839b51ebc9355907c1035b06e1dbecf2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

Automating IE using VB 6
Agenda • Automating IE • HTML DOM • Automating Web Pages • Question and Answers

Automating IE
COM • COM is Component Object Model. • Application developed using COM provides interfaces to third party application for using certain features of the application. • Nearly all Microsoft applications are built using COM. Eg. – Internet Explorer, All Office applications like Outlook, Excel, Word etc… • COM makes it possible to create automation solution for the AUT.
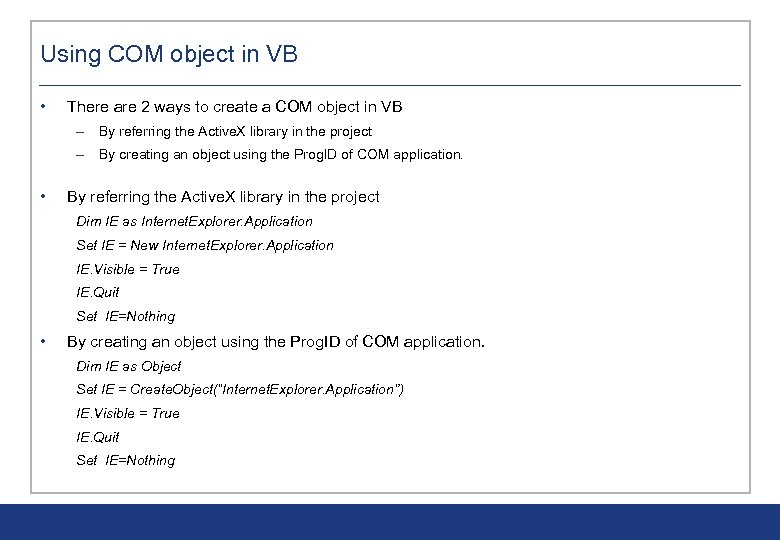
Using COM object in VB • There are 2 ways to create a COM object in VB – By referring the Active. X library in the project – By creating an object using the Prog. ID of COM application. • By referring the Active. X library in the project Dim IE as Internet. Explorer. Application Set IE = New Internet. Explorer. Application IE. Visible = True IE. Quit Set IE=Nothing • By creating an object using the Prog. ID of COM application. Dim IE as Object Set IE = Create. Object(“Internet. Explorer. Application”) IE. Visible = True IE. Quit Set IE=Nothing
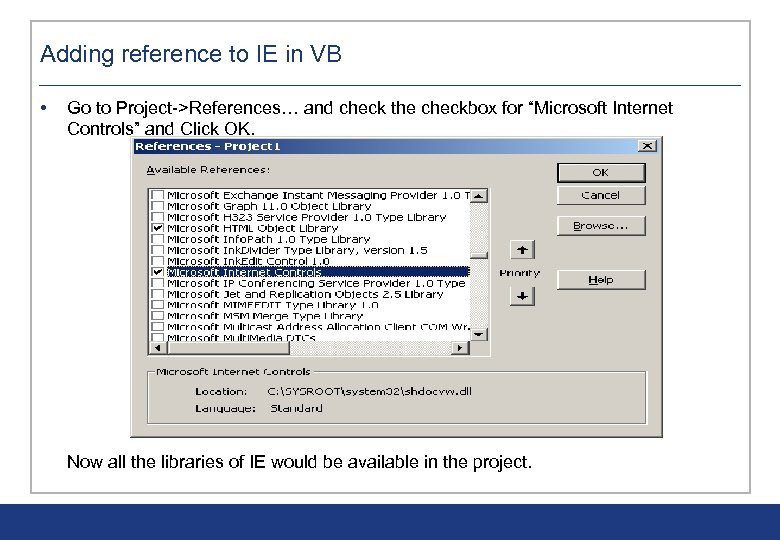
Adding reference to IE in VB • Go to Project->References… and check the checkbox for “Microsoft Internet Controls” and Click OK. Now all the libraries of IE would be available in the project.
Viewing object methods/properties using Object Browser
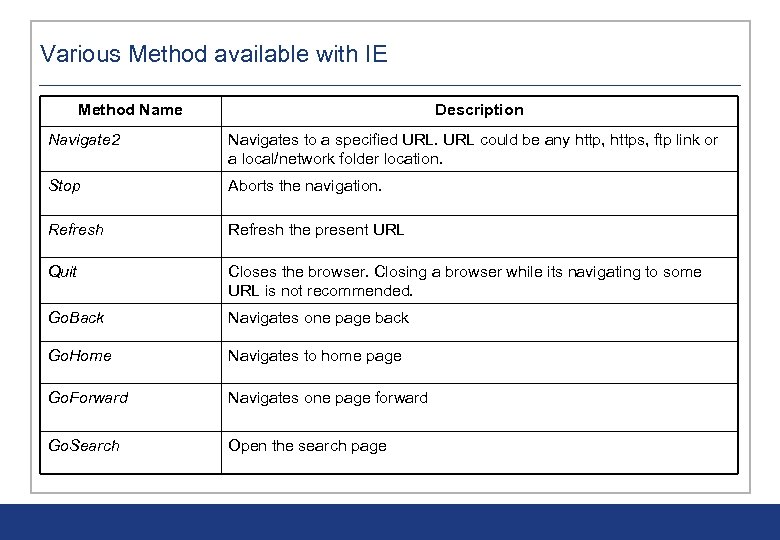
Various Method available with IE Method Name Description Navigate 2 Navigates to a specified URL could be any http, https, ftp link or a local/network folder location. Stop Aborts the navigation. Refresh the present URL Quit Closes the browser. Closing a browser while its navigating to some URL is not recommended. Go. Back Navigates one page back Go. Home Navigates to home page Go. Forward Navigates one page forward Go. Search Open the search page
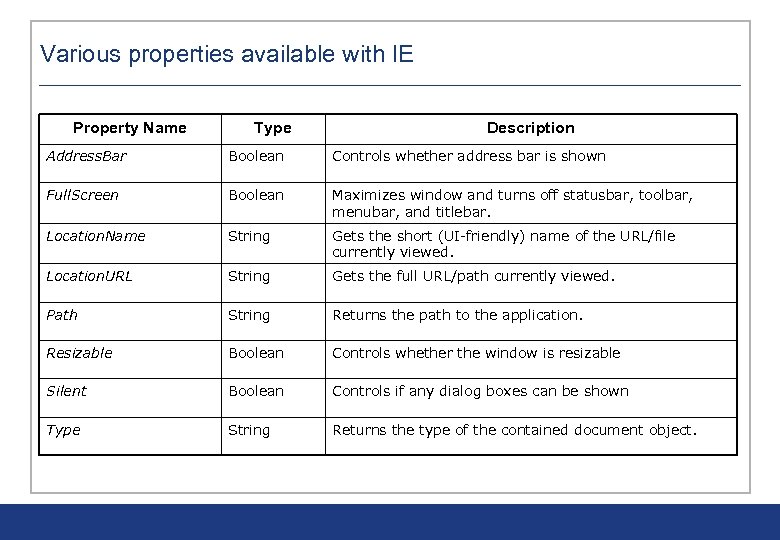
Various properties available with IE Property Name Type Description Address. Bar Boolean Controls whether address bar is shown Full. Screen Boolean Maximizes window and turns off statusbar, toolbar, menubar, and titlebar. Location. Name String Gets the short (UI-friendly) name of the URL/file currently viewed. Location. URL String Gets the full URL/path currently viewed. Path String Returns the path to the application. Resizable Boolean Controls whether the window is resizable Silent Boolean Controls if any dialog boxes can be shown Type String Returns the type of the contained document object.
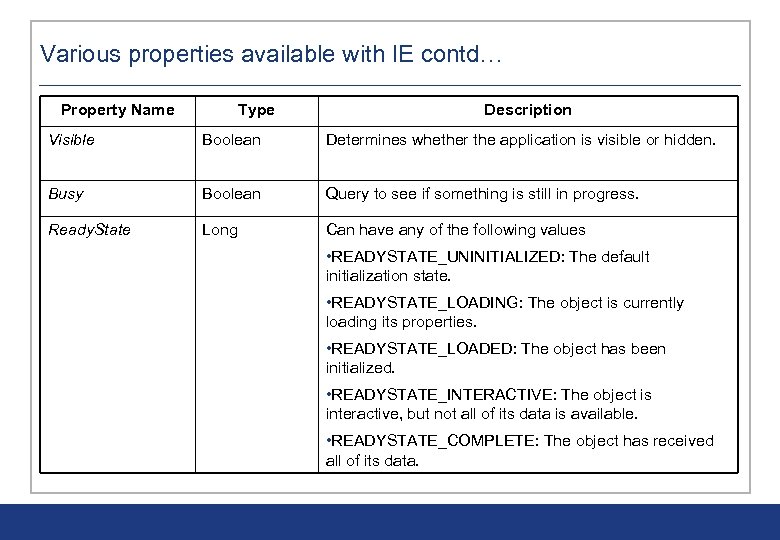
Various properties available with IE contd… Property Name Type Description Visible Boolean Determines whether the application is visible or hidden. Busy Boolean Query to see if something is still in progress. Ready. State Long Can have any of the following values • READYSTATE_UNINITIALIZED: The default initialization state. • READYSTATE_LOADING: The object is currently loading its properties. • READYSTATE_LOADED: The object has been initialized. • READYSTATE_INTERACTIVE: The object is interactive, but not all of its data is available. • READYSTATE_COMPLETE: The object has received all of its data.

Browsing to Website and Waiting for Page to Load Dim IE Set IE = Create. Object(“Internet. Explorer. Application”) IE. Visible = True IE. Navigate 2 “http: //www. yahoo. com” Do Do. Events Loop while IE. Busy = TRUE Msgbox “Page Loaded. Press OK to close the opened IE” IE. Quit Set IE=Nothing

Enumerating all open IE – Method 1 Dim IEWindows As SHDoc. Vw. Shell. Windows Set IEWindows = New SHDoc. Vw. Shell. Windows Dim IEWindow For Each IEWindow In IEWindows Debug. Print "Name: " & IEWindow. Name Debug. Print "Visible: " & IEWindow. Visible Debug. Print "File. Name: " & IEWindow. Full. Name Debug. Print "Location. URL: " & IEWindow. Location. URL Debug. Print "Location. Name: " & IEWindow. Location. Name Next For i = 0 To IEWindows. Count - 1 Set IEWindow = IEWindows. Item(i) Next

Enumerating all open IE – Method 2 Dim obj. Shell. Windows Set obj. Shell = Create. Object("Shell. Application") Set obj. Shell. Windows = obj. Shell. Windows If (Not obj. Shell. Windows Is Nothing) Then Dim obj. Enum. Items For Each obj. Enum. Items In obj. Shell. Windows Msg. Box obj. Enum. Items. Location. URL Next End If Set obj. Shell. Windows = Nothing Set obj. Shell = Nothing

Closing all open IE Dim IEWindows As SHDoc. Vw. Shell. Windows Set IEWindows = New SHDoc. Vw. Shell. Windows Dim IEWindow() Re. Dim IEWindow(1 To IEWindows. Count) Dim i For i = 1 To IEWindows. Count Set IEWindow(i) = IEWindows. Item(i - 1) Next For i = LBound(IEWindow) To UBound(IEWindow) If In. Str(1, IEWindow(i). Full. Name, "iexplore. exe", vb. Text. Compare) Then IEWindow(i). Quit End If Set IEWindow(i) = Nothing Next

Getting reference to already open IE Public Function Get. Open. IE(By. Val str. Url As String) As Internet. Explorer Dim shie As Internet. Explorer Dim sh As New Shell. Windows For Each shie In sh If shie. Location. URL Like str. Url Then Set Get. Open. IE = shie Exit Function End If Next Set Get. Open. IE = Nothing End Function
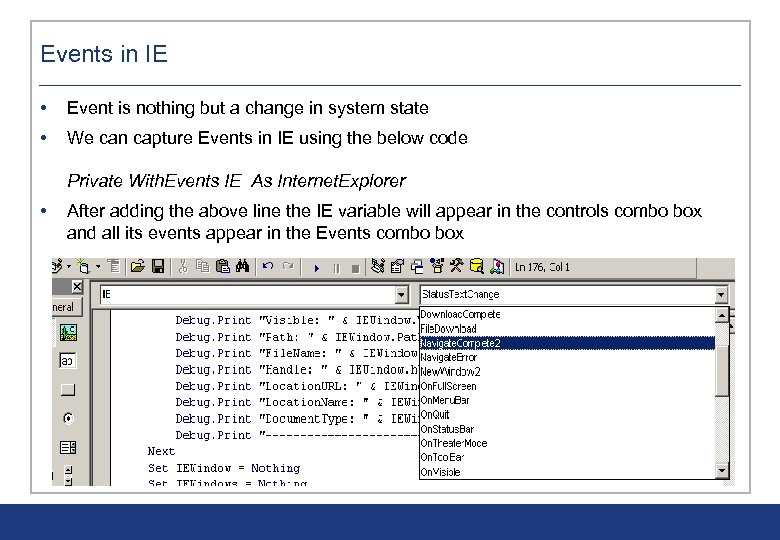
Events in IE • Event is nothing but a change in system state • We can capture Events in IE using the below code Private With. Events IE As Internet. Explorer • After adding the above line the IE variable will appear in the controls combo box and all its events appear in the Events combo box

HTML DOM

DOM • The HTML DOM is the Document Object Model for HTML • The HTML DOM defines a standard set of objects for HTML, and a standard way to access and manipulate HTML documents • The HTML DOM is platform and language independent • The HTML DOM views HTML documents as a tree structure of elements. All elements, along with their text and attributes, can be accessed and manipulated through the DOM tree

DOM Tree • Every TAG in the HTML source represent a node in the DOM tree • Once a TAG is opened, all the tags following it become child nodes of the starting node • Each TAG can have various attributes. Some are predefined and some are userdefined attributes Eg - <INPUT type=“textbox” value=“Name” name=“txt_Name” myval=“Test” • Here pre-defined attributes are type, value and name • myval is a User defined attribute for the INPUT tag
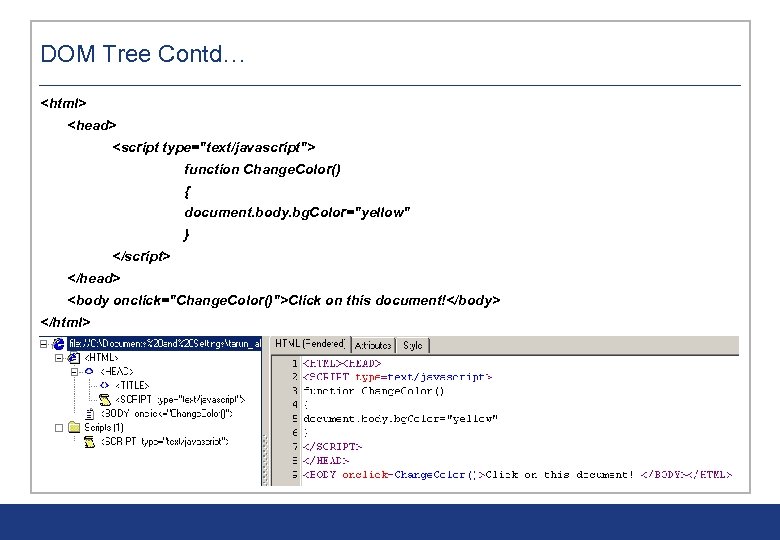
DOM Tree Contd… <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript"> function Change. Color() { document. body. bg. Color="yellow" } </script> </head> <body onclick="Change. Color()">Click on this document!</body> </html>

Document • Document object represents the whole document • It is the top node in the DOM Tree • Document node doesn’t have any sibling nodes • It provides various collections for Links, Anchors, Scripts, Images etc. . . in the Document • It also provides various functions using which we can access an element using the name of the element

Element & Element Collection • Element is an object referring to any particular node in the DOM • Depending on the type of node the element refers to, it would give access to methods and properties related to those type of elements • Every element has the properties outer. Text, outer. Html, inner. Text, inner. Html, tag. Name etc… • Element Collection is a collection of one or more elements. For Eg<INPUT name=“txt_Name” type=“text”> Now see the following VBScript code set txt_Boxes=document. get. Elements. By. Name(“txt_Name”) for i=0 to txt_Boxes. Length - 1 txt_Boxes. item(i). value=“Tarun” txt_Boxes(i). value=“Tarun” next
Collections available in a Document Collection Name Description Links Gives collections of all link elements present in the document Anchor Gives collections of all link elements present in the document which have a non blank id or name. Applets Gives collections of all applet elements present in the document. All Gives collections of all the elements present in the document Scripts Gives collections of all the script elements present in the document style. Sheets Gives collections of all the stylesheet elements present in the document images Gives collections of all the image elements present in the document

How to get an element from the web page <INPUT name=“txt_Name” id=“firstname” type=“text” value=“Tarun”> Various ways to get this element are ‘Mainly used at time of IE 4. Are compatible with higher versions but not recommended Set txt_Elem=Document. All(“firstname”) Set txt_Elem=Document. All(“txt_Name”) ‘Used with IE 5. 0 Set txt_Elem=Document. get. Elements. By. Id(“firstname”) ‘How to check if the elements is present or not If txt_Elem is Nothing then Msgbox “Element Is not present”

How to get an element from the web page contd… Set txt_Elem=Document. get. Elements. By. Tag. Name(“INPUT”). item(0) Set txt_Elem=Document. get. Elements. By. Tag. Name(“INPUT”). item(“txt_Name”) Set txt_Elem=Document. get. Elements. By. Tag. Name(“INPUT”). item(“firstname”) Set txt_Elem=Document. get. Elements. By. Name(“txt_Name”). item(0) The above 2 line would throw error if there is no element having INPUT tag or having name as “txt_Name”. To avoid this we can first check the length of the collection If Document. get. Elements. By. Name(“txt_Name”). length<>0 then Set txt_Elem=Document. get. Elements. By. Name(“txt_Name”). item(0) End if

Various HTML Elements
LINK or BUTTON <A href=http: //www. microsoft. com id=mslinkid name=mssoft>Microsoft</A> <INPUT type="button" id=mslinkid name=mssoft value="Click"> Various ways to click on this link or button: document. Links(“mslinkid”). click document. Links(“mssoft”). click document. get. Element. By. Id(“mslinkid”). click document. get. Elements. By. Name(“mssoft”)(0). click document. all(“mslinkid”). click document. all(“mssoft”). click

Text Box <INPUT myprop=test name="name" id="firstname" type="text" value="initial"> Various ways of changing the value of the text box: document. get. Element. By. Id(“firstname”). value=“Tarun” document. get. Elements. By. Name(“name”)(0). value=“Tarun” (If name and id is not available then use the below example code to change value) Set all. Elems= document. get. Elements. By. Tag. Name(“INPUT”) For each elem in all. Elems if elem. myprop=“test” then elem. value=“Tarun” Exit For end if Next

Combo box or List Box Combo box and list box have an array of options that a user can select. <SELECT size="1" name=“demo_Combo. Box"> <option value=“Actual Value 1">Displayed Value 1</option> <option value=“Value 2" >Value 2</option> <option value=“Value 3" >Value 4</option> </SELECT> Set obj. Combo=document. get. Elements. By. Name(“demo_Combo. Box”). item(0) num. Options=obj. Combo. Options. length ‘ Would give 3 in our case first. Option. Value=obj. Combo. Options(0). value‘ “Actual Value 1” in our case first. Option. Text=obj. Combo. Options(0). text ‘ “Displayed Value 1” in our case To select one of the options use the below code obj. Combo. Options(0). Selected = true obj. Combo. value=“Actual Value 1”

Checkbox A checkbox can be either checked or unchecked <input type="checkbox" name=“demo_Check. Box”> Set obj. Chk. Box=document. get. Elements. By. Name(“demo_Check. Box”). item(0) obj. Chk. Box. Checked=True

Radio button is an array of options out of which only one of the option can be selected. To group the radio buttons the elements are give the same name. <input type="radio" name="Sex" value="male" checked="checked" /> <input type="radio" name="Sex" value="female" /> To select the radio button we need to assign the appropriate value to it’s object Set obj. Radio=document. get. Elements. By. Name(“Sex”). item(0) obj. Radio. checked=True ‘Will select male obj. Radio. value=“female” ‘Will select female even if we point to the male object node

HTML Table <table id="my. Table" border="1"> <tr> <td>Row 1 cell 1</td> <td>Row 1 cell 2</td> </tr> <td>Row 2 cell 1</td> <td>Row 2 cell 2</td> </tr> </table> Table object provides two collections • cells – gives access to all the cells present in the table • rows – gives access to all the rows present in the table. Rows also provides cells collection to access particular cells present in the row.

HTML Table Contd. To access 1 st row and 1 st column, use the below code Set obj. Table=document. get. Element. By. Id(“my. Table”) obj. Table. rows(0). cells(0). outer. Text obj. Table. cells(0). outer. Text To access 2 nd row and 1 st column, use the below code obj. Table. rows(1). cells(0). outer. Text obj. Table. cells(2). outer. Text ‘ Index 2 comes from 0, 1 index going for 1 st row and 2 for the first cell in 2 nd row. obj. Table. rows. length will give total # of rows in the table obj. Table. cells. length will give total # of cells in the table obj. Table. rows(0). cells. length will give total # of cells in the 1 st row of the table
Automating Web pages

Automating web pages • For automating web pages we only need to combine the techniques discussed in the previous 2 sections • Not all pages can be automated due to limitations of DOM, discussed in later slides. • The automation is applicable to normal HTML/DHTML web content. The technique does not work on Java based web sites. • The important task in automating a web page is to identify the element that needs to be worked upon. This could be one of the most challenging task, as the developers usually do not develop considering the automation needs.
Determining the DOM path of an Element • DOM path is nothing but the way we can access a particular element on the web page. • There are two ways to determine the same – Do a View Source on the web page and try to locate the code corresponding to that web element. This technique is sometimes tedious and needs experience to determine the possible access method. – Use a DOM viewer tool to view the entire DOM structure and locate the DOM node for the same. “IE DOM Inspector” is one of the very good shareware softwares available to view the DOM of a web page in IE. It is available at www. inspectorsoft. com.
Demo • www. yahoomail. com • www. google. com • www. gmail. com • www. orkut. com (DOM limitation) • www. rediffmail. com • On the spot web pages.
Searching on google. com Dim IE Set IE = Create. Object(“Internet. Explorer. Application”) IE. Visible = True IE. Navigate 2 “http: //www. google. com” Do Do. Events Loop while IE. Busy = TRUE IE. document. get. Elements. By. Name(“q”)(0). value=“Automation” IE. document. get. Elements. By. Name(“btn. G”)(0). click Set IE=Nothing

Click on a link for a given href Function Click. On. Link(By. Val obj. IE As Internet. Explorer, By. Val str. Href As String) As String Dim Link For Each Link In obj. IE. Document. links If str. Href Like link. href Then Click. On. Link = Link. href Link. Click Exit Function End If Next Click. On. Link = "" End Function
Limitation of DOM • When a web page has a frame having different domain the web page, the access to the DOM of the frame is denied. • For example a web page on www. gmail. com loads a frame which is present on www. google. com, then we can access the DOM of www. gmail. com but not the DOM of the frame. • Microsoft calls this as Cross domain security, to prevent the author of one website to modify content of other’s web site while using frames. • The limitation can be overcome only if both the web pages define the same domain in the web page i. e. they must have the below line in the web page document. domain=“somedomain. com” • For more details on cross domain security refer to the below URL: http: //support. microsoft. com/kb/167796/EN-US/
References • http: //www. w 3 schools. com/htmldom/ • http: //www. w 3 schools. com/vbscript/ • http: //msdn. microsoft. com/workshop/author/dhtml/reference/objects/obj_document. asp • http: //msdn. microsoft. com/library/default. asp? url=/library/enus/vbcon 98/html/vbconloopstructures. asp • http: //msdn. microsoft. com/library/default. asp? url=/library/enus/vbcon 98/html/vbconcollectionsinvisualbasic. asp • http: //msdn. microsoft. com/library/default. asp? url=/library/enus/vbcon 98/html/vbconhowobjectcreationworksinvbcomponents. asp • http: //msdn. microsoft. com/library/default. asp? url=/library/enus/vbcon 98/html/vbconassigninganobjectreferencetoavariable. asp

Thank You!
839b51ebc9355907c1035b06e1dbecf2.ppt