 Augmenting Visualizations with Physical Models in the Moon-Phases Module Meytal Hans, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology Yael Kali, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology Yoav Yair, The Open University, Israel
Augmenting Visualizations with Physical Models in the Moon-Phases Module Meytal Hans, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology Yael Kali, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology Yoav Yair, The Open University, Israel
 Research Rationale • Students have difficulties in understanding the moon phases because: • Requires spatial abilities • Large scale dynamic phenomenon • Involves understanding the phenomenon from multiple perspectives (frames of reference) (e. g. : Mulholland & Ginns, 2007; Nussbaum & Novak, 1976; Callison and Wright , 1993) • Visualizations and physical models can each support learning (e. g. : Hansen et al. , 2004; Coyle, Gregory, Luzader, Sadler & Shapiro, 1993; Gazit, Yair & Chen, 2005; Trumper, 2006)
Research Rationale • Students have difficulties in understanding the moon phases because: • Requires spatial abilities • Large scale dynamic phenomenon • Involves understanding the phenomenon from multiple perspectives (frames of reference) (e. g. : Mulholland & Ginns, 2007; Nussbaum & Novak, 1976; Callison and Wright , 1993) • Visualizations and physical models can each support learning (e. g. : Hansen et al. , 2004; Coyle, Gregory, Luzader, Sadler & Shapiro, 1993; Gazit, Yair & Chen, 2005; Trumper, 2006)
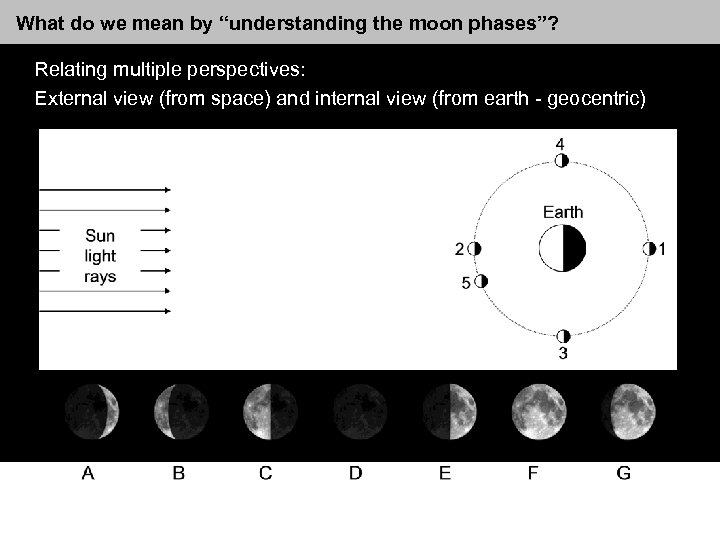 What do we mean by “understanding the moon phases”? Relating multiple perspectives: External view (from space) and internal view (from earth - geocentric)
What do we mean by “understanding the moon phases”? Relating multiple perspectives: External view (from space) and internal view (from earth - geocentric)
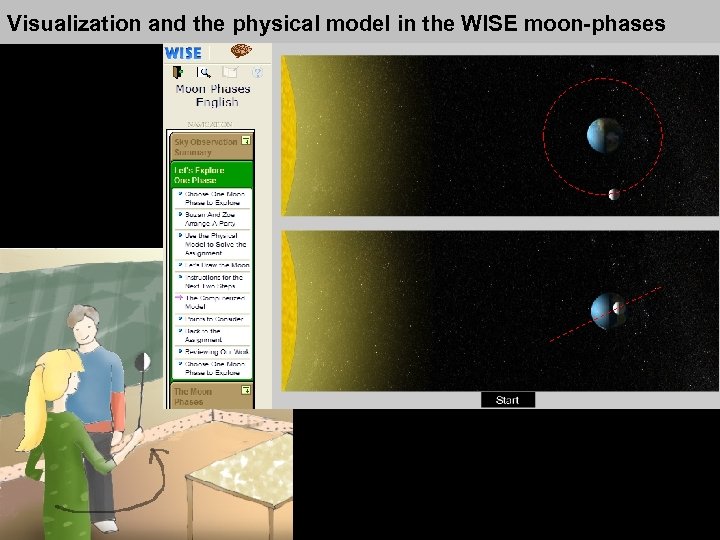 Visualization and the physical model in the WISE moon-phases
Visualization and the physical model in the WISE moon-phases
 Goals To examine the effect of the Moon Phases module on: 1. Students’ ability to solve problems regarding the moon phases 2. Students’ ability to solve general spatial ability problems that require a. relating between different frames of reference b. Mental rotation (Purdue test) To explore how students develop their understanding of the moon phases and their spatial abilities moon phases and spatial abilities in this context.
Goals To examine the effect of the Moon Phases module on: 1. Students’ ability to solve problems regarding the moon phases 2. Students’ ability to solve general spatial ability problems that require a. relating between different frames of reference b. Mental rotation (Purdue test) To explore how students develop their understanding of the moon phases and their spatial abilities moon phases and spatial abilities in this context.
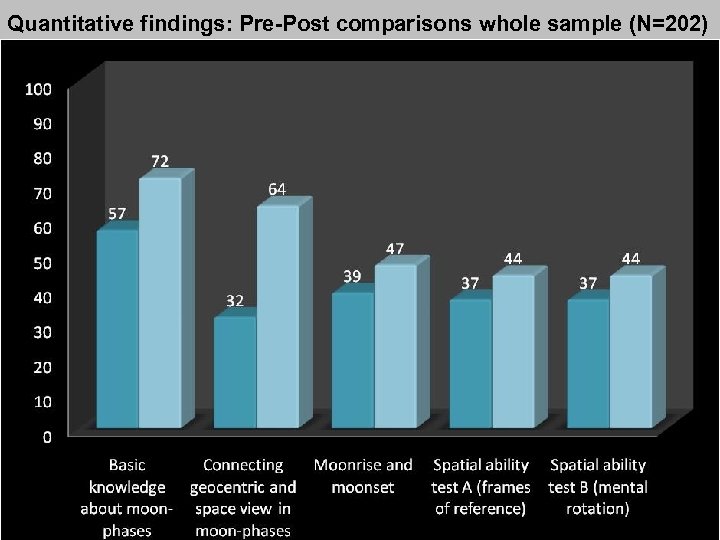 Quantitative findings: Pre-Post comparisons whole sample (N=202)
Quantitative findings: Pre-Post comparisons whole sample (N=202)
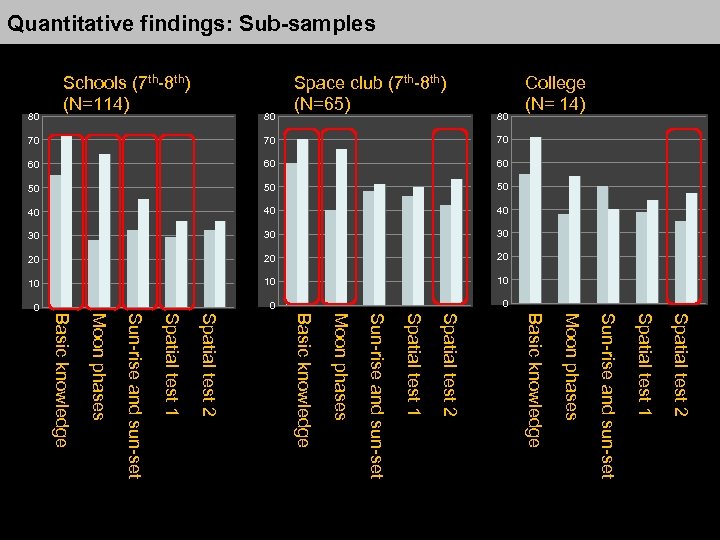 Quantitative findings: Sub-samples 80 70 70 70 60 60 60 50 50 50 40 40 40 30 30 30 20 20 20 10 10 10 0 0 College (N= 14) 80 Space club (7 th-8 th) (N=65) 80 Schools (7 th-8 th) (N=114) 0 Spatial test 2 Spatial test 1 Sun-rise and sun-set Moon phases Basic knowledge
Quantitative findings: Sub-samples 80 70 70 70 60 60 60 50 50 50 40 40 40 30 30 30 20 20 20 10 10 10 0 0 College (N= 14) 80 Space club (7 th-8 th) (N=65) 80 Schools (7 th-8 th) (N=114) 0 Spatial test 2 Spatial test 1 Sun-rise and sun-set Moon phases Basic knowledge
 Stages in the development of understanding of the moon-phases Aha points: 1 - Internal (geocentric) view 2 – Awareness of difference: internal / external views. 3 – Relating internal / external views 4 – Adding relative movement (moon-rise and moon-set)
Stages in the development of understanding of the moon-phases Aha points: 1 - Internal (geocentric) view 2 – Awareness of difference: internal / external views. 3 – Relating internal / external views 4 – Adding relative movement (moon-rise and moon-set)
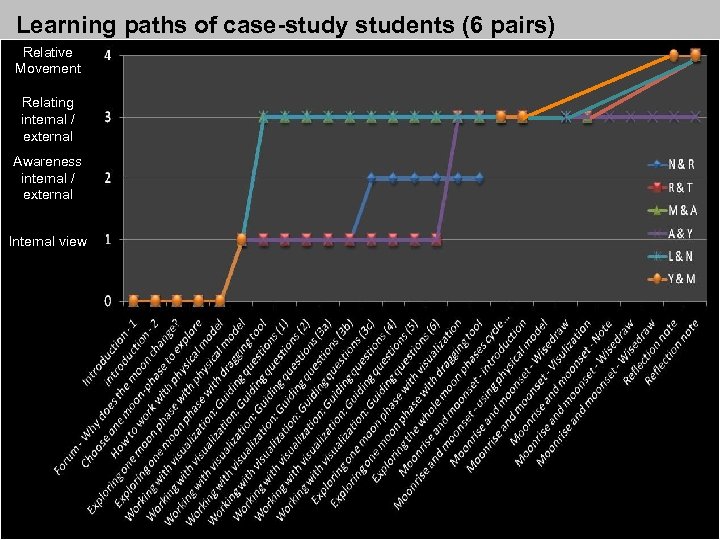 Learning paths of case-study students (6 pairs) Relative Movement Relating internal / external Awareness internal / external Internal view
Learning paths of case-study students (6 pairs) Relative Movement Relating internal / external Awareness internal / external Internal view
 Critical factors in learning (reaching aha points) from the visualization • Back and forth transitions between visualization (external view) and physical model (internal view) • Negotiation of understanding between students • Guidance: • Scaffolding guiding questions in module • Teacher as guide
Critical factors in learning (reaching aha points) from the visualization • Back and forth transitions between visualization (external view) and physical model (internal view) • Negotiation of understanding between students • Guidance: • Scaffolding guiding questions in module • Teacher as guide