a5e92ce0814bcc4930d767f07b0a67c2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Automated Wireless Identification System (AWIS) For Observing Social Interactions Of Animals In The Wild: A Review Of Bluetooth Wireless API’s Sam Knights Rhodes University Supervisors: Dr G. Foster and Prof P. Clayton

Purpose: Report on the findings of my Literature Review, and Progress in Investigating Bluetooth APIs.

Presentation Outline Current Animal Tracking Methods l Other Wireless Technologies l Bluetooth: l l Goals and Vision l Bluetooth Specification: Architecture and Profiles Application Programming Interfaces l Bluetooth Application Development l My Approach and plans l

Project Introduction Individual animal identification and interaction l Behavioral patterns l GPS, infrared imagery, GSM, satellite l Enabled devices - collars l Transmit information when in range of other animals l Transfer to access points (on trees/ rocks) l Motivation for using Bluetooth: l 10 m range, low power and cost, small size l Dynamic nature of networks formed l

Current Animal Tracking Methods l l l Radio Collars – WWF Forward-Looking Infrared Imagery Radio Collars not ideal: l l l GPS logger: pigeons, dogs GPS remote data download: l l High maintenance, expense, injury, fertility Via GSM, Satellite or Radio ‘Blue. Trak’ – uses Bluetooth

Other Wireless Technologies l l Infrared Wireless IEEE 802. 11 b (Wi. Fi) l l “Always on” Induction Wireless Magnetic field. Unsuitable: range 3 m, low data speed l l Ultra Wideband l l l Low power, high transfer. Not standardized. Zig. Bee l Lower power than Bluetooth. Just emerging.

Bluetooth Quick Overview l l Name: James Karach of Intel Goals and Vision: l l l Universal, ubiquitous connectivity From the outset – module small and portable Dynamic nature of BT networks Slow adoption – complex usage “profiles”. Specification – divided into: l l Architecture Profiles
Bluetooth Specification l Architecture (how technology works) l l Single chip design: RF radio, baseband microprocessor ISM radio spectrum (global use, compatibility) transmitted using frequency hopping. Network topologies: Piconets and Scatternets Profiles (how technology used) “vertical slice through the Bluetooth Stack. ” l e. g. generic access, serial port, service discovery, object push… l
Bluetooth Application Development l No definition in specification: l l l Vendors: SDKs l l How application should “talk” to stack How simple exposed API is defined e. g. Widcomm, Socket, Source. Forge (Open Source) Competing groups, specific architectures l l l Only Standard API: Java Universal Home-API Embedded Linux Consortium
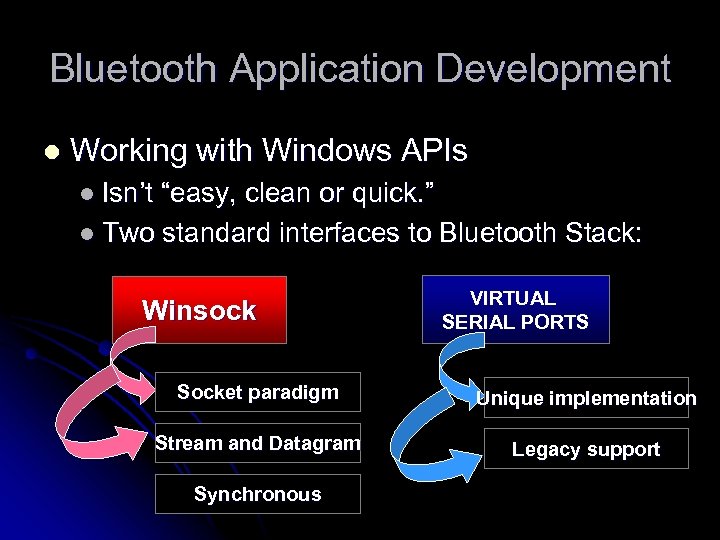
Bluetooth Application Development l Working with Windows APIs l Isn’t “easy, clean or quick. ” l Two standard interfaces to Bluetooth Stack: Winsock VIRTUAL SERIAL PORTS Socket paradigm Unique implementation Stream and Datagram Legacy support Synchronous
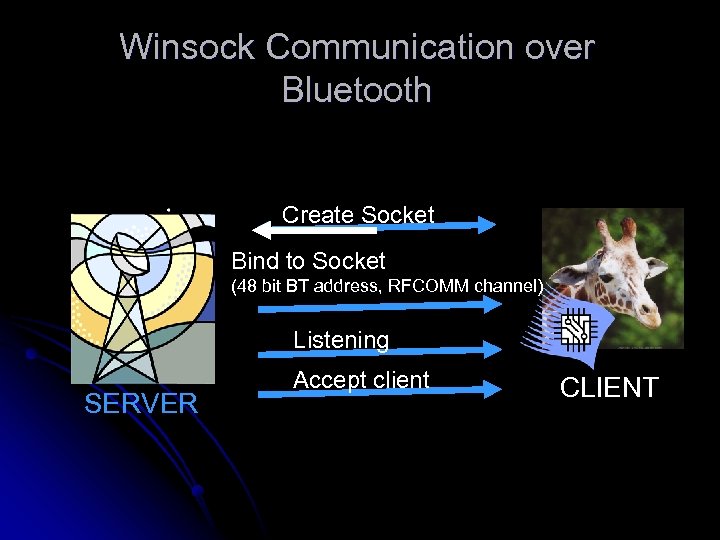
Winsock Communication over Bluetooth Create Socket Bind to Socket (48 bit BT address, RFCOMM channel) Listening SERVER Accept client CLIENT
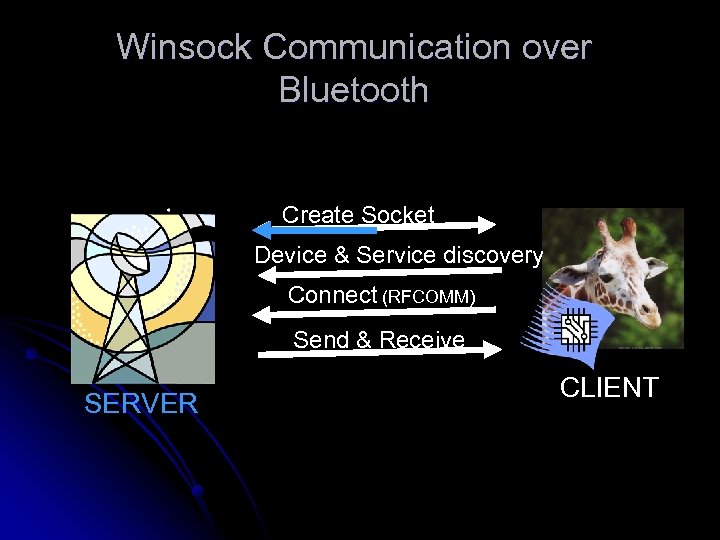
Winsock Communication over Bluetooth Create Socket Device & Service discovery Connect (RFCOMM) Send & Receive SERVER CLIENT
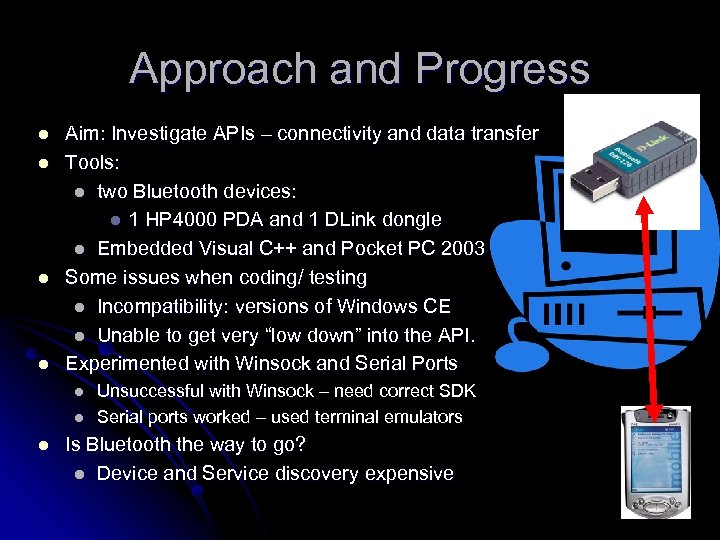
Approach and Progress l l Aim: Investigate APIs – connectivity and data transfer Tools: l two Bluetooth devices: l 1 HP 4000 PDA and 1 DLink dongle l Embedded Visual C++ and Pocket PC 2003 Some issues when coding/ testing l Incompatibility: versions of Windows CE l Unable to get very “low down” into the API. Experimented with Winsock and Serial Ports l l l Unsuccessful with Winsock – need correct SDK Serial ports worked – used terminal emulators Is Bluetooth the way to go? l Device and Service discovery expensive

The way forward l Ordered the Widcomm SDK, provides l l l Development tools: application development and stack testing. User applications: Connection Manager, Configuration Control Panel, and Tray application Scalable, small footprint, using configuration parameters and link-time configuration Source code for Bluetooth Specification 1. 2 compliant embedded protocol stack: all core stack layers and mandatory profiles. This means hopefully more interaction with APIs and Bluetooth Stack

Summary and Conclusion l l l Many other wireless technologies: l Bluetooth Standardised l Size, power and cost Current Animal tracking technology l Limited by power consumption, cost, comfort l Mostly for tracking, not social interaction Application Programming Interfaces: l No standard l Winsock and Virtual Serial Ports l Widcomm Stack

Questions?

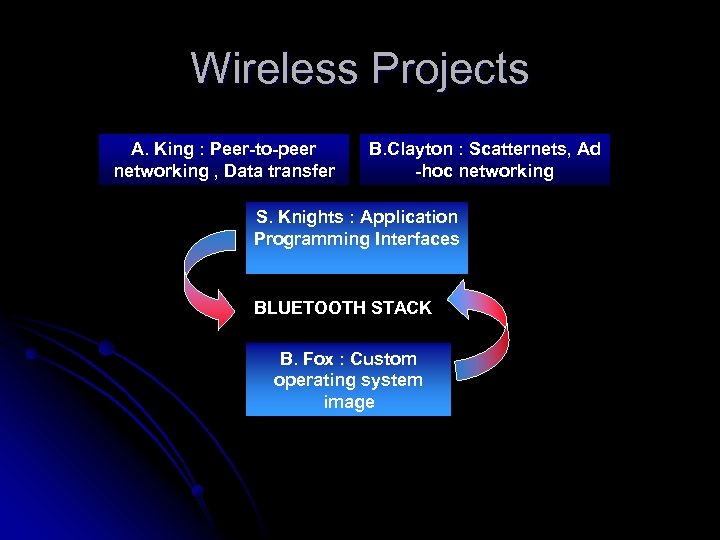
Wireless Projects A. King : Peer-to-peer networking , Data transfer B. Clayton : Scatternets, Ad -hoc networking S. Knights : Application Programming Interfaces BLUETOOTH STACK B. Fox : Custom operating system image
a5e92ce0814bcc4930d767f07b0a67c2.ppt