c4a9b35012ec4f99bd2caba174e4a91e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Automated processes FW: ~ AFP: ATL: AM/ RP: ~ filament winding centrifugal casting automated fibre placement tape laying additive manufacture/ rapid prototyping pultrusion John Summerscales
Automated processes FW: ~ AFP: ATL: AM/ RP: ~ filament winding centrifugal casting automated fibre placement tape laying additive manufacture/ rapid prototyping pultrusion John Summerscales
 Filament winding
Filament winding
 Filament winding • continuous fibre reinforcements precisely positioned in a pre-determined pattern on a rotating mandrel (mould tool for filament winding) • normally computer numerically controlled (CNC) to permit highly automated production of axisymmetric components
Filament winding • continuous fibre reinforcements precisely positioned in a pre-determined pattern on a rotating mandrel (mould tool for filament winding) • normally computer numerically controlled (CNC) to permit highly automated production of axisymmetric components
 Filament winding • simple machine: just two axes rotation of the mandrel • translation of the feed eye on an axis parallel to the machine axis • • complexity characterised by the number of degrees of freedom: up to six separately controlled axes • usually three orthogonal and three rotational axes •
Filament winding • simple machine: just two axes rotation of the mandrel • translation of the feed eye on an axis parallel to the machine axis • • complexity characterised by the number of degrees of freedom: up to six separately controlled axes • usually three orthogonal and three rotational axes •
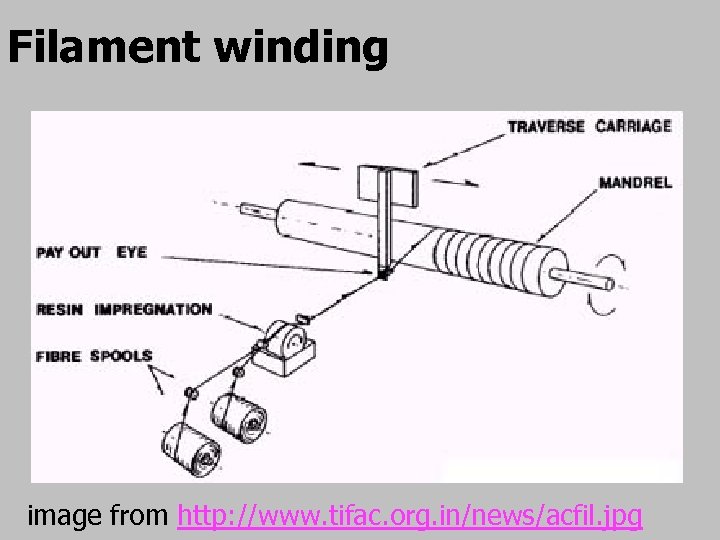 Filament winding image from http: //www. tifac. org. in/news/acfil. jpg
Filament winding image from http: //www. tifac. org. in/news/acfil. jpg
 Filament winding - tension • fibre tension is critical to the operation of a filament winding machine • normal to have fibre tensioners (closed-loop controlled servo-driven "dancers") • tension required depends on type of fibre • part diameter • winding pattern •
Filament winding - tension • fibre tension is critical to the operation of a filament winding machine • normal to have fibre tensioners (closed-loop controlled servo-driven "dancers") • tension required depends on type of fibre • part diameter • winding pattern •
 Filament winding - tension • fibre tension directly affects fibre volume fraction • void content • and, in turn, influences the strength and stiffness of the composite part. • • difficult to maintain tension on flat surfaces • axial winding not a preferred orientation on cylinders.
Filament winding - tension • fibre tension directly affects fibre volume fraction • void content • and, in turn, influences the strength and stiffness of the composite part. • • difficult to maintain tension on flat surfaces • axial winding not a preferred orientation on cylinders.
 Filament winding - impregnation • resin impregnation image from http: //www. pultrex. com/images/productimages/resin 2. jpg
Filament winding - impregnation • resin impregnation image from http: //www. pultrex. com/images/productimages/resin 2. jpg
 Filament winding - winding patterns • hoop (90º) a. k. a girth or circumferential winding angle is normally just below 90° degrees • each complete rotation of the mandrel shifts the fibre band to lie alongside the previous band. • • helical • complete fibre coverage without the band having to lie adjacent to that previously laid. • polar domed ends or spherical components • fibres constrained by bosses on each pole of the component. • • axial (0º) o beware: difficult to maintain fibre tension
Filament winding - winding patterns • hoop (90º) a. k. a girth or circumferential winding angle is normally just below 90° degrees • each complete rotation of the mandrel shifts the fibre band to lie alongside the previous band. • • helical • complete fibre coverage without the band having to lie adjacent to that previously laid. • polar domed ends or spherical components • fibres constrained by bosses on each pole of the component. • • axial (0º) o beware: difficult to maintain fibre tension
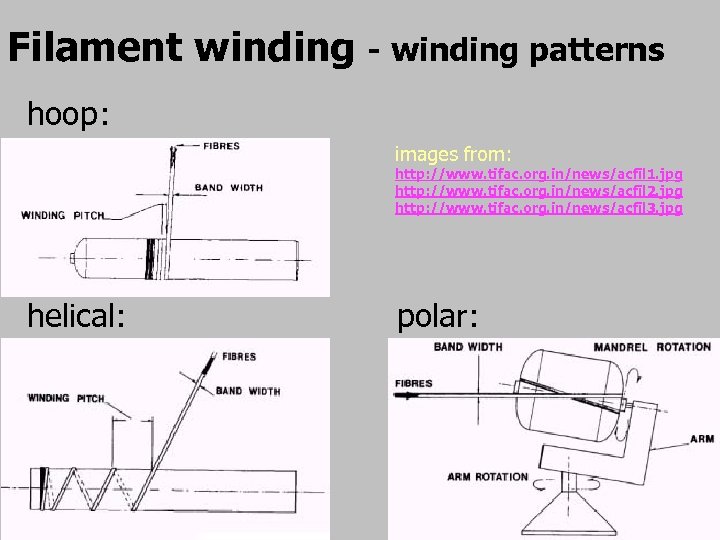 Filament winding - winding patterns hoop: images from: http: //www. tifac. org. in/news/acfil 1. jpg http: //www. tifac. org. in/news/acfil 2. jpg http: //www. tifac. org. in/news/acfil 3. jpg helical: polar:
Filament winding - winding patterns hoop: images from: http: //www. tifac. org. in/news/acfil 1. jpg http: //www. tifac. org. in/news/acfil 2. jpg http: //www. tifac. org. in/news/acfil 3. jpg helical: polar:
 Filament winding - winding pattern • Kevlar component image from http: //www. tifac. org. in/news/acfil 5. jpg
Filament winding - winding pattern • Kevlar component image from http: //www. tifac. org. in/news/acfil 5. jpg
 Filament winding - geodesic path • simplest fibre orientation is the geodesic path o assumes non-slip winding • once winding has commenced, fixed fibre path at any point dictated by the Clairaut angle ( r. sin a = constant) o where r is local radius, a is local angle • at bosses, a = arcsin (rb/r) o where rb = angle at the boss (polar opening) • exploiting friction, it is possible to achieve non-geodesic winding within limits.
Filament winding - geodesic path • simplest fibre orientation is the geodesic path o assumes non-slip winding • once winding has commenced, fixed fibre path at any point dictated by the Clairaut angle ( r. sin a = constant) o where r is local radius, a is local angle • at bosses, a = arcsin (rb/r) o where rb = angle at the boss (polar opening) • exploiting friction, it is possible to achieve non-geodesic winding within limits.
 Productivity • Hunting Engineering produced LAW 80 hand-launch missile tubes at one pair/four minutes using parallel machines cycling circa 20 mandrels • Stor. Hy FP 6 project developed eight-arm ring winding machine for hydrogen storage tanks • • LAW 80: https: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/LAW_80 Stor. Hy = Hydrogen Storage Systems for Automotive Application: http: //www. storhy. net/
Productivity • Hunting Engineering produced LAW 80 hand-launch missile tubes at one pair/four minutes using parallel machines cycling circa 20 mandrels • Stor. Hy FP 6 project developed eight-arm ring winding machine for hydrogen storage tanks • • LAW 80: https: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/LAW_80 Stor. Hy = Hydrogen Storage Systems for Automotive Application: http: //www. storhy. net/
 Lattice structures (anisogrid) • can be produced by partial coverage and careful choice of relative band positions image from Vasiliev et al, Composite Structures, 2001, 54(2 -3). • Geoform. TM communication masts, railway gantries, spray booms, etc
Lattice structures (anisogrid) • can be produced by partial coverage and careful choice of relative band positions image from Vasiliev et al, Composite Structures, 2001, 54(2 -3). • Geoform. TM communication masts, railway gantries, spray booms, etc
 Filament winding - applications • pressure vessels, storage tanks and pipes • rocket motors, launch tubes • Light Anti-armour Weapon (LAW) • Hunting Engineering made a nesting pair in 4 minutes with ~20 mandrels circulated through the machine and a continuous curing oven. • drive shafts • Entec “the world’s largest five-axis filament winding machine” for wind turbine blades • length 45. 7 m, diameter 8. 2 m, weight > 36 tonnes.
Filament winding - applications • pressure vessels, storage tanks and pipes • rocket motors, launch tubes • Light Anti-armour Weapon (LAW) • Hunting Engineering made a nesting pair in 4 minutes with ~20 mandrels circulated through the machine and a continuous curing oven. • drive shafts • Entec “the world’s largest five-axis filament winding machine” for wind turbine blades • length 45. 7 m, diameter 8. 2 m, weight > 36 tonnes.
 Centrifugal casting
Centrifugal casting
 Centrifugal casting • spray-up inside a rotating mould tool • previously discussed (lecture c 5)
Centrifugal casting • spray-up inside a rotating mould tool • previously discussed (lecture c 5)
 AFP: automated fibre placement ATL: automated tape laying
AFP: automated fibre placement ATL: automated tape laying
 AFP: automated fibre placement • multi-axis robot wet-winds fibre around a series of pins (or similar restraints within a mould) in a predetermined pattern. • not limited by geodesic paths • used to produce Geoform (lattice-work with coverage in specific bands) • better for thermoplastic matrix composites • on-line consolidation and cooling permit use without the requirement for the fibre restraints.
AFP: automated fibre placement • multi-axis robot wet-winds fibre around a series of pins (or similar restraints within a mould) in a predetermined pattern. • not limited by geodesic paths • used to produce Geoform (lattice-work with coverage in specific bands) • better for thermoplastic matrix composites • on-line consolidation and cooling permit use without the requirement for the fibre restraints.
 ATL: automated tape laying • computer-numerically controlled (CNC) technique laying prepreg reinforcement tape Cartesian framework for gross positioning (rather than a primarily rotational axis robot) • rotational freedoms close to the work-piece. • • used for thermoset or thermoplastic matrix • limited to flat or low curvature surfaces • high quality aerospace composites e. g. flight control surfaces and wing skins.
ATL: automated tape laying • computer-numerically controlled (CNC) technique laying prepreg reinforcement tape Cartesian framework for gross positioning (rather than a primarily rotational axis robot) • rotational freedoms close to the work-piece. • • used for thermoset or thermoplastic matrix • limited to flat or low curvature surfaces • high quality aerospace composites e. g. flight control surfaces and wing skins.
 Additive manufacture (rapid prototyping)
Additive manufacture (rapid prototyping)
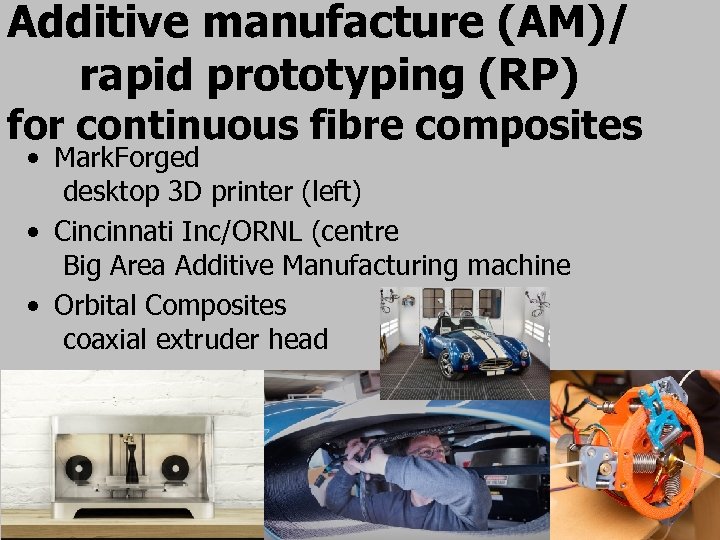 Additive manufacture (AM)/ rapid prototyping (RP) for continuous fibre composites • Mark. Forged desktop 3 D printer (left) • Cincinnati Inc/ORNL (centre Big Area Additive Manufacturing machine • Orbital Composites coaxial extruder head
Additive manufacture (AM)/ rapid prototyping (RP) for continuous fibre composites • Mark. Forged desktop 3 D printer (left) • Cincinnati Inc/ORNL (centre Big Area Additive Manufacturing machine • Orbital Composites coaxial extruder head
 Pultrusion
Pultrusion
 Pultrusion • continuous constant cross-section profile • normally thermoset (thermoplastic possible) impregnate with resin • pull through a heated die • • • resin shrinkage reduces friction in the die polyester easier to process than epoxy • tension control as in filament winding • post-die, profile air-cooled before gripped hand-over-hand hydraulic clamps • conveyor belt/caterpillar track systems. • • moving cut-off machine ("flying cutter")
Pultrusion • continuous constant cross-section profile • normally thermoset (thermoplastic possible) impregnate with resin • pull through a heated die • • • resin shrinkage reduces friction in the die polyester easier to process than epoxy • tension control as in filament winding • post-die, profile air-cooled before gripped hand-over-hand hydraulic clamps • conveyor belt/caterpillar track systems. • • moving cut-off machine ("flying cutter")
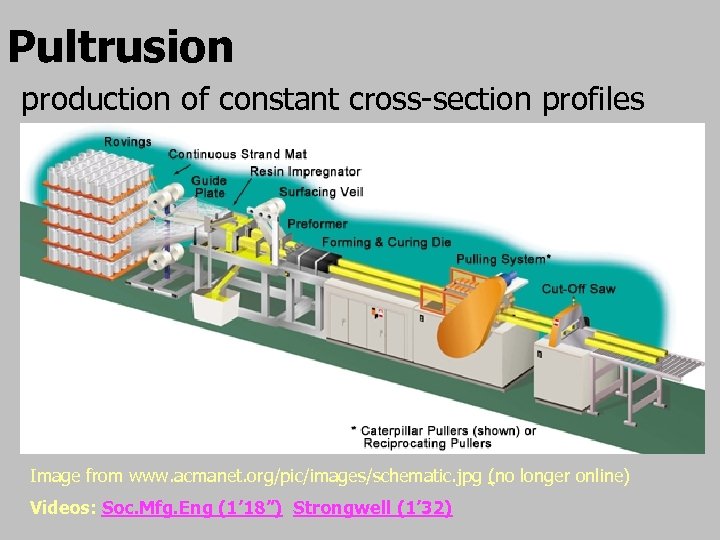 Pultrusion production of constant cross-section profiles Image from www. acmanet. org/pic/images/schematic. jpg (no longer online) Videos: Soc. Mfg. Eng (1’ 18”) Strongwell (1’ 32)
Pultrusion production of constant cross-section profiles Image from www. acmanet. org/pic/images/schematic. jpg (no longer online) Videos: Soc. Mfg. Eng (1’ 18”) Strongwell (1’ 32)
 Pultrusion - design • manuals by Quinn and Hartley • seek uniform thickness in order to achieve uniform cooling and hence minimise residual stress. • hollow profiles require a cantilevered mandrel to enter the die from the fibre-feed end.
Pultrusion - design • manuals by Quinn and Hartley • seek uniform thickness in order to achieve uniform cooling and hence minimise residual stress. • hollow profiles require a cantilevered mandrel to enter the die from the fibre-feed end.
 Pultrusion -applications • • • panels – beams – gratings – ladders tool handles - ski poles – kites electrical insulators and enclosures light poles - hand rails – roll-up doors 450 km of cable trays in the Channel Tunnel plus. . .
Pultrusion -applications • • • panels – beams – gratings – ladders tool handles - ski poles – kites electrical insulators and enclosures light poles - hand rails – roll-up doors 450 km of cable trays in the Channel Tunnel plus. . .
 Pultrusion (ACCS/Composolite®) • Advanced Composite Construction System • components: plank. . . . and connectors • used in Aberfeldy and Bonds Mill Lock bridges Images from. . www. ksci. com/graphics/aberf. gif. . and. . www. stroudwater. co. uk/cpsn/bonds%20 mill%20 bridge%203. jpg (no longer online)
Pultrusion (ACCS/Composolite®) • Advanced Composite Construction System • components: plank. . . . and connectors • used in Aberfeldy and Bonds Mill Lock bridges Images from. . www. ksci. com/graphics/aberf. gif. . and. . www. stroudwater. co. uk/cpsn/bonds%20 mill%20 bridge%203. jpg (no longer online)
 Pultrusion - variations of process • pulwinding/pulbraiding: fibres are wound onto the core of the pultrusion before it enters the heated die. • pulforming: the profile is subjected to post-die shaping.
Pultrusion - variations of process • pulwinding/pulbraiding: fibres are wound onto the core of the pultrusion before it enters the heated die. • pulforming: the profile is subjected to post-die shaping.
 Automated processes • FW: • • AFP: • ATL: filament winding centrifugal casting automated fibre placement tape laying • AM/ RP: additive manufacture/ rapid prototyping • pultrusion
Automated processes • FW: • • AFP: • ATL: filament winding centrifugal casting automated fibre placement tape laying • AM/ RP: additive manufacture/ rapid prototyping • pultrusion


