f768ffc4ee7e1da560e2277cfc899a83.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Authentication attacks, causes and solutions Analyzing man in the middle and dictionary attacks against SSL/TLS and password based authentication systems Fletcher Liverance, 16 April 2009
Authentication attacks, causes and solutions Analyzing man in the middle and dictionary attacks against SSL/TLS and password based authentication systems Fletcher Liverance, 16 April 2009
 Sources n Password-Based Authentication: Preventing Dictionary Attacks n n Saikat Chakrabarti, University of Kentucky Mukesh Singhal, University of Kentucky Computer, IEEE CS Press, June 2007, pp. 68 -74 SSL/TLS Session-Aware User Authentication n n Rolf Oppliger, e. SECURITY Technologies Ralf Hauser, Priva. Sphere AG David Basin, ETH Zurich Computer, IEEE CS Press, March 2008, pp. 59 -65
Sources n Password-Based Authentication: Preventing Dictionary Attacks n n Saikat Chakrabarti, University of Kentucky Mukesh Singhal, University of Kentucky Computer, IEEE CS Press, June 2007, pp. 68 -74 SSL/TLS Session-Aware User Authentication n n Rolf Oppliger, e. SECURITY Technologies Ralf Hauser, Priva. Sphere AG David Basin, ETH Zurich Computer, IEEE CS Press, March 2008, pp. 59 -65
 Overview What is authentication? n Two common attacks n Advanced password authentication protocols n Improvements in SSL/TLS n Preventing future attacks n
Overview What is authentication? n Two common attacks n Advanced password authentication protocols n Improvements in SSL/TLS n Preventing future attacks n
 What is Authentication? Authentication is the binding of an identity to a subject n n n Face Voice Signature Birth certificate Social security number ID card Personal knowledge Key Password Name Phone number
What is Authentication? Authentication is the binding of an identity to a subject n n n Face Voice Signature Birth certificate Social security number ID card Personal knowledge Key Password Name Phone number
 Impersonal Authentication n How do you authenticate over a network? No direct visual cues n No direct auditory cues n No physical connection n Knowledge based authentication n Recreation of human authentication cues n Electronic IDs n
Impersonal Authentication n How do you authenticate over a network? No direct visual cues n No direct auditory cues n No physical connection n Knowledge based authentication n Recreation of human authentication cues n Electronic IDs n
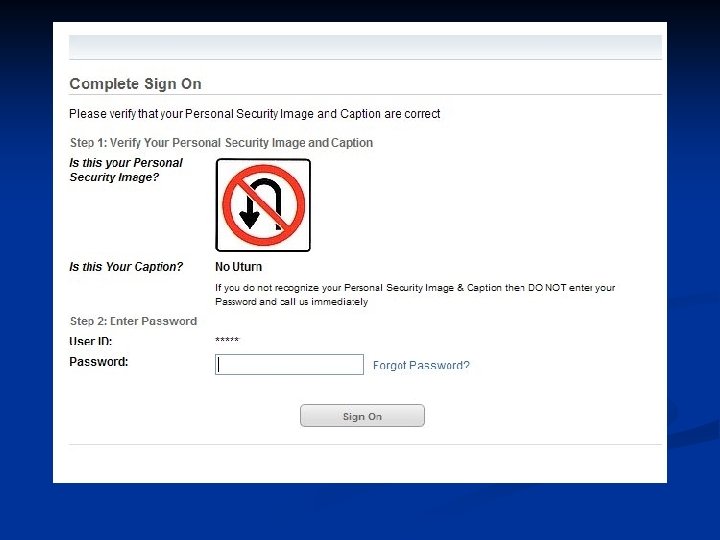
 Dictionary Attack n Online n n Repeated query of authentication server Slow Easy to block Offline n n n Repeated computation and comparison of password hash Faster No interaction required n Top ten passwords: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. (username)123 123456 password 12345 passwd 123 test 1
Dictionary Attack n Online n n Repeated query of authentication server Slow Easy to block Offline n n n Repeated computation and comparison of password hash Faster No interaction required n Top ten passwords: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. (username)123 123456 password 12345 passwd 123 test 1
 Man in the Middle “a form of active wiretapping attack in which the attacker intercepts and selectively modifies communicated data to masquerade as one or more of the entities involved in a communication association. ” RFC 2828 – Internet Security Glossary
Man in the Middle “a form of active wiretapping attack in which the attacker intercepts and selectively modifies communicated data to masquerade as one or more of the entities involved in a communication association. ” RFC 2828 – Internet Security Glossary
 Basic Password Authentication
Basic Password Authentication
 Challenge/Response
Challenge/Response
 EKE Protocol
EKE Protocol
 Plaintext equivalence User and host must have access to the same secret password n Attacker can intercept password hash as it is sent to server n
Plaintext equivalence User and host must have access to the same secret password n Attacker can intercept password hash as it is sent to server n
 Secure remote-password protocol
Secure remote-password protocol
 Behind the scenes Alice and Bob agree on finite field F(x) n Alice gives Bob verifier v = F(Hash(salt, password)) and salt. Alice sends identity to Bob sends salt to Alice n Alice computes K-a = F(Rand-a) and x = Hash(s, pwd) Alice send K-a to Bob n Bob computes K-b = v + F(Rand-b) Bob sends K-b and Rand-r to Alice n n n n Alice sends Cert-a to Bob n n Alice computes K-ab = Hash(K-b – F(Hash(salt, pwd))^(Rand-a + Rand-r*Hash(salt, pwd)) Bob computes K-ab = Hash(Rand-b*Key-a*v^Rand-r) Bob verifies Cert-a is correct Bob sends Cert-b to Alice n Alice verifies Cert-b is correct
Behind the scenes Alice and Bob agree on finite field F(x) n Alice gives Bob verifier v = F(Hash(salt, password)) and salt. Alice sends identity to Bob sends salt to Alice n Alice computes K-a = F(Rand-a) and x = Hash(s, pwd) Alice send K-a to Bob n Bob computes K-b = v + F(Rand-b) Bob sends K-b and Rand-r to Alice n n n n Alice sends Cert-a to Bob n n Alice computes K-ab = Hash(K-b – F(Hash(salt, pwd))^(Rand-a + Rand-r*Hash(salt, pwd)) Bob computes K-ab = Hash(Rand-b*Key-a*v^Rand-r) Bob verifies Cert-a is correct Bob sends Cert-b to Alice n Alice verifies Cert-b is correct
 Alternative Solutions n n Delayed response Account locking Extra computation Reverse Turing Test n Captcha (Completely Automated Public Turing Test to Tell Computers and Humans Apart)
Alternative Solutions n n Delayed response Account locking Extra computation Reverse Turing Test n Captcha (Completely Automated Public Turing Test to Tell Computers and Humans Apart)
 SSL/TLS
SSL/TLS
 SSL/TLS Issues n Prone to man in the middle attack Attacker intercepts server messages n Attacker replaces server certificate with its own n Client encrypts all future transmissions using attacker’s certificate n “the naïve end user usually does SSL/TLS server authentication poorly if at all” n “developers usually decouple SSL/TLS session establishment from user authentication” n
SSL/TLS Issues n Prone to man in the middle attack Attacker intercepts server messages n Attacker replaces server certificate with its own n Client encrypts all future transmissions using attacker’s certificate n “the naïve end user usually does SSL/TLS server authentication poorly if at all” n “developers usually decouple SSL/TLS session establishment from user authentication” n
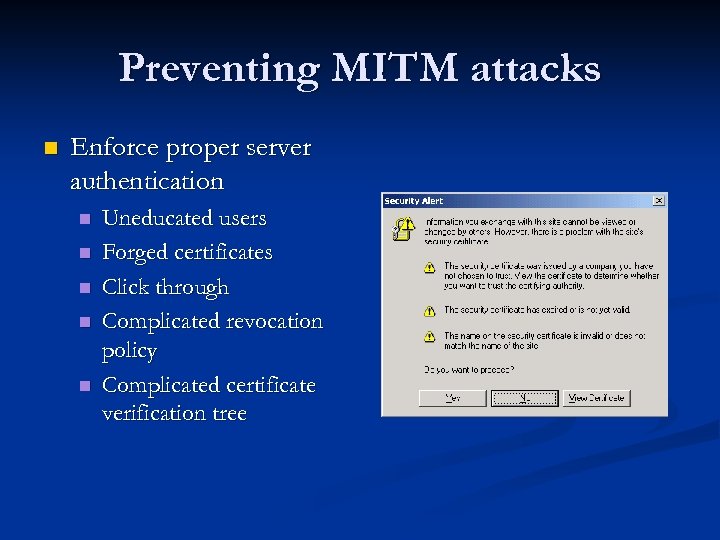 Preventing MITM attacks n Enforce proper server authentication n n Uneducated users Forged certificates Click through Complicated revocation policy Complicated certificate verification tree
Preventing MITM attacks n Enforce proper server authentication n n Uneducated users Forged certificates Click through Complicated revocation policy Complicated certificate verification tree
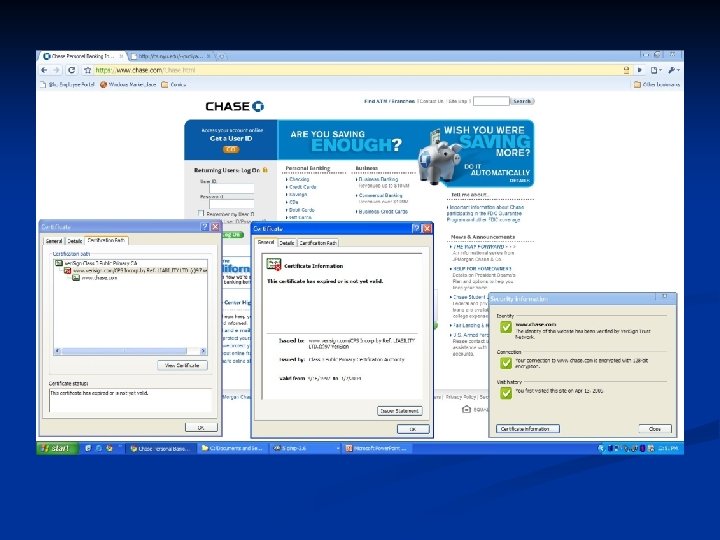
 TLS-SA n Combine user authentication with SSL/TLS session establishment Provide user authentication code (UAC) that depends on credentials and TLS session n Attacker can start session with user and host, but cannot forward messages between them n
TLS-SA n Combine user authentication with SSL/TLS session establishment Provide user authentication code (UAC) that depends on credentials and TLS session n Attacker can start session with user and host, but cannot forward messages between them n
 TLS-SA Implementation n n Normal TLS Client token generates session key based on hash of server cert User enters password UAC is computed from session key and password and is transmitted to server Server authenticates client at any time by requesting user ID, hash of server cert and the UAC.
TLS-SA Implementation n n Normal TLS Client token generates session key based on hash of server cert User enters password UAC is computed from session key and password and is transmitted to server Server authenticates client at any time by requesting user ID, hash of server cert and the UAC.
 A Formal Approach “protocols need more than heuristic arguments to provide security guarantees. ” n Provable security via the Standard model n Uses complexity-theoretic hardness assumptions: n Factoring the product of large primes is hard n Computing the discrete logarithm is hard in certain large groups. n AES is a good pseudorandom permutation
A Formal Approach “protocols need more than heuristic arguments to provide security guarantees. ” n Provable security via the Standard model n Uses complexity-theoretic hardness assumptions: n Factoring the product of large primes is hard n Computing the discrete logarithm is hard in certain large groups. n AES is a good pseudorandom permutation
 A Formal Approach (cont. ) n The random oracle model “A public random function that takes any string as input and outputs n bits” n Use heuristically secure algorithms such as SHA n n The ideal-cipher model A standard block cipher, with k-bit key and n-bit input, chosen uniformly from all block ciphers of this form. n Use pseudorandom permutations such as AES n
A Formal Approach (cont. ) n The random oracle model “A public random function that takes any string as input and outputs n bits” n Use heuristically secure algorithms such as SHA n n The ideal-cipher model A standard block cipher, with k-bit key and n-bit input, chosen uniformly from all block ciphers of this form. n Use pseudorandom permutations such as AES n
 Q&A
Q&A


