90b6e2b3b10e1eaa3269a0eb2e2e4469.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Avon Case Week 12 – April 6, 2006 J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
Avon Case Week 12 – April 6, 2006 J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
 Avon’s Strategy since 1982 u Bought health care firms – Mallinckrodt for $710 million (1982) – Foster Medical Care with shares (1984) – Retirement Inns of America (1985) – Mediplex (1986) u Sold Mallinckrodt in 1986 for $675 million u Bought fashion and scents – Giorgio, Inc. for $165 million cash (1987) – Parfums Stern for $160 million cash (1987) J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
Avon’s Strategy since 1982 u Bought health care firms – Mallinckrodt for $710 million (1982) – Foster Medical Care with shares (1984) – Retirement Inns of America (1985) – Mediplex (1986) u Sold Mallinckrodt in 1986 for $675 million u Bought fashion and scents – Giorgio, Inc. for $165 million cash (1987) – Parfums Stern for $160 million cash (1987) J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
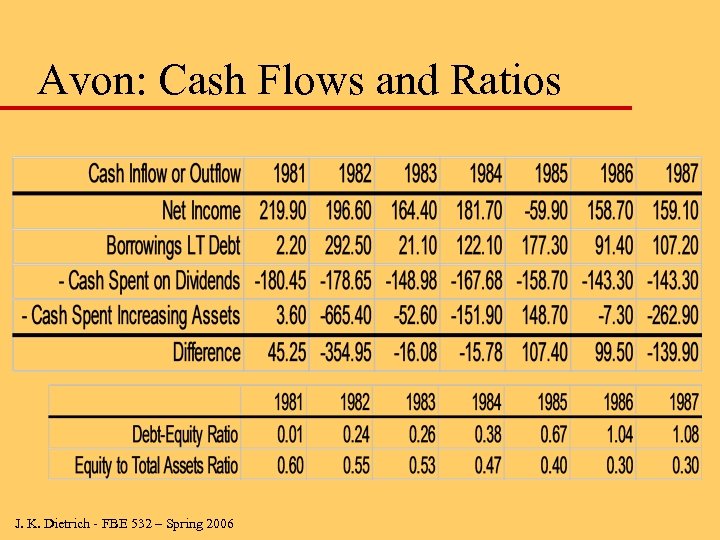 Avon: Cash Flows and Ratios J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
Avon: Cash Flows and Ratios J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
 Avon and Finance Theory u What has been the relationship between Avon’s strategy and its need for cash? u How has dividend policy fit into its financial strategy? u What financial considerations does theory suggest should be made concerning business strategy and dividend policy? u How do you evaluate Avon’s business strategy? J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
Avon and Finance Theory u What has been the relationship between Avon’s strategy and its need for cash? u How has dividend policy fit into its financial strategy? u What financial considerations does theory suggest should be made concerning business strategy and dividend policy? u How do you evaluate Avon’s business strategy? J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
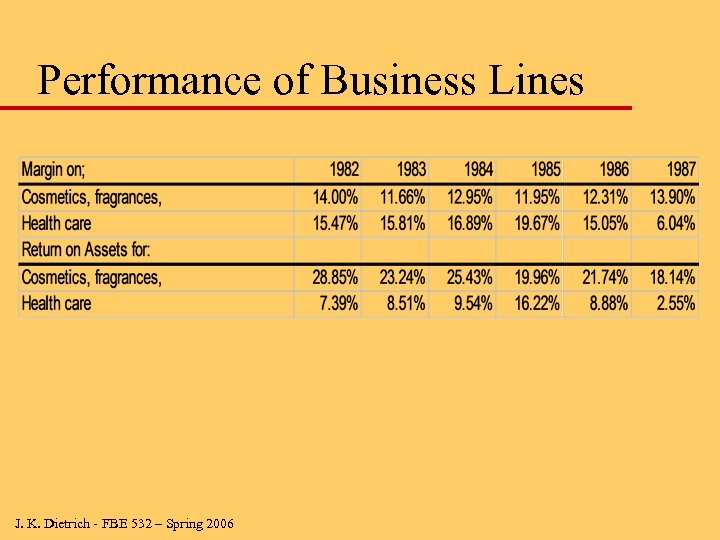 Performance of Business Lines J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
Performance of Business Lines J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
 Avon in 1988 u Cash needed for restructuring – Winding down of Mediplex and Retirement Inns – Rebuilding and expanding beauty product business u Dividends $143 million/year u Concerns about investor clientele – Institutional ownership > 46. 5% – About 1/6 shares desired cash yield J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
Avon in 1988 u Cash needed for restructuring – Winding down of Mediplex and Retirement Inns – Rebuilding and expanding beauty product business u Dividends $143 million/year u Concerns about investor clientele – Institutional ownership > 46. 5% – About 1/6 shares desired cash yield J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
 Morgan Stanley Proposal u Avon offer to exchange up to 18 million common shares for $2. 00 preferred equityredemption cumulative stock (PERCS) u After five years, PERCS redeemed with common shares u Dividend on remaining common shares reduced from $2. 00 to $1. 00 u Cash saved J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
Morgan Stanley Proposal u Avon offer to exchange up to 18 million common shares for $2. 00 preferred equityredemption cumulative stock (PERCS) u After five years, PERCS redeemed with common shares u Dividend on remaining common shares reduced from $2. 00 to $1. 00 u Cash saved J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
 PERCs versus Common (no deal) u PERCs must have same value as common if PERCs were not issued u If PERCs not issued, to achieve same cash flow effect, dividend on common would be reduced to $1. 25 because $1. 25 dividend to all common shares is same cash flow as $2. 00 to PERCS (25% of total) and $1. 00 to non-converting common (75% of total) J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
PERCs versus Common (no deal) u PERCs must have same value as common if PERCs were not issued u If PERCs not issued, to achieve same cash flow effect, dividend on common would be reduced to $1. 25 because $1. 25 dividend to all common shares is same cash flow as $2. 00 to PERCS (25% of total) and $1. 00 to non-converting common (75% of total) J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
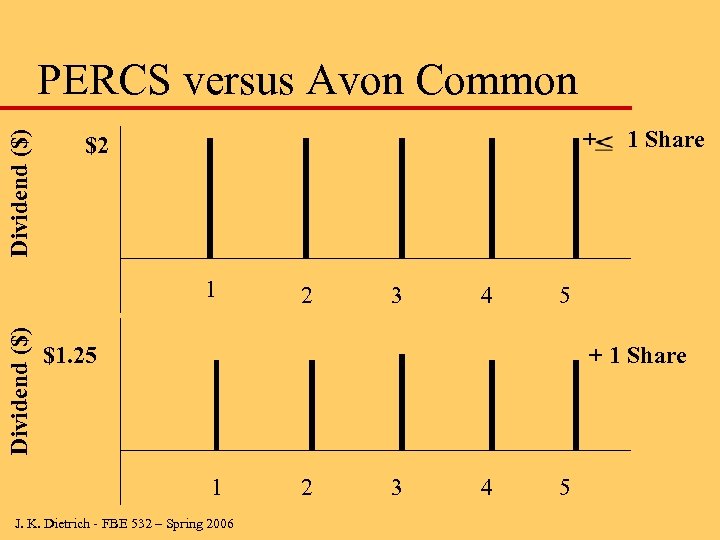 Dividend ($) PERCS versus Avon Common + $2 Dividend ($) 1 2 3 4 1 Share 5 $1. 25 + 1 Share 1 J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006 2 3 4 5
Dividend ($) PERCS versus Avon Common + $2 Dividend ($) 1 2 3 4 1 Share 5 $1. 25 + 1 Share 1 J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006 2 3 4 5
 Concept u Shareholders wanting cash yield will convert to PERCs – Receive higher dividend – No profit from share value above $31. 50 u Other shareholders will be content to hold (lower dividend yielding) Avon common u At margin, value of the two securities (common and PERCS) must be equivalent to common if PERCS not issued at all J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
Concept u Shareholders wanting cash yield will convert to PERCs – Receive higher dividend – No profit from share value above $31. 50 u Other shareholders will be content to hold (lower dividend yielding) Avon common u At margin, value of the two securities (common and PERCS) must be equivalent to common if PERCS not issued at all J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
 PERCS u Receives higher dividend but has a limit on upside gain to stock Lost Profit on Stock – If P+5 > $31. 50, receive $31. 50 in stock value – If P+5 < $ 31. 50, receive share value J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006 $31. 50
PERCS u Receives higher dividend but has a limit on upside gain to stock Lost Profit on Stock – If P+5 > $31. 50, receive $31. 50 in stock value – If P+5 < $ 31. 50, receive share value J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006 $31. 50
 Value of PERCS u Value of PERCS is present value of dividends plus value of common minus value of call option written u Value of common and value of PERCS (with the assumption of no issuance of PERCS) must be equal u Common priced at $24. 125, before announcement of exchange offer. J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
Value of PERCS u Value of PERCS is present value of dividends plus value of common minus value of call option written u Value of common and value of PERCS (with the assumption of no issuance of PERCS) must be equal u Common priced at $24. 125, before announcement of exchange offer. J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
 Valuation of PERCs u Value of PERCS composed of value of stock, value of extra dividends, minus value of call: u Valuation issues then are the appropriate discount rate on extra dividends and value of call J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
Valuation of PERCs u Value of PERCS composed of value of stock, value of extra dividends, minus value of call: u Valuation issues then are the appropriate discount rate on extra dividends and value of call J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
 Avon Case: Summary and Issues u What has been the rationale behind Avon’s strategy and how does its current situation relate to its past dividend policy? u What are the key factors in the success of the PERCS proposal and what contribution does it make towards the goals of Avon’s management? u Do the PERCS satisfy investor expectations so that Avon will achieve desired outcome? J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006
Avon Case: Summary and Issues u What has been the rationale behind Avon’s strategy and how does its current situation relate to its past dividend policy? u What are the key factors in the success of the PERCS proposal and what contribution does it make towards the goals of Avon’s management? u Do the PERCS satisfy investor expectations so that Avon will achieve desired outcome? J. K. Dietrich - FBE 532 – Spring 2006


