a8a8c1fc229fcac5f5e7bd4b443df7c8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Automating Fermentation INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
Automating Fermentation INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
 Presenters Todd Ham – Automation Engineer Emerson Process Management, Life Sciences, Food, and Beverage Todd Edgington – Automation Engineer Genentech NIMO Facility, Oceanside, CA INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
Presenters Todd Ham – Automation Engineer Emerson Process Management, Life Sciences, Food, and Beverage Todd Edgington – Automation Engineer Genentech NIMO Facility, Oceanside, CA INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
 The NIMO Project Overview • NIMO is a large scale, multi-product biopharmaceutical complex. • Fermentation/Recovery process – Fermentation – Centrifuges, Chromatography, UF/DF, … – CIP/SIP • Fully automated – – Recipe-level batch control Warehouse management Electronic signatures Electronic records INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
The NIMO Project Overview • NIMO is a large scale, multi-product biopharmaceutical complex. • Fermentation/Recovery process – Fermentation – Centrifuges, Chromatography, UF/DF, … – CIP/SIP • Fully automated – – Recipe-level batch control Warehouse management Electronic signatures Electronic records INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
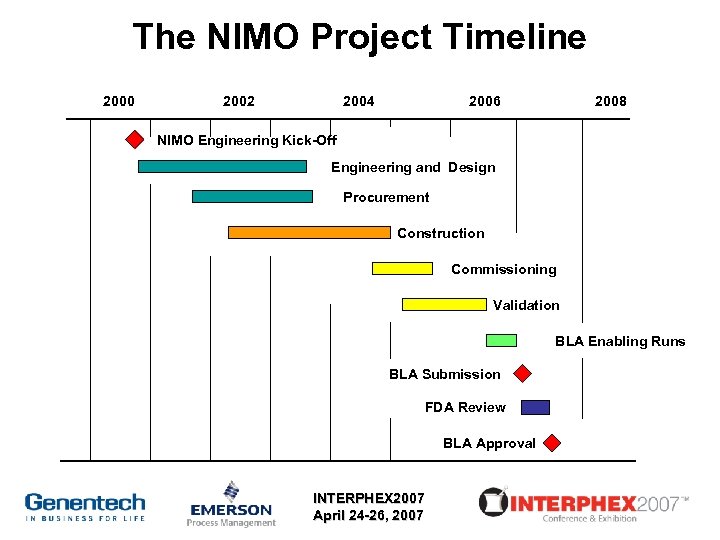 The NIMO Project Timeline 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 NIMO Engineering Kick-Off Engineering and Design Procurement Construction Commissioning Validation BLA Enabling Runs BLA Submission FDA Review BLA Approval INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
The NIMO Project Timeline 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 NIMO Engineering Kick-Off Engineering and Design Procurement Construction Commissioning Validation BLA Enabling Runs BLA Submission FDA Review BLA Approval INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
 NIMO Philosophy • Fully automated • Paperless, dock-to-dock – Electronic record – Handheld units for plant operations – Barcode scanning for material additions, filters • Consistency for operator / Use of industry standards – Bus technologies – S 88 / S 95 • Fermentation was integral to entire project – Project philosophy impacted fermentation – Fermentation impacted project philosophy INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
NIMO Philosophy • Fully automated • Paperless, dock-to-dock – Electronic record – Handheld units for plant operations – Barcode scanning for material additions, filters • Consistency for operator / Use of industry standards – Bus technologies – S 88 / S 95 • Fermentation was integral to entire project – Project philosophy impacted fermentation – Fermentation impacted project philosophy INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
 The Fermentation Process Overview Feed Vessel (for Large Fermenters) Inoculation CIP/SIP Pressure Control Media Additive Sparge Sampling Base INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
The Fermentation Process Overview Feed Vessel (for Large Fermenters) Inoculation CIP/SIP Pressure Control Media Additive Sparge Sampling Base INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
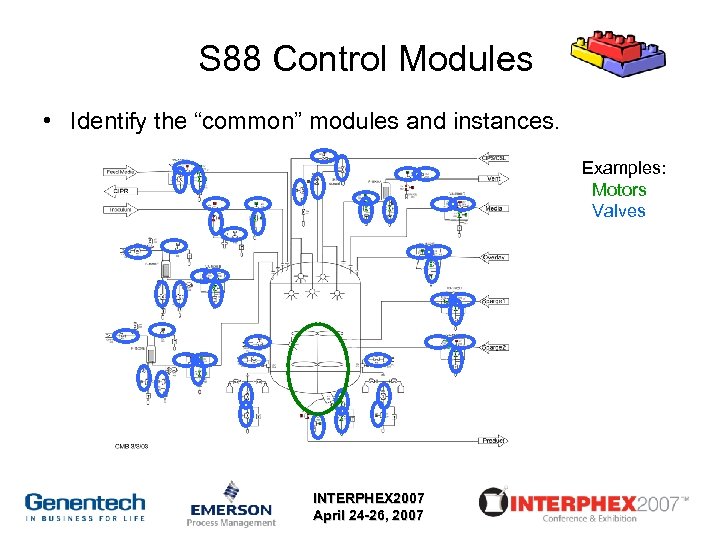 S 88 Control Modules • Identify the “common” modules and instances. Examples: Motors Valves INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
S 88 Control Modules • Identify the “common” modules and instances. Examples: Motors Valves INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
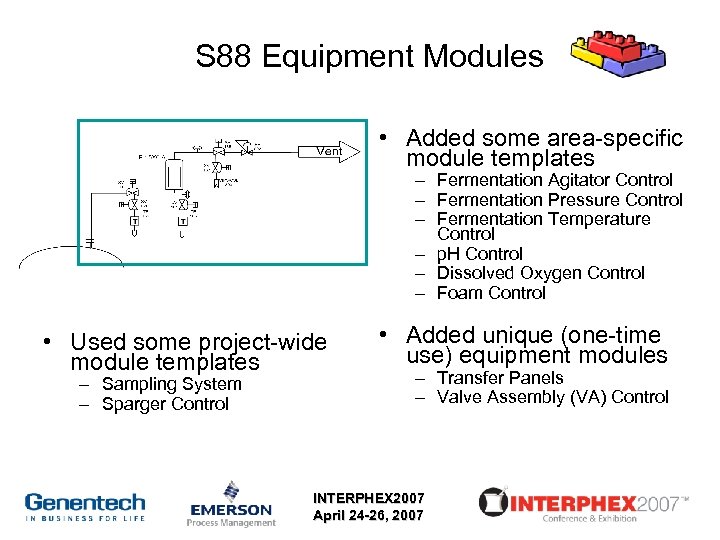 S 88 Equipment Modules • Added some area-specific module templates – Fermentation Agitator Control – Fermentation Pressure Control – Fermentation Temperature Control – p. H Control – Dissolved Oxygen Control – Foam Control • Used some project-wide module templates – Sampling System – Sparger Control • Added unique (one-time use) equipment modules – Transfer Panels – Valve Assembly (VA) Control INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
S 88 Equipment Modules • Added some area-specific module templates – Fermentation Agitator Control – Fermentation Pressure Control – Fermentation Temperature Control – p. H Control – Dissolved Oxygen Control – Foam Control • Used some project-wide module templates – Sampling System – Sparger Control • Added unique (one-time use) equipment modules – Transfer Panels – Valve Assembly (VA) Control INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
 Transfer Panel INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
Transfer Panel INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
 S 88 Units • Identify classes and instances based on. . – Physical similarity – Phases that they use • • Batch Media Inoculate Ferment Etc. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
S 88 Units • Identify classes and instances based on. . – Physical similarity – Phases that they use • • Batch Media Inoculate Ferment Etc. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
 Phase Control • • • Batch Feed Vessel Batch Fermenter Pre-inoculation Prep Inoculate Ferment Sample Additive Add Base Add Feed Media Transfer Pressure Test The following CIP Phases for Feed Vessel, Production Fermenter, Seed Fermenter, Discharge Line, and Media Line – CIP Setup – CIP Circuit – CIP Complete • • • INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007 Pre-SIP Pressure Test Seed Fermenter Pre-SIP Pressure Test Production Fermenter Pre-SIP Setup SIP Sample Line SIP Production Fermenter SIP Inoculation Line
Phase Control • • • Batch Feed Vessel Batch Fermenter Pre-inoculation Prep Inoculate Ferment Sample Additive Add Base Add Feed Media Transfer Pressure Test The following CIP Phases for Feed Vessel, Production Fermenter, Seed Fermenter, Discharge Line, and Media Line – CIP Setup – CIP Circuit – CIP Complete • • • INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007 Pre-SIP Pressure Test Seed Fermenter Pre-SIP Pressure Test Production Fermenter Pre-SIP Setup SIP Sample Line SIP Production Fermenter SIP Inoculation Line
 Recipes 1) Group Phases into Operations 2) Group Operations into Unit Procedures 3) Group Unit Procedures into Procedures INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
Recipes 1) Group Phases into Operations 2) Group Operations into Unit Procedures 3) Group Unit Procedures into Procedures INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
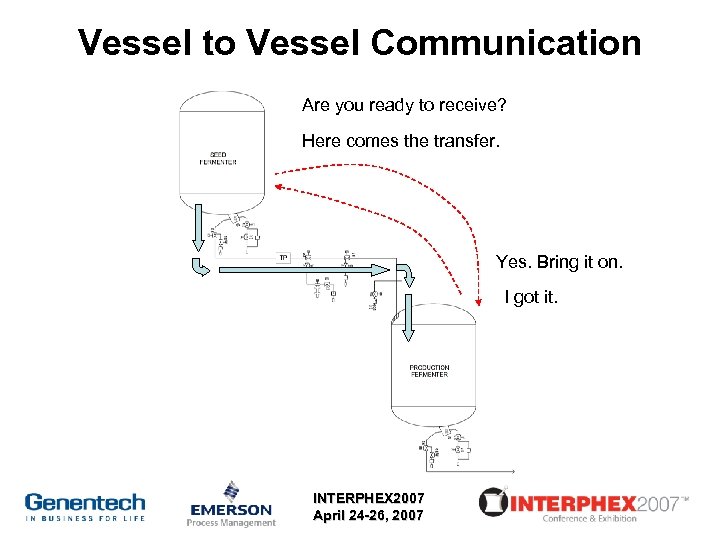 Vessel to Vessel Communication Are you ready to receive? Here comes the transfer. Yes. Bring it on. I got it. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
Vessel to Vessel Communication Are you ready to receive? Here comes the transfer. Yes. Bring it on. I got it. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
 Manufacturing Procedures • Material Management • Container Management • Filter Management • Sampling INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007 MAT 2. 200 GR
Manufacturing Procedures • Material Management • Container Management • Filter Management • Sampling INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007 MAT 2. 200 GR
 Testing • Emerson and Genentech worked together closely on requirements • Emerson performed modulelevel and integration–level testing • Emerson and Genentech ran a full Customer Acceptance Test (CAT) prior to delivery INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
Testing • Emerson and Genentech worked together closely on requirements • Emerson performed modulelevel and integration–level testing • Emerson and Genentech ran a full Customer Acceptance Test (CAT) prior to delivery INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
 Lessons Learned – Modularity • As much as possible, keep process units the same. • With similar units, make sure operations are as uniform as possible as well! • Beware of alias over-load. • Enforcement of classes can be a negative thing. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
Lessons Learned – Modularity • As much as possible, keep process units the same. • With similar units, make sure operations are as uniform as possible as well! • Beware of alias over-load. • Enforcement of classes can be a negative thing. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
 Lessons Learned – Level of Automation • High levels of automation are a double edged sword. • With high levels of automation and modularity, documents can become very numerous. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
Lessons Learned – Level of Automation • High levels of automation are a double edged sword. • With high levels of automation and modularity, documents can become very numerous. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
 Lessons Learned – Up-Front Testing • Time spent upfront saves on back end effort. • Easier to fix problems off-site when you are in control of the software. • Risk based software validation works. • No level of testing will capture all mistakes or prevent changes. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
Lessons Learned – Up-Front Testing • Time spent upfront saves on back end effort. • Easier to fix problems off-site when you are in control of the software. • Risk based software validation works. • No level of testing will capture all mistakes or prevent changes. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
 Lessons Learned – Raw Material Handling and other Manufacturing Procedures • Make sure everyone is on the same page from the start. • Make sure everyone uses the same language. • Get operators time on the equipment. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
Lessons Learned – Raw Material Handling and other Manufacturing Procedures • Make sure everyone is on the same page from the start. • Make sure everyone uses the same language. • Get operators time on the equipment. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
 Conclusion • Leverage the S 88 model as much as possible. • Take as much time as possible upfront. • Prepare for an effort commensurate with your level of automation. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007 Right-Size
Conclusion • Leverage the S 88 model as much as possible. • Take as much time as possible upfront. • Prepare for an effort commensurate with your level of automation. INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007 Right-Size
 Acknowledgements Genentech • Johannes Roebers • Christoph Lebl • Dave Stewart • Sean Stephan • Debi Marshall • Christopher Birnie • Leonidas Castaneda • Jim Merrit • Dirk Ellison Emerson • Christie Deitz • Craig Bieda • Brian Crandall • Molly Firkins • Dick Seeman • Chen Yang • Shelley Richards • Ajay Savargaonkar • Ketaki Raste INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007
Acknowledgements Genentech • Johannes Roebers • Christoph Lebl • Dave Stewart • Sean Stephan • Debi Marshall • Christopher Birnie • Leonidas Castaneda • Jim Merrit • Dirk Ellison Emerson • Christie Deitz • Craig Bieda • Brian Crandall • Molly Firkins • Dick Seeman • Chen Yang • Shelley Richards • Ajay Savargaonkar • Ketaki Raste INTERPHEX 2007 April 24 -26, 2007


