614c3bc2c5c7699916802457618f67a8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Automated External Defibrillation

“Chain of Survival” • Early access • Early CPR • Early defibrillation • Early advanced life support

Defibrillation is “Part of BLS” • Basic Life Support includes CPR and defibrillation • Early defibrillation with an automated external defibrillator (AED) has established benefit • The principle of early defibrillation suggests that the first person to arrive at the scene of a cardiac arrest should have a defibrillator • This principle is now internationally accepted Guidelines 2000 for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care p. I-68
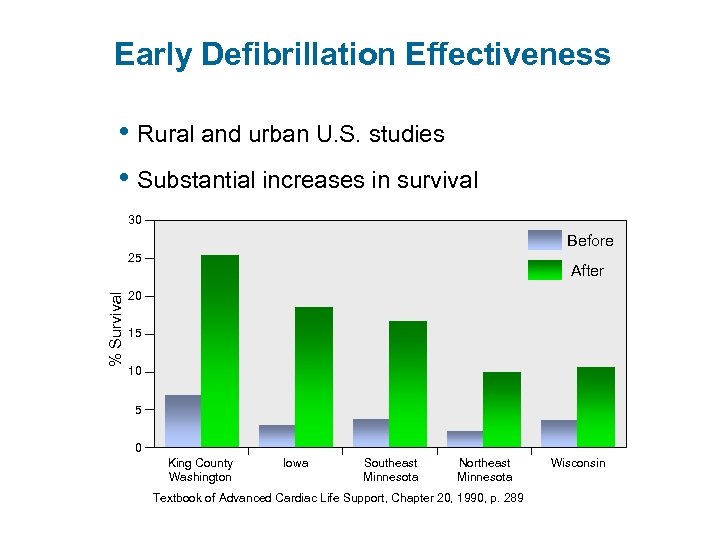
Early Defibrillation Effectiveness • Rural and urban U. S. studies • Substantial increases in survival 30 Before % Survival 25 After 20 15 10 5 0 King County Washington Iowa Southeast Minnesota Northeast Minnesota Textbook of Advanced Cardiac Life Support, Chapter 20, 1990, p. 289 Wisconsin
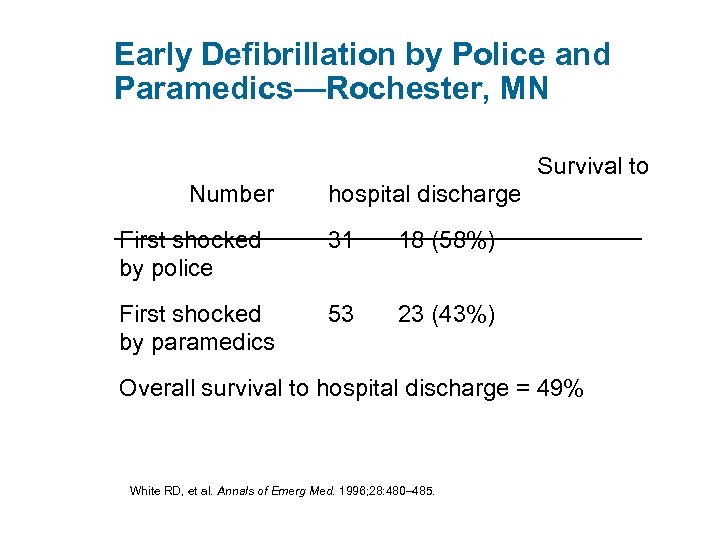
Early Defibrillation by Police and Paramedics—Rochester, MN Survival to Number hospital discharge First shocked by police 31 18 (58%) First shocked by paramedics 53 23 (43%) Overall survival to hospital discharge = 49% White RD, et al. Annals of Emerg Med. 1996; 28: 480– 485.
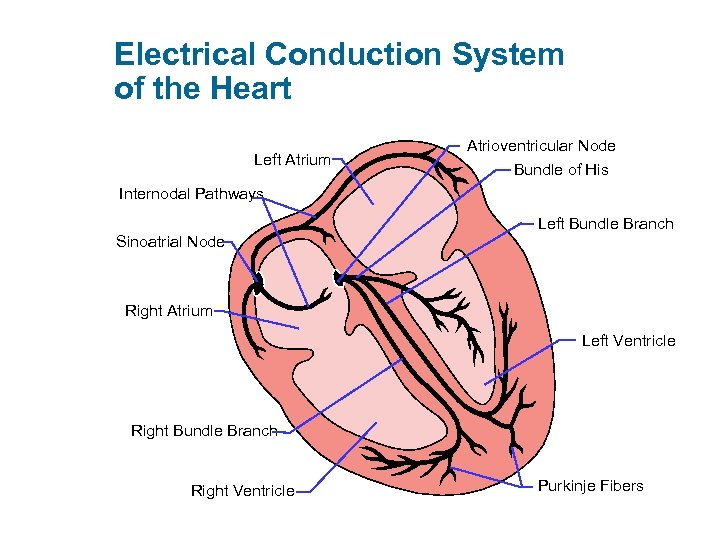
Electrical Conduction System of the Heart Left Atrium Atrioventricular Node Bundle of His Internodal Pathways Sinoatrial Node Left Bundle Branch Right Atrium Left Ventricle Right Bundle Branch Right Ventricle Purkinje Fibers
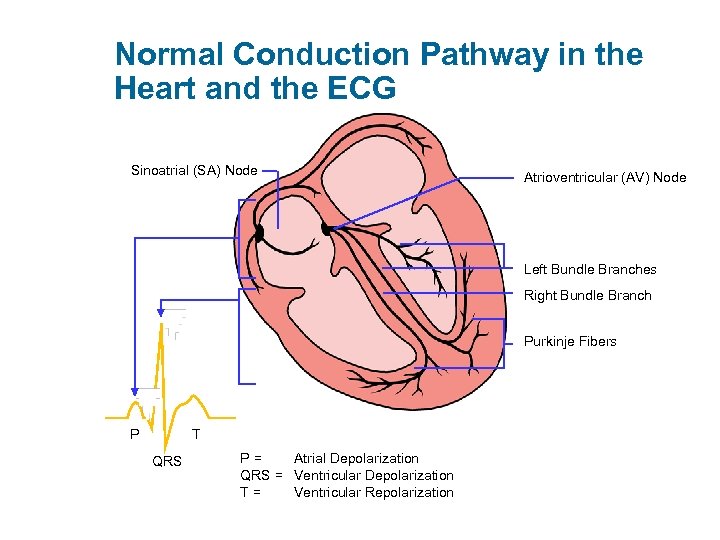
Normal Conduction Pathway in the Heart and the ECG Sinoatrial (SA) Node Atrioventricular (AV) Node Left Bundle Branches Right Bundle Branch Purkinje Fibers P T QRS P= Atrial Depolarization QRS = Ventricular Depolarization T= Ventricular Repolarization
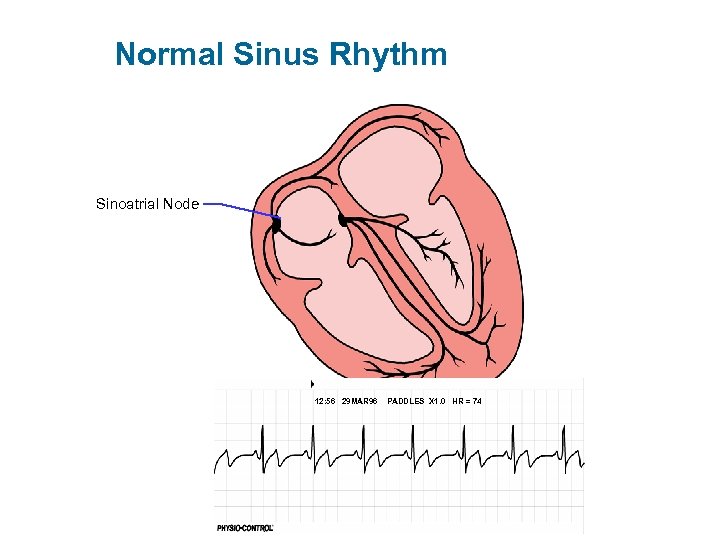
Normal Sinus Rhythm Sinoatrial Node 12: 56 29 MAR 96 PADDLES X 1. 0 HR = 74
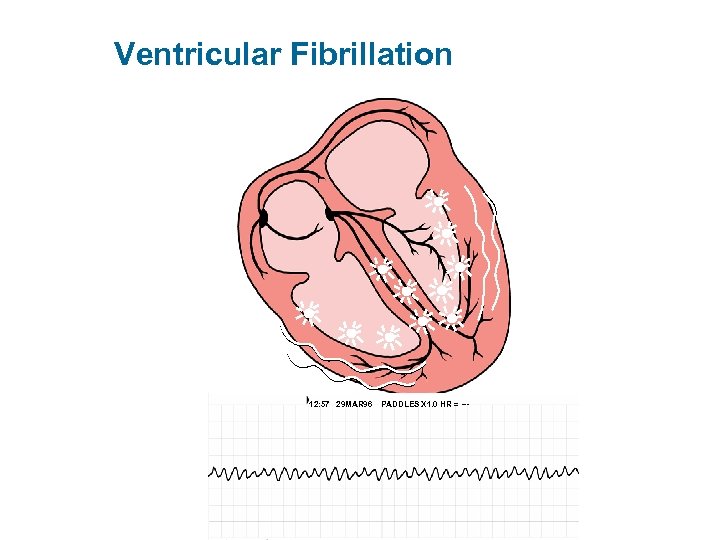
Ventricular Fibrillation 12: 57 29 MAR 96 PADDLES X 1. 0 HR = ---
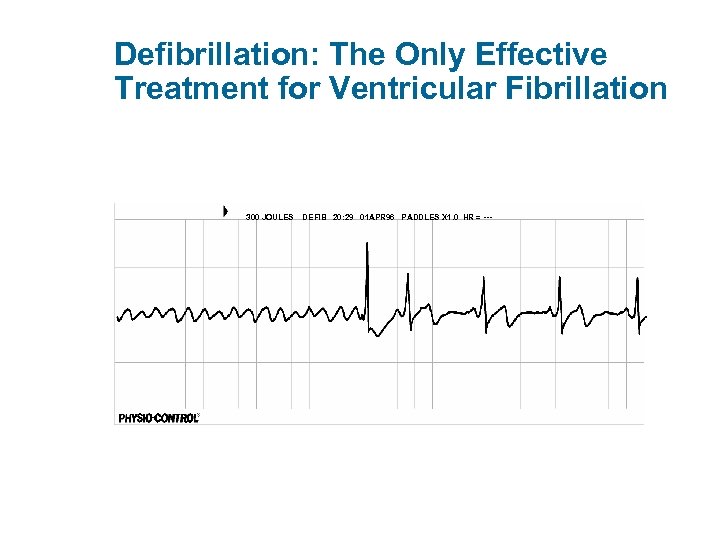
Defibrillation: The Only Effective Treatment for Ventricular Fibrillation 300 JOULES DEFIB 20: 29 01 APR 96 PADDLES X 1. 0 HR = ---

“Thanks, I needed that!”

Why Early Defibrillation? • VF most frequent initial rhythm in sudden cardiac arrest • Defibrillation most effective treatment • Probability of defibrillation success diminishes with time • VF tends to rapidly deteriorate into asystole Textbook of Advanced Cardiac Life Support, Chapter 20, 1990; p. 287.
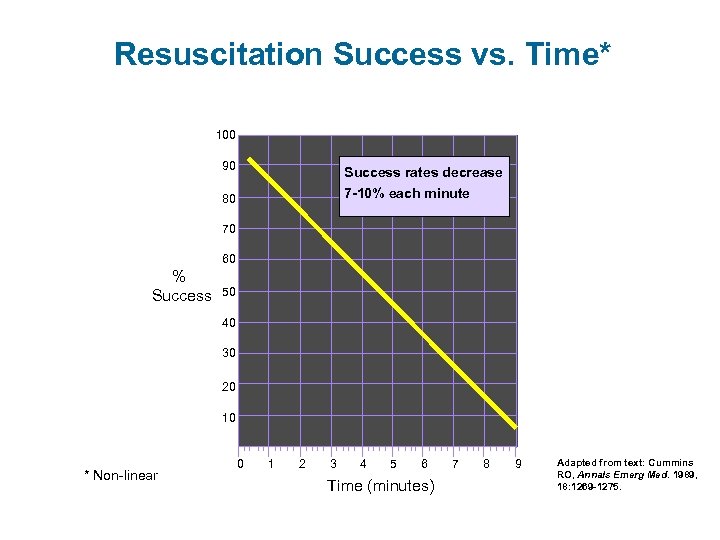
Resuscitation Success vs. Time* 100 90 Success rates decrease 7 -10% each minute 80 70 60 % Success 50 40 30 20 10 * Non-linear 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Time (minutes) 7 8 9 Adapted from text: Cummins RO, Annals Emerg Med. 1989, 18: 1269 -1275.
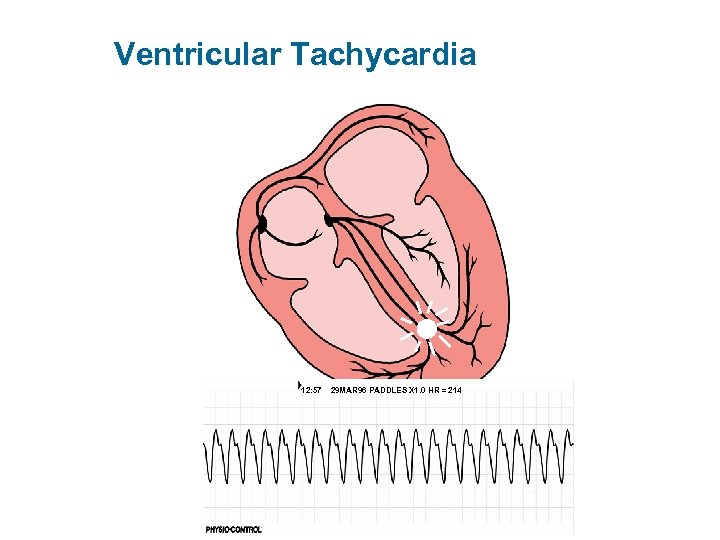
Ventricular Tachycardia 12: 57 29 MAR 96 PADDLES X 1. 0 HR = 214
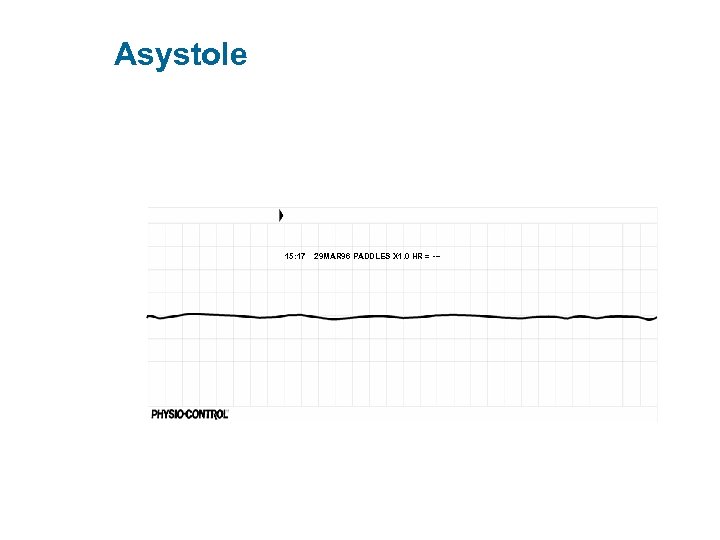
Asystole 15: 17 29 MAR 96 PADDLES X 1. 0 HR = ---
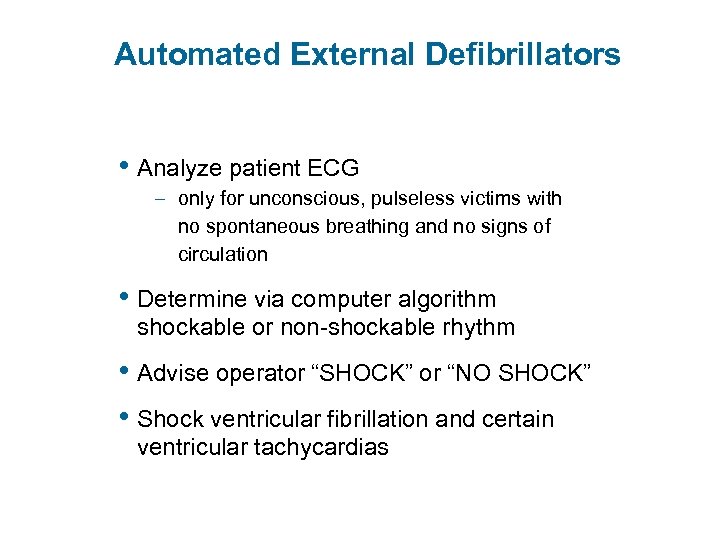
Automated External Defibrillators • Analyze patient ECG – only for unconscious, pulseless victims with no spontaneous breathing and no signs of circulation • Determine via computer algorithm shockable or non-shockable rhythm • Advise operator “SHOCK” or “NO SHOCK” • Shock ventricular fibrillation and certain ventricular tachycardias

LIFEPAK® 500 Automated External Defibrillators

Defibrillation Electrode Placement Anterior Lateral Anterior-lateral placement

Next time, remove his shirt!
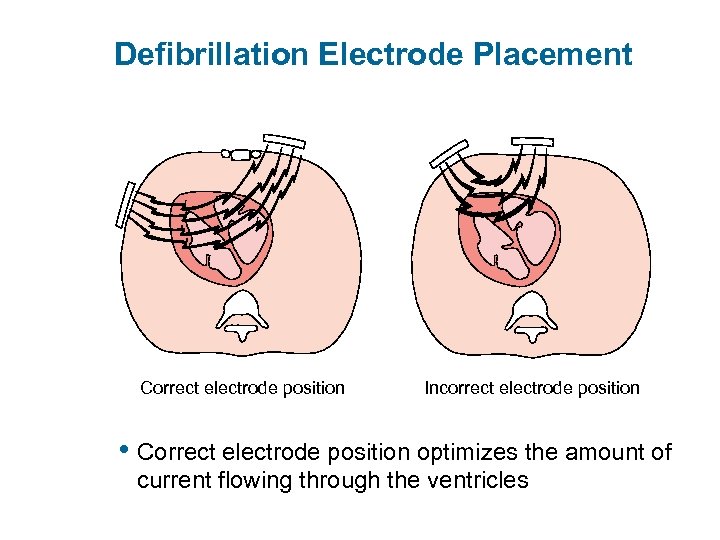
Defibrillation Electrode Placement Correct electrode position Incorrect electrode position • Correct electrode position optimizes the amount of current flowing through the ventricles

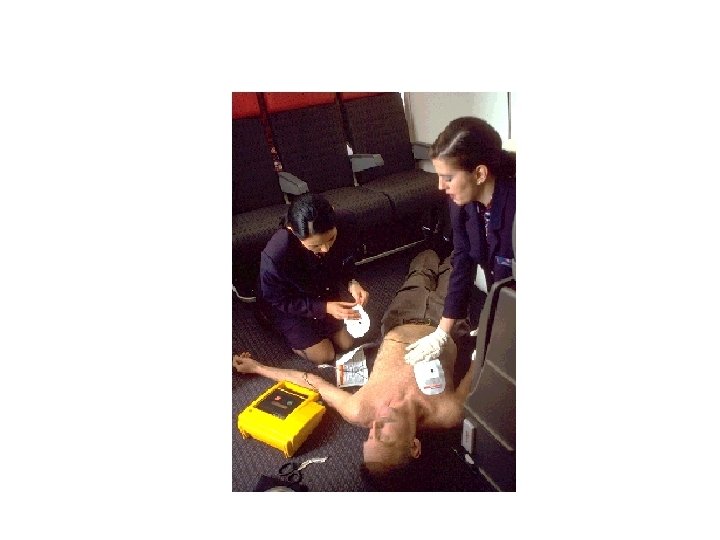
How to Defibrillate • Verify the victim is unconscious, not breathing, without a pulse or signs of circulation • Turn on AED and attach electrodes • ANALYZE heart rhythm • Follow the voice prompts and screen messages

Safety First • Attach the defibrillator only to someone not breathing and without a pulse or signs of circulation • Make sure no one is touching the victim • Be sure the electrodes are firmly adhered to the victim’s chest • Move oxygen away from the rescue effort before defibrillation

You should have said “clear”!

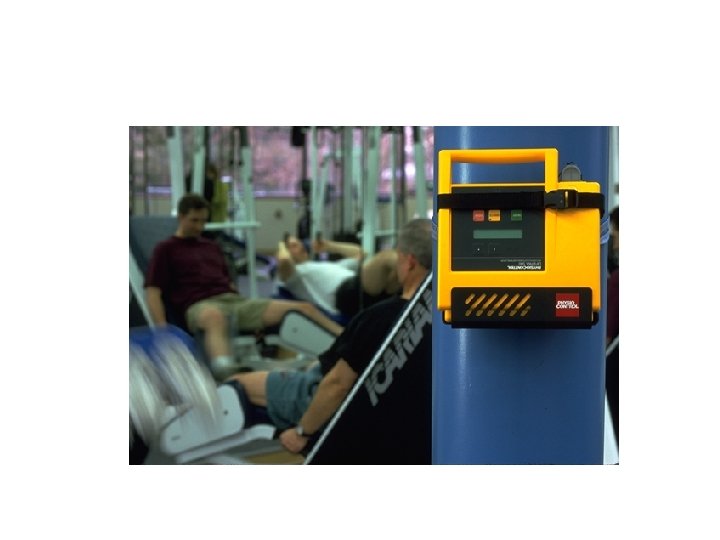
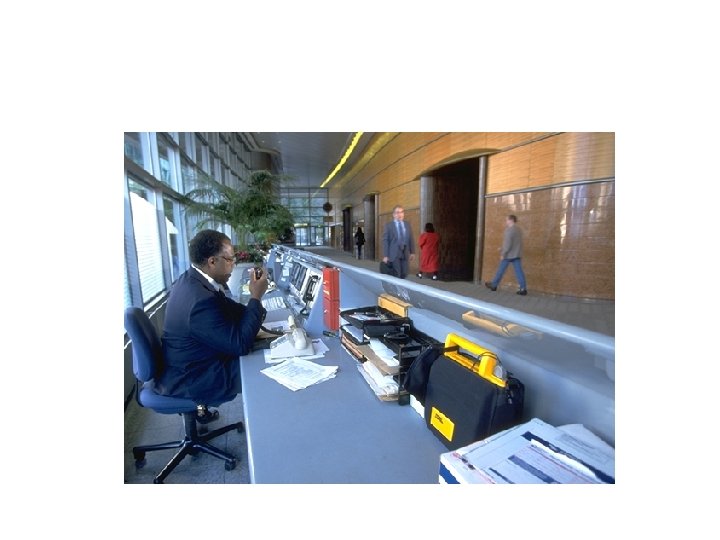
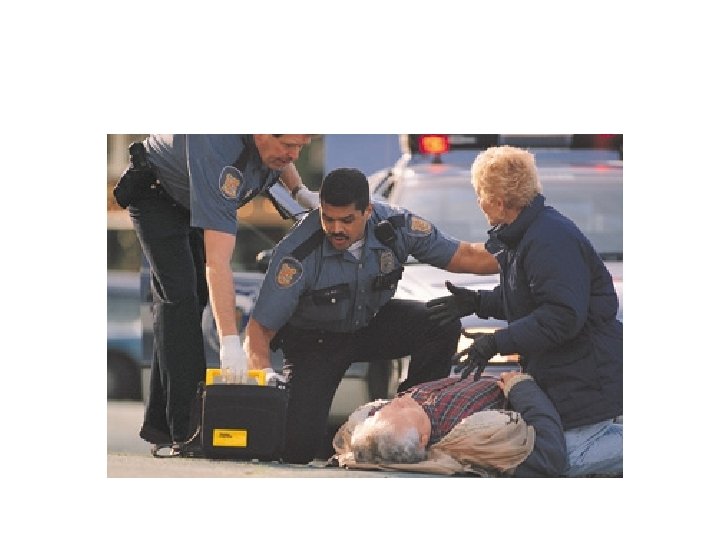
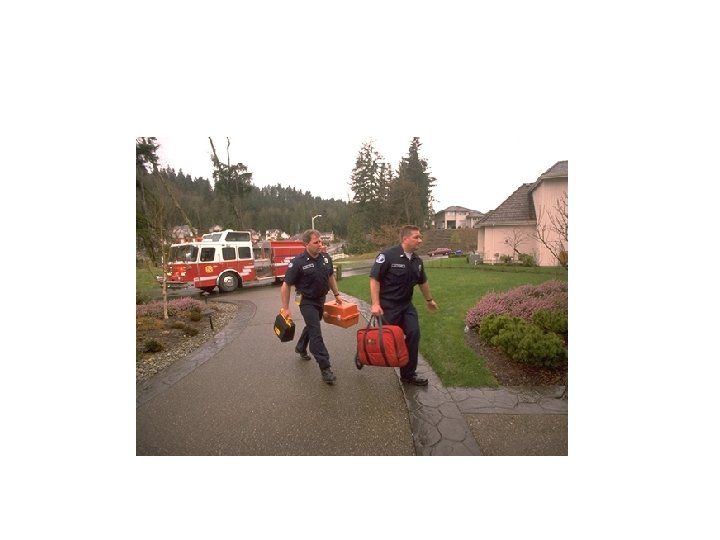
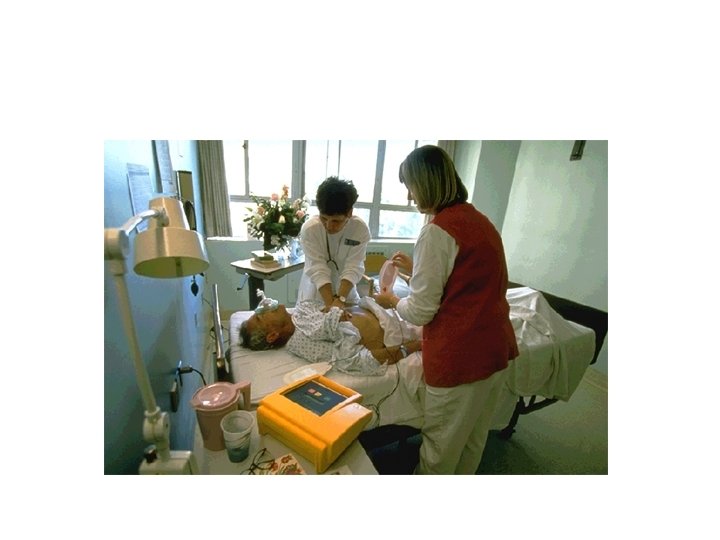
Who is Using AEDs Today? • Flight Attendants • Police • Firefighters • Golf Pros • EMTs • Lifeguards • Corporate Emergency • Health Club Employees Response Teams • Security Officers

Advantages of AEDs • Eliminates need to recognize rhythms • Personnel with less training can defibrillate • May reduce time to therapy—access to more treatable rhythms • Makes early defibrillation practical and achievable





614c3bc2c5c7699916802457618f67a8.ppt