7b702e996c80ed49cab1477e6ddd743d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

 Australia’s Vocational Education & Training (VET) System § Nationally agreed § Strong industry leadership and engagement § Provides skills and knowledge for work § Client focussed
Australia’s Vocational Education & Training (VET) System § Nationally agreed § Strong industry leadership and engagement § Provides skills and knowledge for work § Client focussed
 Over 5000 training providers & 1. 7 million students § Technical & further education (TAFE) institutes § Private training providers § Dual sector institutes universities delivering higher education & VET § Community training providers § Secondary schools § Business
Over 5000 training providers & 1. 7 million students § Technical & further education (TAFE) institutes § Private training providers § Dual sector institutes universities delivering higher education & VET § Community training providers § Secondary schools § Business
 Funding for VET in Australia § Arrangements between § Shared between states & federal & state governments territories ($4 billion p. a. ) now covered in National § States & territories are Skills and Workforce responsible for training delivery Development Agreement & including determining the training National Partnership for the needs of industry Productivity Places Program § National leadership & § Student loan scheme VET contributions to overall funding Fee Help introduced in 2009 ($1. 3 billion p. a. ) § Strong links & support by industry
Funding for VET in Australia § Arrangements between § Shared between states & federal & state governments territories ($4 billion p. a. ) now covered in National § States & territories are Skills and Workforce responsible for training delivery Development Agreement & including determining the training National Partnership for the needs of industry Productivity Places Program § National leadership & § Student loan scheme VET contributions to overall funding Fee Help introduced in 2009 ($1. 3 billion p. a. ) § Strong links & support by industry
 The national governance and accountability framework Ministerial Council for Training, Education and Employment National Senior Officials Committee (NSOC) Client Advisory Alliance National Training Statistics Committee National Centre for Vocational Education Research (NCVER) National Industry Skills Committee (NISC) National Quality Council (NQC) National Action Groups and Taskforces Industry Skills Councils (ISCs) Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) Australia Ltd
The national governance and accountability framework Ministerial Council for Training, Education and Employment National Senior Officials Committee (NSOC) Client Advisory Alliance National Training Statistics Committee National Centre for Vocational Education Research (NCVER) National Industry Skills Committee (NISC) National Quality Council (NQC) National Action Groups and Taskforces Industry Skills Councils (ISCs) Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) Australia Ltd
 Quality assurance operates through a standards approach
Quality assurance operates through a standards approach
 Organisation of training
Organisation of training
 Industry Skills Councils www. isc. org. au
Industry Skills Councils www. isc. org. au
 Training Packages promote flexibility § Flexible delivery against standards § Teachers require industry experience and VET teaching qualification § Delivery tailored to meet local region, employer needs and learner circumstances
Training Packages promote flexibility § Flexible delivery against standards § Teachers require industry experience and VET teaching qualification § Delivery tailored to meet local region, employer needs and learner circumstances
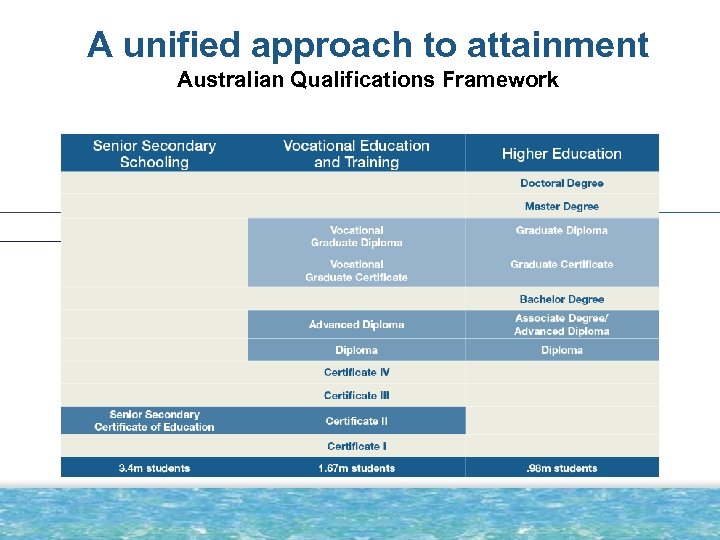 A unified approach to attainment Australian Qualifications Framework
A unified approach to attainment Australian Qualifications Framework
 AQTF: Three key components § Essential Standards for Registration § Standards for state and territory registering bodies § Excellence Criteria
AQTF: Three key components § Essential Standards for Registration § Standards for state and territory registering bodies § Excellence Criteria
 Regulating the AQTF § Regulation of standards for training providers is the responsibility of states and territory governments. § There are: § Eight state and territory regulators § National Audit and Registration Agency § Underperforming providers are a key challenge for regulation § Balance between protection for students and due process for providers
Regulating the AQTF § Regulation of standards for training providers is the responsibility of states and territory governments. § There are: § Eight state and territory regulators § National Audit and Registration Agency § Underperforming providers are a key challenge for regulation § Balance between protection for students and due process for providers
 Review of the AQTF § Pressures on the current quality assurance arrangements: § Weak initial registration requirements § Heavy emphasis on outcomes § Heavy continuous improvement focus
Review of the AQTF § Pressures on the current quality assurance arrangements: § Weak initial registration requirements § Heavy emphasis on outcomes § Heavy continuous improvement focus
 Regulating quality of training products § National recognition assured through standards and regulation § National Quality Council
Regulating quality of training products § National recognition assured through standards and regulation § National Quality Council
 National Regulation § National Regulation for VET will have two key elements: § National Regulator § National Standards Council
National Regulation § National Regulation for VET will have two key elements: § National Regulator § National Standards Council
 Future directions Council of Australian Governments’ targets §Lift Year 12 or equivalent attainment to 90% by 2015 §Halve proportion of 20 to 64 year olds with below Certificate III qualifications by 2020 §Double higher qualification completions (Diploma and Advanced Diploma) by 2020 § 40% of 25 -34 year olds attain a higher education qualification by 2025
Future directions Council of Australian Governments’ targets §Lift Year 12 or equivalent attainment to 90% by 2015 §Halve proportion of 20 to 64 year olds with below Certificate III qualifications by 2020 §Double higher qualification completions (Diploma and Advanced Diploma) by 2020 § 40% of 25 -34 year olds attain a higher education qualification by 2025
 Future directions Strengthening the apprentice system § Seamless access, re-entry & deferral § Incentives for commencements and retention of trade apprentices § Prep-apprenticeship scheme for school students § Apprenticeship incentive program
Future directions Strengthening the apprentice system § Seamless access, re-entry & deferral § Incentives for commencements and retention of trade apprentices § Prep-apprenticeship scheme for school students § Apprenticeship incentive program
 Future directions Sustainable & green education § Clean Sustainable Skills Package 50, 000 green jobs and training opportunities A$94 m § Skills for a low carbon economy — carbon challenge measure § National Green Skills Agreement — new trade apprentices to graduate with green skills, knowledge and training
Future directions Sustainable & green education § Clean Sustainable Skills Package 50, 000 green jobs and training opportunities A$94 m § Skills for a low carbon economy — carbon challenge measure § National Green Skills Agreement — new trade apprentices to graduate with green skills, knowledge and training
 Conclusion § § Flexible system – responsive to change Integrated with industry Continuing process of improvement Increasing skill levels of Australians www. deewr. gov. au/Skills
Conclusion § § Flexible system – responsive to change Integrated with industry Continuing process of improvement Increasing skill levels of Australians www. deewr. gov. au/Skills


