817e9a93dd99d4b69d21e18589fc2e48.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Automated Systems Standard Grade
Automated Systems Standard Grade
 What Is An Automated System? • A system in which computers are used to control machines and equipment • For example: – Traffic light system – Robot arms in car manufacturing industry – To control and monitor the temperatures of dangerous chemicals processes in such places as oil refineries
What Is An Automated System? • A system in which computers are used to control machines and equipment • For example: – Traffic light system – Robot arms in car manufacturing industry – To control and monitor the temperatures of dangerous chemicals processes in such places as oil refineries
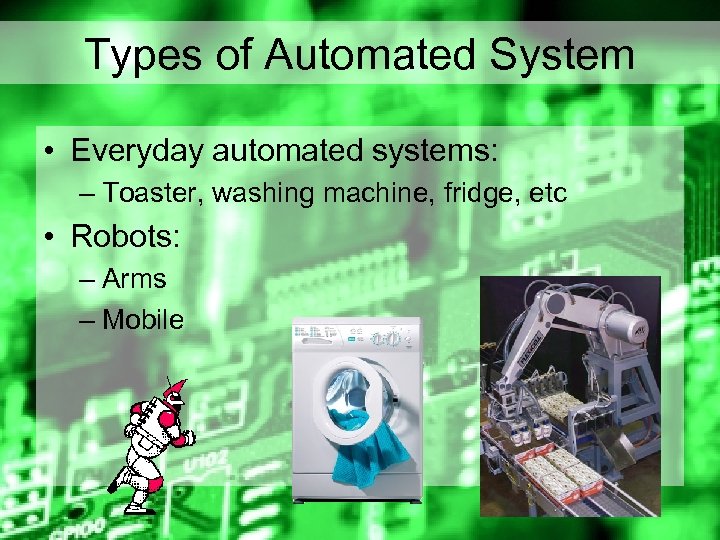 Types of Automated System • Everyday automated systems: – Toaster, washing machine, fridge, etc • Robots: – Arms – Mobile
Types of Automated System • Everyday automated systems: – Toaster, washing machine, fridge, etc • Robots: – Arms – Mobile
 The Need for Automated Systems • • • Hazardous Environment Repetitive Tasks Speed Efficiency Accuracy Adaptability
The Need for Automated Systems • • • Hazardous Environment Repetitive Tasks Speed Efficiency Accuracy Adaptability
 Sensors & Feedback • A sensor is used to detect something and then give feedback to computer • Feedback allows the computer to make a decision based on the information • Examples of sensors: – heat – light – collisions – proximity – magnetic fields – Pressure
Sensors & Feedback • A sensor is used to detect something and then give feedback to computer • Feedback allows the computer to make a decision based on the information • Examples of sensors: – heat – light – collisions – proximity – magnetic fields – Pressure
 Signal Converters • A computer is connected to a device by a circuit called an interface. • The interface must be able to convert the computer’s digital signals to analogue signals if required. • This is done by a digital to analogue converter. • Signals can be changed in the other direction by an analogue to digital converter.
Signal Converters • A computer is connected to a device by a circuit called an interface. • The interface must be able to convert the computer’s digital signals to analogue signals if required. • This is done by a digital to analogue converter. • Signals can be changed in the other direction by an analogue to digital converter.
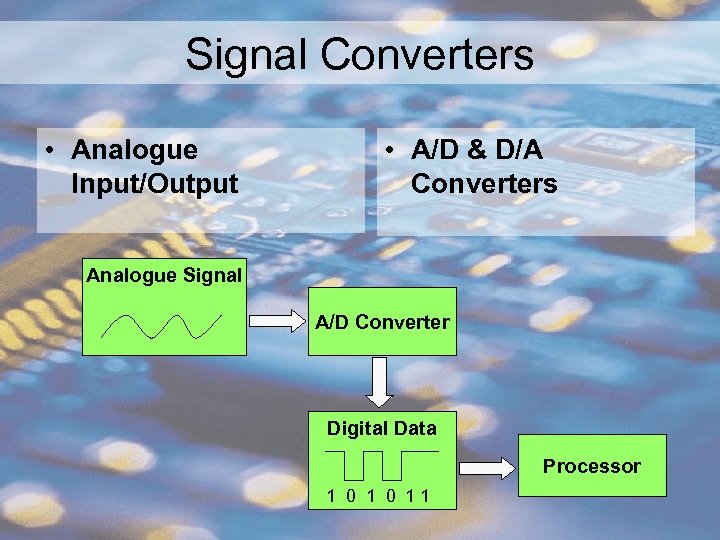 Signal Converters • Analogue Input/Output • A/D & D/A Converters Analogue Signal A/D Converter Digital Data Processor 1 0 11
Signal Converters • Analogue Input/Output • A/D & D/A Converters Analogue Signal A/D Converter Digital Data Processor 1 0 11
 Real-Time Processing Example: • A nuclear power station uses an automated system to control temperature of the dangerous chemicals • The temperature rises above safe levels which could cause a major explosion • The system is not real-time and will get to the problem when it next gets the chance!
Real-Time Processing Example: • A nuclear power station uses an automated system to control temperature of the dangerous chemicals • The temperature rises above safe levels which could cause a major explosion • The system is not real-time and will get to the problem when it next gets the chance!
 Hardware & Software • ROM Software – ROM is faster to load than disk – But are more expensive • Embedded systems – Are a small computer inside a large piece of machinery (Like a washing machine or mobile phone) • Control languages – The programming language that is used to control the automated system
Hardware & Software • ROM Software – ROM is faster to load than disk – But are more expensive • Embedded systems – Are a small computer inside a large piece of machinery (Like a washing machine or mobile phone) • Control languages – The programming language that is used to control the automated system
 Simulations • Used to model real-life situations – Training • Flight simulators – Practise • Emergency procedures – Testing • Car crash simulators
Simulations • Used to model real-life situations – Training • Flight simulators – Practise • Emergency procedures – Testing • Car crash simulators
 Computer Aided Design (CAD) • Using specialised software and hardware to design anything from kitchens to cars. • Hardware used: – Graphics Tablet – Computer Software – High Resolution Monitor – Plotter
Computer Aided Design (CAD) • Using specialised software and hardware to design anything from kitchens to cars. • Hardware used: – Graphics Tablet – Computer Software – High Resolution Monitor – Plotter
 Computer Aided Manufacture (CAM) • Computer uses the information given to create the item • Always perfect
Computer Aided Manufacture (CAM) • Computer uses the information given to create the item • Always perfect
 Automated Systems Standard Grade
Automated Systems Standard Grade
 Robots : Stationary • Stay in one place all the time – e. g. used on factory assembly lines • Control programs are stored on disc or tape • Can be reprogrammed to do a different task
Robots : Stationary • Stay in one place all the time – e. g. used on factory assembly lines • Control programs are stored on disc or tape • Can be reprogrammed to do a different task
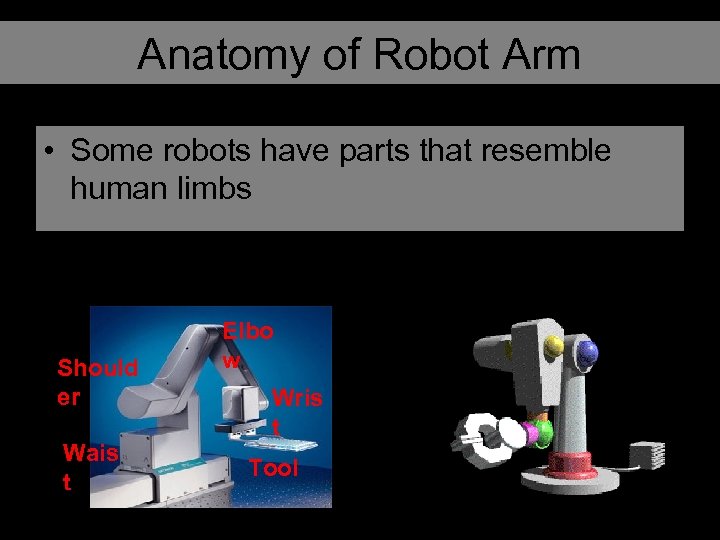 Anatomy of Robot Arm • Some robots have parts that resemble human limbs Should er Wais t Elbo w Wris t Tool
Anatomy of Robot Arm • Some robots have parts that resemble human limbs Should er Wais t Elbo w Wris t Tool
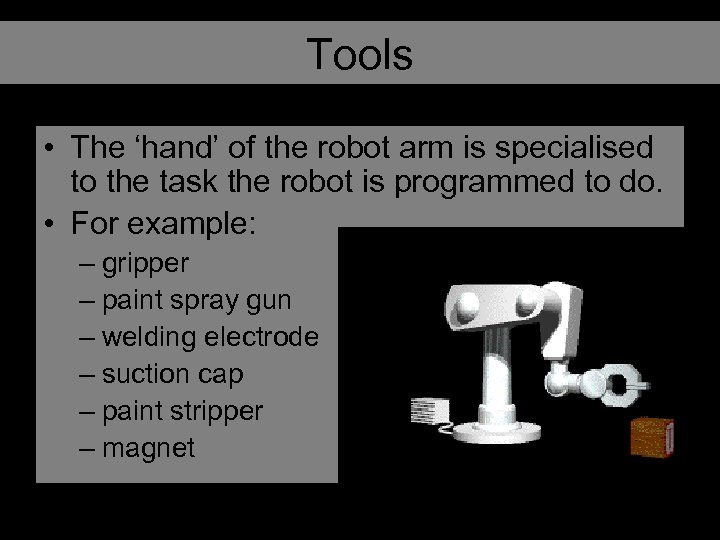 Tools • The ‘hand’ of the robot arm is specialised to the task the robot is programmed to do. • For example: – gripper – paint spray gun – welding electrode – suction cap – paint stripper – magnet
Tools • The ‘hand’ of the robot arm is specialised to the task the robot is programmed to do. • For example: – gripper – paint spray gun – welding electrode – suction cap – paint stripper – magnet
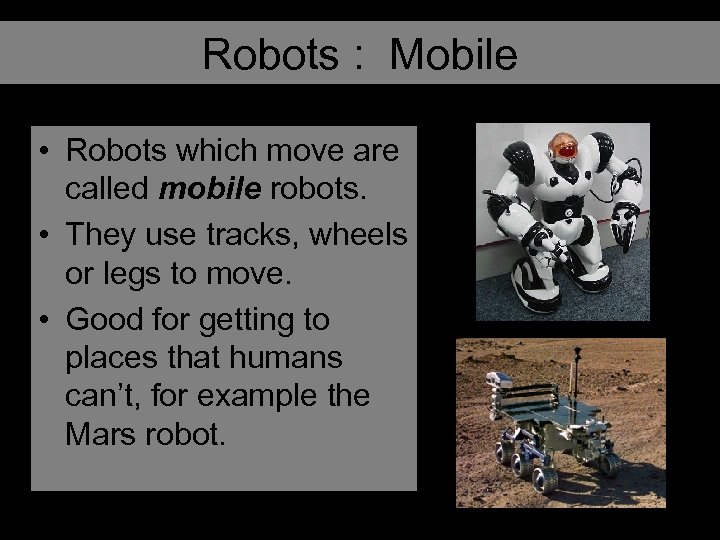 Robots : Mobile • Robots which move are called mobile robots. • They use tracks, wheels or legs to move. • Good for getting to places that humans can’t, for example the Mars robot.
Robots : Mobile • Robots which move are called mobile robots. • They use tracks, wheels or legs to move. • Good for getting to places that humans can’t, for example the Mars robot.
 Robots : AGVs • Autonomous Guided Vehicles • These are robots which move around factories following guides. • AGVs can practically work on its own.
Robots : AGVs • Autonomous Guided Vehicles • These are robots which move around factories following guides. • AGVs can practically work on its own.
 Guides • If a mobile robot is designed to move around a factory it may use guides • Guides can be – Magnetic: Magnetic strips are placed under the surface of the factory floor • Expensive but will not need to be replaced – Light: White lines are painted on floor and robot follows these with light sensors • Very cheap but can wear easily.
Guides • If a mobile robot is designed to move around a factory it may use guides • Guides can be – Magnetic: Magnetic strips are placed under the surface of the factory floor • Expensive but will not need to be replaced – Light: White lines are painted on floor and robot follows these with light sensors • Very cheap but can wear easily.
 Programmable • A robot follows an instruction called a program • Programs are written in High Level Language • This is a language similar to everyday English. • This program can be changed so robot can be used for other tasks, e. g. – A robot arm that welds cars can be reprogrammed to paint cars
Programmable • A robot follows an instruction called a program • Programs are written in High Level Language • This is a language similar to everyday English. • This program can be changed so robot can be used for other tasks, e. g. – A robot arm that welds cars can be reprogrammed to paint cars
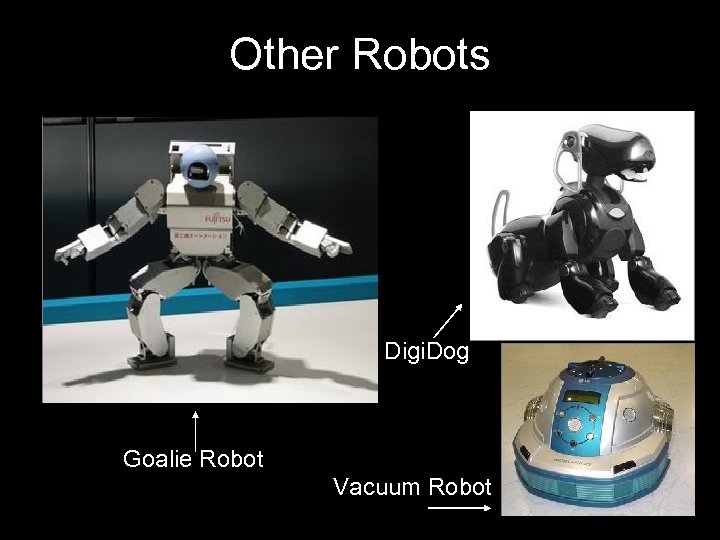 Other Robots Digi. Dog Goalie Robot Vacuum Robot
Other Robots Digi. Dog Goalie Robot Vacuum Robot
 The Future?
The Future?
 Implications: Social • • Retraining Redundancy Nature of the job Increased leisure time
Implications: Social • • Retraining Redundancy Nature of the job Increased leisure time
 Implications: Technical • Safety Precautions must be taken when using industrial automation • Workplace Design – With humans we need the right temperature, frequent breaks, low noise, etc – Automated systems don’t.
Implications: Technical • Safety Precautions must be taken when using industrial automation • Workplace Design – With humans we need the right temperature, frequent breaks, low noise, etc – Automated systems don’t.
 Systems Analysis • Before designing a new factory a Systems Analysis needs to be carried out • A Systems Analyst looks at how various jobs are done manually and sees if these can be done by computer
Systems Analysis • Before designing a new factory a Systems Analysis needs to be carried out • A Systems Analyst looks at how various jobs are done manually and sees if these can be done by computer
 Factories of the Future • We now have very few people working in factories • This means that factories can be designed around the automated systems, not the humans
Factories of the Future • We now have very few people working in factories • This means that factories can be designed around the automated systems, not the humans
 Implications : Economic • Labour Intensive – Relies on Workers • Capital Intensive – Uses expensive machinery • Productivity • Replacement Costs • High Initial Cost – Purchasing equipment – Modernising factory • Long term savings – Increased Productivity – Wages £$£$£$£
Implications : Economic • Labour Intensive – Relies on Workers • Capital Intensive – Uses expensive machinery • Productivity • Replacement Costs • High Initial Cost – Purchasing equipment – Modernising factory • Long term savings – Increased Productivity – Wages £$£$£$£


