edd2c0c1804874e41160c273becd6b2d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Automatic Analysis of Chromosomal Assays Lecture Module 9 IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency
Automatic Analysis of Chromosomal Assays Lecture Module 9 IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency
 Chromosomal aberrations seen in mitosis phase +… Dicentrics And rings Unstable chromosomal aberrations IAEA Two way translocation Terminal translocation Stable chromosomal aberrations 2
Chromosomal aberrations seen in mitosis phase +… Dicentrics And rings Unstable chromosomal aberrations IAEA Two way translocation Terminal translocation Stable chromosomal aberrations 2
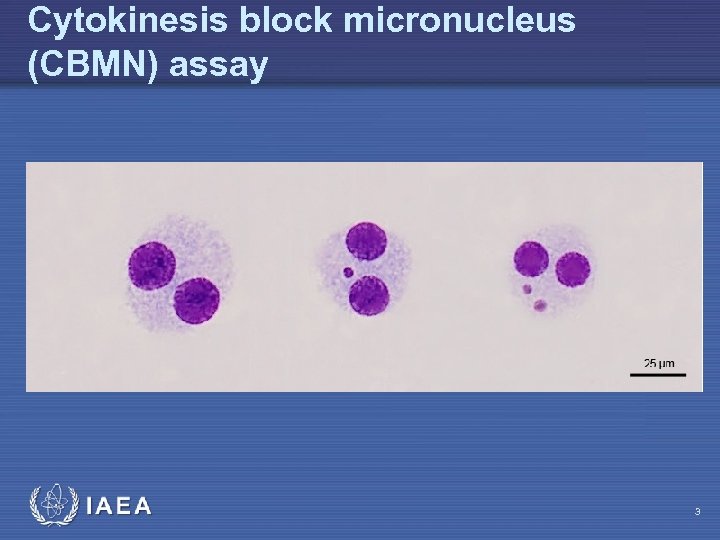 Cytokinesis block micronucleus (CBMN) assay IAEA 3
Cytokinesis block micronucleus (CBMN) assay IAEA 3
 Needs for automation Several steps require operator intervention during the process • Setting up cultures • Processing cultures through to making slides • In case of mass casualty many tubes have to be handled: Difficult; Risk of mistakes • Most time consuming is scoring IAEA 4
Needs for automation Several steps require operator intervention during the process • Setting up cultures • Processing cultures through to making slides • In case of mass casualty many tubes have to be handled: Difficult; Risk of mistakes • Most time consuming is scoring IAEA 4
 Methodology for automated sample processing Blood sampling 2 days incubation time 1 Cell culture Cell division arrest Red cells lysis 2 Metaphase harvester 3 Metaphase spreader 4 Slide autostainer Spreading Staining IAEA Robotic blood handler 5
Methodology for automated sample processing Blood sampling 2 days incubation time 1 Cell culture Cell division arrest Red cells lysis 2 Metaphase harvester 3 Metaphase spreader 4 Slide autostainer Spreading Staining IAEA Robotic blood handler 5
 1 Robotic blood handler Tecan Genesis Tecan Freedom Evo (Hanson et al, 2001) (Martin et al, 2007) ü Automatic liquid handling system: Ø automatic scan of barcodes Ø pipettor IAEA ü 96 samples per run 6
1 Robotic blood handler Tecan Genesis Tecan Freedom Evo (Hanson et al, 2001) (Martin et al, 2007) ü Automatic liquid handling system: Ø automatic scan of barcodes Ø pipettor IAEA ü 96 samples per run 6
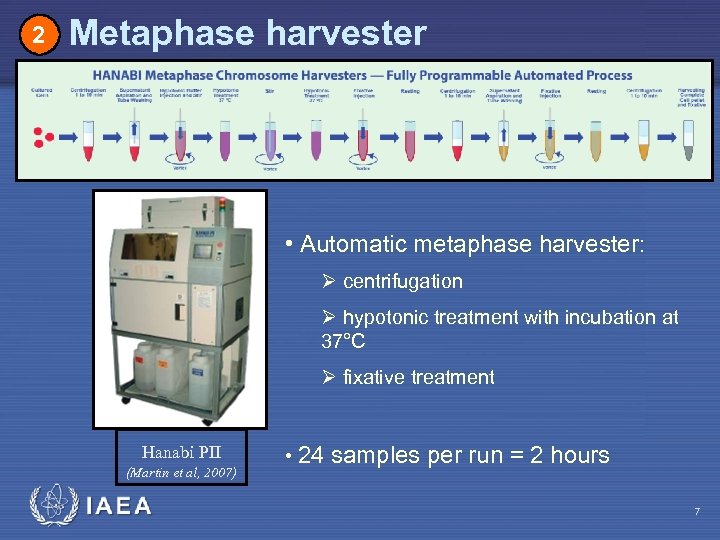 2 Metaphase harvester • Automatic metaphase harvester: Ø centrifugation Ø hypotonic treatment with incubation at 37°C Ø fixative treatment Hanabi PII (Martin et al, 2007) IAEA • 24 samples per run = 2 hours 7
2 Metaphase harvester • Automatic metaphase harvester: Ø centrifugation Ø hypotonic treatment with incubation at 37°C Ø fixative treatment Hanabi PII (Martin et al, 2007) IAEA • 24 samples per run = 2 hours 7
 3 Metaphase spreader • Manual spreading • Temperature, humidity and airflow controlled Hanabi Metaphase Spreader • 5 slides per run = 5 mins (Martin et al, 2007) IAEA 8
3 Metaphase spreader • Manual spreading • Temperature, humidity and airflow controlled Hanabi Metaphase Spreader • 5 slides per run = 5 mins (Martin et al, 2007) IAEA 8
 4 Slide auto-stainer Thermo Shandon Varistain Gemini slide stainer Thermo Shandon Consul coverslipper (Martin et al, 2007) • Automatic staining and coverslips IAEA • 150 slides per run = 40 mins 9
4 Slide auto-stainer Thermo Shandon Varistain Gemini slide stainer Thermo Shandon Consul coverslipper (Martin et al, 2007) • Automatic staining and coverslips IAEA • 150 slides per run = 40 mins 9
 Automating the microscopy • Aberration scoring is time consuming • Cytogenetic labs only have few technical staff • Many victims could require dose estimation • Many cells have to be scored This lecture will concentrate on the dicentric assay IAEA 10
Automating the microscopy • Aberration scoring is time consuming • Cytogenetic labs only have few technical staff • Many victims could require dose estimation • Many cells have to be scored This lecture will concentrate on the dicentric assay IAEA 10
 Scoring more cells contributes to reduction of confidence intervals Number of cells scored Number of Corresponding dicentrics to have a dose (Gy) significant dose Low CI (Gy) High CI (Gy) 1000 0. 11 0. 006 0. 28 10000 34 0. 001 0. 10 100000 259 0. 03 0. 001 0. 06 1000000 IAEA 7 2400 0. 02 0. 001 0. 05 11
Scoring more cells contributes to reduction of confidence intervals Number of cells scored Number of Corresponding dicentrics to have a dose (Gy) significant dose Low CI (Gy) High CI (Gy) 1000 0. 11 0. 006 0. 28 10000 34 0. 001 0. 10 100000 259 0. 03 0. 001 0. 06 1000000 IAEA 7 2400 0. 02 0. 001 0. 05 11
 Several options for automation • Develop your own system: • Customized system • Not so expensive • Technically demanding • Buy a ready to use system (METASYSTEMS, CELLSSCAN, IMSTAR, CYTOVISION…) • More expensive • Already validated • Build with available components (Furukawa 2010) • Less expensive • Depends on previous developments IAEA 12
Several options for automation • Develop your own system: • Customized system • Not so expensive • Technically demanding • Buy a ready to use system (METASYSTEMS, CELLSSCAN, IMSTAR, CYTOVISION…) • More expensive • Already validated • Build with available components (Furukawa 2010) • Less expensive • Depends on previous developments IAEA 12
 Validation process • Compare efficiency with manual processing (reference) • Evaluating sources of variations • Construct calibration curves under identical conditions used for dose estimation IAEA 13
Validation process • Compare efficiency with manual processing (reference) • Evaluating sources of variations • Construct calibration curves under identical conditions used for dose estimation IAEA 13
 Methodology for Automatic Detection of Dicentrics 1 From lymphocytes metaphases spread over microscopy slide 2 Search and acquisition of metaphases by a microscope 3 4 7 Estimation of the dose with a dose-effect curve IAEA 6 Estimation of the yield of dicentrics per cell 5 Deletion of non analyzable metaphases Analysis of metaphase Images by DCScore software Validation of detected dicentrics by an operator 14
Methodology for Automatic Detection of Dicentrics 1 From lymphocytes metaphases spread over microscopy slide 2 Search and acquisition of metaphases by a microscope 3 4 7 Estimation of the dose with a dose-effect curve IAEA 6 Estimation of the yield of dicentrics per cell 5 Deletion of non analyzable metaphases Analysis of metaphase Images by DCScore software Validation of detected dicentrics by an operator 14
 History • First metaphase finder • Developed in 1960 s for conventional staining (Wald, 1967) • Developed in 1990 s for fluorescence staining (Vrolijk, 1994) • Aberration scoring systems • For dicentrics: Bayley, 1991 and Lörch 1989 • For translocation by FISH: and Piper 1994 • For micronuclei: Castelain, 1993 and Verhaegen, 2994 • In 2000 s development of machines for cell culture and samples management IAEA 15
History • First metaphase finder • Developed in 1960 s for conventional staining (Wald, 1967) • Developed in 1990 s for fluorescence staining (Vrolijk, 1994) • Aberration scoring systems • For dicentrics: Bayley, 1991 and Lörch 1989 • For translocation by FISH: and Piper 1994 • For micronuclei: Castelain, 1993 and Verhaegen, 2994 • In 2000 s development of machines for cell culture and samples management IAEA 15
 1. Search and acquisition of metaphases by microscope Microscope drive by Metafer 4 software (Meta. Systems) 1 Search for metaphases on slide (objectivex 10) IAEA 2 Acquisition of metaphases of gallery (objectivex 63) 16
1. Search and acquisition of metaphases by microscope Microscope drive by Metafer 4 software (Meta. Systems) 1 Search for metaphases on slide (objectivex 10) IAEA 2 Acquisition of metaphases of gallery (objectivex 63) 16
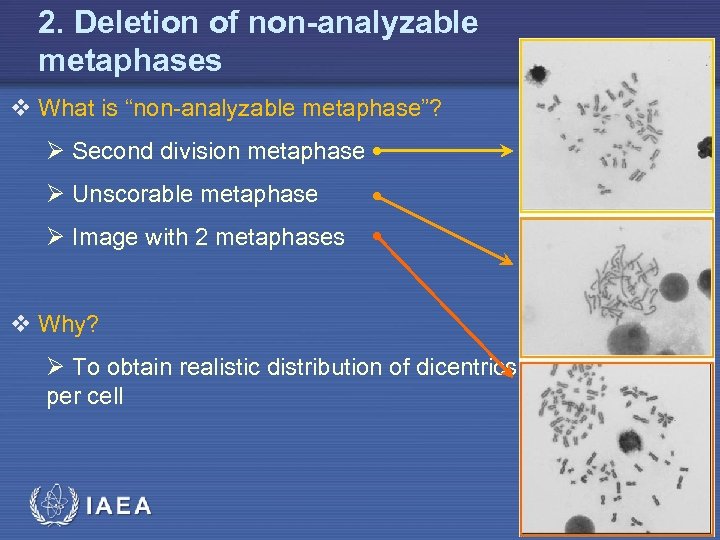 2. Deletion of non-analyzable metaphases v What is “non-analyzable metaphase”? Ø Second division metaphase Ø Unscorable metaphase Ø Image with 2 metaphases v Why? Ø To obtain realistic distribution of dicentrics per cell IAEA 17
2. Deletion of non-analyzable metaphases v What is “non-analyzable metaphase”? Ø Second division metaphase Ø Unscorable metaphase Ø Image with 2 metaphases v Why? Ø To obtain realistic distribution of dicentrics per cell IAEA 17
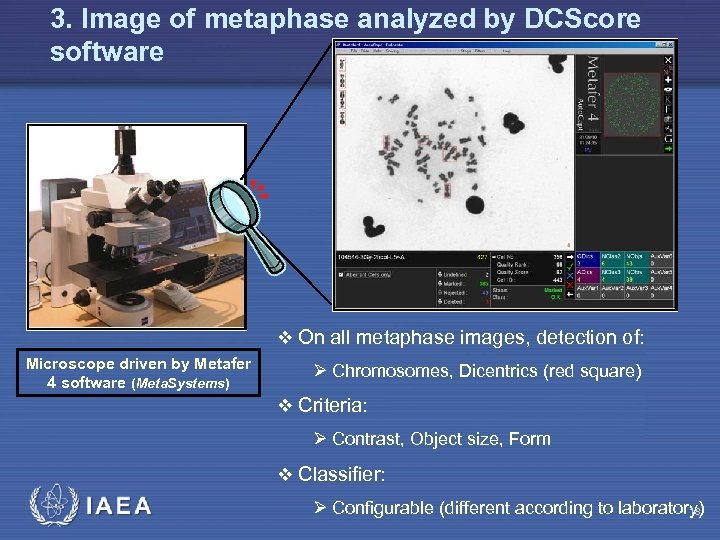 3. Image of metaphase analyzed by DCScore software v On all metaphase images, detection of: Microscope driven by Metafer 4 software (Meta. Systems) Ø Chromosomes, Dicentrics (red square) v Criteria: Ø Contrast, Object size, Form v Classifier: IAEA Ø Configurable (different according to laboratory) 18
3. Image of metaphase analyzed by DCScore software v On all metaphase images, detection of: Microscope driven by Metafer 4 software (Meta. Systems) Ø Chromosomes, Dicentrics (red square) v Criteria: Ø Contrast, Object size, Form v Classifier: IAEA Ø Configurable (different according to laboratory) 18
 4. Validation step • Each dicentric candidate is confirmed or rejected False positive dicentrics IAEA 19
4. Validation step • Each dicentric candidate is confirmed or rejected False positive dicentrics IAEA 19
 5. Estimation of yield of dicentric • Validated dicentrics/number of cells evaluated (whatever number of chromosomes identified) • Result is used either to construct calibration curves or to estimate dose IAEA 20
5. Estimation of yield of dicentric • Validated dicentrics/number of cells evaluated (whatever number of chromosomes identified) • Result is used either to construct calibration curves or to estimate dose IAEA 20
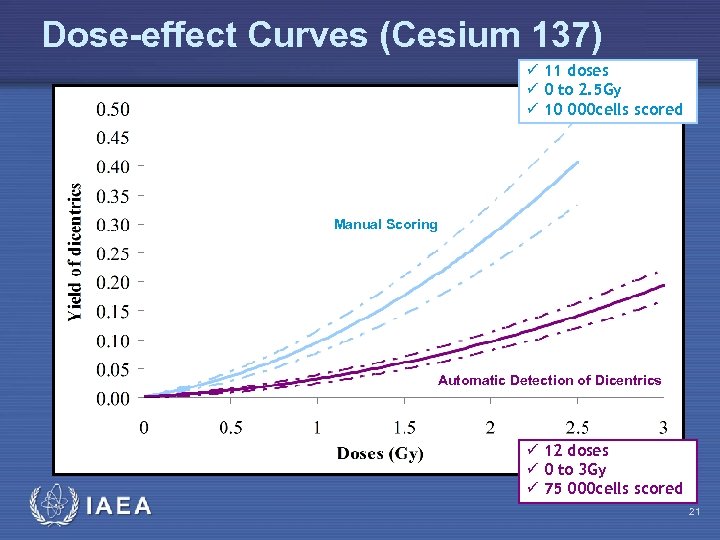 Dose-effect Curves (Cesium 137) ü 11 doses ü 0 to 2. 5 Gy ü 10 000 cells scored Manual Scoring Automatic Detection of Dicentrics IAEA ü 12 doses ü 0 to 3 Gy ü 75 000 cells scored 21
Dose-effect Curves (Cesium 137) ü 11 doses ü 0 to 2. 5 Gy ü 10 000 cells scored Manual Scoring Automatic Detection of Dicentrics IAEA ü 12 doses ü 0 to 3 Gy ü 75 000 cells scored 21
 Application to population triage • Objectives • Analyse large number of samples quickly • First step : • Discriminate individuals in 3 classes: • Exposed • Potentially exposed • Unexposed • Second step : • Dose estimation with best accuracy possible IAEA 22
Application to population triage • Objectives • Analyse large number of samples quickly • First step : • Discriminate individuals in 3 classes: • Exposed • Potentially exposed • Unexposed • Second step : • Dose estimation with best accuracy possible IAEA 22
 Application to population triage v. Methodology currently used Ø First step: Manual scoring on 50 metaphases Ø Second step: Manual scoring on 500 metaphases v. Response Ø First step: Quick but low accuracy Ø Second step: Very long and good accuracy v. What is response of automatic detection of dicentrics? Ø Experimental model • Dakar accident - 63 individuals potentially exposed IAEA 23
Application to population triage v. Methodology currently used Ø First step: Manual scoring on 50 metaphases Ø Second step: Manual scoring on 500 metaphases v. Response Ø First step: Quick but low accuracy Ø Second step: Very long and good accuracy v. What is response of automatic detection of dicentrics? Ø Experimental model • Dakar accident - 63 individuals potentially exposed IAEA 23
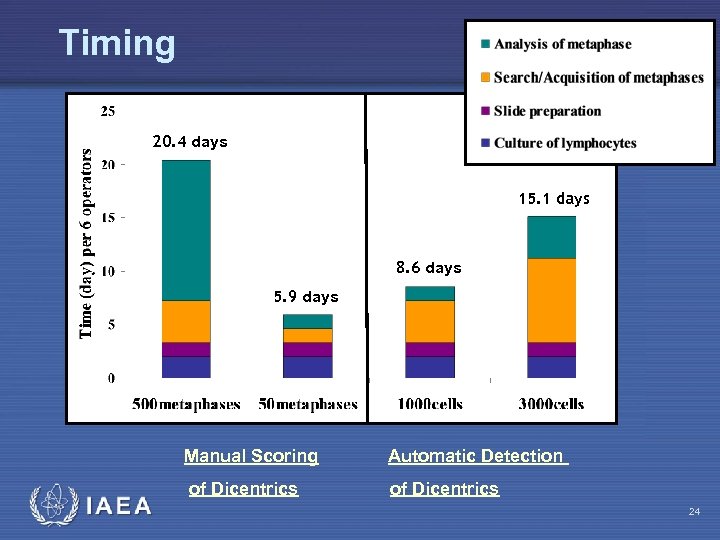 Timing 20. 4 days 15. 1 days 8. 6 days 5. 9 days Manual Scoring IAEA Automatic Detection of Dicentrics 24
Timing 20. 4 days 15. 1 days 8. 6 days 5. 9 days Manual Scoring IAEA Automatic Detection of Dicentrics 24
 First step: victims classification according to first dose estimation = the reference 50% under-estimation IAEA 4. 3% under-estimation Better results with automatic system 25
First step: victims classification according to first dose estimation = the reference 50% under-estimation IAEA 4. 3% under-estimation Better results with automatic system 25
 First conclusion on population triage Automatic detection of dicentrics performance: • Timing quite similar to manual scoring on 50 metaphases but slightly longer • Classification similar to manual scoring on 500 metaphases IAEA 26
First conclusion on population triage Automatic detection of dicentrics performance: • Timing quite similar to manual scoring on 50 metaphases but slightly longer • Classification similar to manual scoring on 500 metaphases IAEA 26
 Second step: dose estimation • Dose obtained with automatic dicentric scoring close to dose obtained with manual scoring of 500 metaphases IAEA (Vaurijoux et al, 2009) 27
Second step: dose estimation • Dose obtained with automatic dicentric scoring close to dose obtained with manual scoring of 500 metaphases IAEA (Vaurijoux et al, 2009) 27
 Conclusion of second step • Automatic detection of dicentrics is • 3 times faster than manual scoring on 500 metaphases • Dose estimation close to manual scoring on 500 metaphases IAEA 28
Conclusion of second step • Automatic detection of dicentrics is • 3 times faster than manual scoring on 500 metaphases • Dose estimation close to manual scoring on 500 metaphases IAEA 28
 Application to individual biological dosimetry • Question • Can automatic detection of dicentrics detect heterogeneity of exposure? • Experimental models • In vitro simulations with blood irradiated to 2 Gy and diluted with unexposed blood • Real cases of accidental exposure previously analysed manually IAEA 29
Application to individual biological dosimetry • Question • Can automatic detection of dicentrics detect heterogeneity of exposure? • Experimental models • In vitro simulations with blood irradiated to 2 Gy and diluted with unexposed blood • Real cases of accidental exposure previously analysed manually IAEA 29
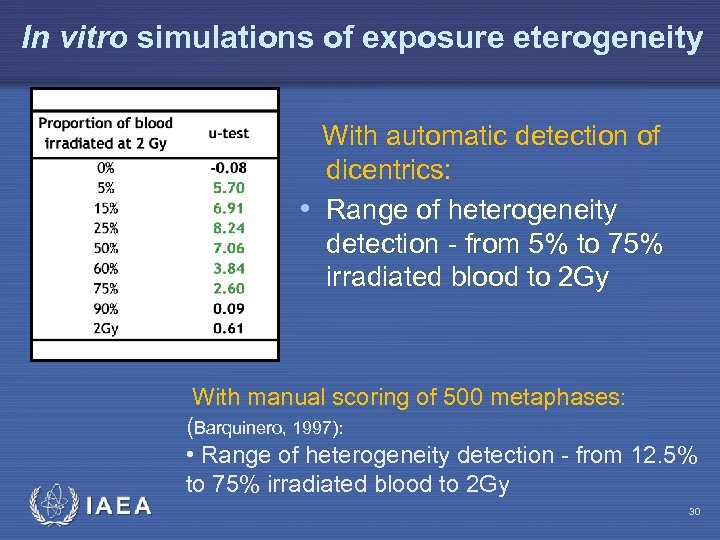 In vitro simulations of exposure eterogeneity With automatic detection of dicentrics: • Range of heterogeneity detection - from 5% to 75% irradiated blood to 2 Gy IAEA With manual scoring of 500 metaphases: (Barquinero, 1997): • Range of heterogeneity detection - from 12. 5% to 75% irradiated blood to 2 Gy 30
In vitro simulations of exposure eterogeneity With automatic detection of dicentrics: • Range of heterogeneity detection - from 5% to 75% irradiated blood to 2 Gy IAEA With manual scoring of 500 metaphases: (Barquinero, 1997): • Range of heterogeneity detection - from 12. 5% to 75% irradiated blood to 2 Gy 30
 Real cases of accidental exposure (1) • Heterogeneity was detected similarly with automatic and manual scoring • One exception - case 6 IAEA 31
Real cases of accidental exposure (1) • Heterogeneity was detected similarly with automatic and manual scoring • One exception - case 6 IAEA 31
 Real cases of accidental exposure (2) Doses obtained are similar by both methods IAEA (Vaurijoux, Gruel et al, in submission) 32
Real cases of accidental exposure (2) Doses obtained are similar by both methods IAEA (Vaurijoux, Gruel et al, in submission) 32
 Real cases of accidental exposure (3) Fraction of irradiated blood are similar by both methods IAEA 33
Real cases of accidental exposure (3) Fraction of irradiated blood are similar by both methods IAEA 33
 Telescoring • Acquired images can be shared electronically between laboratories • Sent via the Internet • Requires homogeneous scoring criteria • Several networks are working on this IAEA 34
Telescoring • Acquired images can be shared electronically between laboratories • Sent via the Internet • Requires homogeneous scoring criteria • Several networks are working on this IAEA 34
 Conclusion for automatic detection of dicentrics Applications • population triage • individual cases Automatic detection of dicentrics can • estimate doses with results close to those obtained by manual scoring on 500 metaphases • detect heterogeneous exposure • allow dose reconstitution of irradiated fraction using Dolphin mathematical model IAEA 35
Conclusion for automatic detection of dicentrics Applications • population triage • individual cases Automatic detection of dicentrics can • estimate doses with results close to those obtained by manual scoring on 500 metaphases • detect heterogeneous exposure • allow dose reconstitution of irradiated fraction using Dolphin mathematical model IAEA 35
 Other assays Micronucleus (CBMN) This is covered separately in another lecture Translocation • DAPI stained metaphase finder is well developed and validated • No commercial software yet for translocation scoring • Digitally captured images do not fade IAEA 36
Other assays Micronucleus (CBMN) This is covered separately in another lecture Translocation • DAPI stained metaphase finder is well developed and validated • No commercial software yet for translocation scoring • Digitally captured images do not fade IAEA 36


