fa3b180cc99ad71668e8ac1a9277fd45.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Auto. Focus: A Tool for Automatic Traffic Analysis Cristian Estan, University of California, San Diego
Auto. Focus: A Tool for Automatic Traffic Analysis Cristian Estan, University of California, San Diego
 Who is using my link? October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 2
Who is using my link? October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 2
 Informal problem definition Traffic reports Analysis Applications: Gigabytes of measurement data 50% of traffic is Kazaa Sources: 20% is from Steve’s PC October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 3
Informal problem definition Traffic reports Analysis Applications: Gigabytes of measurement data 50% of traffic is Kazaa Sources: 20% is from Steve’s PC October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 3
 Informal problem definition Traffic reports Analysis Gigabytes of measurement data October 2003 20% is Kazaa from Steve’s PC 50% is Kazaa from network A Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 4
Informal problem definition Traffic reports Analysis Gigabytes of measurement data October 2003 20% is Kazaa from Steve’s PC 50% is Kazaa from network A Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 4
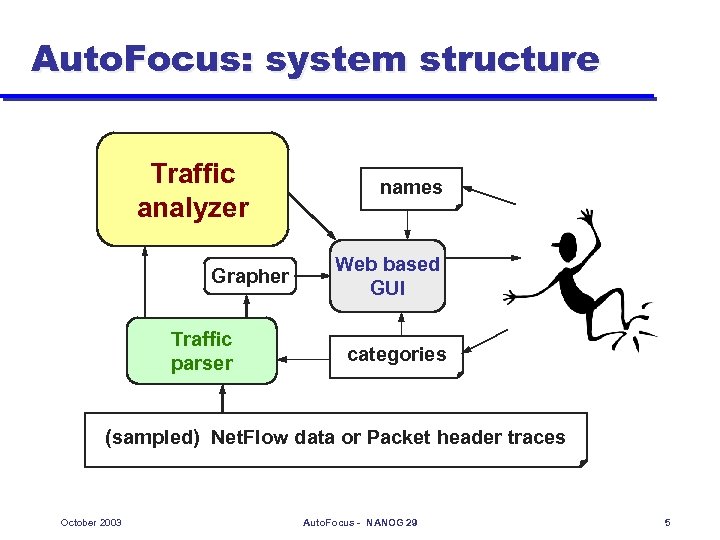 Auto. Focus: system structure Traffic analyzer Grapher Traffic parser names Web based GUI categories (sampled) Net. Flow data or Packet header traces October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 5
Auto. Focus: system structure Traffic analyzer Grapher Traffic parser names Web based GUI categories (sampled) Net. Flow data or Packet header traces October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 5
 System details l Availability Downloadable u Free for educational, research and non-profit use u l Requirements Linux or BSD (might run on other Unix OSes) u 256 Megs of RAM at least u 1 -10 gigabytes of hard disk (depends on traffic) u Recent Netscape, Mozilla or I. E. (Javascript) u Needs no web server – no server side scripting u October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 6
System details l Availability Downloadable u Free for educational, research and non-profit use u l Requirements Linux or BSD (might run on other Unix OSes) u 256 Megs of RAM at least u 1 -10 gigabytes of hard disk (depends on traffic) u Recent Netscape, Mozilla or I. E. (Javascript) u Needs no web server – no server side scripting u October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 6
 Traffic analysis approach l Characterize traffic mix by describing all important traffic clusters u u u Multi-field clusters (e. g. flash crowd described by protocol, port number and IP address) At the right level of granularity (e. g. computer, proper prefix length) Analysis is automated – finds insightful data without human guidance October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 7
Traffic analysis approach l Characterize traffic mix by describing all important traffic clusters u u u Multi-field clusters (e. g. flash crowd described by protocol, port number and IP address) At the right level of granularity (e. g. computer, proper prefix length) Analysis is automated – finds insightful data without human guidance October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 7
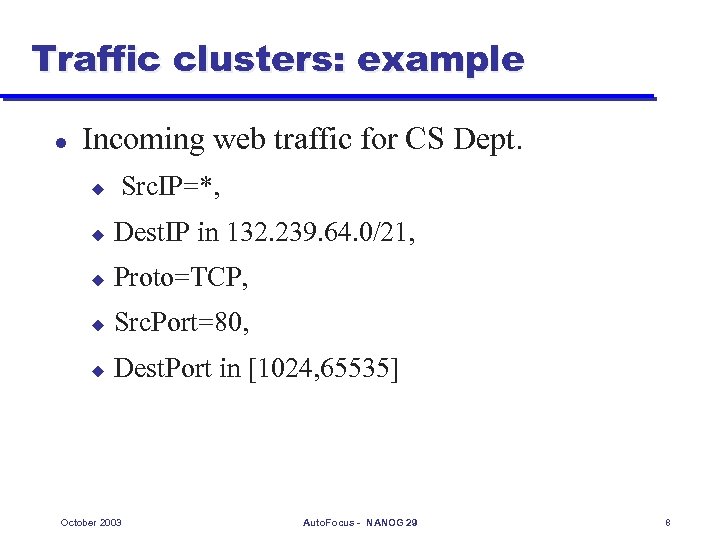 Traffic clusters: example l Incoming web traffic for CS Dept. u Src. IP=*, u Dest. IP in 132. 239. 64. 0/21, u Proto=TCP, u Src. Port=80, u Dest. Port in [1024, 65535] October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 8
Traffic clusters: example l Incoming web traffic for CS Dept. u Src. IP=*, u Dest. IP in 132. 239. 64. 0/21, u Proto=TCP, u Src. Port=80, u Dest. Port in [1024, 65535] October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 8
 Traffic report l l l Traffic reports automatically list significant traffic clusters Describe only clusters above threshold (e. g. T=total of traffic/20) Compression removes redundant clusters whose traffic can be inferred from more specific clusters October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 9
Traffic report l l l Traffic reports automatically list significant traffic clusters Describe only clusters above threshold (e. g. T=total of traffic/20) Compression removes redundant clusters whose traffic can be inferred from more specific clusters October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 9
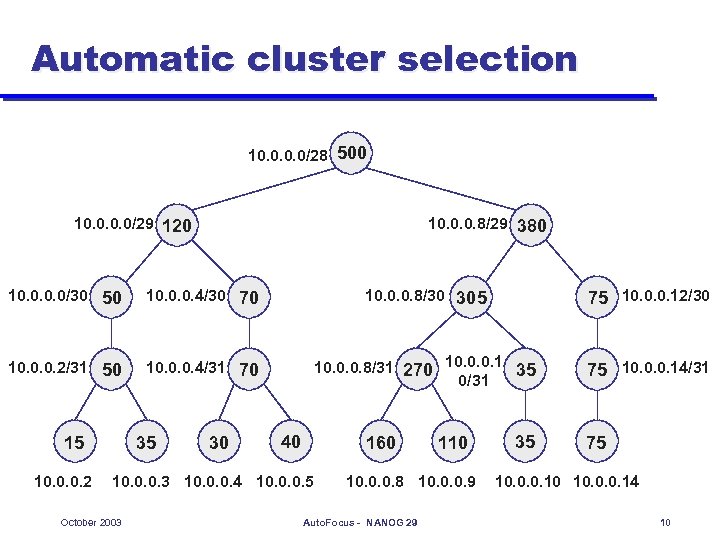 Automatic cluster selection 10. 0/28 500 10. 0/29 120 10. 0. 0. 8/29 380 10. 0/30 50 10. 0. 0. 4/30 70 10. 0. 0. 8/30 305 75 10. 0. 0. 12/30 10. 0. 0. 2/31 50 10. 0. 0. 4/31 70 10. 0. 0. 8/31 270 10. 0. 0. 1 35 0/31 75 10. 0. 0. 14/31 15 10. 0. 0. 2 35 30 40 160 10. 0. 0. 3 10. 0. 0. 4 10. 0. 0. 5 October 2003 110 10. 0. 0. 8 10. 0. 0. 9 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 35 75 10. 0. 0. 10 10. 0. 0. 14 10
Automatic cluster selection 10. 0/28 500 10. 0/29 120 10. 0. 0. 8/29 380 10. 0/30 50 10. 0. 0. 4/30 70 10. 0. 0. 8/30 305 75 10. 0. 0. 12/30 10. 0. 0. 2/31 50 10. 0. 0. 4/31 70 10. 0. 0. 8/31 270 10. 0. 0. 1 35 0/31 75 10. 0. 0. 14/31 15 10. 0. 0. 2 35 30 40 160 10. 0. 0. 3 10. 0. 0. 4 10. 0. 0. 5 October 2003 110 10. 0. 0. 8 10. 0. 0. 9 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 35 75 10. 0. 0. 10 10. 0. 0. 14 10
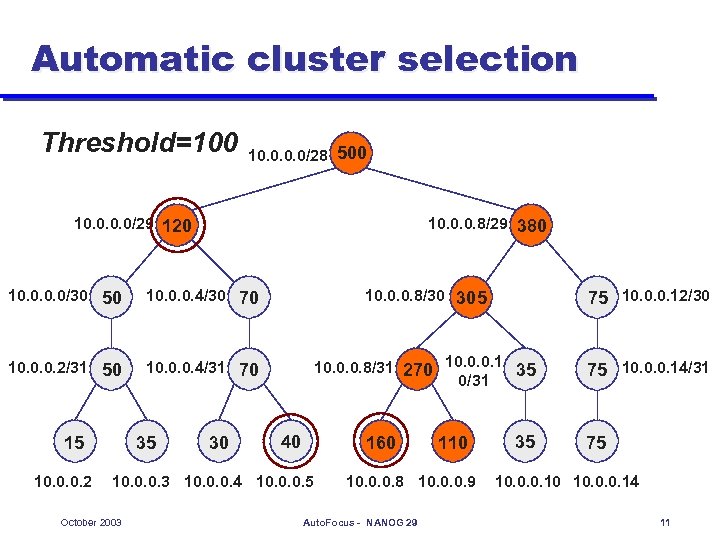 Automatic cluster selection Threshold=100 10. 0/28 500 10. 0/29 120 10. 0. 0. 8/29 380 10. 0/30 50 10. 0. 0. 4/30 70 10. 0. 0. 8/30 305 75 10. 0. 0. 12/30 10. 0. 0. 2/31 50 10. 0. 0. 4/31 70 10. 0. 0. 8/31 270 10. 0. 0. 1 35 0/31 75 10. 0. 0. 14/31 15 10. 0. 0. 2 35 30 40 160 10. 0. 0. 3 10. 0. 0. 4 10. 0. 0. 5 October 2003 110 10. 0. 0. 8 10. 0. 0. 9 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 35 75 10. 0. 0. 10 10. 0. 0. 14 11
Automatic cluster selection Threshold=100 10. 0/28 500 10. 0/29 120 10. 0. 0. 8/29 380 10. 0/30 50 10. 0. 0. 4/30 70 10. 0. 0. 8/30 305 75 10. 0. 0. 12/30 10. 0. 0. 2/31 50 10. 0. 0. 4/31 70 10. 0. 0. 8/31 270 10. 0. 0. 1 35 0/31 75 10. 0. 0. 14/31 15 10. 0. 0. 2 35 30 40 160 10. 0. 0. 3 10. 0. 0. 4 10. 0. 0. 5 October 2003 110 10. 0. 0. 8 10. 0. 0. 9 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 35 75 10. 0. 0. 10 10. 0. 0. 14 11
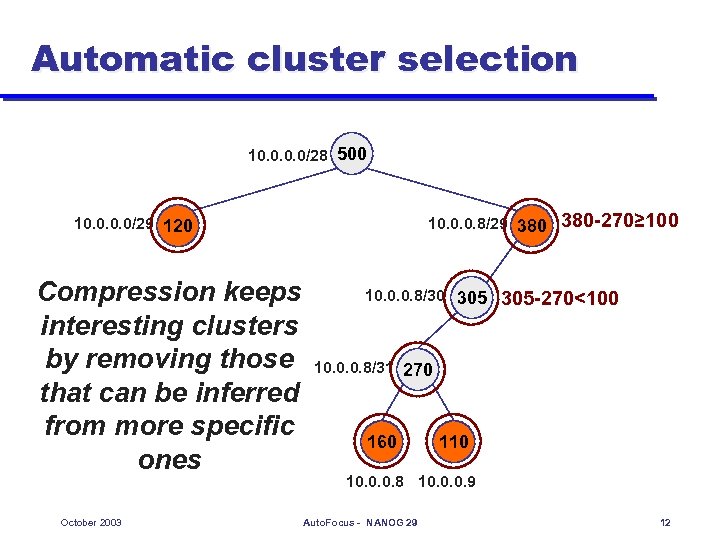 Automatic cluster selection 10. 0/28 500 10. 0/29 120 Compression keeps interesting clusters by removing those that can be inferred from more specific ones October 2003 10. 0. 0. 8/29 380 10. 0. 0. 8/30 305 380 -270≥ 100 305 -270<100 10. 0. 0. 8/31 270 160 110 10. 0. 0. 8 10. 0. 0. 9 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 12
Automatic cluster selection 10. 0/28 500 10. 0/29 120 Compression keeps interesting clusters by removing those that can be inferred from more specific ones October 2003 10. 0. 0. 8/29 380 10. 0. 0. 8/30 305 380 -270≥ 100 305 -270<100 10. 0. 0. 8/31 270 160 110 10. 0. 0. 8 10. 0. 0. 9 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 12
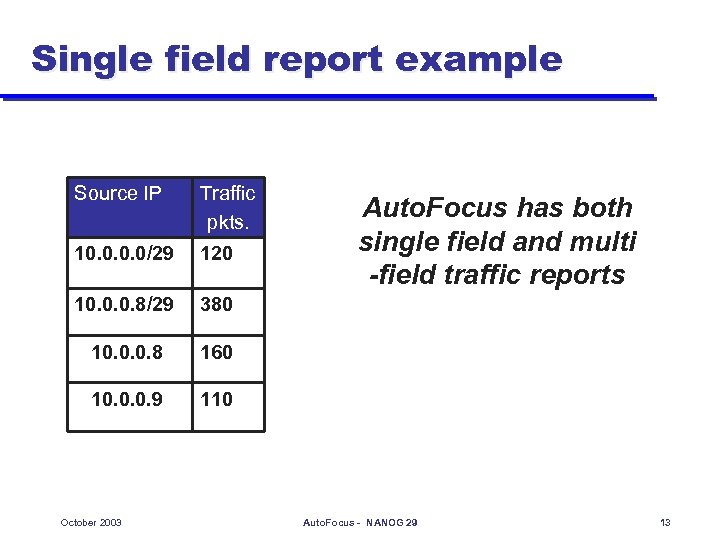 Single field report example Source IP Traffic pkts. 10. 0/29 120 10. 0. 0. 8/29 380 10. 0. 0. 8 160 10. 0. 0. 9 110 October 2003 Auto. Focus has both single field and multi -field traffic reports Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 13
Single field report example Source IP Traffic pkts. 10. 0/29 120 10. 0. 0. 8/29 380 10. 0. 0. 8 160 10. 0. 0. 9 110 October 2003 Auto. Focus has both single field and multi -field traffic reports Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 13
 Graphical user interface l l Web based interface Many pre-computed traffic reports Interactive drill-down Traffic categories defined by user October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 14
Graphical user interface l l Web based interface Many pre-computed traffic reports Interactive drill-down Traffic categories defined by user October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 14
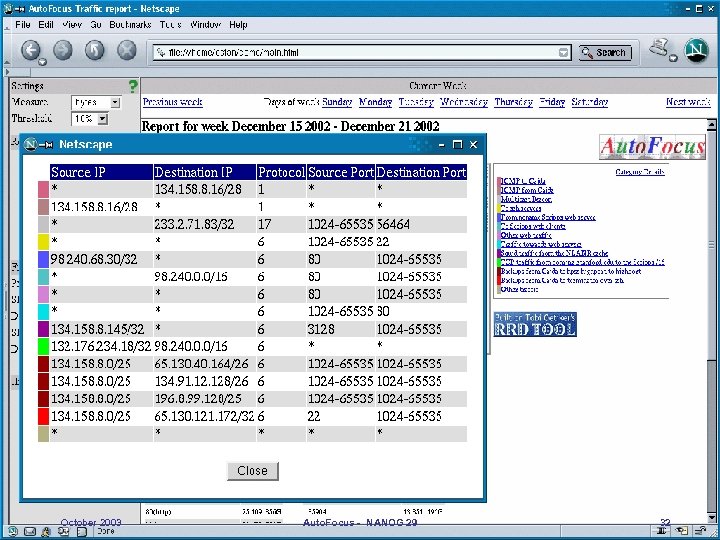
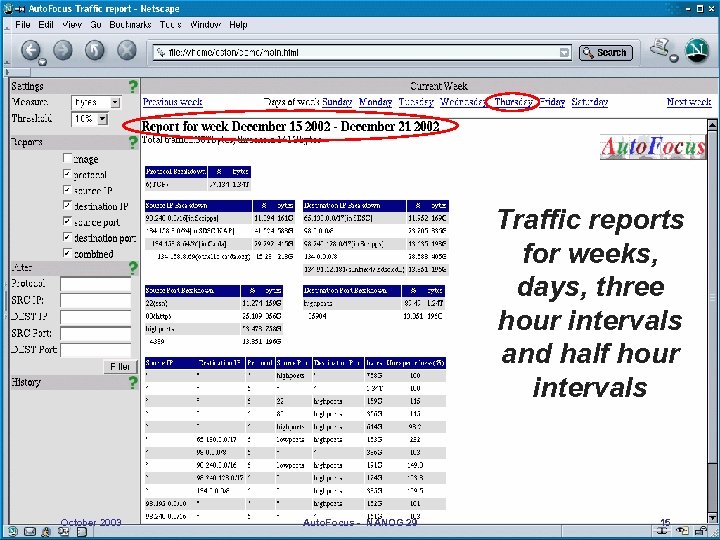 Traffic reports for weeks, days, three hour intervals and half hour intervals October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 15
Traffic reports for weeks, days, three hour intervals and half hour intervals October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 15
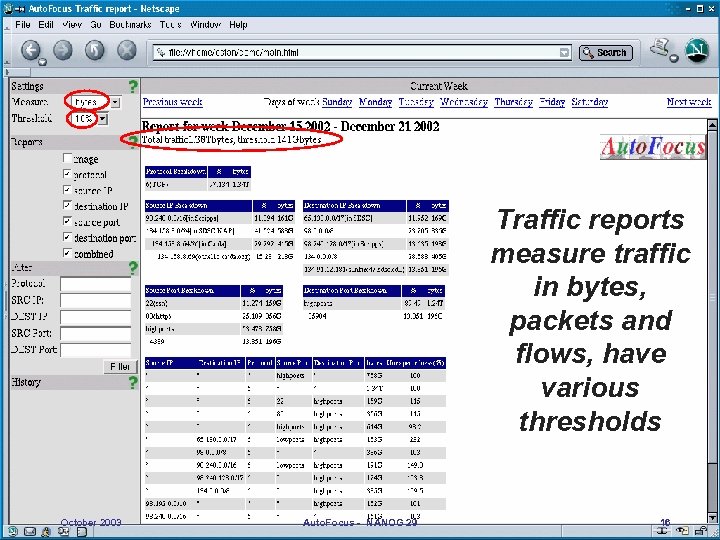 Traffic reports measure traffic in bytes, packets and flows, have various thresholds October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 16
Traffic reports measure traffic in bytes, packets and flows, have various thresholds October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 16
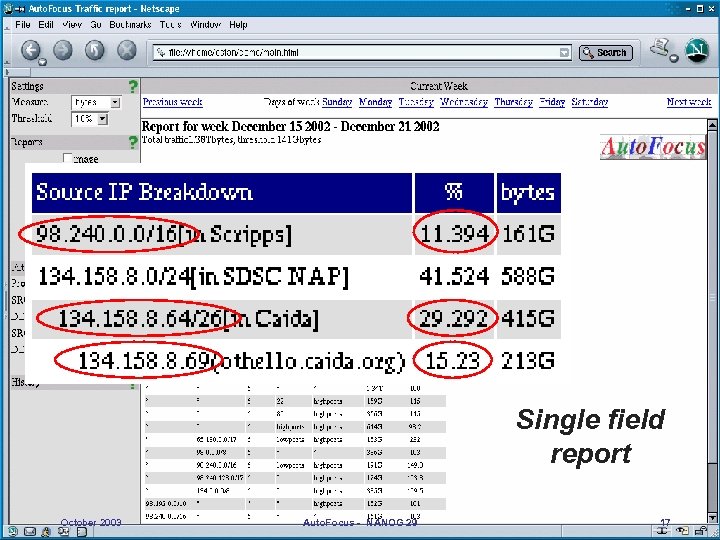 Single field report October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 17
Single field report October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 17
 October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 18
October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 18
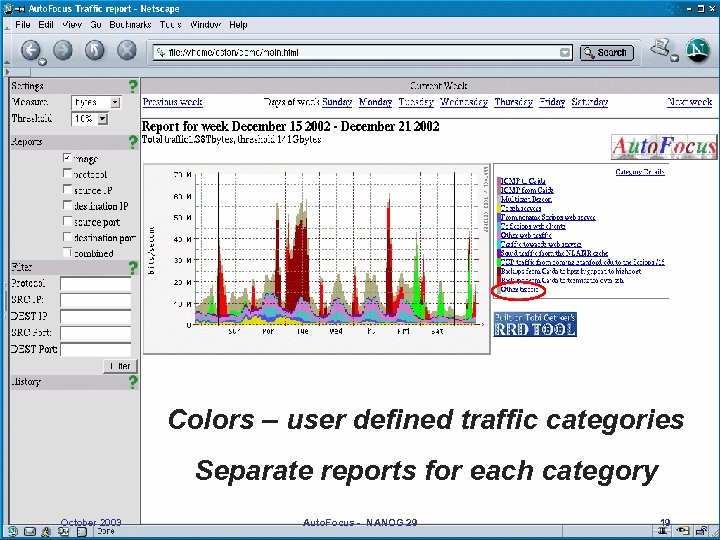 Colors – user defined traffic categories Separate reports for each category October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 19
Colors – user defined traffic categories Separate reports for each category October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 19
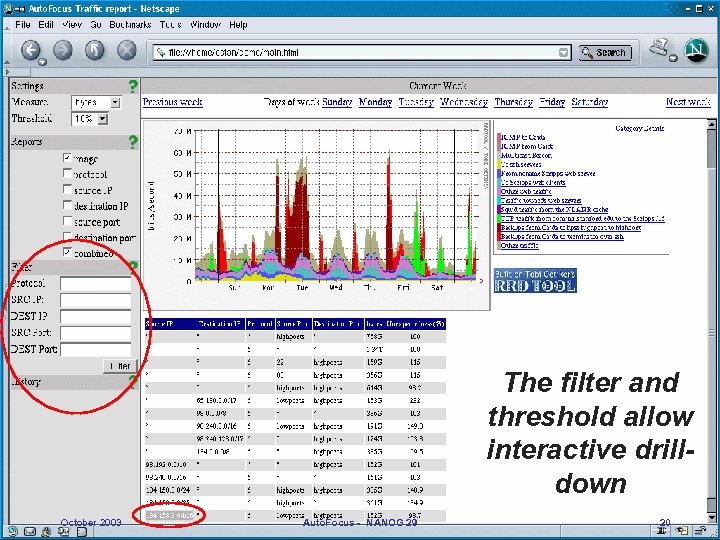 The filter and threshold allow interactive drilldown October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 20
The filter and threshold allow interactive drilldown October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 20
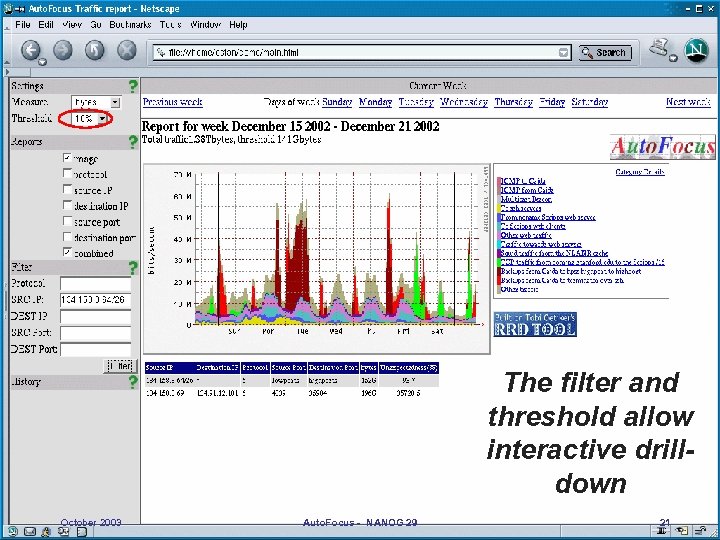 The filter and threshold allow interactive drilldown October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 21
The filter and threshold allow interactive drilldown October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 21
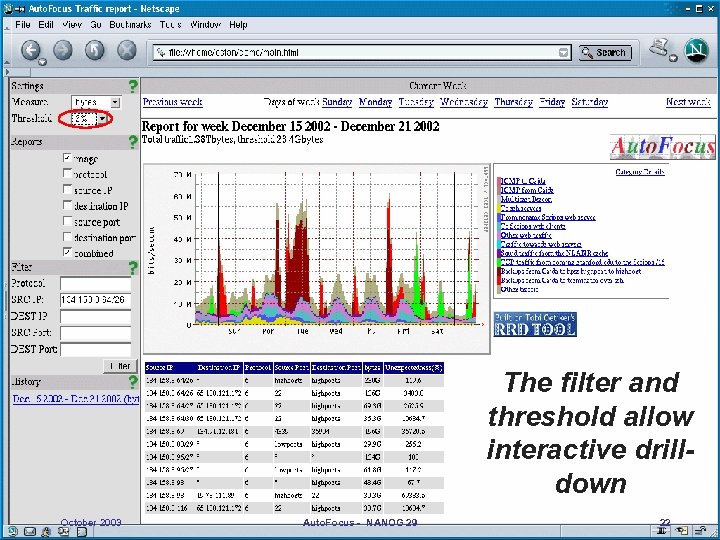 The filter and threshold allow interactive drilldown October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 22
The filter and threshold allow interactive drilldown October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 22
 Case study : SD-NAP l Structure of regular traffic mix u u FTP from SLAC Stanford u Scripps web traffic u Web & Squid servers u Large ssh traffic u l Backups from CAIDA to tape server Steady ICMP probing from CAIDA Unexpected events October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 23
Case study : SD-NAP l Structure of regular traffic mix u u FTP from SLAC Stanford u Scripps web traffic u Web & Squid servers u Large ssh traffic u l Backups from CAIDA to tape server Steady ICMP probing from CAIDA Unexpected events October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 23
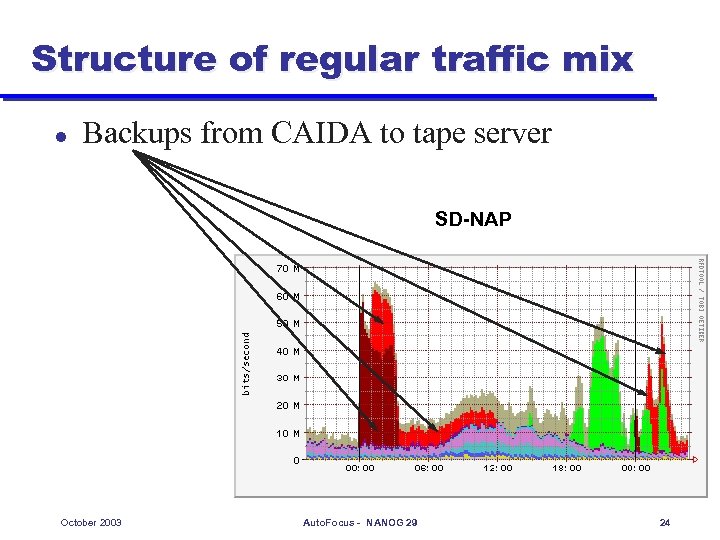 Structure of regular traffic mix l Backups from CAIDA to tape server SD-NAP October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 24
Structure of regular traffic mix l Backups from CAIDA to tape server SD-NAP October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 24
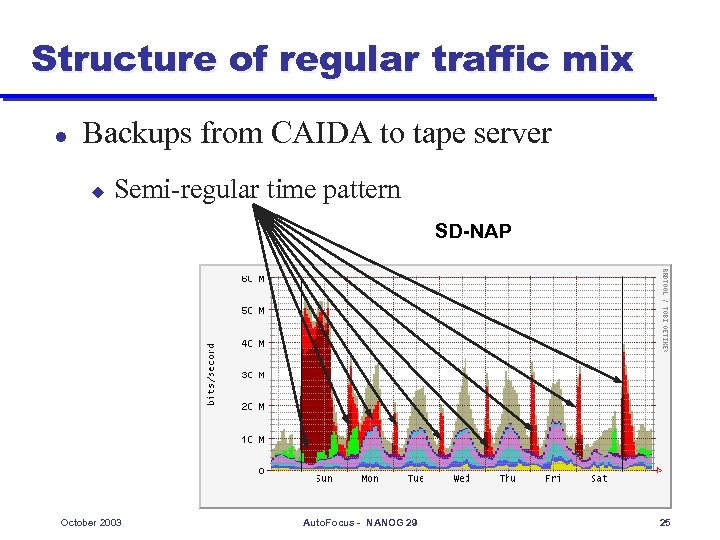 Structure of regular traffic mix l Backups from CAIDA to tape server u Semi-regular time pattern SD-NAP October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 25
Structure of regular traffic mix l Backups from CAIDA to tape server u Semi-regular time pattern SD-NAP October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 25
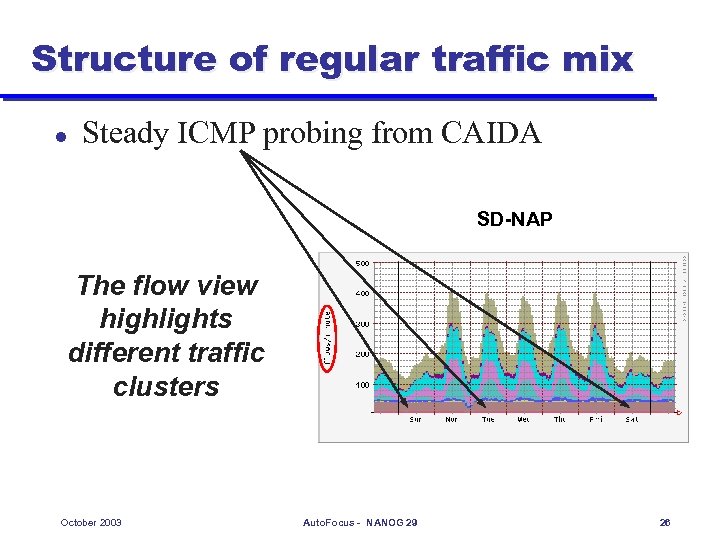 Structure of regular traffic mix l Steady ICMP probing from CAIDA SD-NAP The flow view highlights different traffic clusters October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 26
Structure of regular traffic mix l Steady ICMP probing from CAIDA SD-NAP The flow view highlights different traffic clusters October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 26
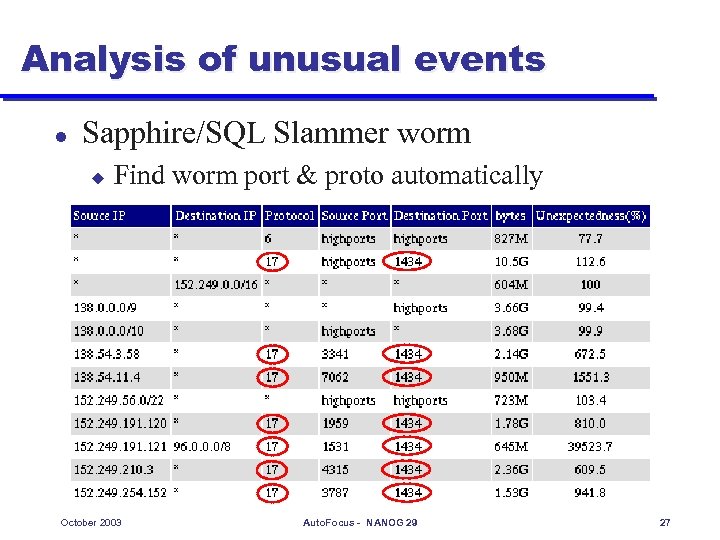 Analysis of unusual events l Sapphire/SQL Slammer worm u Find worm port & proto automatically October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 27
Analysis of unusual events l Sapphire/SQL Slammer worm u Find worm port & proto automatically October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 27
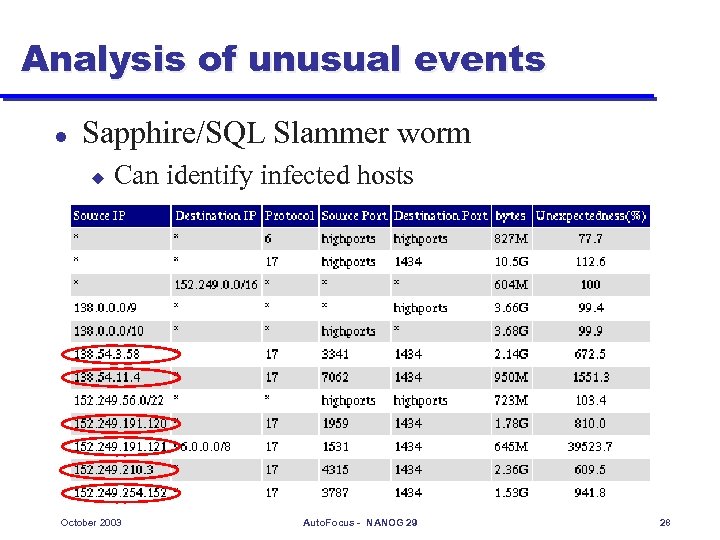 Analysis of unusual events l Sapphire/SQL Slammer worm u Can identify infected hosts October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 28
Analysis of unusual events l Sapphire/SQL Slammer worm u Can identify infected hosts October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 28
 How can Auto. Focus help you? l Understand your regular traffic mix better u u l Better planning of network growth Better traffic policing Understand unusual events u More effective reactions to worms, Do. S attacks u Notice effects of route changes on traffic October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 29
How can Auto. Focus help you? l Understand your regular traffic mix better u u l Better planning of network growth Better traffic policing Understand unusual events u More effective reactions to worms, Do. S attacks u Notice effects of route changes on traffic October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 29
 Benefits w. r. t. existing tools l l l Multi-field aggregation Automatically finds right granularity Drill-down u Per category reports u Using filter October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 30
Benefits w. r. t. existing tools l l l Multi-field aggregation Automatically finds right granularity Drill-down u Per category reports u Using filter October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 30
 Thank you! Beta version of Auto. Focus downloadable from http: //ial. ucsd. edu/Auto. Focus/ Any questions? Acknowledgements: Stefan Savage, George Varghese, Vern Paxson, David Moore, Liliana Estan, Mike Hunter, Pat Wilson, Jennifer Rexford, K Claffy, Alex Snoeren, Geoff Voelker, NIST, NSF October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 31
Thank you! Beta version of Auto. Focus downloadable from http: //ial. ucsd. edu/Auto. Focus/ Any questions? Acknowledgements: Stefan Savage, George Varghese, Vern Paxson, David Moore, Liliana Estan, Mike Hunter, Pat Wilson, Jennifer Rexford, K Claffy, Alex Snoeren, Geoff Voelker, NIST, NSF October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 31
 October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 32
October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 32
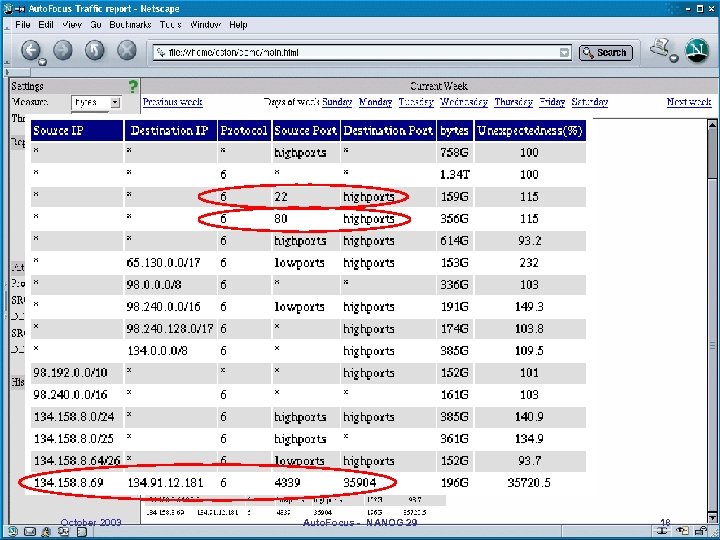
 Definition: unexpectedness l To highlight non-obvious traffic clusters by using unexpectedness label 50% of all traffic is web u Prefix B receives 20% of all traffic u The web traffic received by prefix B is 15% instead of 50%*20%=10%, unexpectedness label is 15%/10%=150% u October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 33
Definition: unexpectedness l To highlight non-obvious traffic clusters by using unexpectedness label 50% of all traffic is web u Prefix B receives 20% of all traffic u The web traffic received by prefix B is 15% instead of 50%*20%=10%, unexpectedness label is 15%/10%=150% u October 2003 Auto. Focus - NANOG 29 33


