3e4775f319a81b84d96e69fad30eb247.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9

Automated Systems Lesson 3: Getting the Robot to do work

Lesson 3: Automated Systems By the end of this lesson you will be able to: 1. Identify what the controlling computer does. 2. Explain what a control program is. 3. Explain what a sensor is. 4. Explain why sensors are needed. 5. Explain the term feedback. 6. Explain what happens to the feedback. 7. Explain why an interface is required. 8. Explain the term analogue signal. 9. Explain the term digital signal 10. Explain what a AD to DA converter does.

Lesson 3: Automated Systems Controlling Computer A robot must be connected to a controlling computer. The controlling computer sends instructions to the arm. The controlling computer is the "brain" of the robot. The controlling computer will have a control program uploaded onto it ie a set of instructions written in code.
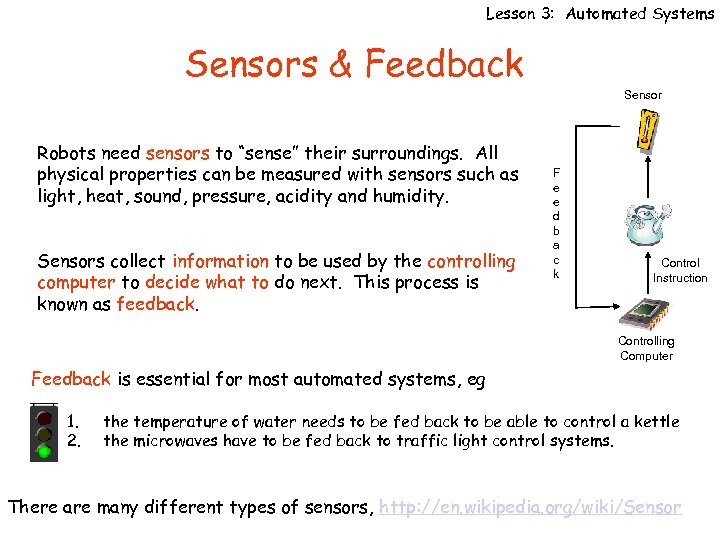
Lesson 3: Automated Systems Sensors & Feedback Sensor Robots need sensors to “sense” their surroundings. All physical properties can be measured with sensors such as light, heat, sound, pressure, acidity and humidity. Sensors collect information to be used by the controlling computer to decide what to do next. This process is known as feedback. F e e d b a c k Control Instruction Controlling Computer Feedback is essential for most automated systems, eg 1. 2. the temperature of water needs to be fed back to be able to control a kettle the microwaves have to be fed back to traffic light control systems. There are many different types of sensors, http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Sensor
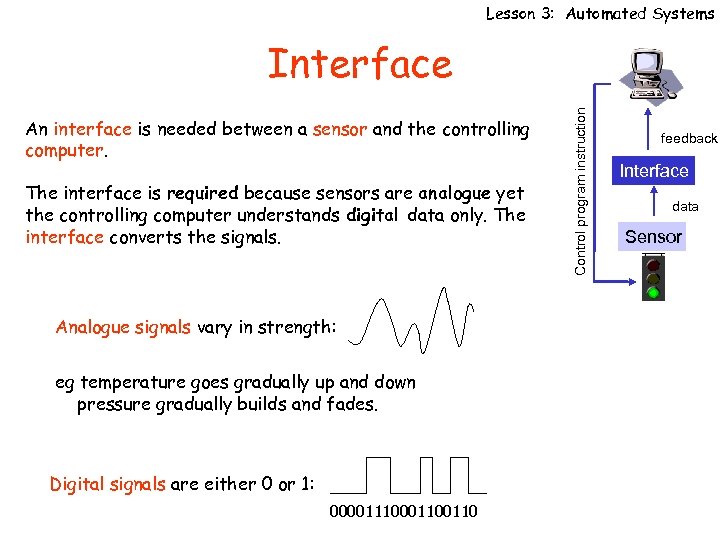
Lesson 3: Automated Systems An interface is needed between a sensor and the controlling computer. The interface is required because sensors are analogue yet the controlling computer understands digital data only. The interface converts the signals. Analogue signals vary in strength: eg temperature goes gradually up and down pressure gradually builds and fades. Digital signals are either 0 or 1: 0000111000110 Control program instruction Interface feedback Interface data Sensor
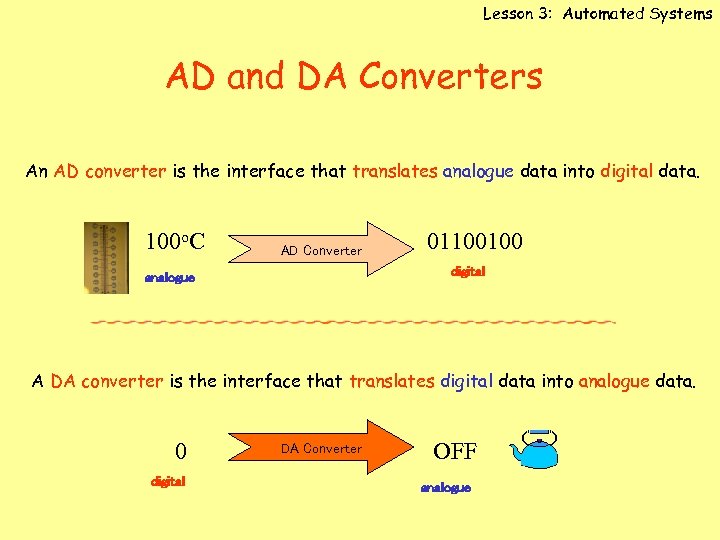
Lesson 3: Automated Systems AD and DA Converters An AD converter is the interface that translates analogue data into digital data. 100 o. C AD Converter 01100100 digital analogue A DA converter is the interface that translates digital data into analogue data. 0 digital DA Converter OFF analogue

Questions Lesson 3: Automated Systems Answer the following questions in your jotter. 1) Name the part of the automated system that control the action. 2) Why is a sensor needed? 3) List 3 types of sensors and explain what each could be used for. 4) Explain the term feedback. 5) Why is feedback necessary? 6) What happens as a result of feedback? 7) Explain why a interface is required. 8) Draw a diagram of where an interface will be positioned in system. 9) What is an AD converter? 10)What does a DA converter do and why?

Fun Things To Do Try programming the Picobot using it’s sensor. Try programming Lego Robot cars. Robots with a sense of touch http: //news. nationalgeographic. com/news/2005/08/0817_050817_robotskin. html Beetles & Sensors http: //news. nationalgeographic. com/news/2003/03/0314_030314_secretweapons 3. html Robot Cars http: //news. nationalgeographic. com/news/2005/10/1006_051006_robot_car_2. html Smart Cars http: //news. nationalgeographic. com/news/2004/05/0521_040521_smartcars. html

3e4775f319a81b84d96e69fad30eb247.ppt