 Authentication
Authentication
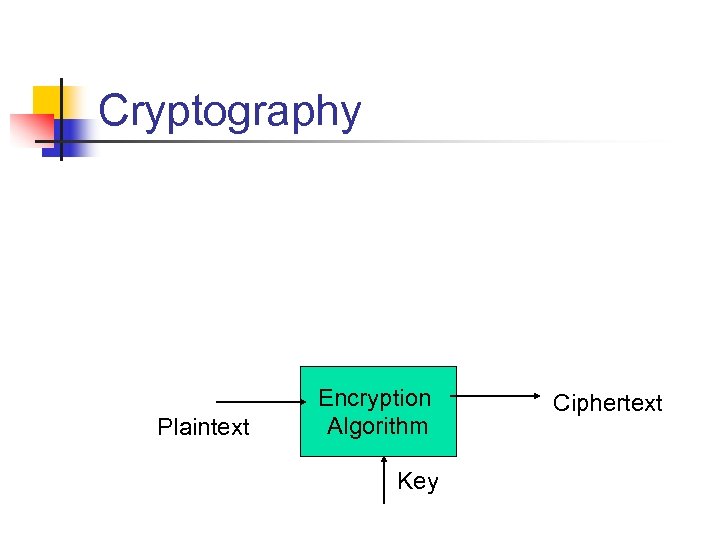 Cryptography Plaintext Encryption Algorithm Key Ciphertext
Cryptography Plaintext Encryption Algorithm Key Ciphertext
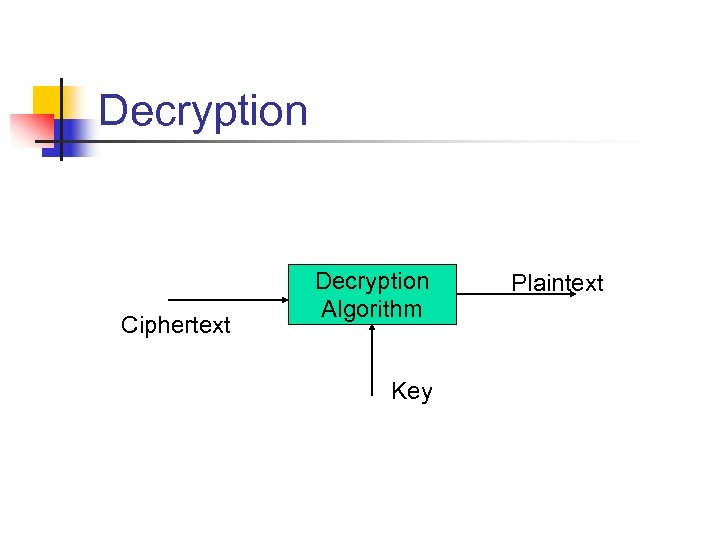 Decryption Ciphertext Decryption Algorithm Key Plaintext
Decryption Ciphertext Decryption Algorithm Key Plaintext
 Kerckhoff’s principle
Kerckhoff’s principle
 Decryption Device
Decryption Device
 Two Definitions
Two Definitions
 Function Random input
Function Random input
 Birthday Bound
Birthday Bound
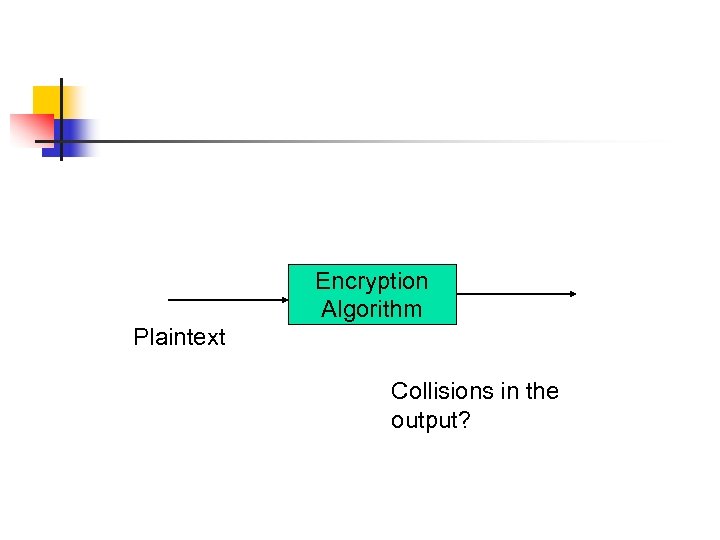 Encryption Algorithm Plaintext Collisions in the output?
Encryption Algorithm Plaintext Collisions in the output?
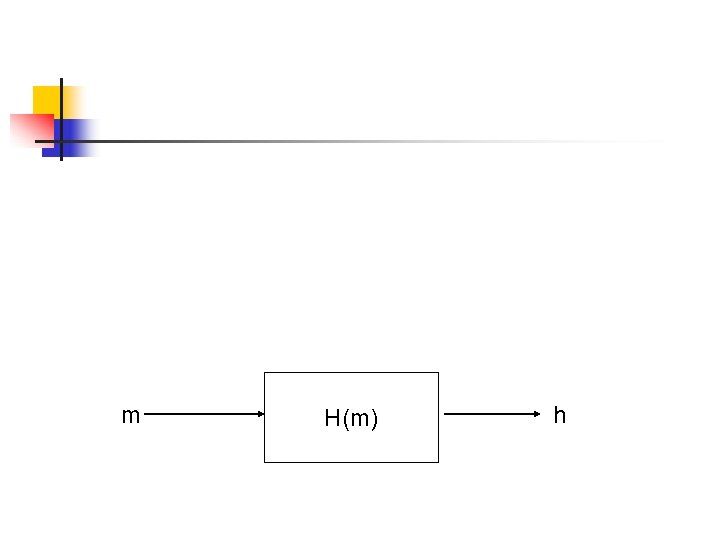 m H(m) h
m H(m) h
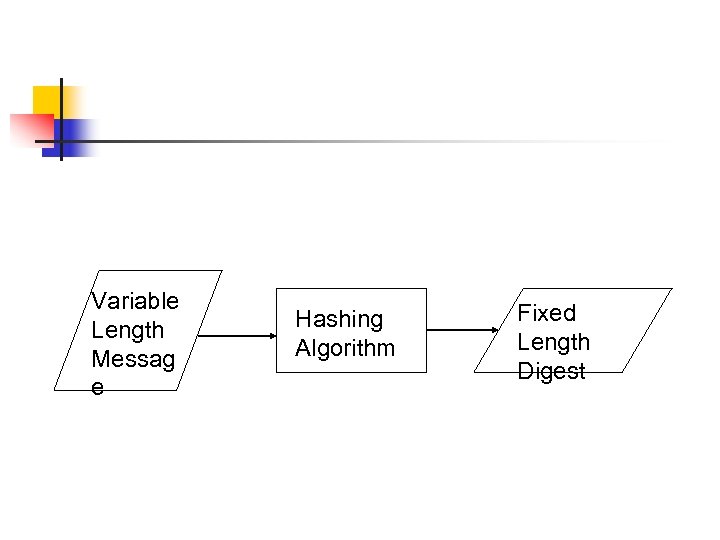 Variable Length Messag e Hashing Algorithm Fixed Length Digest
Variable Length Messag e Hashing Algorithm Fixed Length Digest
 Uses of Hash Functions
Uses of Hash Functions
 A Cryptographic Hash function
A Cryptographic Hash function
 Definitions
Definitions
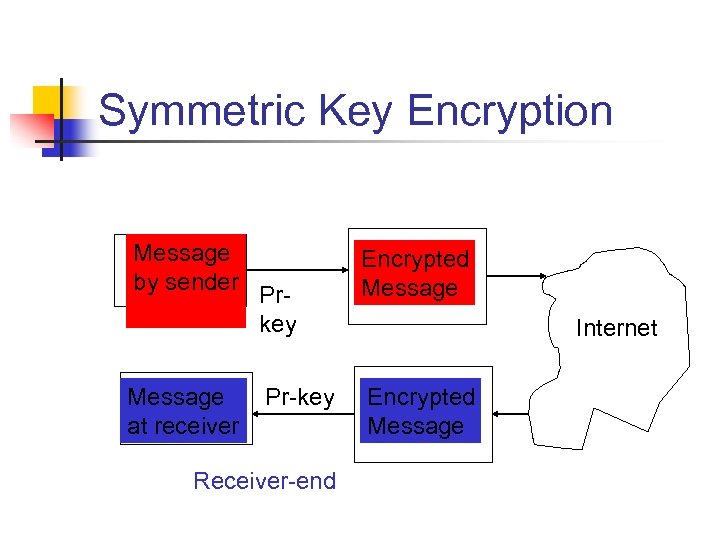 Symmetric Key Encryption Message by sender Message at receiver Prkey Pr-key Receiver-end Encrypted Message Internet Encrypted Message
Symmetric Key Encryption Message by sender Message at receiver Prkey Pr-key Receiver-end Encrypted Message Internet Encrypted Message
 Others contribute
Others contribute
 The P-K systems
The P-K systems
 Patents
Patents
 Diffie-Hellman algorithm
Diffie-Hellman algorithm
 Diffie-Hellman algorithm
Diffie-Hellman algorithm
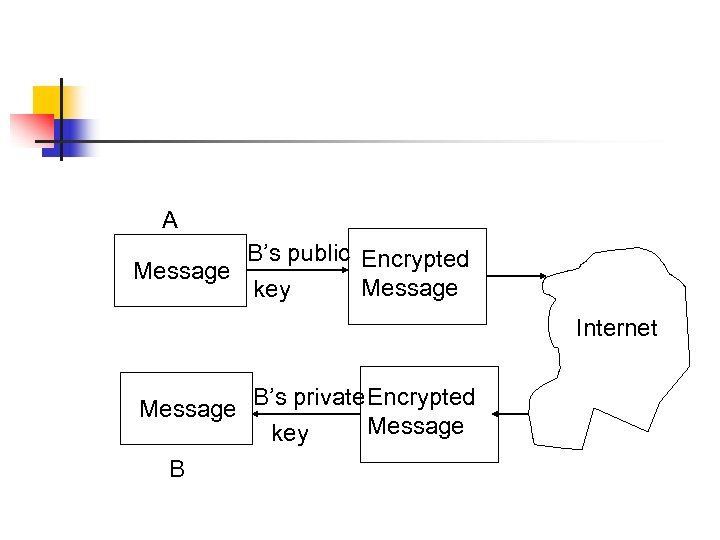 A B’s public Encrypted Message key Internet Message B’s private Encrypted Message key B
A B’s public Encrypted Message key Internet Message B’s private Encrypted Message key B
 Public Key of Alice
Public Key of Alice
 Certifying Authorities
Certifying Authorities
 Digital Certificate
Digital Certificate
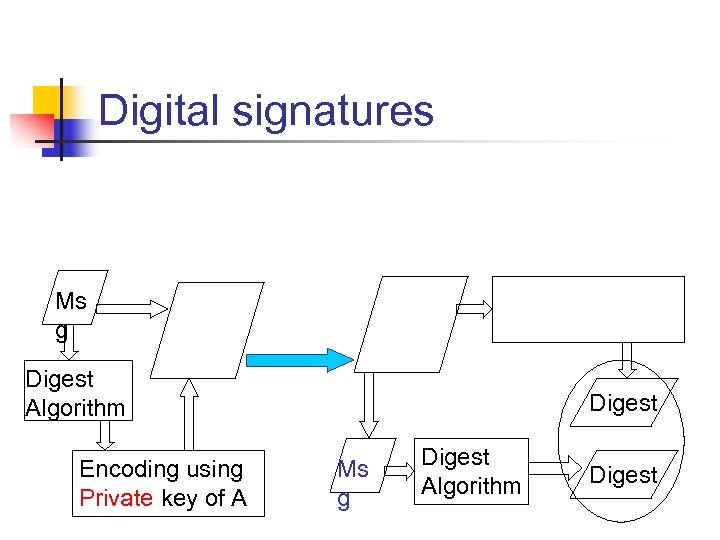 Digital signatures Ms g Digest Algorithm Encoding using Private key of A Digest Ms g Digest Algorithm Digest
Digital signatures Ms g Digest Algorithm Encoding using Private key of A Digest Ms g Digest Algorithm Digest
 Secure Socket Layer
Secure Socket Layer
 Pretty Good Privacy
Pretty Good Privacy
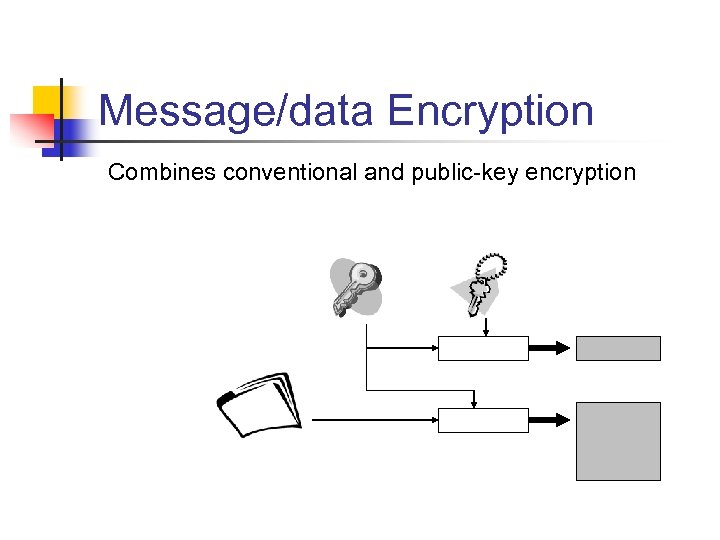 Message/data Encryption Combines conventional and public-key encryption
Message/data Encryption Combines conventional and public-key encryption
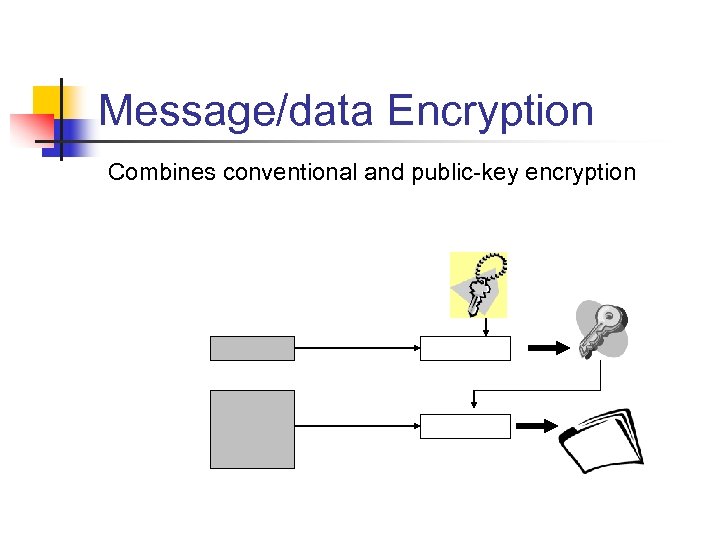 Message/data Encryption Combines conventional and public-key encryption
Message/data Encryption Combines conventional and public-key encryption
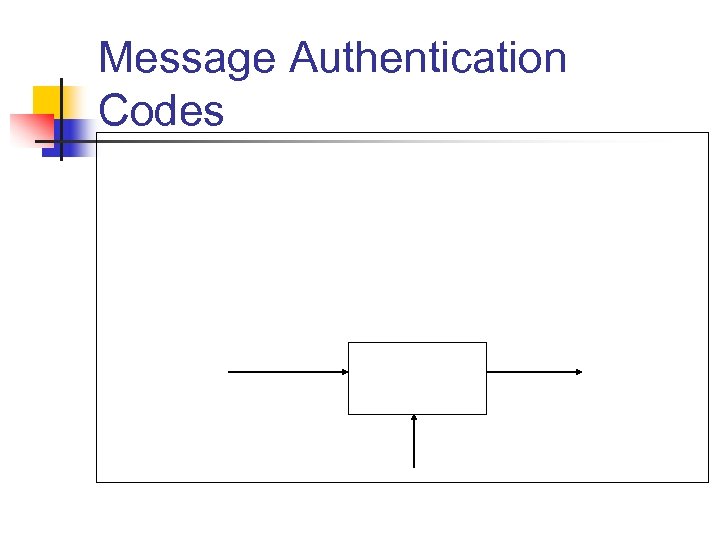 Message Authentication Codes
Message Authentication Codes
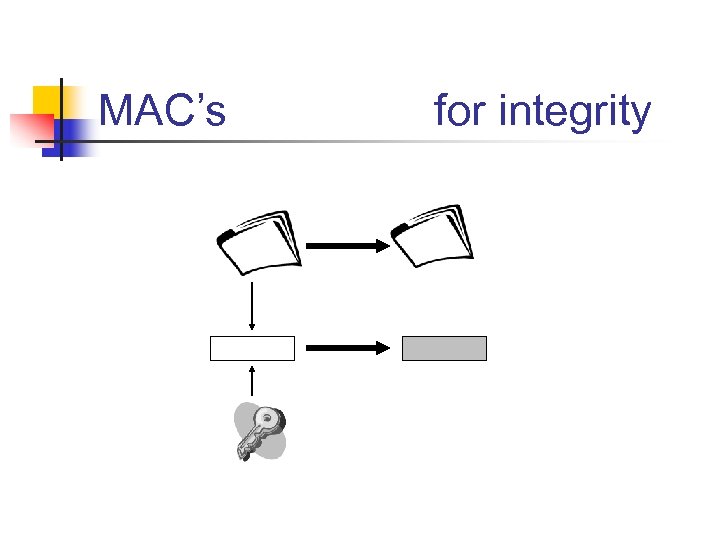 MAC’s for integrity
MAC’s for integrity
 Function for MAC
Function for MAC
 Authentication issues
Authentication issues
 International Laws
International Laws
 Difference between SCTP and TCP
Difference between SCTP and TCP
 Uses of SIP
Uses of SIP
 Session Initiation Protocol
Session Initiation Protocol
 H. 323 and H. 248
H. 323 and H. 248
 H. 248/MEGACO
H. 248/MEGACO
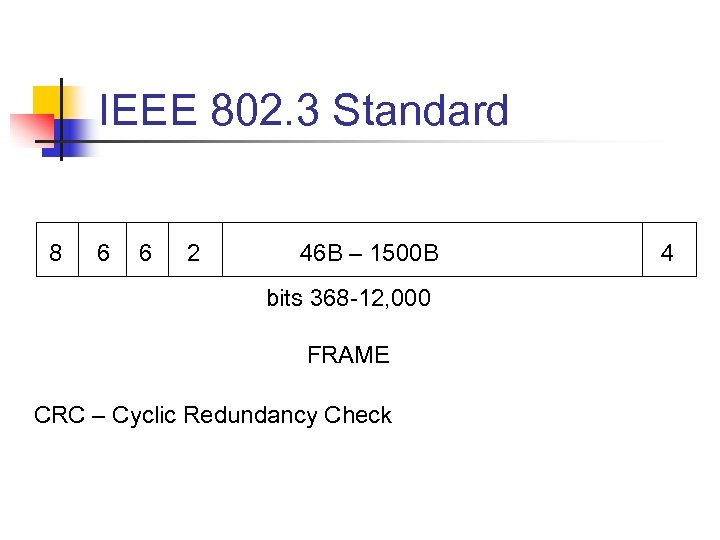 IEEE 802. 3 Standard 8 6 6 2 46 B – 1500 B bits 368 -12, 000 FRAME CRC – Cyclic Redundancy Check 4
IEEE 802. 3 Standard 8 6 6 2 46 B – 1500 B bits 368 -12, 000 FRAME CRC – Cyclic Redundancy Check 4