c872c9e26359131ccb75bccdc82c0dfb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
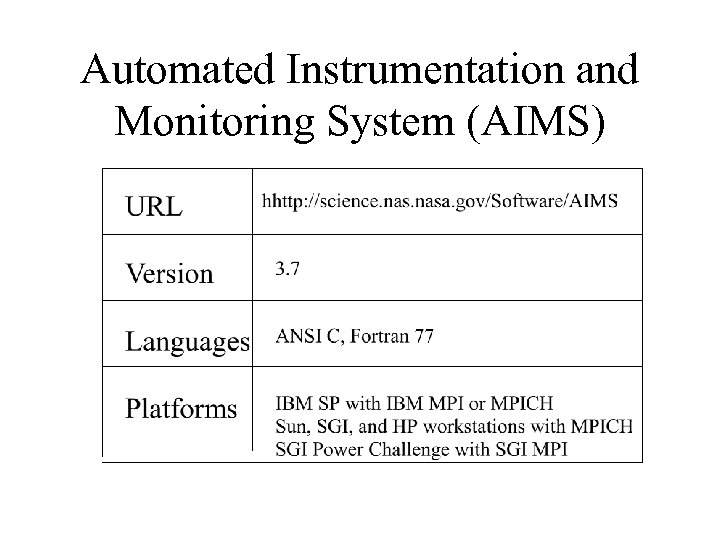 Automated Instrumentation and Monitoring System (AIMS)
Automated Instrumentation and Monitoring System (AIMS)
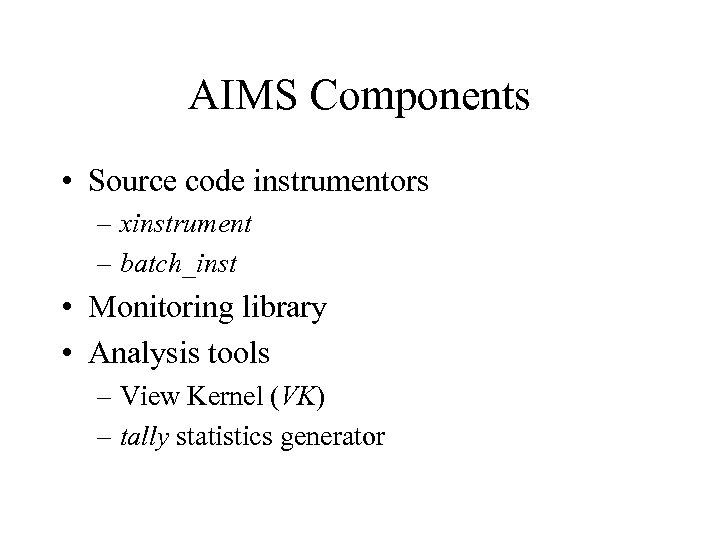 AIMS Components • Source code instrumentors – xinstrument – batch_inst • Monitoring library • Analysis tools – View Kernel (VK) – tally statistics generator
AIMS Components • Source code instrumentors – xinstrument – batch_inst • Monitoring library • Analysis tools – View Kernel (VK) – tally statistics generator
 xinstrument • GUI allows user to select specific source code constructs to be instrumented • Default is to instrument all communication routines • Other possibilities – All subroutines – All I/O – Enable by Type – Point and click on particular constructs in Construct Tree diagrams
xinstrument • GUI allows user to select specific source code constructs to be instrumented • Default is to instrument all communication routines • Other possibilities – All subroutines – All I/O – Enable by Type – Point and click on particular constructs in Construct Tree diagrams
 xinstrument (cont. ) • Regards source code as nested collection of constructs – conditionals – loops – subroutines – communication calls • Instrumented construct is replaced or surrounded by calls to AIMS monitor routines • Execution of instrumented construct generates timestamped event
xinstrument (cont. ) • Regards source code as nested collection of constructs – conditionals – loops – subroutines – communication calls • Instrumented construct is replaced or surrounded by calls to AIMS monitor routines • Execution of instrumented construct generates timestamped event
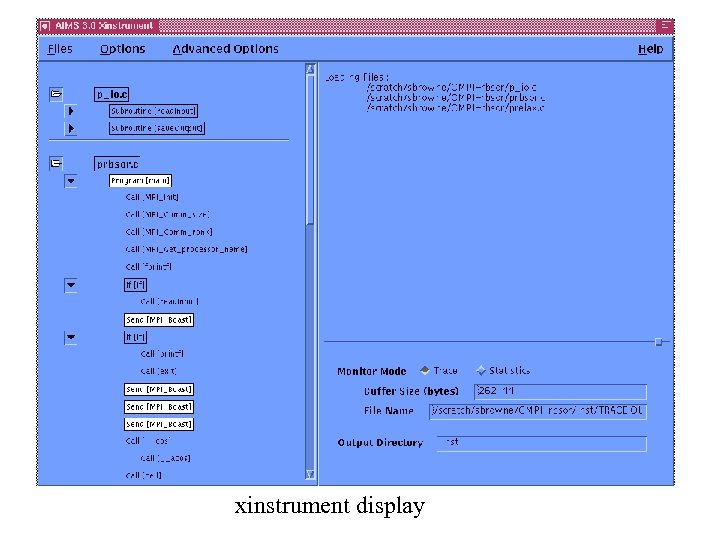 xinstrument display
xinstrument display
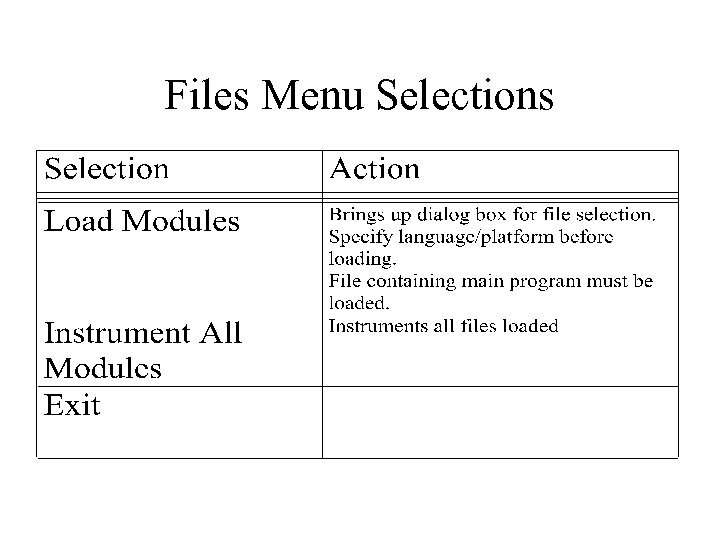 Files Menu Selections
Files Menu Selections
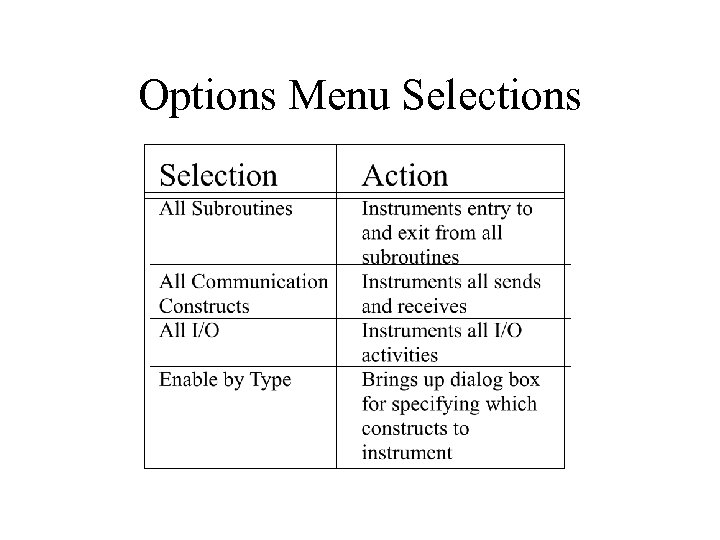 Options Menu Selections
Options Menu Selections
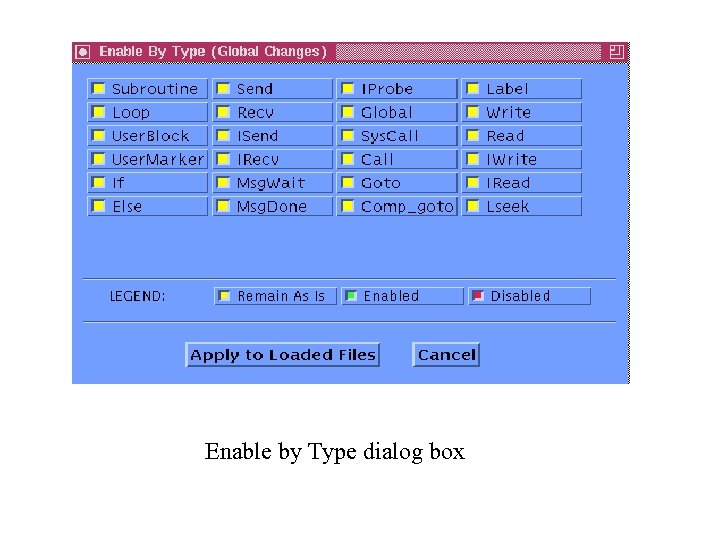 Enable by Type dialog box
Enable by Type dialog box
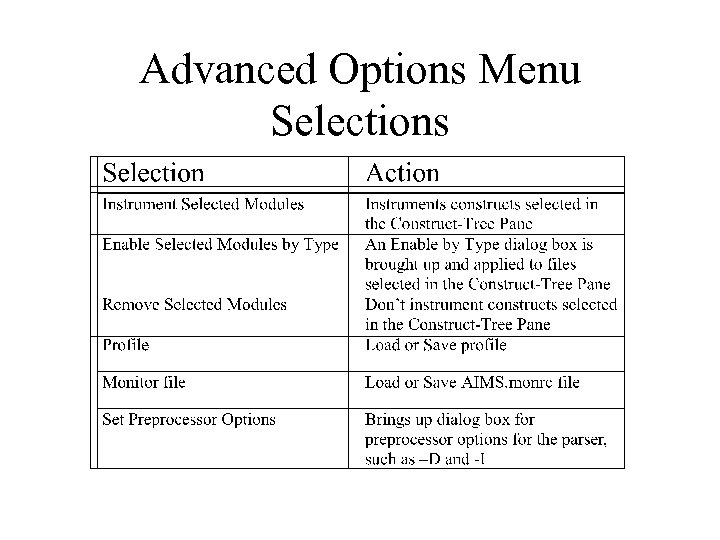 Advanced Options Menu Selections
Advanced Options Menu Selections
 Files created by xinstrument • The following files are created by xinstrument and placed in. /inst or designated output directory – Instrumented source code – AIMS. monrc - parameters from Settings pane plus other options – Application database • default name is APPL_DB • Stores information about static structure of application • Used by analysis tools to relate traced events to Instrumented constructs • Incorporated at beginning of trace file – Profile • Table of flags, one for each construct in The application database • Can be edited to change instrumentation
Files created by xinstrument • The following files are created by xinstrument and placed in. /inst or designated output directory – Instrumented source code – AIMS. monrc - parameters from Settings pane plus other options – Application database • default name is APPL_DB • Stores information about static structure of application • Used by analysis tools to relate traced events to Instrumented constructs • Incorporated at beginning of trace file – Profile • Table of flags, one for each construct in The application database • Can be edited to change instrumentation
![batch_inst • Command-line instrumentor batch_inst [-options] [filenames] where options include: batch_inst • Command-line instrumentor batch_inst [-options] [filenames] where options include:](https://present5.com/presentation/c872c9e26359131ccb75bccdc82c0dfb/image-11.jpg) batch_inst • Command-line instrumentor batch_inst [-options] [filenames] where options include:
batch_inst • Command-line instrumentor batch_inst [-options] [filenames] where options include:
 Compiling and Running Instrumented Code • Copy necessary files to inst directory – Makefile – Header files – Source files not instrumented – Input files
Compiling and Running Instrumented Code • Copy necessary files to inst directory – Makefile – Header files – Source files not instrumented – Input files
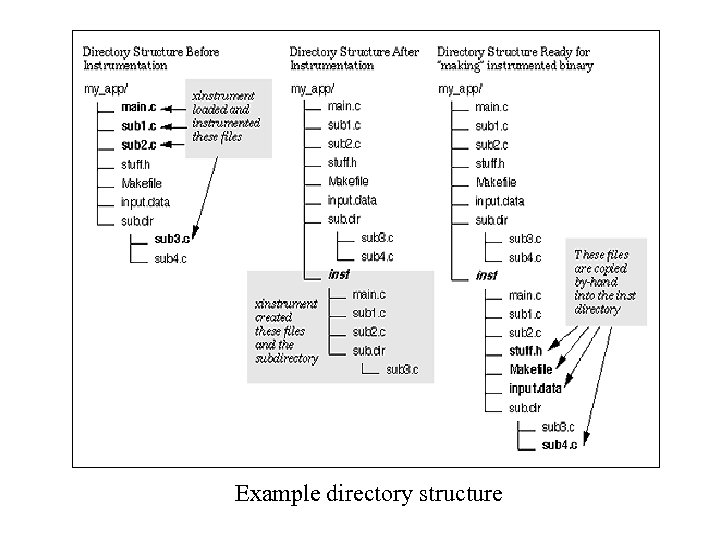 Example directory structure
Example directory structure
 Compiling and Running (cont. ) • Link with AIMS MPI monitor library MON_LIB = $(AIMS_DIR)/lib app: $(F 77) -o app_program $(APP_OBJS) $(MON_LIB)/mpilib. a • Set $AIMS_TMP_DIR environment variable to location to store local trace files • Make sure AIMS scripts and executables are in your path • Per-process trace files are automatically collected and merged at end of execution
Compiling and Running (cont. ) • Link with AIMS MPI monitor library MON_LIB = $(AIMS_DIR)/lib app: $(F 77) -o app_program $(APP_OBJS) $(MON_LIB)/mpilib. a • Set $AIMS_TMP_DIR environment variable to location to store local trace files • Make sure AIMS scripts and executables are in your path • Per-process trace files are automatically collected and merged at end of execution
 Visualizing Trace Files with VK • View Kernel (VK) animates a trace file • VCR-like controls for tracefile playback • Can set breakpoints by time or in specific source code constructs • Source code click-back capability • Timeline display • Spokes view animates messages passed between tasks
Visualizing Trace Files with VK • View Kernel (VK) animates a trace file • VCR-like controls for tracefile playback • Can set breakpoints by time or in specific source code constructs • Source code click-back capability • Timeline display • Spokes view animates messages passed between tasks
 Timeline Display • Toggles between three different views • Over. VIEW – Horizontal bars represent tasks – Colors represent different instrumented subroutines – White space indicates task is blocked waiting to complete send or receive – XX pattern indicates time spent writing AIMS trace files to disk – Lines between bars represent messages transmitted between ta. Sks – Use keystroke and click combinations to get more information
Timeline Display • Toggles between three different views • Over. VIEW – Horizontal bars represent tasks – Colors represent different instrumented subroutines – White space indicates task is blocked waiting to complete send or receive – XX pattern indicates time spent writing AIMS trace files to disk – Lines between bars represent messages transmitted between ta. Sks – Use keystroke and click combinations to get more information
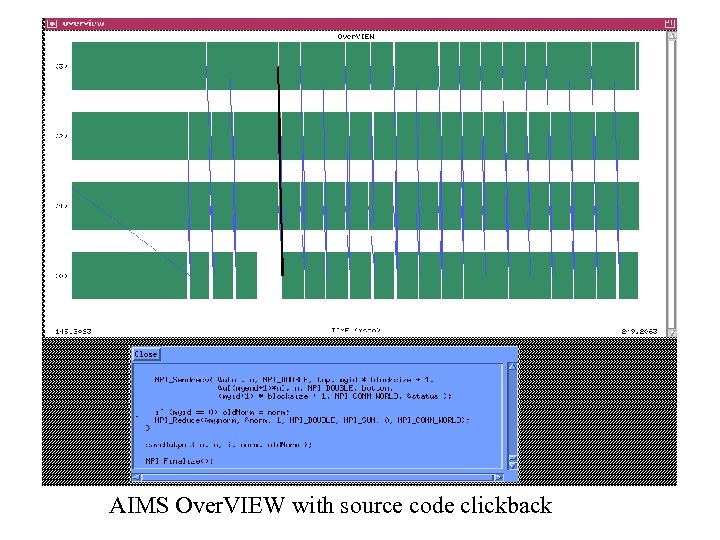 AIMS Over. VIEW with source code clickback
AIMS Over. VIEW with source code clickback
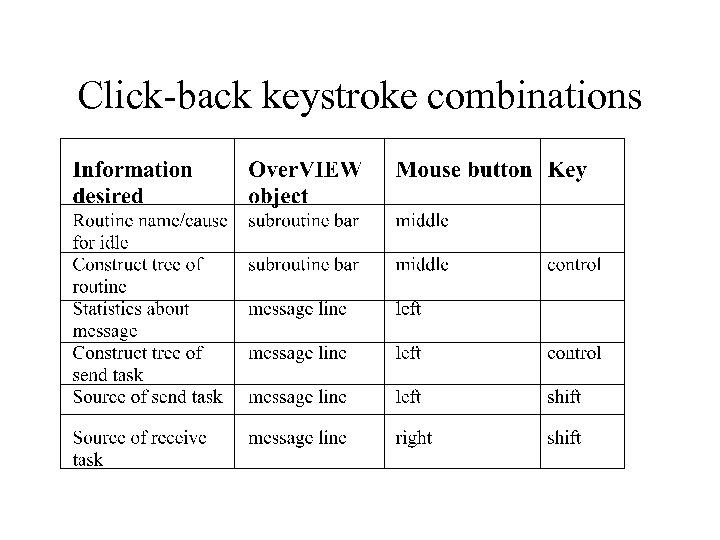 Click-back keystroke combinations
Click-back keystroke combinations
 Timeline Display (cont. ) • I/Over. VIEW – Colored bars indicate read, write, seek, etc. – Height of bar represents size of message • Msg. VIEW – Idle time shown with two colors, one for send idling and one for receive idling – Time spent computing shown as white space – Message lines – Height of bar represents message size
Timeline Display (cont. ) • I/Over. VIEW – Colored bars indicate read, write, seek, etc. – Height of bar represents size of message • Msg. VIEW – Idle time shown with two colors, one for send idling and one for receive idling – Time spent computing shown as white space – Message lines – Height of bar represents message size
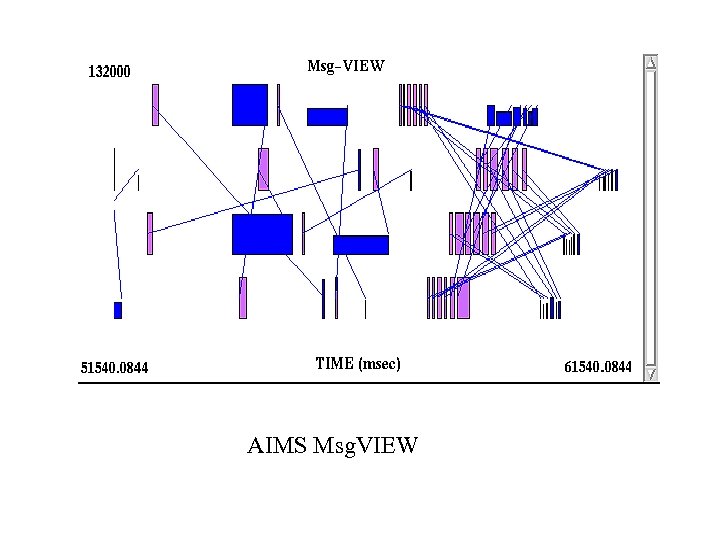 AIMS Msg. VIEW
AIMS Msg. VIEW
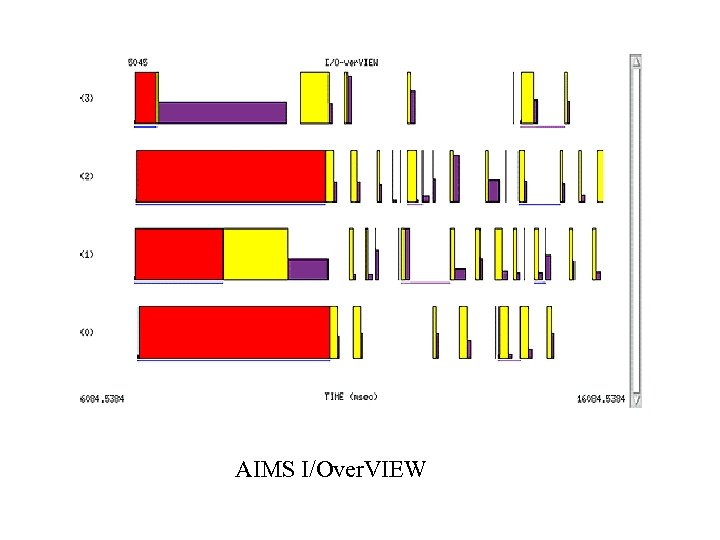 AIMS I/Over. VIEW
AIMS I/Over. VIEW
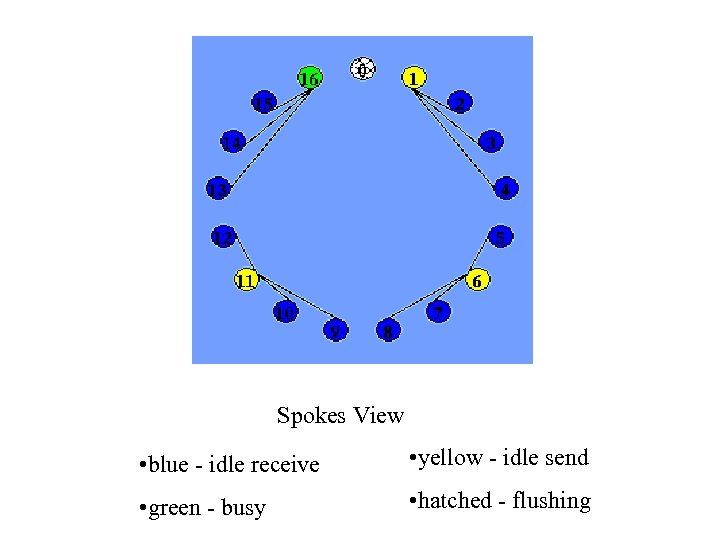 Spokes View • blue - idle receive • yellow - idle send • green - busy • hatched - flushing
Spokes View • blue - idle receive • yellow - idle send • green - busy • hatched - flushing
 Controlling Scale and Speed of Playback • No scrolling or zooming capabilities • Set jump factor between 0 and 1 to speed up animation • Set pause times or breakpoints to slow down animation • Set scale to view larger or smaller time interval (default is 100 milliseconds)
Controlling Scale and Speed of Playback • No scrolling or zooming capabilities • Set jump factor between 0 and 1 to speed up animation • Set pause times or breakpoints to slow down animation • Set scale to view larger or smaller time interval (default is 100 milliseconds)
 tally • Processes trace file to produce resource utilization statistics on node-by-node and routine-by-routine basis • tally output can be input to statistical drawing packages such as Excel or Wing. Z
tally • Processes trace file to produce resource utilization statistics on node-by-node and routine-by-routine basis • tally output can be input to statistical drawing packages such as Excel or Wing. Z
![tally [options] [sorted tracefile] where options include: tally [options] [sorted tracefile] where options include:](https://present5.com/presentation/c872c9e26359131ccb75bccdc82c0dfb/image-25.jpg) tally [options] [sorted tracefile] where options include:
tally [options] [sorted tracefile] where options include:
 tally output - tally. summary • Information for each procedure/function: – – – busy time: time spent performing useful work global blocking: time spent in global blocking operation send blocking: time spent in send operation receive blocking: time spent in receive operation life time: exclusive time percentage communication: percentage of total execution time spent in communication – communication index: time spent in routine with respect to total time of program, as well as percentage of time spent in communication in this routine
tally output - tally. summary • Information for each procedure/function: – – – busy time: time spent performing useful work global blocking: time spent in global blocking operation send blocking: time spent in send operation receive blocking: time spent in receive operation life time: exclusive time percentage communication: percentage of total execution time spent in communication – communication index: time spent in routine with respect to total time of program, as well as percentage of time spent in communication in this routine
 tally. summary (cont. ) • Information for each node (and routine): – busy time – global blocking – send blocking – recv blocking – percentage communication
tally. summary (cont. ) • Information for each node (and routine): – busy time – global blocking – send blocking – recv blocking – percentage communication
 tally output - ncpu. summary • NCPU for a given subroutine and a given k is the amount of CPU time used by that subroutine when k processors are busy, divided by k. • Routine Concurrency - amount of time spent by each subroutine when k copies were executing simultaneously (indicates degree to which each routine was parallelized)
tally output - ncpu. summary • NCPU for a given subroutine and a given k is the amount of CPU time used by that subroutine when k processors are busy, divided by k. • Routine Concurrency - amount of time spent by each subroutine when k copies were executing simultaneously (indicates degree to which each routine was parallelized)
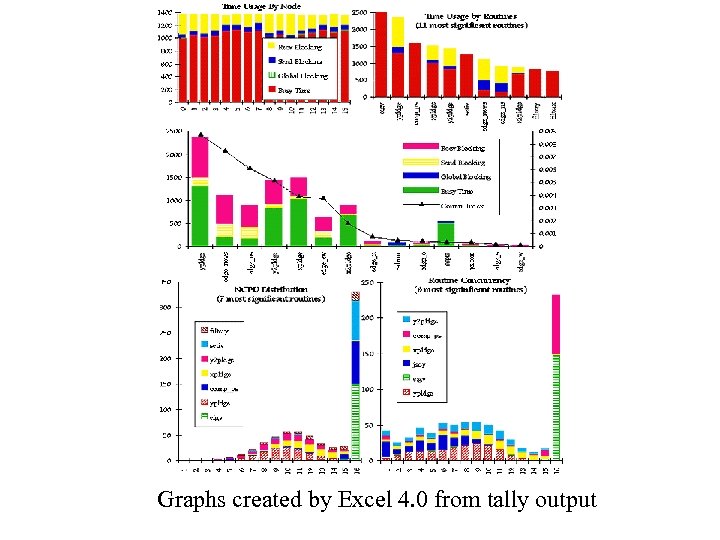 Graphs created by Excel 4. 0 from tally output
Graphs created by Excel 4. 0 from tally output


