14115ca67ebf89fe115d3506b30bef00.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

Automated Summaries of Audio/Video Presentations Abigail Curden

Main Objectives n n To create automated summaries of audio/video presentations To integrate these summaries into a multimedia database and create a single visual display for retrieval/browsing

Possible Web Layout Electrical and Computer Engineering 20 th June 2003 QUESTIONS Title: Presentation Analysis and Scene Change Detection
Key Elements Of Project n n n Slide location Slide change detection Slide identification Audio analysis Integration of all aspects of project-High level model

Presentation samples 1. Dark Background 4. Blank background left & right camera view 2. Lightly Coloured background 3. Lightly Coloured background 5. Lightly Coloured background left & right camera view 6. Blue background 7. Black background

Slide Location n Purpose: To determine the co-ordinates of the slide in the video frame and so restrict further analysis to this region Strategy: The slide would most likely be rectangular shaped, coordinates given by corners Techniques n n Hough transform Corner detection

Slide Location: Hough Transform STEP 1: GRAYSCALE IMAGE STEP 2: HOUGH ARRAY STEP 3: HOUGH LINES STEP 4: INTERSECTION POINTS

Slide Location: Harris Corner Detection , difference in x (column) direction , difference in y (row) direction Corners: , difference in x and y direction

Slide Location n Combining Hough Transform and Corner Detector n n n Hough Transform and Corner Detection applied to N frames chosen throughout the presentation Form a histogram of slide location points found by both methods Slide location points, assumed to correspond to count values greater than 75%N. n hough intersection points>0. 75 N & corner points>0. 75 N

Slide Location Results
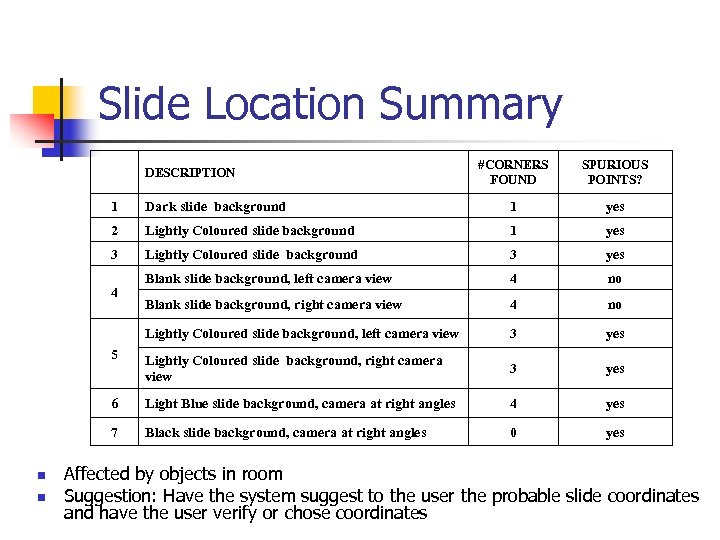
Slide Location Summary DESCRIPTION #CORNERS FOUND SPURIOUS POINTS? 1 Dark slide background 1 yes 2 Lightly Coloured slide background 1 yes 3 Lightly Coloured slide background 3 yes Blank slide background, left camera view 4 no Blank slide background, right camera view 4 no Lightly Coloured slide background, left camera view 3 yes 5 Lightly Coloured slide background, right camera view 3 yes 6 Light Blue slide background, camera at right angles 4 yes 7 Black slide background, camera at right angles 0 yes 4 n n Affected by objects in room Suggestion: Have the system suggest to the user the probable slide coordinates and have the user verify or chose coordinates

Slide Change Detection n Purpose: To parse the video according to scene cuts. Performed only within region of slide coordinates Strategy: At slide change boundaries there will be large change in color/grayscale content Techniques n n Histogram Change Frame Difference
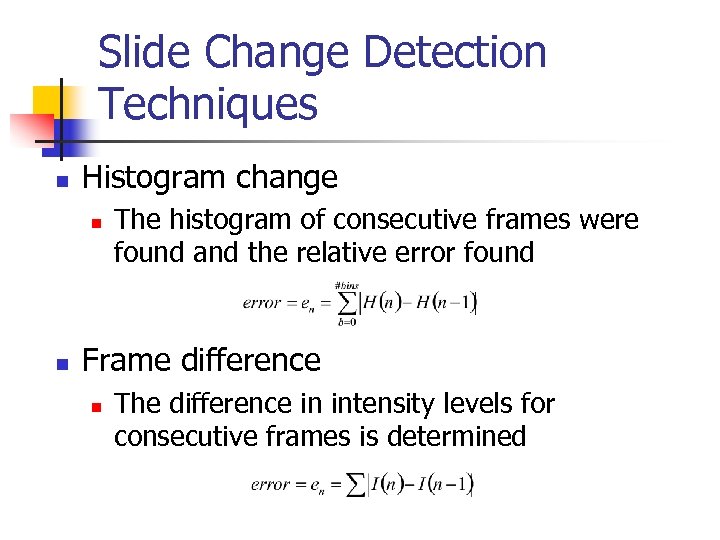
Slide Change Detection Techniques n Histogram change n n The histogram of consecutive frames were found and the relative error found Frame difference n The difference in intensity levels for consecutive frames is determined
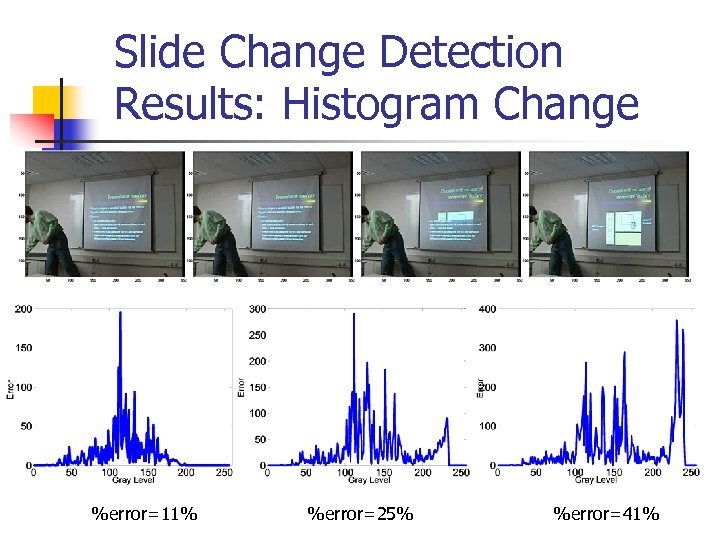
Slide Change Detection Results: Histogram Change %error=11% %error=25% %error=41%

Slide Change Detection Results: Frame Difference Error=8 Error=11 Error=20
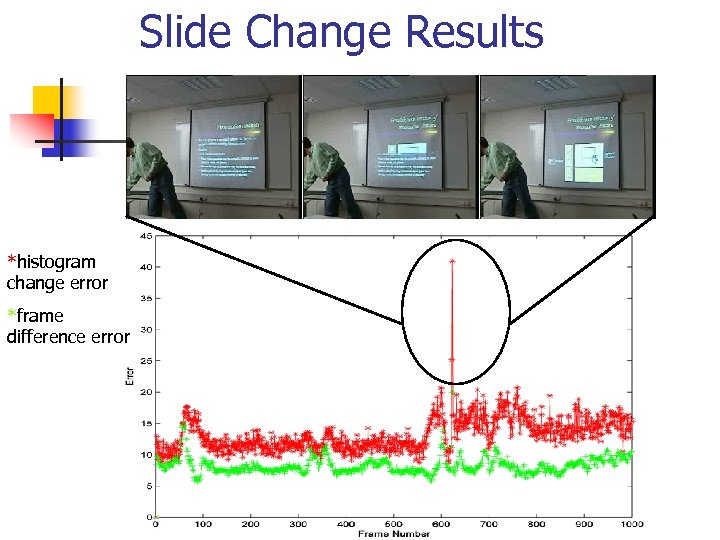
Slide Change Results *histogram change error *frame difference error
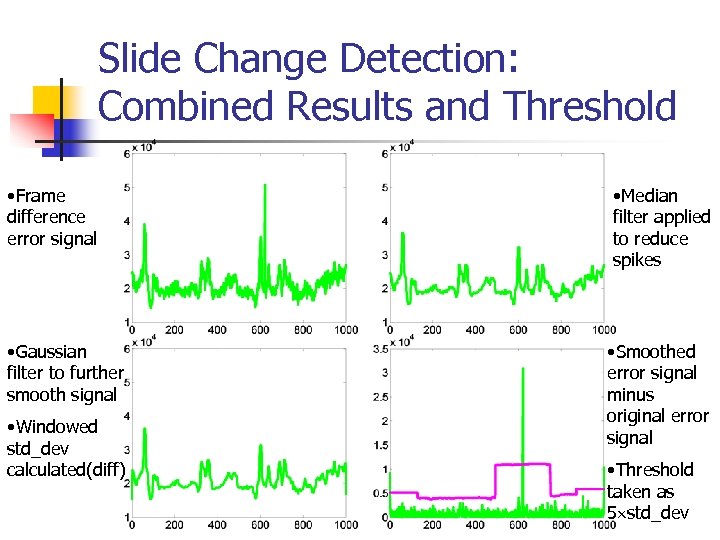
Slide Change Detection: Combined Results and Threshold • Frame difference error signal • Gaussian filter to further smooth signal • Windowed std_dev calculated(diff) • Median filter applied to reduce spikes • Smoothed error signal minus original error signal • Threshold taken as 5 std_dev

Slide Change: Occlusion Frame 1 Motion mask previous two frames Frame 2 Frame 3 Current Frame difference after masking
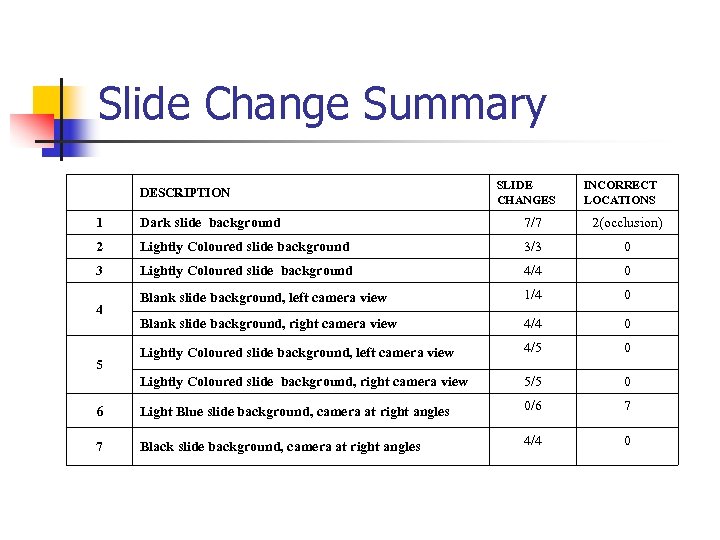
Slide Change Summary DESCRIPTION SLIDE CHANGES INCORRECT LOCATIONS 1 Dark slide background 7/7 2(occlusion) 2 Lightly Coloured slide background 3/3 0 3 Lightly Coloured slide background 4/4 0 Blank slide background, left camera view 1/4 0 Blank slide background, right camera view 4/4 0 Lightly Coloured slide background, left camera view 4/5 0 Lightly Coloured slide background, right camera view 5/5 0 6 Light Blue slide background, camera at right angles 0/6 7 7 Black slide background, camera at right angles 4/4 0 4 5

Slide Identification n Purpose: To obtain the sequence of the presentation Strategy: Slides can be identified by matching frame from video to ppt slide Techniques n n Warping of frame from video to ppt slide Displacement rectification Matching Penalty
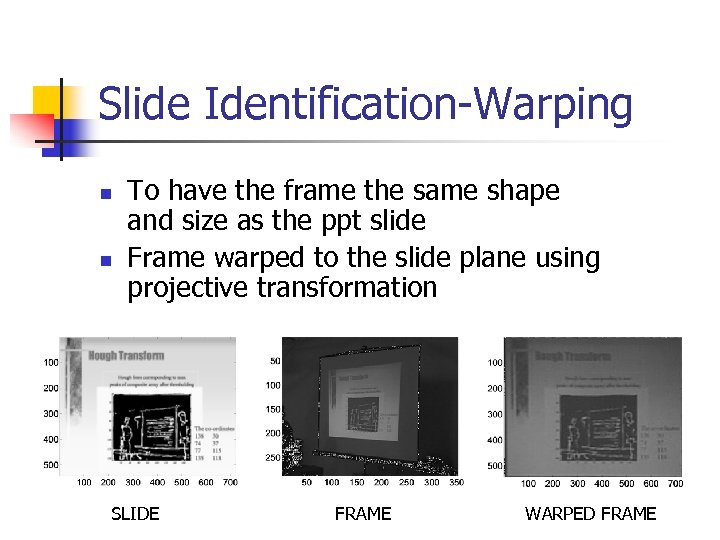
Slide Identification-Warping n n To have the frame the same shape and size as the ppt slide Frame warped to the slide plane using projective transformation SLIDE FRAME WARPED FRAME
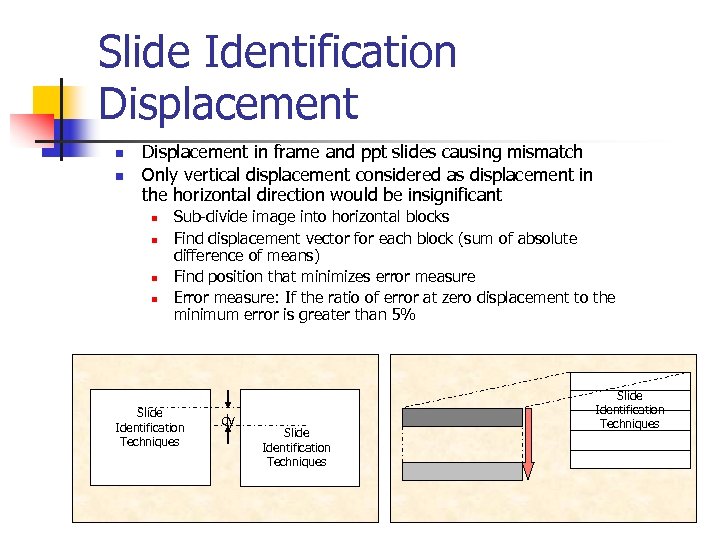
Slide Identification Displacement n n Displacement in frame and ppt slides causing mismatch Only vertical displacement considered as displacement in the horizontal direction would be insignificant n n Sub-divide image into horizontal blocks Find displacement vector for each block (sum of absolute difference of means) Find position that minimizes error measure Error measure: If the ratio of error at zero displacement to the minimum error is greater than 5% Slide Identification Techniques dy Slide Identification Techniques
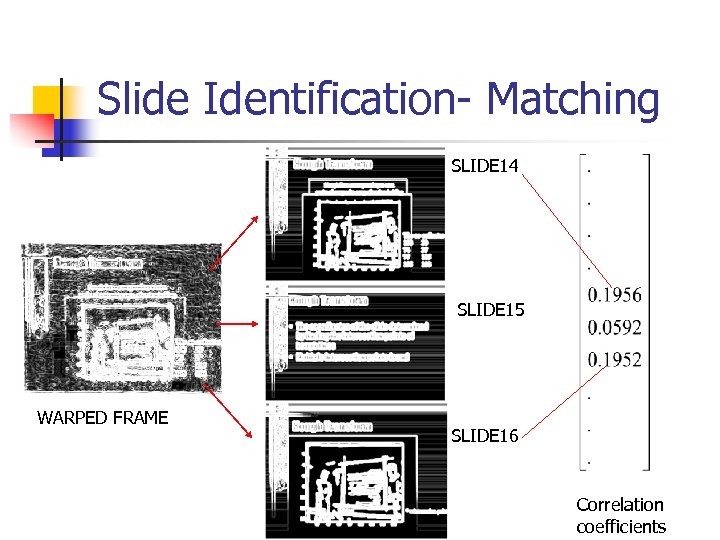
Slide Identification- Matching SLIDE 14 SLIDE 15 WARPED FRAME SLIDE 16 Correlation coefficients
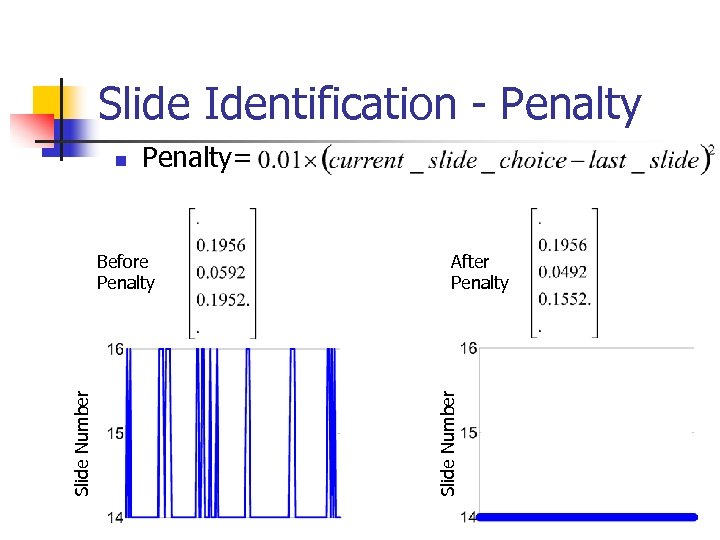
Slide Identification - Penalty= Slide Number Before Penalty After Penalty Slide Number n
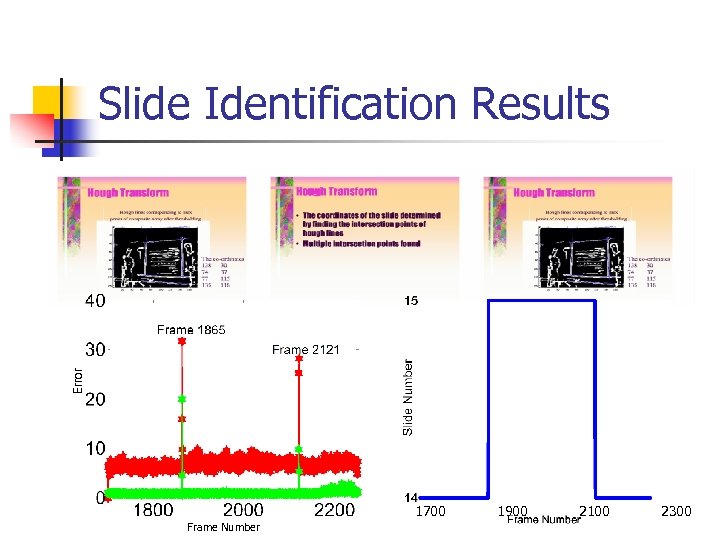
Error Slide Identification Results 1700 Frame Number 1900 2100 2300

Slide Identification: Occlusion n Four Different Presentations
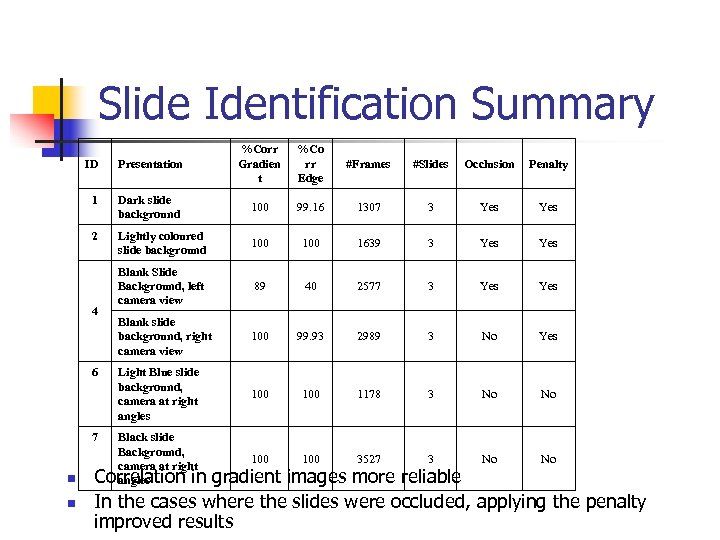
Slide Identification Summary ID Presentation %Corr Gradien t %Co rr Edge #Frames #Slides Occlusion Penalty 1 Dark slide background 100 99. 16 1307 3 Yes 2 Lightly coloured slide background 100 1639 3 Yes Blank Slide Background, left camera view 89 40 2577 3 Yes Blank slide background, right camera view 100 99. 93 2989 3 No Yes Light Blue slide background, camera at right angles 100 1178 3 No No 100 3527 3 No No 4 6 7 n n Black slide Background, camera at right Correlation in angles gradient images more reliable In the cases where the slides were occluded, applying the penalty improved results

Audio Analysis n Purpose: Audio content could also provide useful information about presentation. n n Portions of long silence Pitch of the speaker Speaker change points Detecting Boundaries of silence implemented

Silence Detection n Techniques n Short term Zero crossing rate n Short term energy n Ideally, zero crossing rate and average energy zero for silence
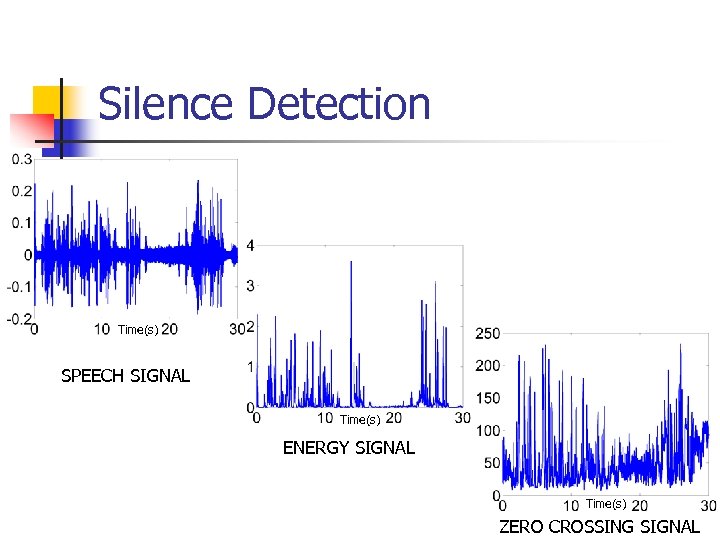
Silence Detection Time(s) SPEECH SIGNAL Time(s) ENERGY SIGNAL Time(s) ZERO CROSSING SIGNAL

Silence Detection-Thresholds n Zero crossing count and energy non-zero for silence n n n Assume first 100 ms of audio signal to be silence, find energy and zero crossing rate for this region Thresholds for energy and zero crossing taken as mean + 2 standard deviation Threshold for the minimum length of silence n n n Silent regions found for the entire audio signal The number of times the signal stays below the threshold is counted Threshold for length taken as mean + 4 standard deviation of the count values
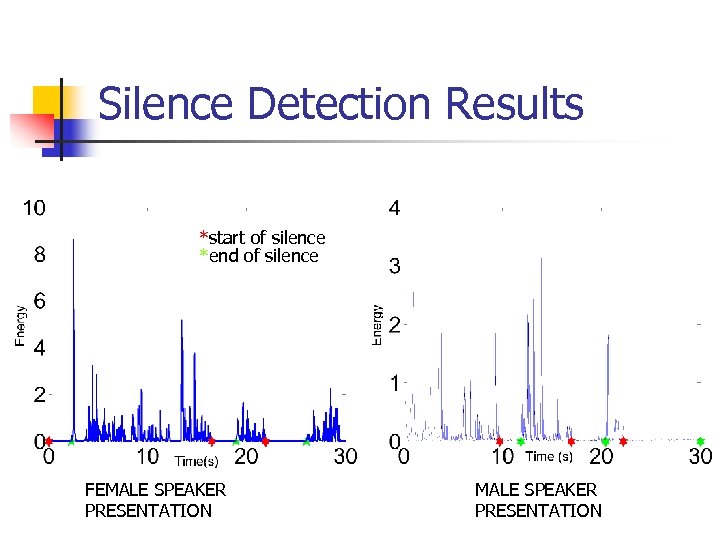
Silence Detection Results *start of silence *end of silence FEMALE SPEAKER PRESENTATION
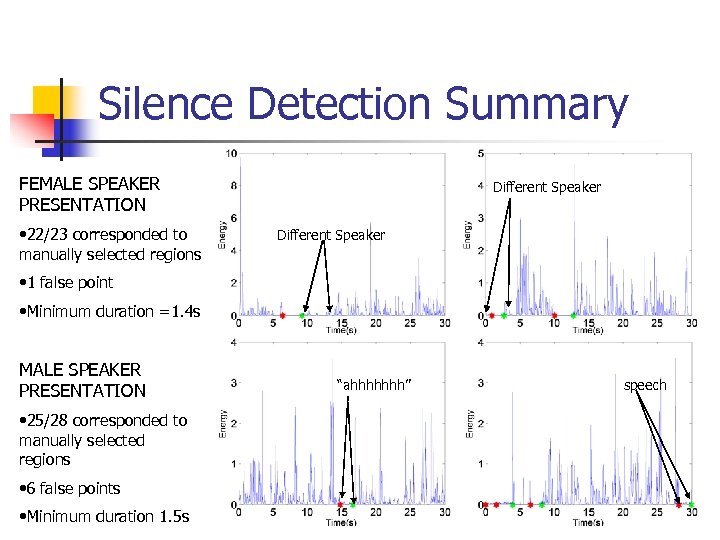
Silence Detection Summary FEMALE SPEAKER PRESENTATION • 22/23 corresponded to manually selected regions Different Speaker • 1 false point • Minimum duration =1. 4 s MALE SPEAKER PRESENTATION • 25/28 corresponded to manually selected regions • 6 false points • Minimum duration 1. 5 s “ahhhhhhh” speech

High Level Model–Hidden Markov Model n Purpose: To investigate Hidden Markov Model (HMM) and its application to: n Slide change detection, slide identification n HMM is a “doubly embedded stochastic process that is not observable (it is hidden), but can only be observed through another set of stochastic processes that produce the sequence of observations” (Rabiner 1989 in Tutorial on HMM)
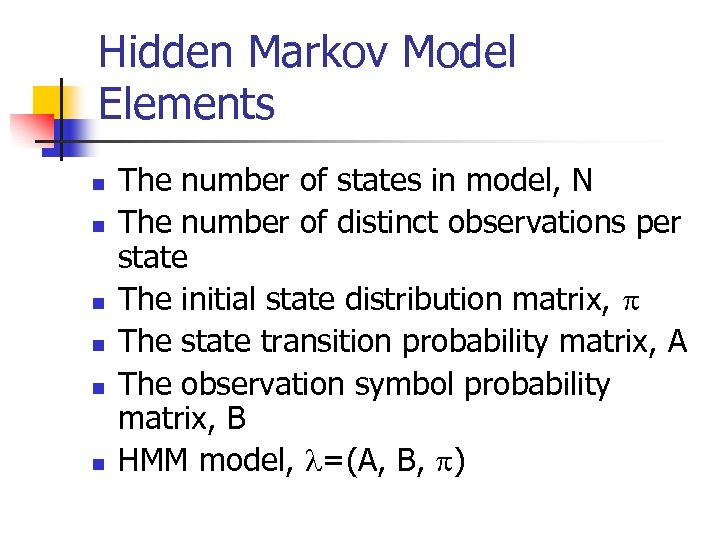
Hidden Markov Model Elements n n n The number of states in model, N The number of distinct observations per state The initial state distribution matrix, The state transition probability matrix, A The observation symbol probability matrix, B HMM model, =(A, B, )

HMM for Presentation n n The HMM have been applied to video but used to classify camera motion HMM for this presentation, applied to classify information content The model , is represented by the presentation The states would then correspond to the slides in the presentation The observation sequence would be the histograms from slide change detection or the correlation matrices from slide identification
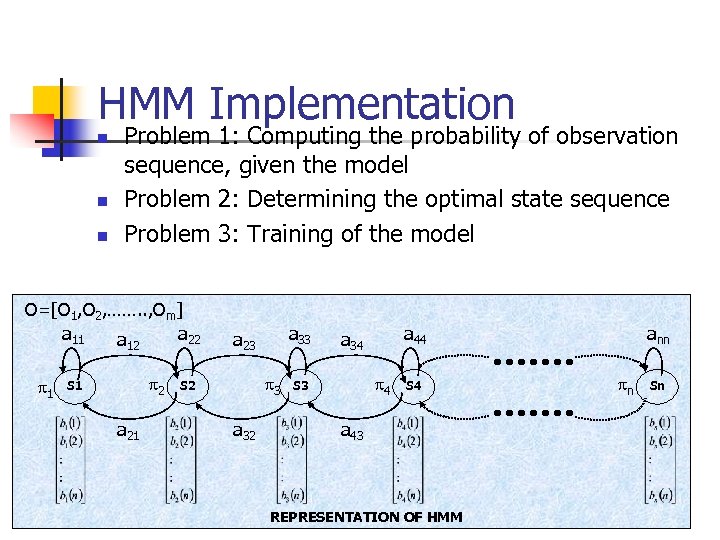
HMM Implementation n Problem 1: Computing the probability of observation sequence, given the model Problem 2: Determining the optimal state sequence Problem 3: Training of the model O=[O 1, O 2, ……. . , Om] a 11 a 22 a 12 1 2 S 1 a 21 a 33 a 23 3 S 2 a 32 a 44 a 34 4 S 3 S 4 a 43 REPRESENTATION OF HMM ann n Sn

Further Work n n n n Further exploration of HMM Exploring non ppt presentations Implementation and testing-user feedback Future expansions n n n Develop another HMM for Speaker change detection Keyword detection in speech Speech to text processing
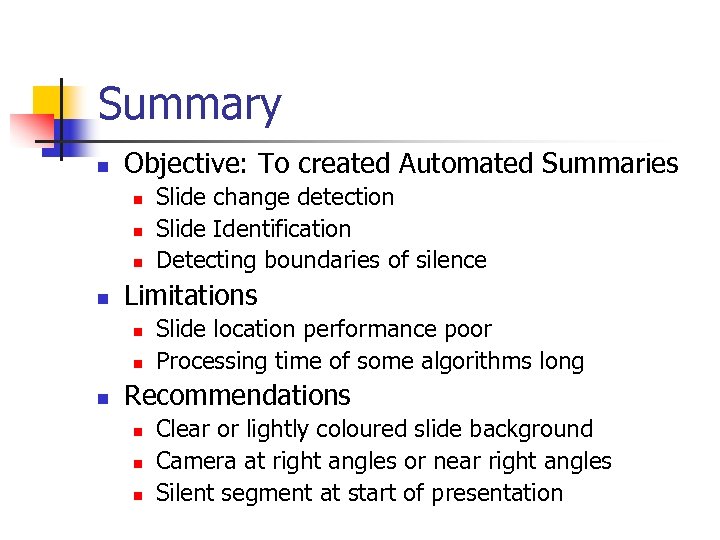
Summary n Objective: To created Automated Summaries n n Limitations n n n Slide change detection Slide Identification Detecting boundaries of silence Slide location performance poor Processing time of some algorithms long Recommendations n n n Clear or lightly coloured slide background Camera at right angles or near right angles Silent segment at start of presentation

Related Work n Microsoft research n n n Emphasis on minimizing length of presentation Slide change performed automatically by power point X Ju et al in IEEE transactions on circuits and systems for video technology Vol. 8, #5, Sep’ 98 n n Used motion estimation to detect slide change Sequencing was not achieved No audio analysis was performed Constraint in test samples

Acknowledgements n n n n Supervisors n Dr. Anil Kokaram n Dr. Cathy Radix Dr. Francis Asamoah The Multimedia Department, School of Education Colleagues n Niall Rea, Rozenn Dahyot & Vijaya Ragoonanan CPR 4 AG fund from campus Research and Publication Fund committee, School for Graduate Studies & Research, U. W. I. St Augustine Financial Support from Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Enterprise Ireland International Collaboration Grants 2001/02 and 2002/03
14115ca67ebf89fe115d3506b30bef00.ppt