31d5aadadc3abb77aefab7f356bc6b5d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38

Automatic Analysis of Ion Mobility Spectrometry – Mass Spectrometry (IMS-MS) Data Hyejin Yoon Advisor: Dr. Haixu Tang School of Informatics Indiana University Bloomington December 5, 2008
Outline 1. Introduction 2. Motivation 3. Workflow of IMS-MS Data Analysis 4. IMS-MS Analyzer 5. Results 6. Future Work 7. References 8. Acknowledgements
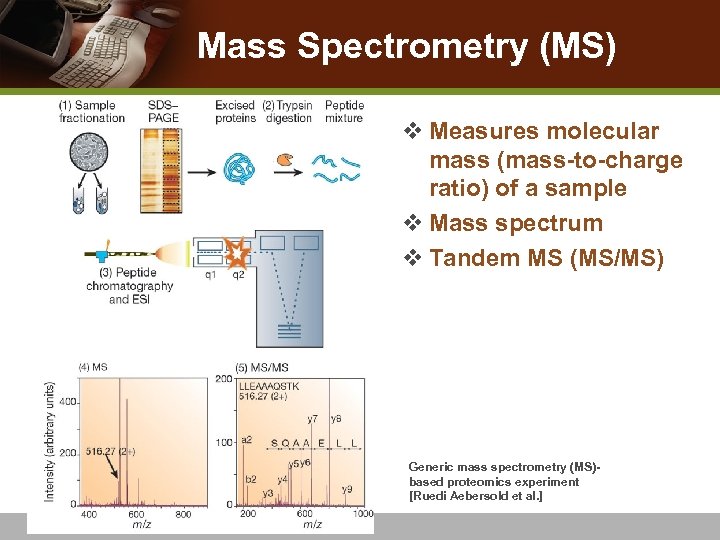
Mass Spectrometry (MS) v Measures molecular mass (mass-to-charge ratio) of a sample v Mass spectrum v Tandem MS (MS/MS) Generic mass spectrometry (MS)based proteomics experiment [Ruedi Aebersold et al. ]

Application of MS v Molecule identification/quantitation n accurate molecular weight confirm the molecular formula substitution of a amino acid or post-translational modification v Structural and sequence information from MS/MS
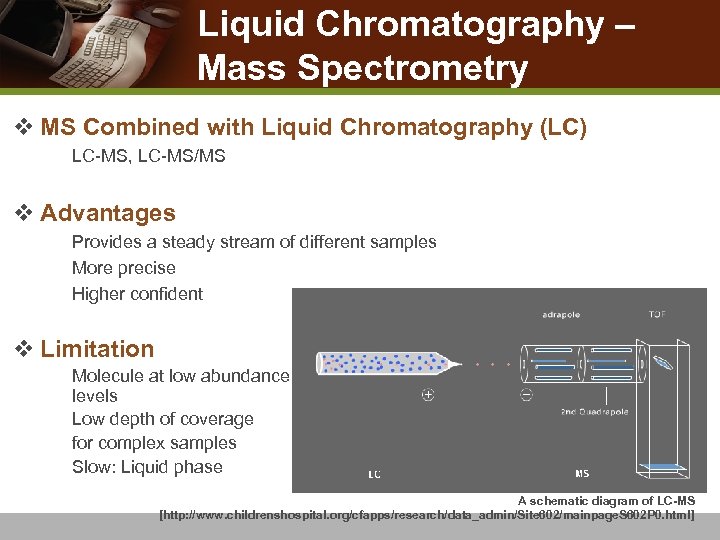
Liquid Chromatography – Mass Spectrometry v MS Combined with Liquid Chromatography (LC) n LC-MS, LC-MS/MS v Advantages n n n Provides a steady stream of different samples More precise Higher confident v Limitation n Molecule at low abundance levels Low depth of coverage for complex samples Slow: Liquid phase A schematic diagram of LC-MS [http: //www. childrenshospital. org/cfapps/research/data_admin/Site 602/mainpage. S 602 P 0. html]
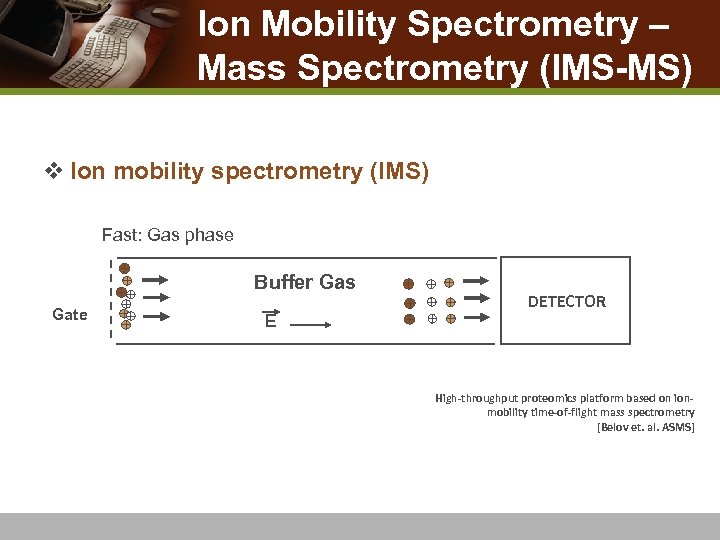
Ion Mobility Spectrometry – Mass Spectrometry (IMS-MS) v Ion mobility spectrometry (IMS) n Fast: Gas phase Buffer Gas Gate E DETECTOR High-throughput proteomics platform based on ionmobility time-of-flight mass spectrometry [Belov et. al. ASMS]
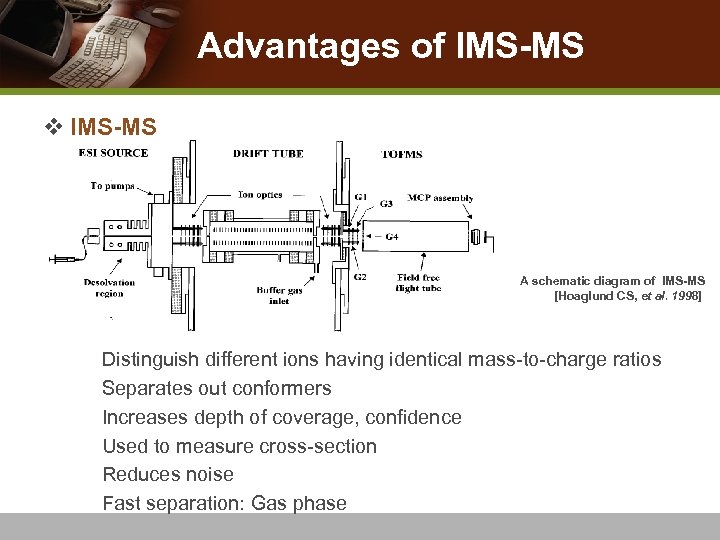
Advantages of IMS-MS v IMS-MS A schematic diagram of IMS-MS [Hoaglund CS, et al. 1998] n n n Distinguish different ions having identical mass-to-charge ratios Separates out conformers Increases depth of coverage, confidence Used to measure cross-section Reduces noise Fast separation: Gas phase
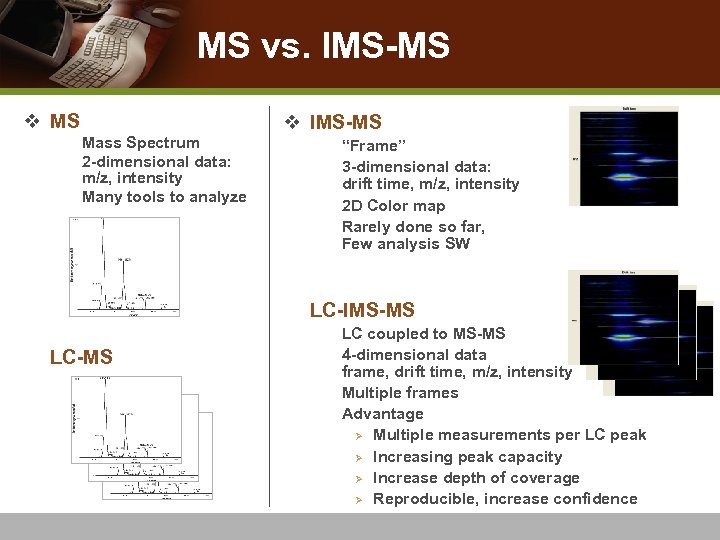
MS vs. IMS-MS v MS n n n v IMS-MS Mass Spectrum 2 -dimensional data: m/z, intensity Many tools to analyze n n “Frame” 3 -dimensional data: drift time, m/z, intensity 2 D Color map Rarely done so far, Few analysis SW LC-IMS-MS n LC-MS n n n LC coupled to MS-MS 4 -dimensional data frame, drift time, m/z, intensity Multiple frames Advantage Ø Multiple measurements per LC peak Ø Increasing peak capacity Ø Increase depth of coverage Ø Reproducible, increase confidence

Motivation for Automatic IMS-MS Analysis v Challenging data analysis, due to multi-dimensional nature of data v Need for an automatic data analysis tool for the studies using IMS-MS/LC-IMS-MS instruments v Visualize IMS-MS, LC-IMS-MS data n n m/z, drift time space Mass, drift time space v Feature/Peak detection Deisotope isotopic distributions to get monoisotopic mass & charge state Identify IMS-MS peaks using two dimensions (mass/ drift time) n n v User-friendly
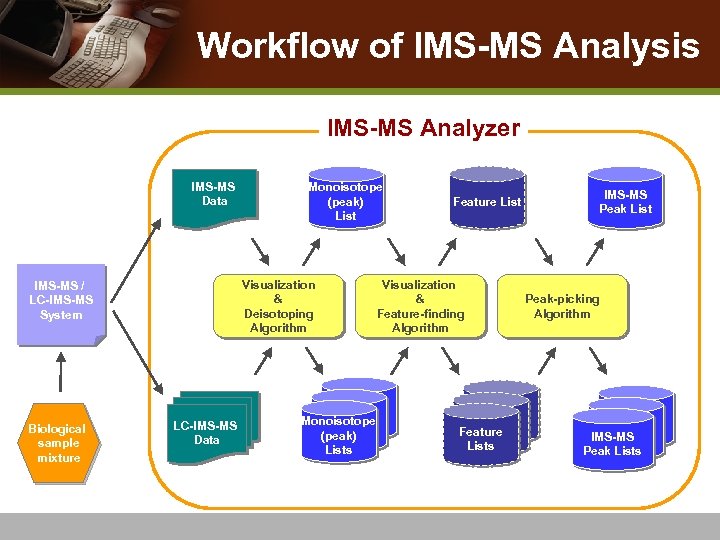
Workflow of IMS-MS Analysis IMS-MS Analyzer IMS-MS Data Visualization & Deisotoping Algorithm IMS-MS / LC-IMS-MS System Biological sample mixture Monoisotope (peak) List LC-IMS-MS Data Monoisotope (peak) Lists Feature List Visualization & Feature-finding Algorithm Feature Lists IMS-MS Peak List Peak-picking Algorithm IMS-MS Peak Lists
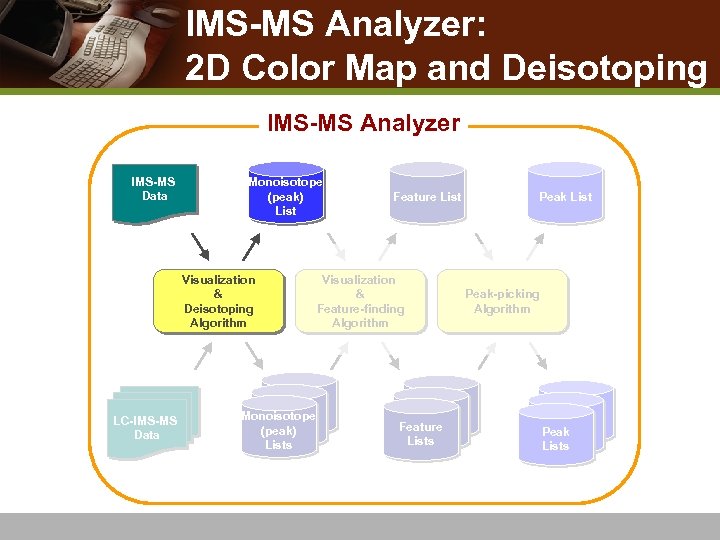
IMS-MS Analyzer: 2 D Color Map and Deisotoping IMS-MS Analyzer IMS-MS Data Monoisotope (peak) List Visualization & Deisotoping Algorithm LC-IMS-MS Data Monoisotope (peak) Lists Feature List Visualization & Feature-finding Algorithm Feature Lists Peak List Peak-picking Algorithm Peak Lists
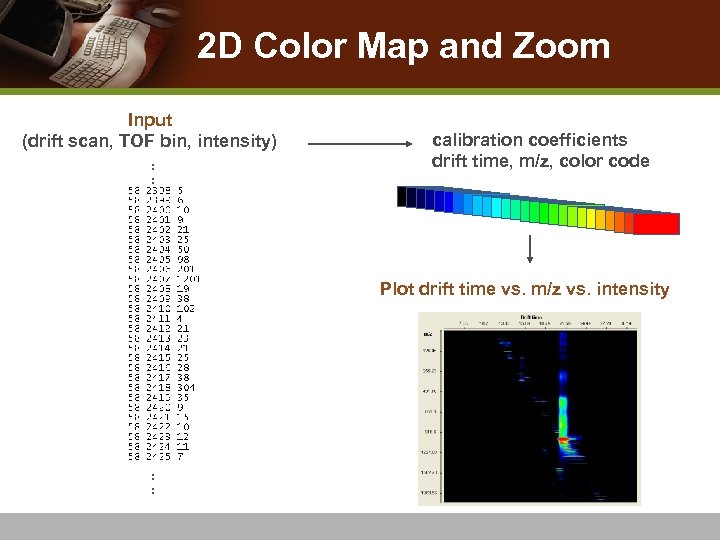
2 D Color Map and Zoom Input (drift scan, TOF bin, intensity) : : calibration coefficients drift time, m/z, color code Plot drift time vs. m/z vs. intensity : :
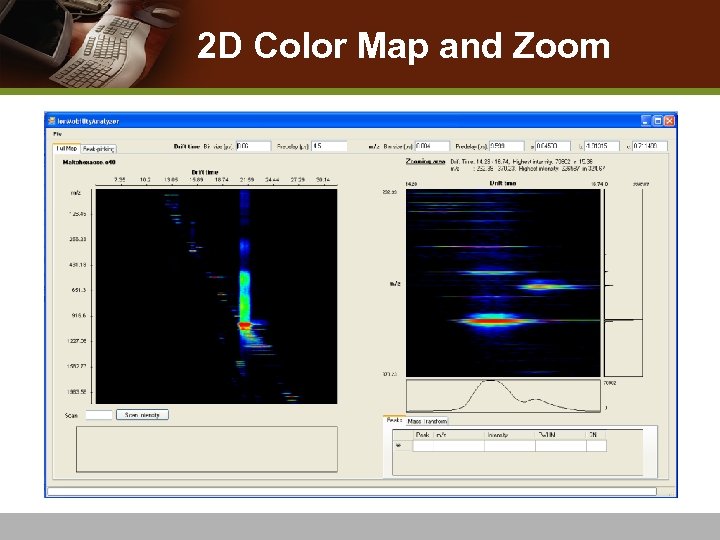
2 D Color Map and Zoom
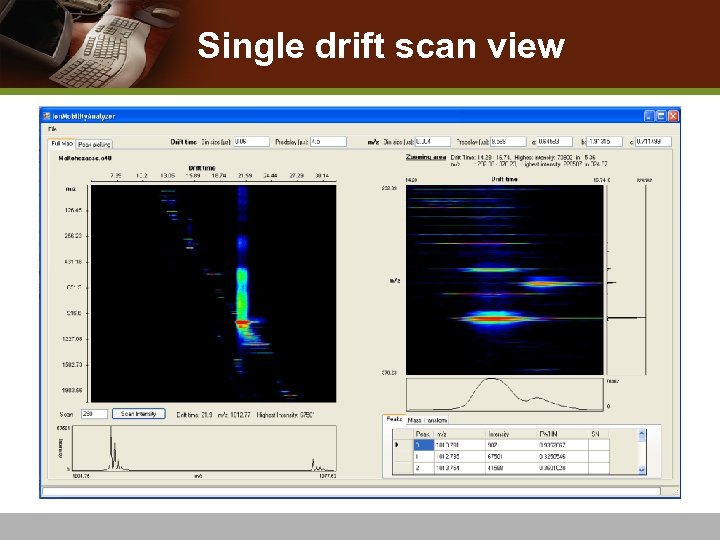
Single drift scan view
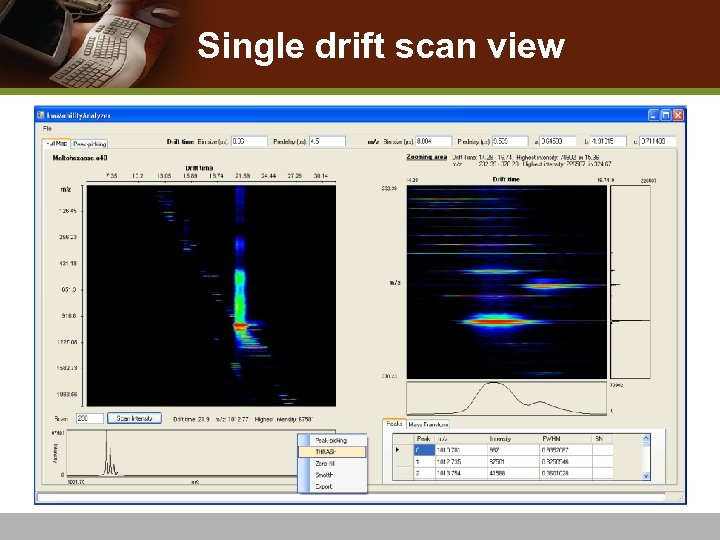
Single drift scan view
Single Drift Scan Processing v Peak-picking on spectra n Remove spectral noise v Deisotoping Algorithm n THRASH [Horn et al. 2000] algorithm n Detect accurate monoisotopic mass and charge state

THRASH on a frame v THRASH entire frame n n n THRASH scan by scan a peak list in the form of monoisotopic masses observed across continuous drift-times. Results saved as a csv file
IMS-MS Analyzer: THRASH 2 D map and Feature Finding IMS-MS Analyzer IMS-MS Data Monoisotope (peak) List Visualization & Deisotoping Algorithm LC-IMS-MS Data Monoisotope (peak) Lists Feature List Visualization & Feature-finding Algorithm Feature Lists Peak List Peak-picking Algorithm Peak Lists
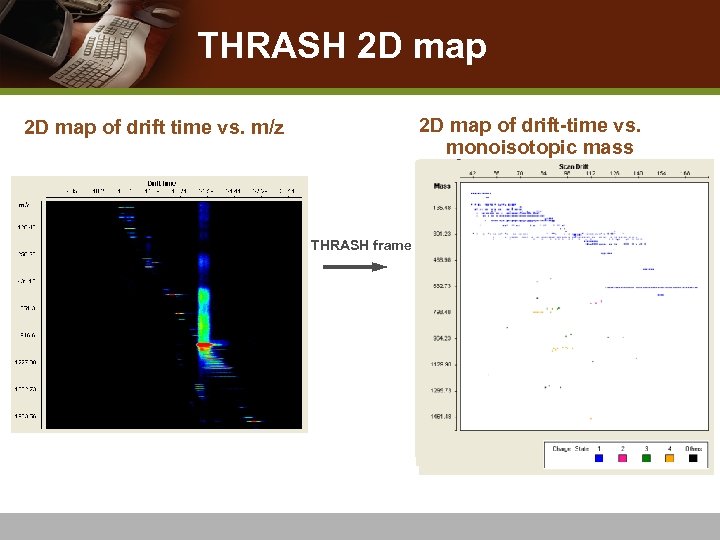
THRASH 2 D map of drift-time vs. monoisotopic mass 2 D map of drift time vs. m/z THRASH frame

Feature Finding v Feature: a drift profile for a specific mass value v Preliminary step to Identify IMS-MS peaks v Sliding Window approach n n Cluster monoisotopic ions located across continuous drift-times Report representative monoisotopic mass, drift-time value, maximum intensity, total intensity, charge and range of drift-time that correspond to a particular feature v Feature profile view v Manually visualizing Gaussian fitting to the feature
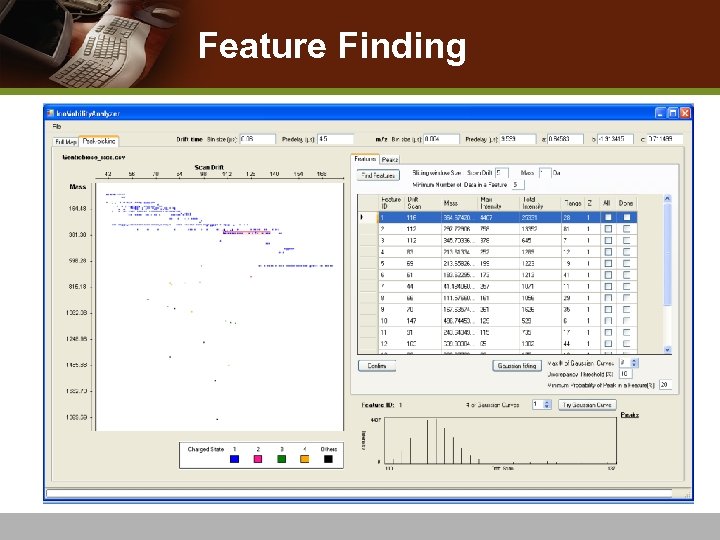
Feature Finding
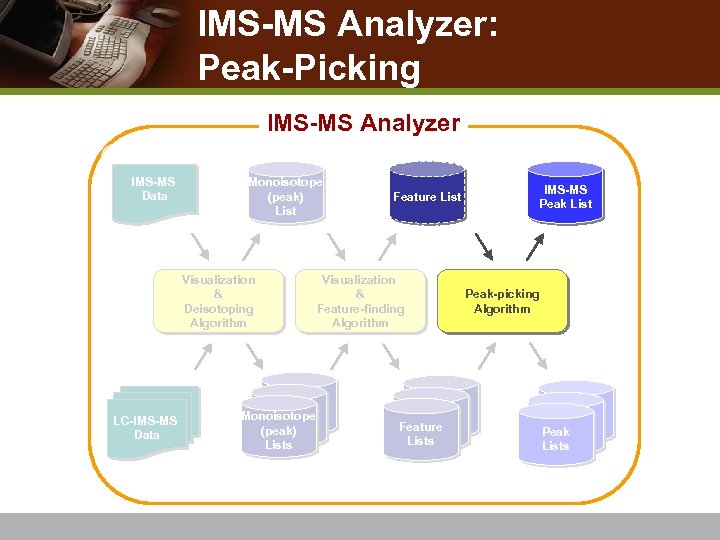
IMS-MS Analyzer: Peak-Picking IMS-MS Analyzer IMS-MS Data Monoisotope (peak) List Visualization & Deisotoping Algorithm LC-IMS-MS Data Monoisotope (peak) Lists Feature List Visualization & Feature-finding Algorithm Feature Lists IMS-MS Peak List Peak-picking Algorithm Peak Lists

Peak-Picking v Overlapping peaks: isomeric molecules or conformational change in a molecules v Apply Gaussian mixture models v Use Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm v Goodness-of-fit to find the best fitting Gaussian mixture v Choose Gaussian means to represent IMS-MS peaks
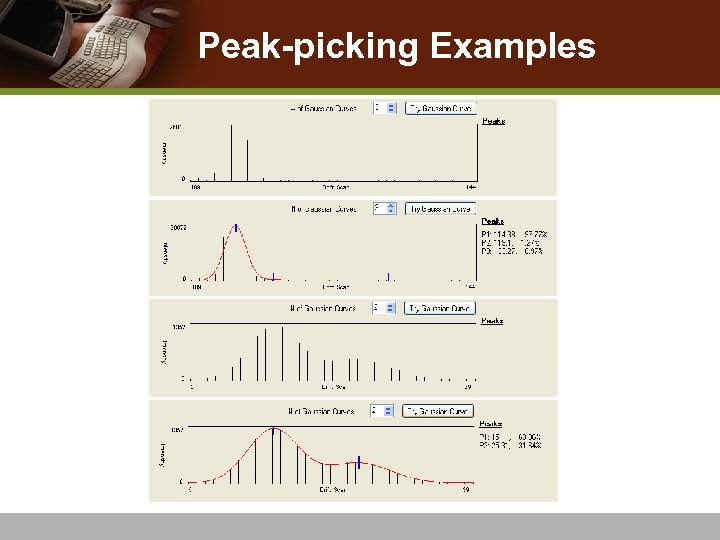
Peak-picking Examples

Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs) v There are k components of Gaussian v i’th component: wi v Mean of component wi : μi v Each component generates data from a Gaussian function with mean μi and variance σi 2 v Each datapoint is generated according to n probability of component i: P(wi) n N(μi, σi 2) We need to find μ 1, μ 2, …, μk which give maximum likelihood

EM Algorithm v Alternate between Expectation (E) step and Maximization (M) step v E step n computes an expectation of the likelihood by including the unobserved variables as if they were observed v M step n computes the maximum likelihood estimates of the parameters by maximizing the expected likelihood found on the E step v Begin next round of the E step using the parameters found on the M step and repeat the process

EM for GMMs v On the t’th iteration let our estimates be v E step v M step

Goodness-of-Fit v How well the model fits a set of observed data v Discrepancy between observed values and the values expected under the model v Based on goodness-of-fit we determine the best fitting Gaussian mixture within user specified max components
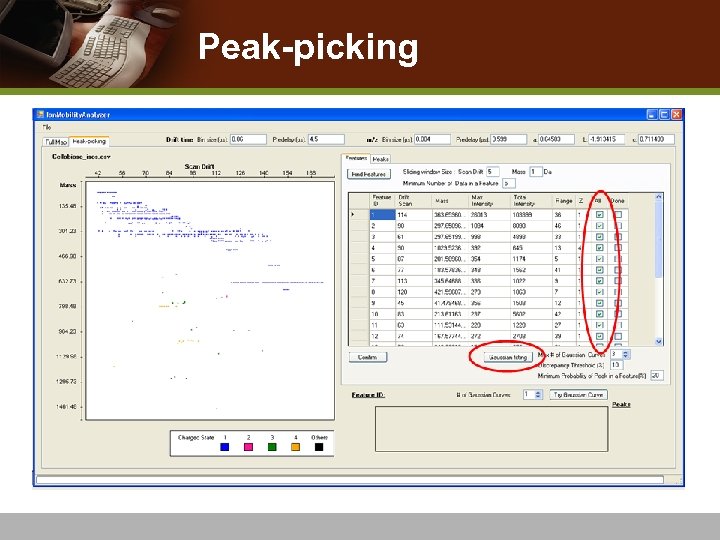
Peak-picking
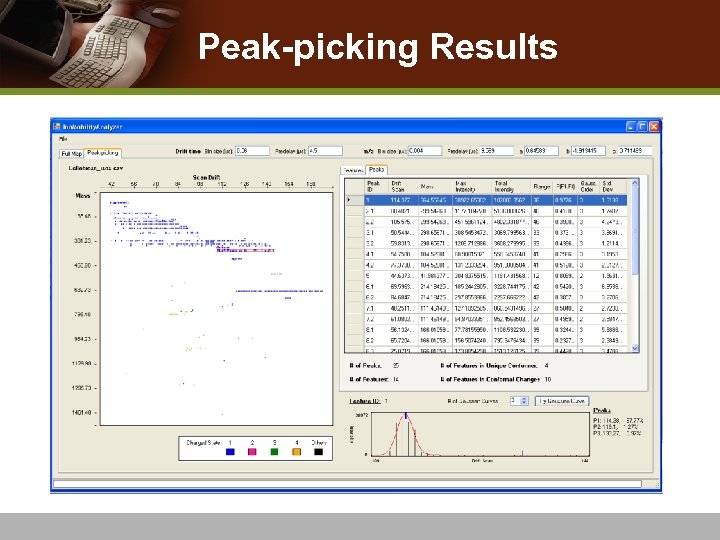
Peak-picking Results
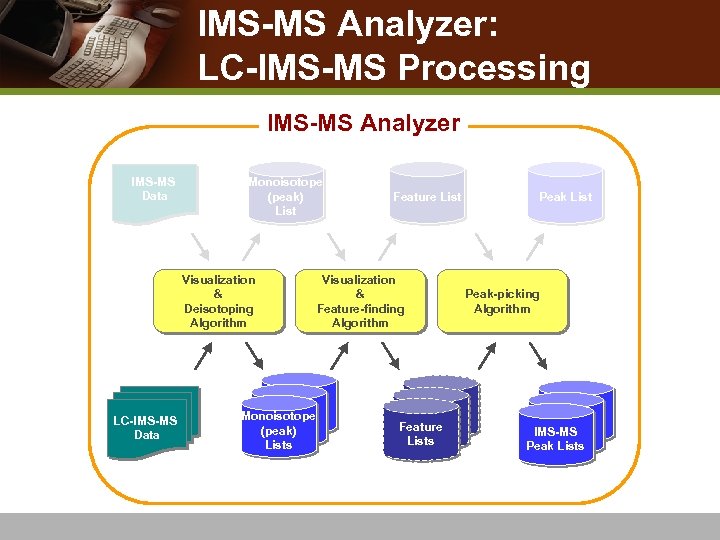
IMS-MS Analyzer: LC-IMS-MS Processing IMS-MS Analyzer IMS-MS Data Monoisotope (peak) List Visualization & Deisotoping Algorithm LC-IMS-MS Data Monoisotope (peak) Lists Feature List Visualization & Feature-finding Algorithm Feature Lists Peak List Peak-picking Algorithm IMS-MS Peak Lists
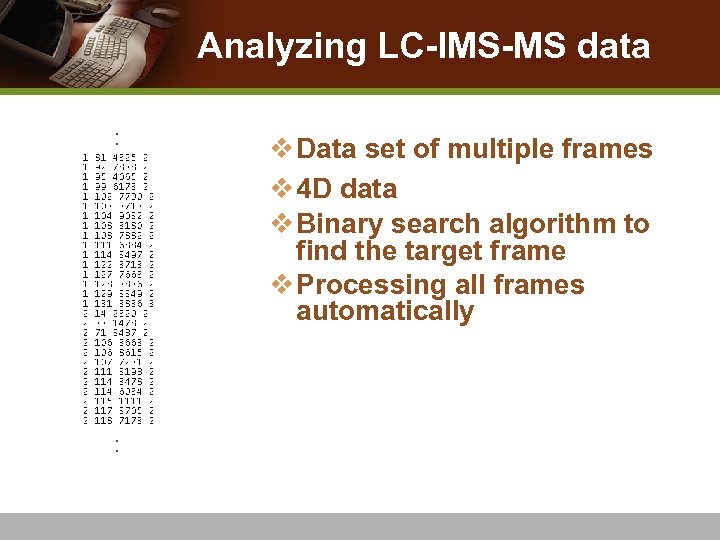
Analyzing LC-IMS-MS data : : v Data set of multiple frames v 4 D data v Binary search algorithm to find the target frame v Processing all frames automatically
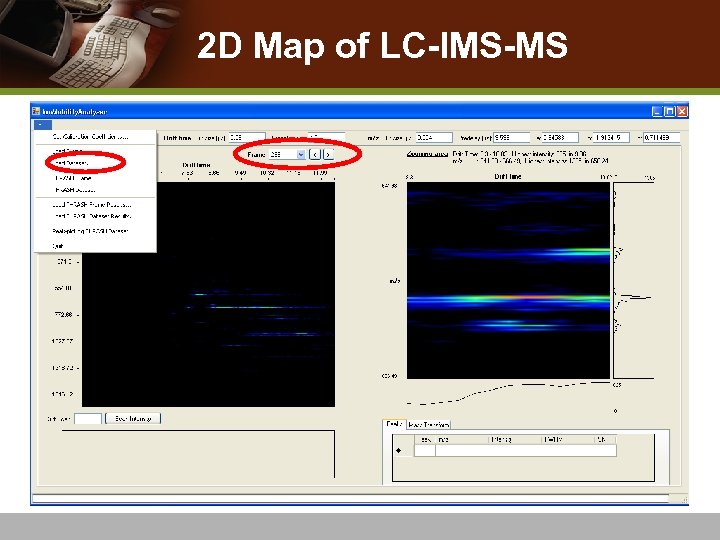
2 D Map of LC-IMS-MS
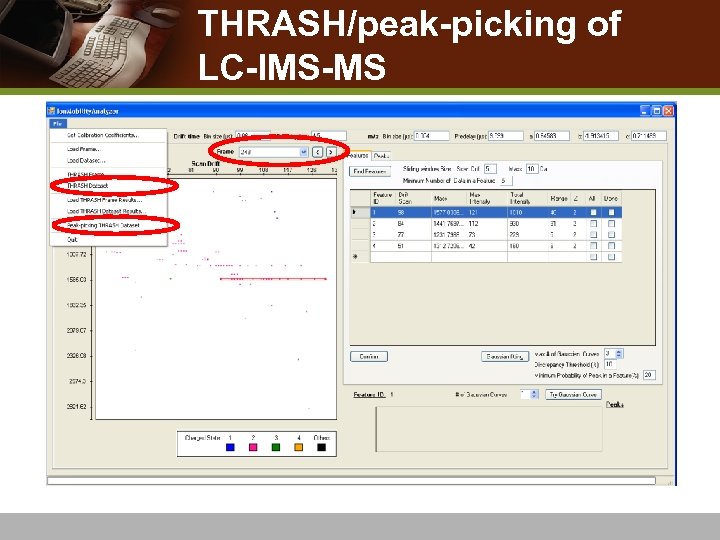
THRASH/peak-picking of LC-IMS-MS
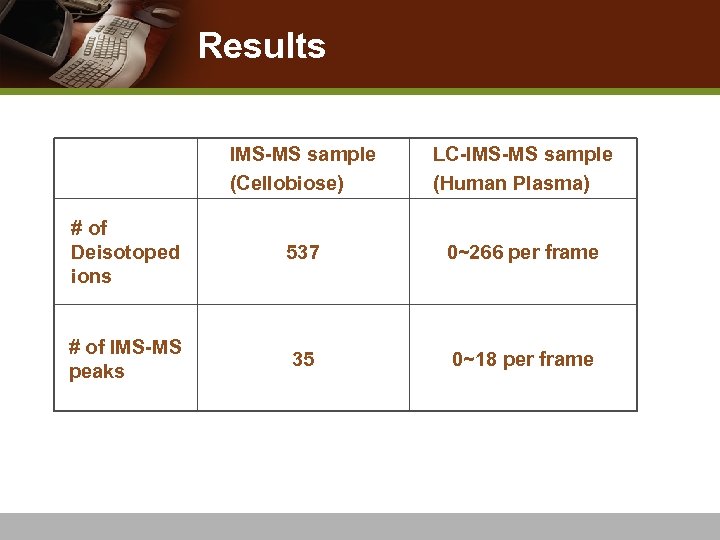
Results IMS-MS sample (Cellobiose) LC-IMS-MS sample (Human Plasma) # of Deisotoped ions 537 0~266 per frame # of IMS-MS peaks 35 0~18 per frame
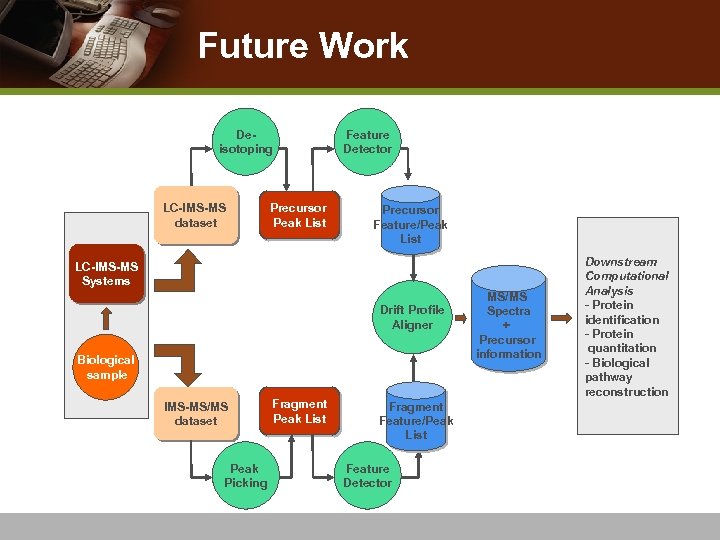
Future Work Deisotoping LC-IMS-MS dataset Precursor Peak List Feature Detector Precursor Feature/Peak List LC-IMS-MS Systems Drift Profile Aligner Biological sample IMS-MS/MS dataset Peak Picking Fragment Peak List Fragment Feature/Peak List Feature Detector MS/MS Spectra + Precursor information Downstream Computational Analysis - Protein identification - Protein quantitation - Biological pathway reconstruction

References v Aebersold R, Mann M, Mass spectrometry-based proteomics, Nature. 2003 Mar 13; 422(6928): 198 -207 v Guerrera IC, Kleiner O. Application of mass spectrometry in proteomics, Biosci Rep. 2005 Feb-Apr; 25(1 -2): 71 -93. v Clemmer DE, Jarrold MF, Ion mobility measurements and their applications to clusters and biomolecules, J Mass Spectrom. 1997; 32: 577 -592. v Hoaglund CS, Valentine SJ, Sporleder CR, Reilly JP, Clemmer DE, Three-dimensional ion mobility/TOFMS analysis of electrosprayed biomolecules, Anal Chem. 1998 Jun 1; 70(11): 2236 -42. v Baker ES, Clowers BH, Li F, Tang K, Tolmachev AV, Prior DC, Belov ME, Smith RD, Ion Mobility Spectrometry–Mass Spectrometry Performance Using Electrodynamic Ion Funnels and Elevated Drift Gas Pressures, J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2007 Jul; 18(7): 1176 -87. v Horn DM, Zubarev RA, Mc. Lafferty FW, Automated reduction and interpretation of high resolution electrospray mass spectra of large molecules, J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2000 Apr; 11(4): 320 -32. v http: //www. astbury. leeds. ac. uk/facil/MStut/mstutorial. htm v http: //www. childrenshospital. org/cfapps/research/data_admin/Site 602/mainpage. S 602 P 0. ht ml v http: //www. autonlab. org/tutorials/gmm. html

Acknowledgements v. Prof. Haixu Tang, School of Informatics v. Lab-mates Anoop Mayampurath, Mina Rho, Jun Ma, Yong Li, Paul Yu, Chao Ji, Indrani Sarkar v. Chemistry Department Stephen Valentine Manny Plasenci Ruwan Thushara Kurulugama Prof. David E. Clemmer v. Faculty and staff, School of Informatics
31d5aadadc3abb77aefab7f356bc6b5d.ppt