a2ec190687b7040409ed188eaf00cdab.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

Automated System for Combinatorial Synthesis and High-throughput Characterization of Polymeric Sensor Materials Application in development and optimizing of sensors for gaseous hydrogen chloride (cable fire alarms) Valentin Kulikov Munich 2004 Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov

Outlook of the presentation • • • Introduction to conducting polymers Electropolymerization concept and its realization Measurement concept and its realization Data analysis of experiment Influence of temperature to experiments Optimal thickness of polymer layer Representative results on HCl sensor based on aniline derivates Conclusion Outlook, application range of conducting polymers Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov

History of conducting polymers One has been taught that plastics, do not conduct electricity. Usually plastics are used as insulation around the copper wires in ordinary electrical cables. Photo acknowledged from report of Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2000 In 1977 three scientists Prof. A. J. Heeger, Prof. A. G. Mac. Diarmid and Prof. H. Shirakawa cointidentaly discowered and report conductive properties of the alternating-bond conjugated polymers (Polyacetylene). They found that the polymer could be (n- or p-) doped to the metallic state and thereby transformed into a good electrical conductor. * Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2000 being awarded to Profs. A. J. Heeger, A. G. Mac. Diarmid and H. Shirakawa (Mac. Diarmid A. G. , "Synthetic metals: A novel role for organic polymers (Nobel Lecture)", Angewandte Chemie, International Edition 40, 2581 -2590, 2001) Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
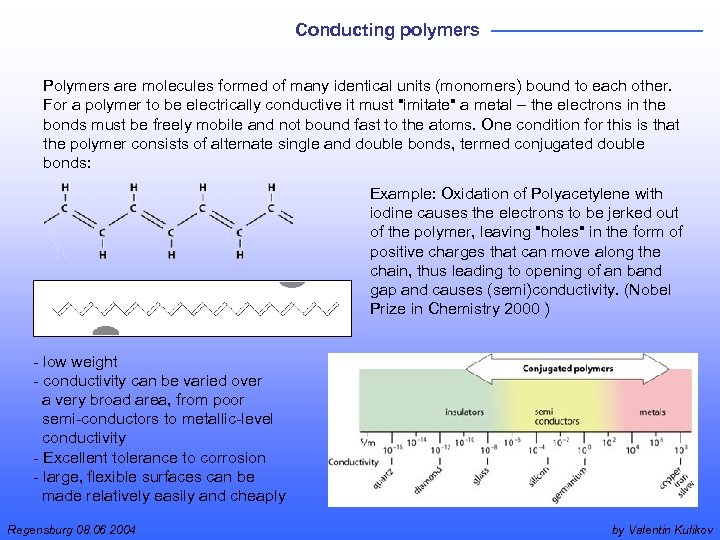
Conducting polymers Polymers are molecules formed of many identical units (monomers) bound to each other. For a polymer to be electrically conductive it must "imitate" a metal – the electrons in the bonds must be freely mobile and not bound fast to the atoms. One condition for this is that the polymer consists of alternate single and double bonds, termed conjugated double bonds: Example: Oxidation of Polyacetylene with iodine causes the electrons to be jerked out of the polymer, leaving "holes" in the form of positive charges that can move along the chain, thus leading to opening of an band gap and causes (semi)conductivity. (Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2000 ) - low weight - conductivity can be varied over a very broad area, from poor semi-conductors to metallic-level conductivity - Excellent tolerance to corrosion - large, flexible surfaces can be made relatively easily and cheaply Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
Wide application range of polymers - electrochemical devices (ion exchangers, catalysts, batteries. . . ) - semiconductor electronics (wires, diodes, transistors, LEDs, displays, solar cells, . . . ) - supercapacitors, whole integrated circuits. . . ) - functional coatings (antistatic coating, electrochromic windows. . . ) Analytical devices: - chemical and biological sensors (immobilization of sensor components, electrical contact between electrode and enzyme or intermediator) - formation of molecularly imprinted polymers - gas sensors (HCl, NH 3, O 3, artificial nose. . . ) - many others Target applications summary: - Flat displays for TVs, monitors, mobile phones, terminals, etc. - Cheap solar cells for energy conversion - Sensors (artificial nose - gas, chemo-, bio-) - Cheap semiconductors for general use - Corrosion protection and electrochromic windows - many others Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
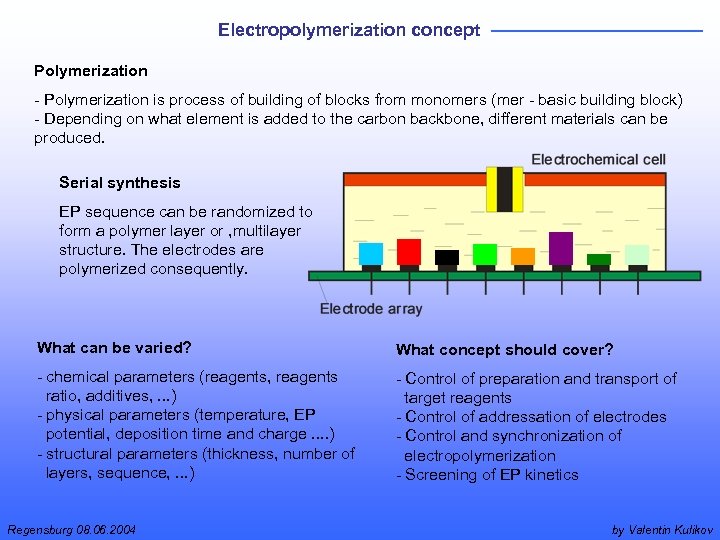
Electropolymerization concept Polymerization - Polymerization is process of building of blocks from monomers (mer - basic building block) - Depending on what element is added to the carbon backbone, different materials can be produced. Serial synthesis EP sequence can be randomized to form a polymer layer or , multilayer structure. The electrodes are polymerized consequently. What can be varied? What concept should cover? - chemical parameters (reagents, reagents ratio, additives, . . . ) - physical parameters (temperature, EP potential, deposition time and charge. . ) - structural parameters (thickness, number of layers, sequence, . . . ) - Control of preparation and transport of target reagents - Control of addressation of electrodes - Control and synchronization of electropolymerization - Screening of EP kinetics Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
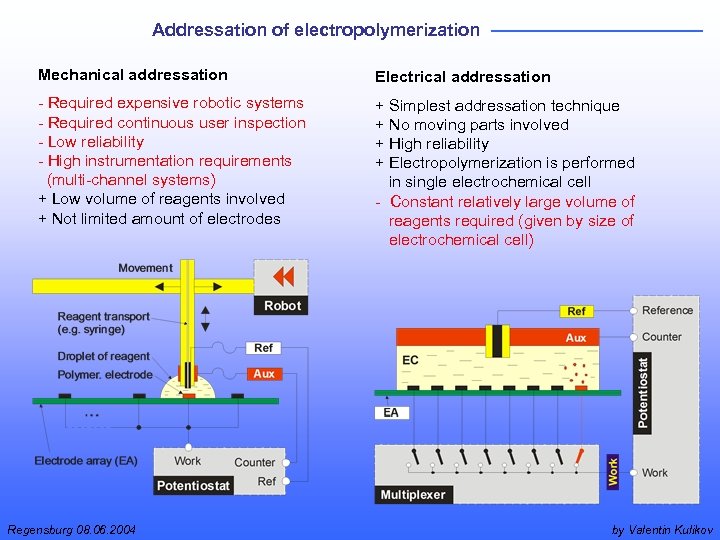
Addressation of electropolymerization Mechanical addressation Electrical addressation - Required expensive robotic systems - Required continuous user inspection - Low reliability - High instrumentation requirements (multi-channel systems) + Low volume of reagents involved + Not limited amount of electrodes + Simplest addressation technique + No moving parts involved + High reliability + Electropolymerization is performed in single electrochemical cell - Constant relatively large volume of reagents required (given by size of electrochemical cell) Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
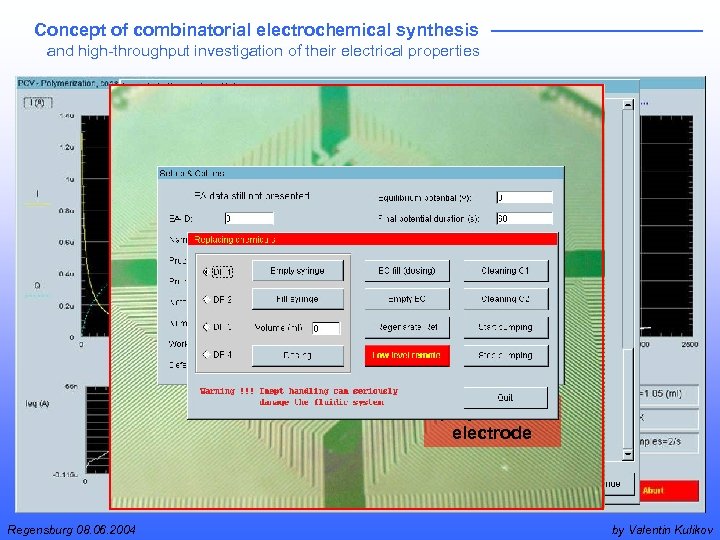
Concept of combinatorial electrochemical synthesis and high-throughput investigation of their electrical properties polymerized electrode Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
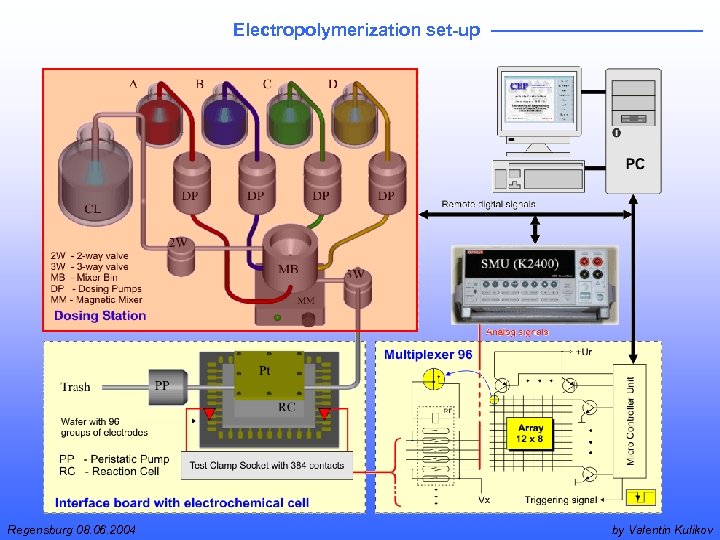
Electropolymerization set-up Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
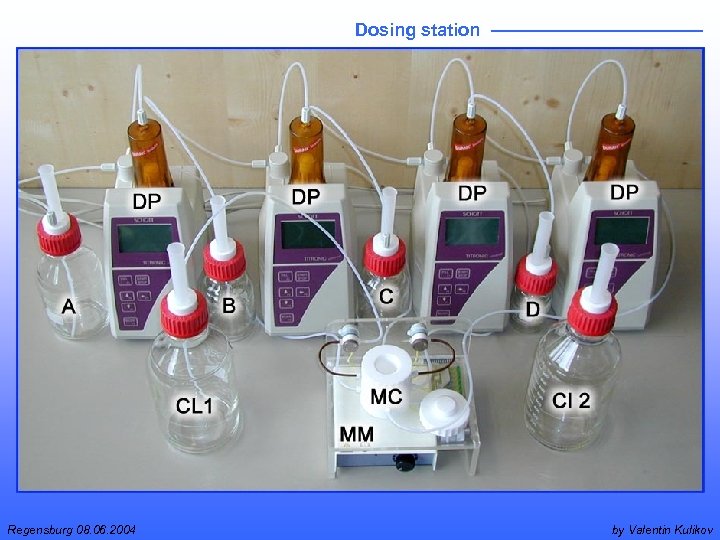

Dosing station Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
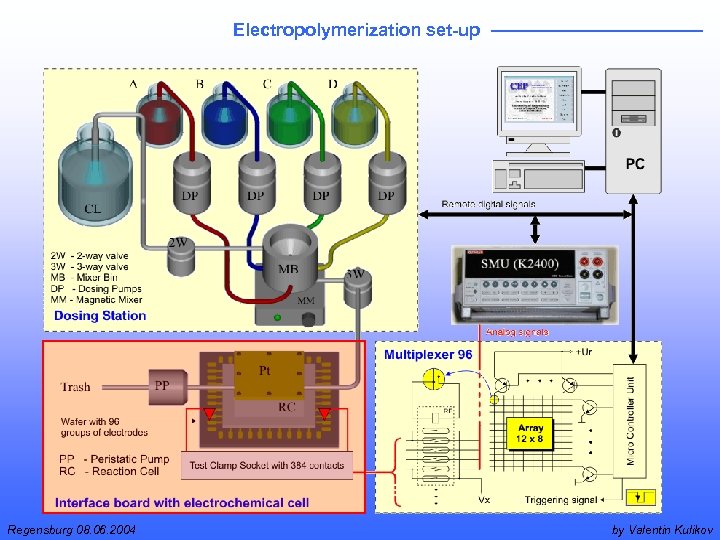
Electropolymerization set-up Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
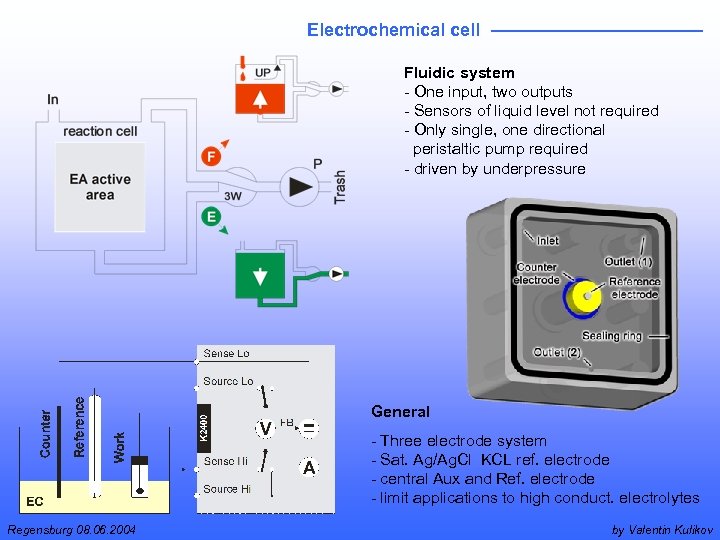
Electrochemical cell Fluidic system - One input, two outputs - Sensors of liquid level not required - Only single, one directional peristaltic pump required - driven by underpressure General - Three electrode system - Sat. Ag/Ag. Cl KCL ref. electrode - central Aux and Ref. electrode - limit applications to high conduct. electrolytes Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
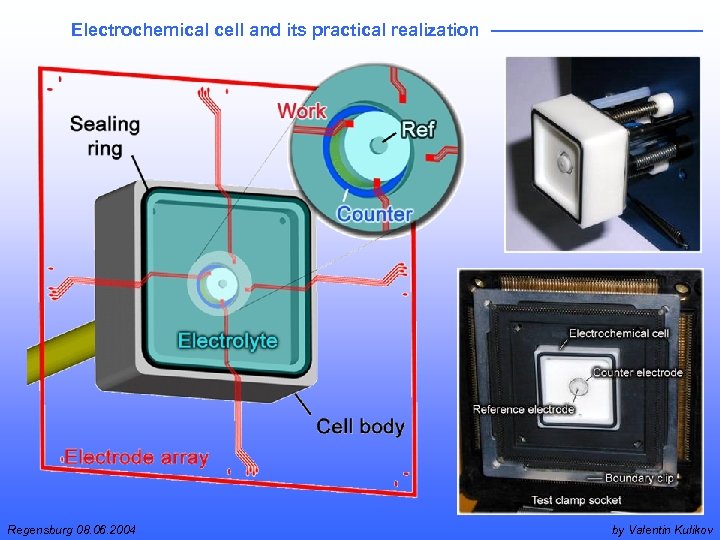
Electrochemical cell and its practical realization Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
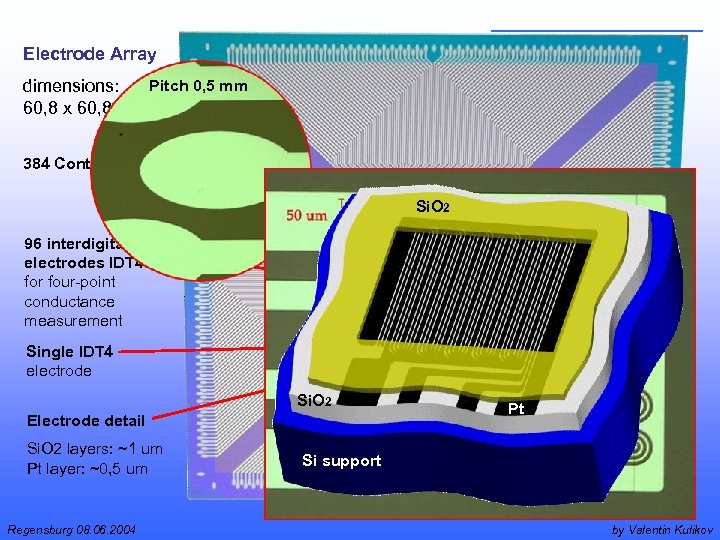
Electrode Array Pitch 0, 5 mm dimensions: 60, 8 x 60, 8 mm 384 Contact pins Si. O 2 96 interdigital electrodes IDT 4 for four-point conductance measurement Single IDT 4 electrode Si. O 2 Electrode detail Si. O 2 layers: ~1 um Pt layer: ~0, 5 um Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 Pt Pt Si support by Valentin Kulikov
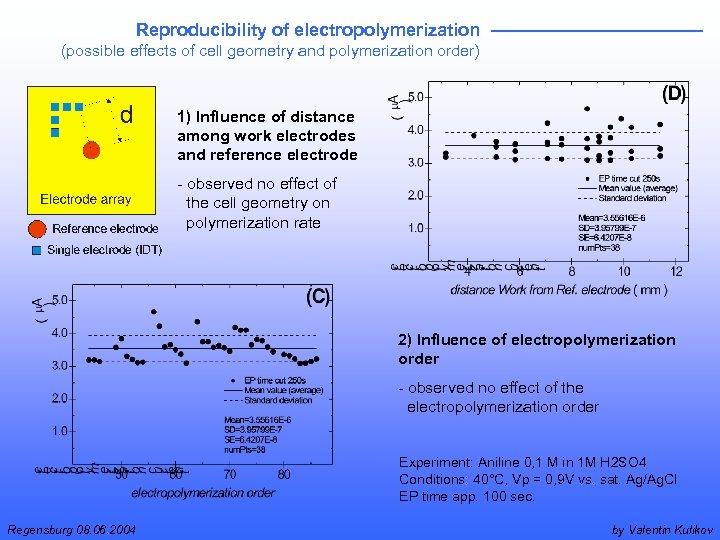
Reproducibility of electropolymerization (possible effects of cell geometry and polymerization order) 1) Influence of distance among work electrodes and reference electrode - observed no effect of the cell geometry on polymerization rate 2) Influence of electropolymerization order - observed no effect of the electropolymerization order Experiment: Aniline 0, 1 M in 1 M H 2 SO 4 Conditions: 40°C, Vp = 0, 9 V vs. sat. Ag/Ag. Cl EP time app. 100 sec. Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
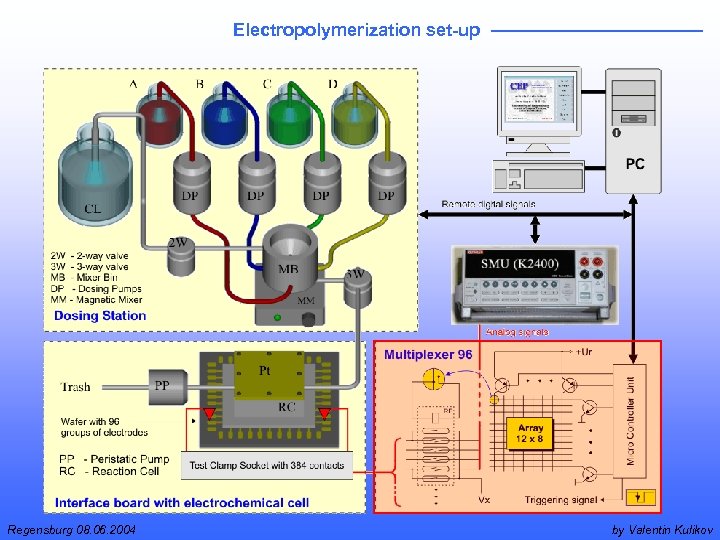
Electropolymerization set-up Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
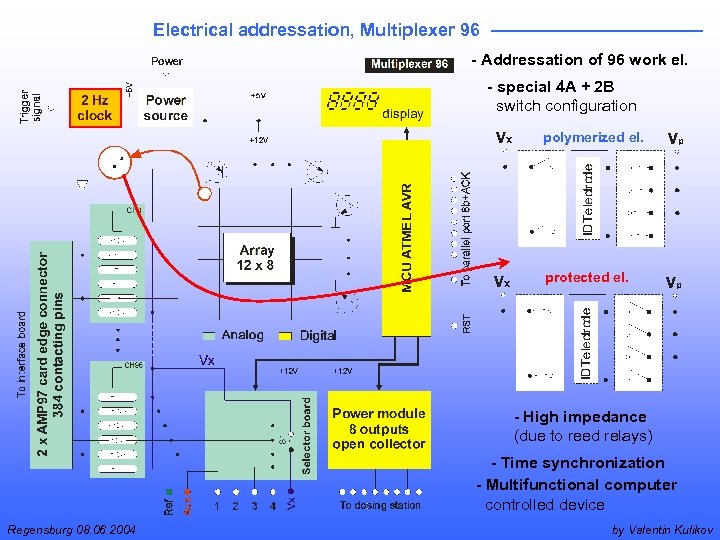
Electrical addressation, Multiplexer 96 - Addressation of 96 work el. - special 4 A + 2 B switch configuration polymerized el. protected el. - High impedance (due to reed relays) - Time synchronization - Multifunctional computer controlled device Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
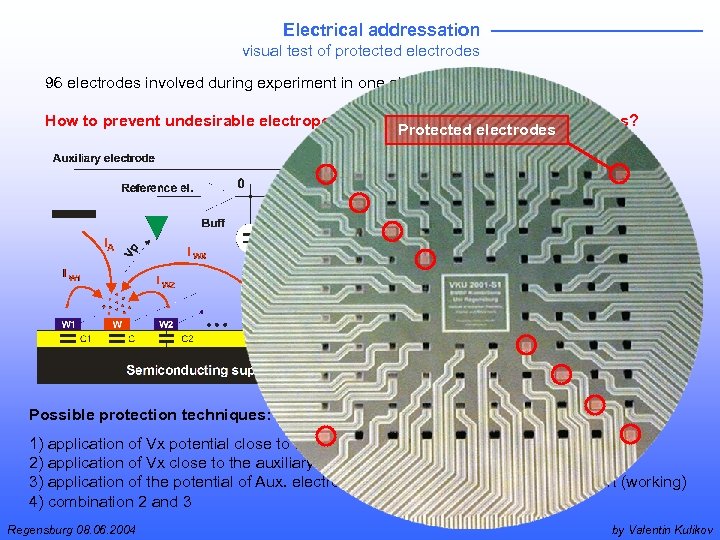
Electrical addressation visual test of protected electrodes 96 electrodes involved during experiment in one electrochemical cell How to prevent undesirable electropolymerization on neighboring electrodes? Protected electrodes Possible protection techniques: 1) application of Vx potential close to the reference level (not working) 2) application of Vx close to the auxiliary electrode potential level (working) 3) application of the potential of Aux. electrode to the semiconducting array support (working) 4) combination 2 and 3 Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
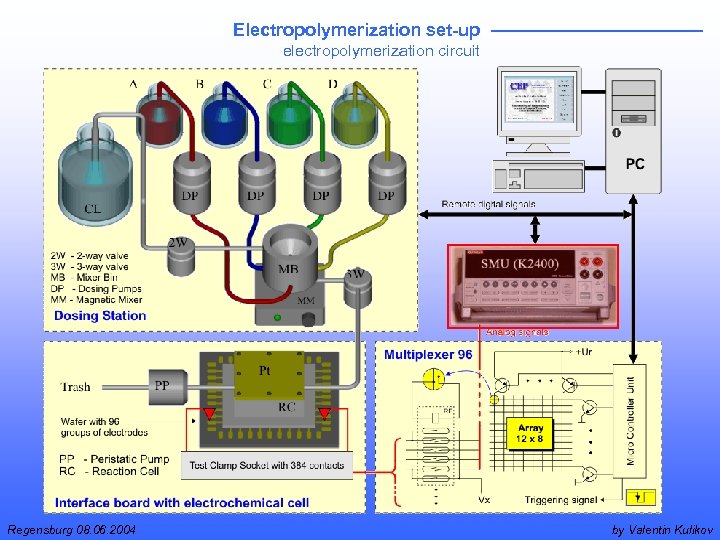
Electropolymerization set-up electropolymerization circuit Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
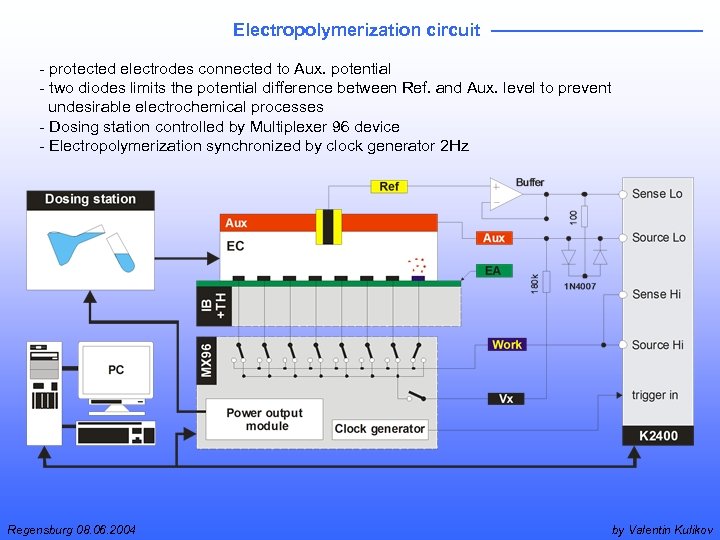
Electropolymerization circuit - protected electrodes connected to Aux. potential - two diodes limits the potential difference between Ref. and Aux. level to prevent undesirable electrochemical processes - Dosing station controlled by Multiplexer 96 device - Electropolymerization synchronized by clock generator 2 Hz Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
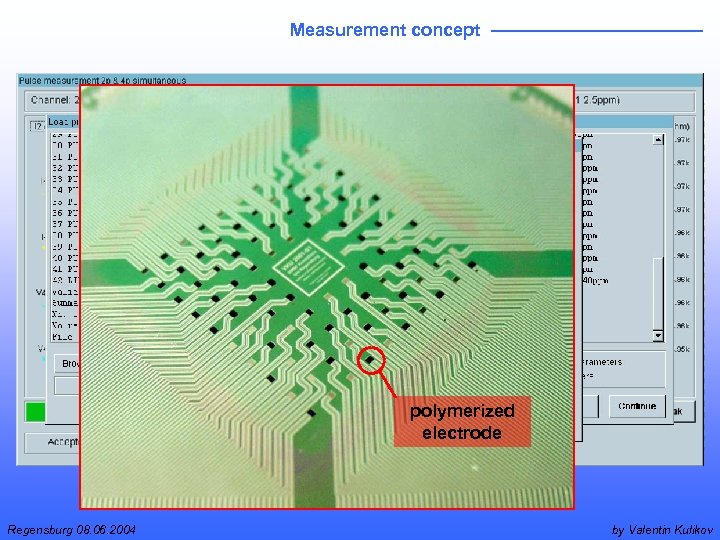
Measurement concept polymerized electrode Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
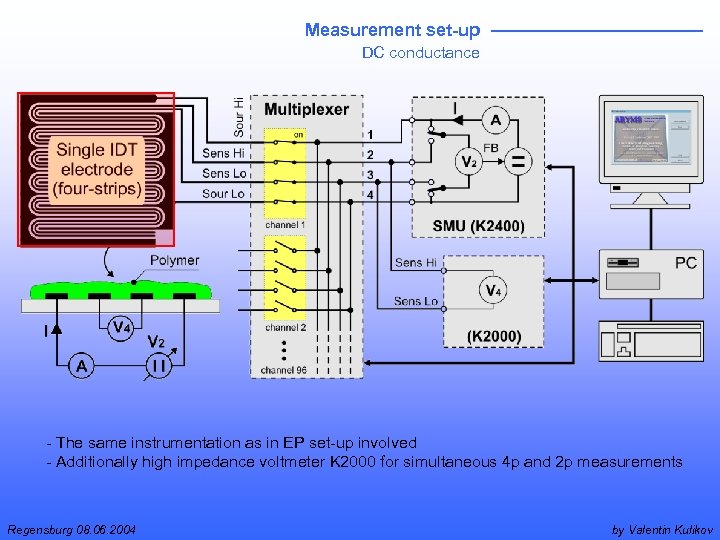
Measurement set-up DC conductance - The same instrumentation as in EP set-up involved - Additionally high impedance voltmeter K 2000 for simultaneous 4 p and 2 p measurements Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
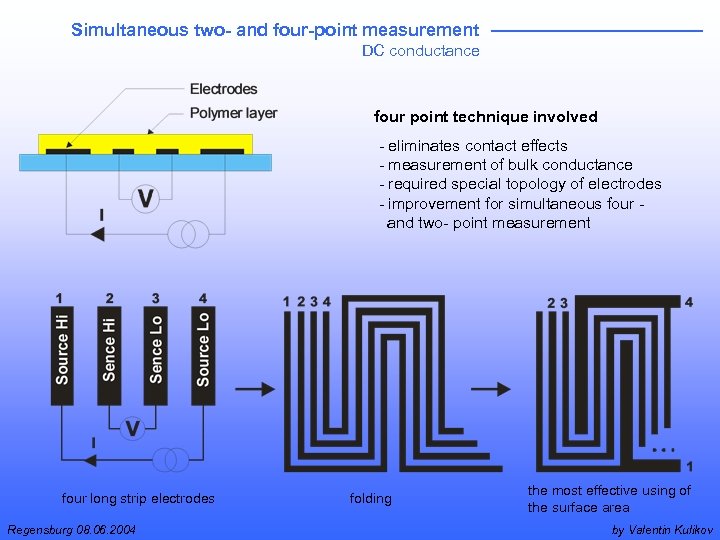
Simultaneous two- and four-point measurement DC conductance four point technique involved - eliminates contact effects - measurement of bulk conductance - required special topology of electrodes - improvement for simultaneous four - and two- point measurement four long strip electrodes Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 folding the most effective using of the surface area by Valentin Kulikov
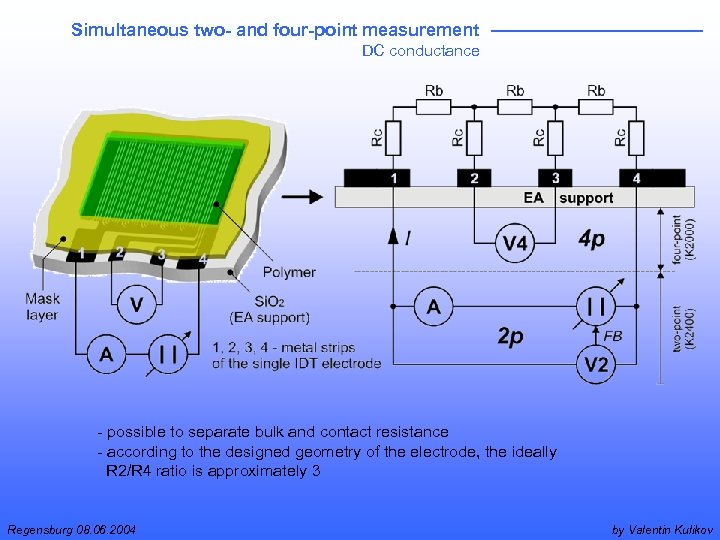
Simultaneous two- and four-point measurement DC conductance - possible to separate bulk and contact resistance - according to the designed geometry of the electrode, the ideally R 2/R 4 ratio is approximately 3 Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
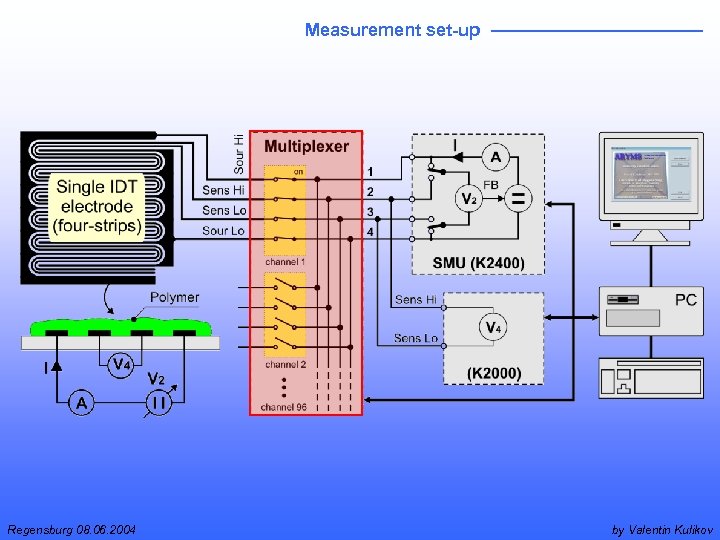
Measurement set-up Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
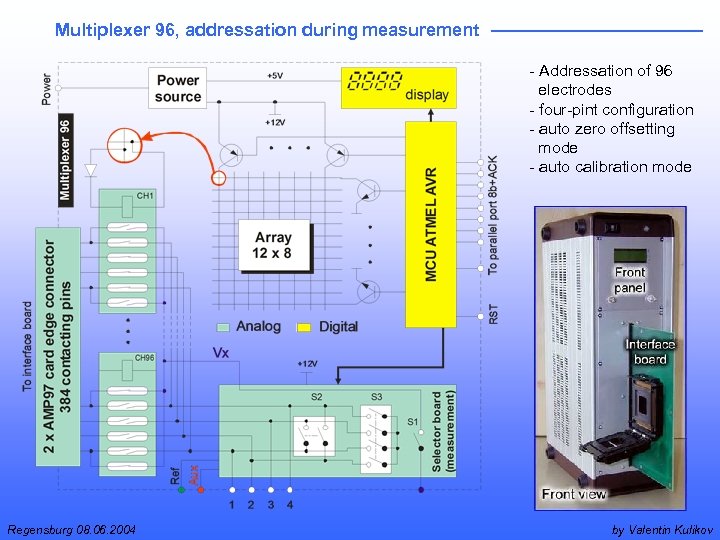
Multiplexer 96, addressation during measurement - Addressation of 96 electrodes - four-pint configuration - auto zero offsetting mode - auto calibration mode Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
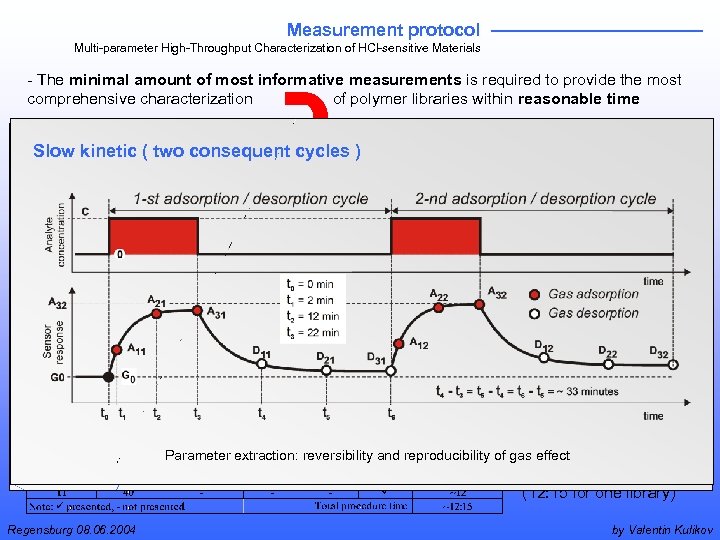
Measurement protocol Multi-parameter High-Throughput Characterization of HCl-sensitive Materials - The minimal amount of most informative measurements is required to provide the most comprehensive characterization of polymer libraries within reasonable time Measurement cycles Slow kinetic two consequentcycles )) and protocol Fast kinetic ((two consequentprocedure + analyte concentration sweep - comprehensive meas. + reversibility + reproducibility + response + drifts + concentration depend. + fitting models Parameter extraction: reversibility and reproducibility of gas effect, fitting to Langmuir or Henry model - reasonable invest. time (12: 15 for one library) Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
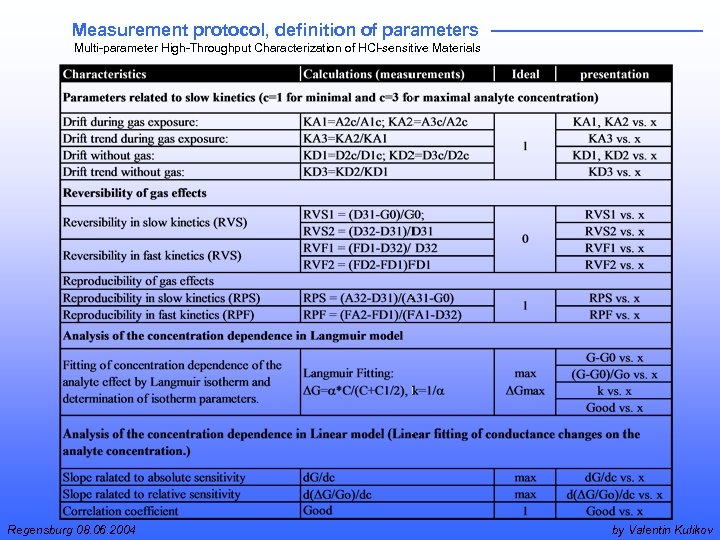
Measurement protocol, definition of parameters Multi-parameter High-Throughput Characterization of HCl-sensitive Materials Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
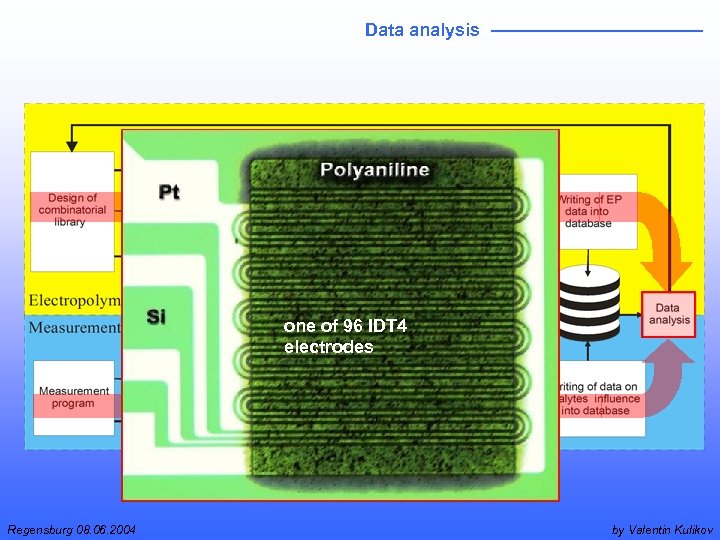
Data analysis one of 96 IDT 4 electrodes Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
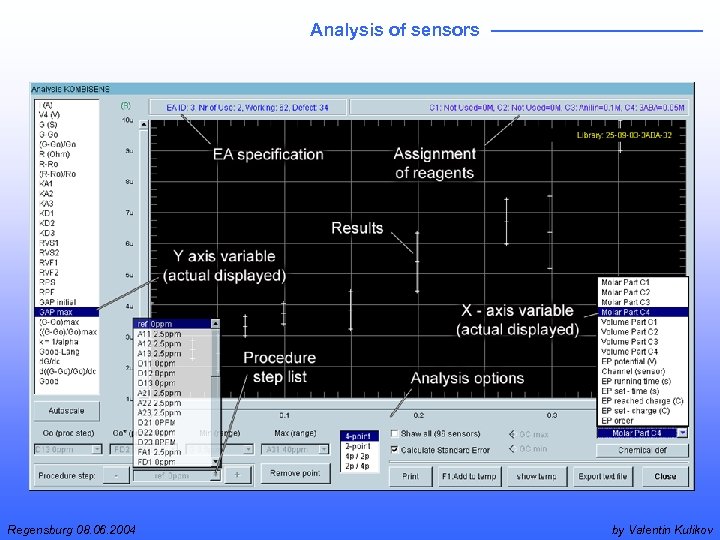
Analysis of sensors Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
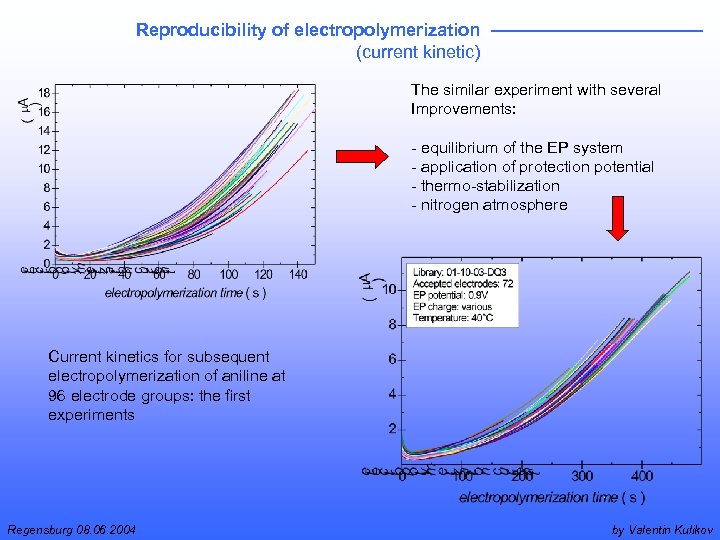
Reproducibility of electropolymerization (current kinetic) The similar experiment with several Improvements: - equilibrium of the EP system - application of protection potential - thermo-stabilization - nitrogen atmosphere Current kinetics for subsequent electropolymerization of aniline at 96 electrode groups: the first experiments Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
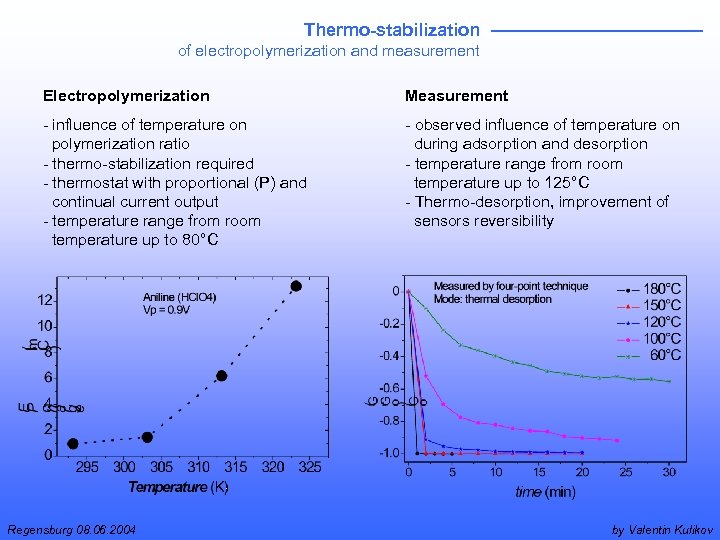
Thermo-stabilization of electropolymerization and measurement Electropolymerization Measurement - influence of temperature on polymerization ratio - thermo-stabilization required - thermostat with proportional (P) and continual current output - temperature range from room temperature up to 80°C - observed influence of temperature on during adsorption and desorption - temperature range from room temperature up to 125°C - Thermo-desorption, improvement of sensors reversibility Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov

Application in conductometric polymer gas sensors (Sensors for gaseous hydrogen chloride) Why the sensor for gaseous HCl is needed? polyvinylchloride (PVC) + O 2 -> HCl +. . . Application in fire alarm systems for cable burning - PVC cables - PVC interior details in cars, planes, trains, etc. Prevention of fire disasters caused by burning of cable isolation, PVC (in buildings, transport, and others) Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
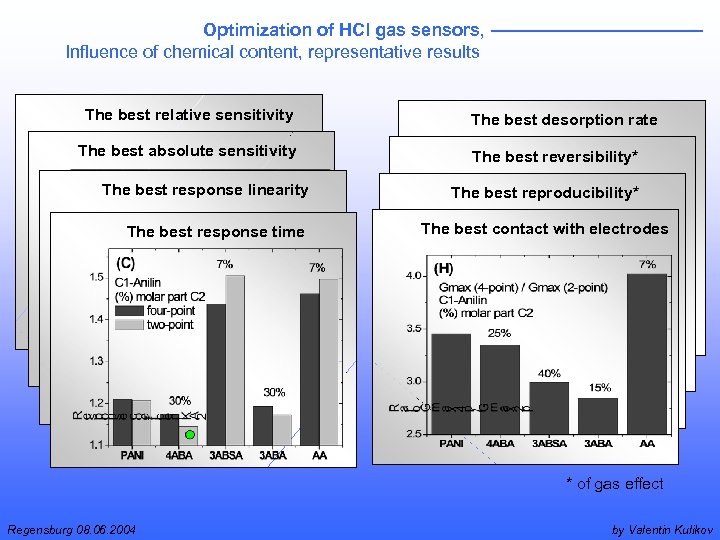
Optimization of HCl gas sensors, Influence of chemical content, representative results The best relative sensitivity The best absolute sensitivity The best response linearity The best response time The best desorption rate The best reversibility* The best reproducibility* The best contact with electrodes * of gas effect Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov

Conclusion - Developed and realized: - concept for combinatorial electropolymerization (including hardware, fluidic system and control software) - concept for high-throughput screening (including hardware and control software) - Developed comprehensive measurement protocol for characterization of gas sensors - Developed analysis software, which simplifies work with results, calculates, visualizes and exports all defined parameters such reversibility, reproducibility, response, desorption ratio, allows fitting to Langmuir and Henry model, etc. . . - This combinatorial set-up was used for optimization of sensors for gaseous hydrogen chloride based on aniline derivates - The representative results illustrates the wide range of application of the developed tool Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
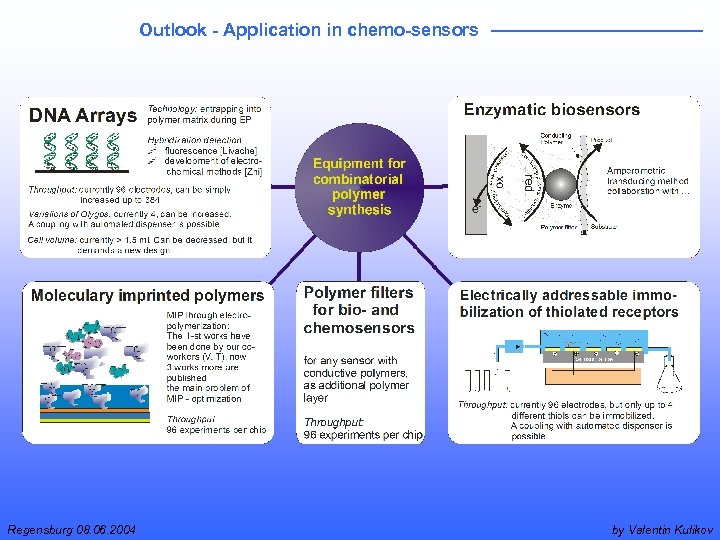
Outlook - Application in chemo-sensors Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
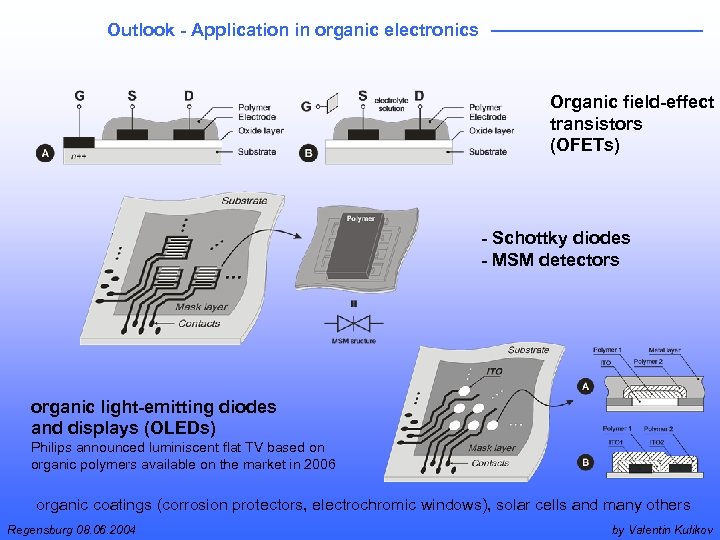
Outlook - Application in organic electronics Organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) - Schottky diodes - MSM detectors organic light-emitting diodes and displays (OLEDs) Philips announced luminiscent flat TV based on organic polymers available on the market in 2006 organic coatings (corrosion protectors, electrochromic windows), solar cells and many others Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov

Acknowledgment Prof. Alexander Koch Prof. Otto. S. Wolfbeis PD. Dr. Vladimir M. Mirsky Prof. Daniel Donoval Dr. Qingli Hao and others This work was supported by the project "KOMBISENS" from German Ministry for Science and Technology. Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov

Thank you for your attention Regensburg 08. 06. 2004 by Valentin Kulikov
a2ec190687b7040409ed188eaf00cdab.ppt