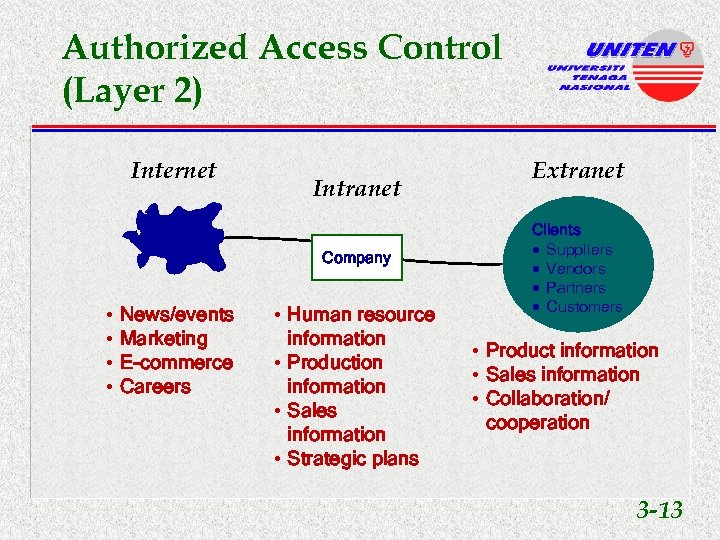
Authorized Access Control (Layer 2) Internet Intranet Public Company • • News/events Marketing E-commerce Careers • Human resource information • Production information • Sales information • Strategic plans Extranet Clients · Suppliers · Vendors · Partners · Customers • Product information • Sales information • Collaboration/ cooperation 3 -13

Collaborative Intelligence and Filtering (Layer 3) l Personalized views based on stored knowledge l Groupware to facilitate both synchronous and asynchronous interaction & discussion l Intelligent agents reduce search time for needed information 3 -14
Knowledge-Enabling Application (Layer 4) l Referred to as value- added layer l Creates a competitive edge for the learning organization 3 -15
Knowledge-Enabling Application (Layer 4) l Provides u u u knowledge bases discussion databases automation tools, etc. l Ultimate goal u show knowledge sharing could improve the employees 3 -16
Transport Layer (Layer 5) l Most technical layer to implement l Includes u u u LANs WANs intranets extranets Internet 3 -17
Transport Layer (Layer 5) l Ensures that the com- pany will become a network of relationships l Considers u u u multimedia URLs, graphics connectivity speeds bandwidths 3 -18
Middleware (Layer 6) l Focus on interfacing with legacy systems and programs residing on other platforms l Designer should address databases & applications with which KM system interfaces l Makes it possible to connect between old and new data formats 3 -19
Physical Repositories (Layer 7) l Bottom layer in the KM architecture l Represents the physical layer u where repositories are installed 3 -20
Physical Repositories (Layer 7) l Includes u u u intelligent data warehouses legacy applications operational databases special applications for security traffic management 3 -21
Knowledge Creation & KM Architecture Build Vs. Buy Decision
Build In-House, Buy, or Outsource? l Trend is toward ready- to-use, generalized software packages l Outsourcing is also a trend, releasing technological design to outsiders 3 -23
Build In-House, Buy, or Outsource? l Regardless of choice, it is important to set criteria for selection l Question of who owns the KM system should be considered 3 -24
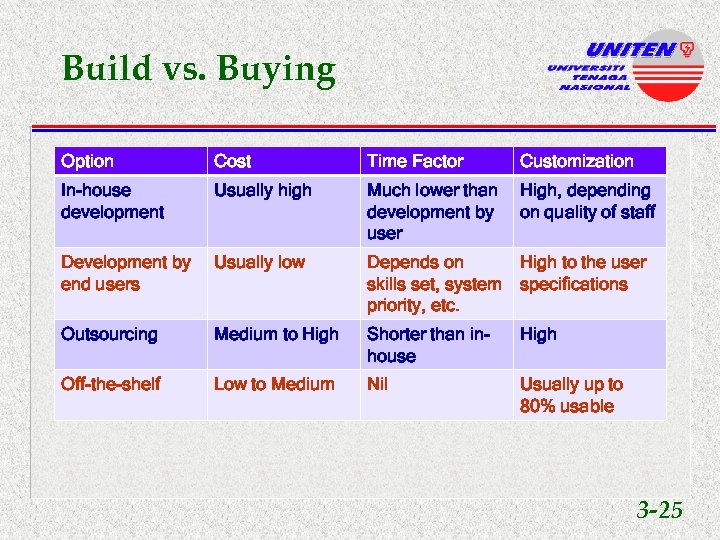
Build vs. Buying Option Cost Time Factor Customization In-house development Usually high Much lower than High, depending development by on quality of staff user Development by end users Usually low Depends on High to the user skills set, system specifications priority, etc. Outsourcing Medium to High Shorter than inhouse High Off-the-shelf Low to Medium Nil Usually up to 80% usable 3 -25
THE END Copyright (c) 2010 Mohd. Sharifuddin Ahmad, Ph. D College of Information Technology
3c8a25dc4015fc2f7286decf03031aba.ppt