89079930a9a32ad96c90f8710f0fb31c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Atonement Theories Historical views on how God makes reconciliation possible
Atonement Theories Historical views on how God makes reconciliation possible
 ATONEMENT • Atonement brings to mind many ideas… - Animal sacrifices - Forgiveness - Redemption - Death - Priesthood - Ransom - Debt - Wrath • Since the 2 nd century AD, theologians have proposed numerous theories to explain how God accomplishes atonement • ATONEMENT = Being made “at one” with God, being reconciled, being reunited
ATONEMENT • Atonement brings to mind many ideas… - Animal sacrifices - Forgiveness - Redemption - Death - Priesthood - Ransom - Debt - Wrath • Since the 2 nd century AD, theologians have proposed numerous theories to explain how God accomplishes atonement • ATONEMENT = Being made “at one” with God, being reconciled, being reunited
 Why Atonement is Needed • God’s eternal intention (desire) is to be in communion with man • Each person who sins separates himself from God • Atonement restores the broken communion • OT “atonement” ≈ NT “reconciliation” • But how does God’s reconciliation work? • “In the early church there seems to have been little attention given to the way atonement works” (Horton, 2006)
Why Atonement is Needed • God’s eternal intention (desire) is to be in communion with man • Each person who sins separates himself from God • Atonement restores the broken communion • OT “atonement” ≈ NT “reconciliation” • But how does God’s reconciliation work? • “In the early church there seems to have been little attention given to the way atonement works” (Horton, 2006)
 New Testament Words for God’s Role • • • Justify (Romans 5: 9) – to regard one as innocent, as righteous Sanctify (Hebrews 10: 29) – to set apart for a purpose Redeem (Titus 2: 4) – to buy back, reclaim, restore to rightful owner Forgive (Ephesians 1: 7) – to not hold sin against a person Ransom (1 Timothy 2: 6) – price to purchase another’s freedom Propitiation (1 John 4: 10) – turns away God’s wrath by removing sin Reconcile (2 Corinthians 5: 18 -19) – unify, bring together Raise up (Romans 6: 4) – to bestow or restore life Grace (Ephesians 2: 8) – unearned favor Ø God made these available to man in Christ Ø Any “atonement theory” must consider all of them Ø But none of man’s theories have been all-inclusive…
New Testament Words for God’s Role • • • Justify (Romans 5: 9) – to regard one as innocent, as righteous Sanctify (Hebrews 10: 29) – to set apart for a purpose Redeem (Titus 2: 4) – to buy back, reclaim, restore to rightful owner Forgive (Ephesians 1: 7) – to not hold sin against a person Ransom (1 Timothy 2: 6) – price to purchase another’s freedom Propitiation (1 John 4: 10) – turns away God’s wrath by removing sin Reconcile (2 Corinthians 5: 18 -19) – unify, bring together Raise up (Romans 6: 4) – to bestow or restore life Grace (Ephesians 2: 8) – unearned favor Ø God made these available to man in Christ Ø Any “atonement theory” must consider all of them Ø But none of man’s theories have been all-inclusive…
 Ransom Theory • Taught by Origen and Gregory of Nyssa (3 rd century) • Based on Scriptures that Christ came as a ransom • Matthew 20: 28; Mark 10: 45; 1 Timothy 2: 6 • Ransom Theory • • • AKA: Classical theory, Satan theory God abandoned mankind when Adam sinned, Satan took souls hostage Jesus was offered to Satan as ransom in exchange for the souls of men Satan honored the deal, but God didn’t Problems: • • Makes God compromise with Satan Makes Satan honorable & God the deceiver Does not provide forgiveness of man’s sins Not comprehensive of all facets of salvation
Ransom Theory • Taught by Origen and Gregory of Nyssa (3 rd century) • Based on Scriptures that Christ came as a ransom • Matthew 20: 28; Mark 10: 45; 1 Timothy 2: 6 • Ransom Theory • • • AKA: Classical theory, Satan theory God abandoned mankind when Adam sinned, Satan took souls hostage Jesus was offered to Satan as ransom in exchange for the souls of men Satan honored the deal, but God didn’t Problems: • • Makes God compromise with Satan Makes Satan honorable & God the deceiver Does not provide forgiveness of man’s sins Not comprehensive of all facets of salvation
 Satisfaction Theory • 11 th century: Anselm of Canterbury rejected classical Ransom theory, denied that God paid ransom to Satan • Man owes honor to God, but is unable to satisfy it adequately • God’s honor is offended by man’s sin, His honor must be satisfied • Jesus satisfied God’s honor, was rewarded for it because He was sinless, and passed the reward (eternal life) to man • AKA: Commercial Theory • Ransom was paid to God, not Satan • Problems: – Overlooks God’s ability to forgive sins – Does not require man’s participation – Does not connect Christ’s death to salvation
Satisfaction Theory • 11 th century: Anselm of Canterbury rejected classical Ransom theory, denied that God paid ransom to Satan • Man owes honor to God, but is unable to satisfy it adequately • God’s honor is offended by man’s sin, His honor must be satisfied • Jesus satisfied God’s honor, was rewarded for it because He was sinless, and passed the reward (eternal life) to man • AKA: Commercial Theory • Ransom was paid to God, not Satan • Problems: – Overlooks God’s ability to forgive sins – Does not require man’s participation – Does not connect Christ’s death to salvation
 Moral Influence Theory • 12 the century: Peter Abelard’s response to Anselm’s theory • Christ died to influence mankind toward moral improvement • Emphasizes God’s love, exemplified in Christ’s self-sacrifice, which inspires man to respond with repentance & following His example • Found in hymns like “When I Survey The Wondrous Cross” and “Ten Thousand Angels” and “None of self and all of Thee” • Based on 1 Peter 2: 21 and 1 John 3: 16: “We know love by this, that He laid down His life for us; and we ought to lay down our lives for the brethren” • Emotional appeals based on this theory are popular today • Problems: There is some truth in this theory, but alone it does not capture the entirety of reconciliation. It does not attribute saving power to Christ’s death, but portrays it as a demonstration of love that calls us to change.
Moral Influence Theory • 12 the century: Peter Abelard’s response to Anselm’s theory • Christ died to influence mankind toward moral improvement • Emphasizes God’s love, exemplified in Christ’s self-sacrifice, which inspires man to respond with repentance & following His example • Found in hymns like “When I Survey The Wondrous Cross” and “Ten Thousand Angels” and “None of self and all of Thee” • Based on 1 Peter 2: 21 and 1 John 3: 16: “We know love by this, that He laid down His life for us; and we ought to lay down our lives for the brethren” • Emotional appeals based on this theory are popular today • Problems: There is some truth in this theory, but alone it does not capture the entirety of reconciliation. It does not attribute saving power to Christ’s death, but portrays it as a demonstration of love that calls us to change.
 Governmental Theory • Proposed by Hugo Grotius (16 th century) • God hates sin so much, He proffered the threat of death to man by killing His Own Son; this threat should deter man from sinning • Based on Ezekiel 18: 4 “The soul who sins will die” • But God didn’t really want everyone to die, so… • God accepted the reduced penalty of Christ’s physical death • Grotius taught that God is not required to follow through with the penalty of His law • Hymn: “The All-Seeing Eye” • Taught today by Methodists, Nazarenes • Problems: makes God’s law arbitrary and penalty flexible
Governmental Theory • Proposed by Hugo Grotius (16 th century) • God hates sin so much, He proffered the threat of death to man by killing His Own Son; this threat should deter man from sinning • Based on Ezekiel 18: 4 “The soul who sins will die” • But God didn’t really want everyone to die, so… • God accepted the reduced penalty of Christ’s physical death • Grotius taught that God is not required to follow through with the penalty of His law • Hymn: “The All-Seeing Eye” • Taught today by Methodists, Nazarenes • Problems: makes God’s law arbitrary and penalty flexible
 Penal Substitution Theory • Product of 16 th century Reformation • John Calvin, a lawyer, re-interpreted Anselm’s Satisfaction Theory in terms of a legal system of penalty • Says that Jesus substituted Himself in our place, obeyed the Law perfectly in our place, had our sins transferred to Himself, took all of God’s wrath in our place, died on the cross in our place. • Substitution theory terminology is dangerously pervasive! • Hymns like “Hallelujah What a Savior!” and “He bore it all” and “They are nailed to the cross” and “He paid a debt” • Calvin’s “TULIP” is based on this theory • NIV, translated by Calvinists, is slanted toward this theory • Problems are very numerous: next 5 slides…
Penal Substitution Theory • Product of 16 th century Reformation • John Calvin, a lawyer, re-interpreted Anselm’s Satisfaction Theory in terms of a legal system of penalty • Says that Jesus substituted Himself in our place, obeyed the Law perfectly in our place, had our sins transferred to Himself, took all of God’s wrath in our place, died on the cross in our place. • Substitution theory terminology is dangerously pervasive! • Hymns like “Hallelujah What a Savior!” and “He bore it all” and “They are nailed to the cross” and “He paid a debt” • Calvin’s “TULIP” is based on this theory • NIV, translated by Calvinists, is slanted toward this theory • Problems are very numerous: next 5 slides…
 Problems with Penal Substitution Theory • The Law of Moses does not permit this theory – The Law of Moses specifically prohibits substitution • Deut. 24: 16; Jer. 31: 30; Ezek. 18: 19 -20; 2 Chron. 25: 3 -4 – The Lamb of God died like a sacrificial animal. Sacrificial animals were not punished, nor did they receive God’s wrath. – Sacrificial offerings were made on one’s behalf not in one’s place • Lev. 1: 4; 5: 6; 5: 10; 8: 34; 14: 18, 29, 31; 15: 15, 30; 23: 28; et al. – If Jesus fulfilled the Law of Moses for anyone, it was for the Jews, and that doesn’t help the rest of us (Gal. 4: 5) – If Jesus’ vicarious perfect obedience to the Law merits salvation, then we are saved by law and not by grace
Problems with Penal Substitution Theory • The Law of Moses does not permit this theory – The Law of Moses specifically prohibits substitution • Deut. 24: 16; Jer. 31: 30; Ezek. 18: 19 -20; 2 Chron. 25: 3 -4 – The Lamb of God died like a sacrificial animal. Sacrificial animals were not punished, nor did they receive God’s wrath. – Sacrificial offerings were made on one’s behalf not in one’s place • Lev. 1: 4; 5: 6; 5: 10; 8: 34; 14: 18, 29, 31; 15: 15, 30; 23: 28; et al. – If Jesus fulfilled the Law of Moses for anyone, it was for the Jews, and that doesn’t help the rest of us (Gal. 4: 5) – If Jesus’ vicarious perfect obedience to the Law merits salvation, then we are saved by law and not by grace
 Problems with Penal Substitution Theory • When we read the phrase “for us” in the Bible, we tend to think “in our place. ” But the original Greek word huper which is translated for actually means on behalf of or for the sake of (Strong’s #5228) • Huper appears 160 times in Greek New Testament , such as: • • Luke 22: 19 -20 – “body which is given for you…blood which is shed for you” John 10: 11 – “shepherd lays down his life for the sheep” (is the wolf fooled? ) Rom. 5: 8 – “while we were yet sinners, Christ died for us” (no imputed sin!) Rom. 8: 34 – “Christ…intercedes for us” (I cannot intercede for myself) • Christ came “for my sake” not “in my place” • 1 Cor. 8: 11 • 2 Cor. 8: 9 • 1 Pet. 1: 20 -21 • When we read or speak of Christ doing something for us, we need to understand that He does it for our sake, not in our place!
Problems with Penal Substitution Theory • When we read the phrase “for us” in the Bible, we tend to think “in our place. ” But the original Greek word huper which is translated for actually means on behalf of or for the sake of (Strong’s #5228) • Huper appears 160 times in Greek New Testament , such as: • • Luke 22: 19 -20 – “body which is given for you…blood which is shed for you” John 10: 11 – “shepherd lays down his life for the sheep” (is the wolf fooled? ) Rom. 5: 8 – “while we were yet sinners, Christ died for us” (no imputed sin!) Rom. 8: 34 – “Christ…intercedes for us” (I cannot intercede for myself) • Christ came “for my sake” not “in my place” • 1 Cor. 8: 11 • 2 Cor. 8: 9 • 1 Pet. 1: 20 -21 • When we read or speak of Christ doing something for us, we need to understand that He does it for our sake, not in our place!
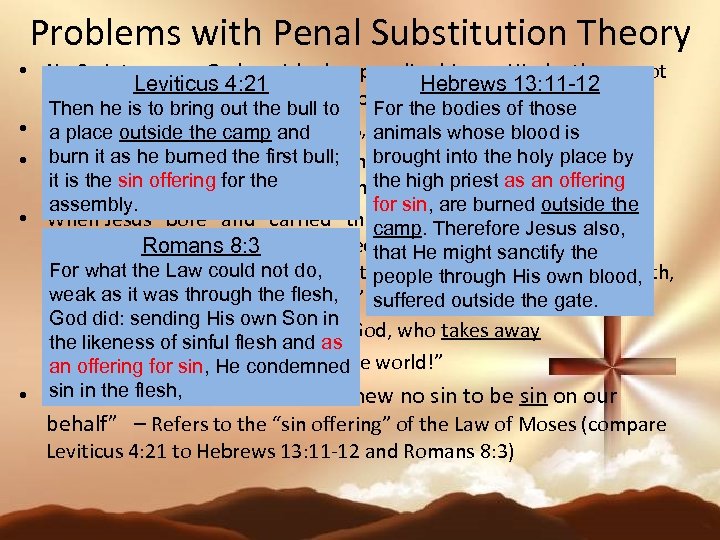 Problems with Penal Substitution Theory • No Scripture says God punished or penalized Jesus. His death was not Leviticus 4: 21 Hebrews 13: 11 -12 God’s he is to bring andthe bull not bear my penalty. of those punishment, out He did to For the bodies Then • If my sins were transferred to Jesus, He was not a sinless sacrifice a place outside the camp and animals whose blood is burn it as he burned the first bull; brought into the in full” then • If God does not forgive my debts until they are “paid holy place by. I it is the sin offering for the high priest as an offering don’t have to forgive my debtors until they are “paid in full” as well assembly. for sin, are burned outside the • When Jesus “bore” and “carried” thecamp. Therefore Jesus also, sorrows and infirmities of people, He. Romans 8: 3 and “carriedthat He those sorrows the “bore away” might sanctify and For what the Law could not do, infirmities, without becoming infected by them. Likewise, in His death, people through His own blood, weak as away” and “carried away” suffered outside the gate. He “bore it was through the flesh, our sins, as in John 1: 29: God did: sending His own Son in “Behold, the Lamb of God, who takes away the likeness of sinful flesh and as the sin of the an offering for sin, He condemned world!” sin in 5: 21 “He • 2 Cor. the flesh, made Him who knew no sin to be sin on our behalf” – Refers to the “sin offering” of the Law of Moses (compare Leviticus 4: 21 to Hebrews 13: 11 -12 and Romans 8: 3)
Problems with Penal Substitution Theory • No Scripture says God punished or penalized Jesus. His death was not Leviticus 4: 21 Hebrews 13: 11 -12 God’s he is to bring andthe bull not bear my penalty. of those punishment, out He did to For the bodies Then • If my sins were transferred to Jesus, He was not a sinless sacrifice a place outside the camp and animals whose blood is burn it as he burned the first bull; brought into the in full” then • If God does not forgive my debts until they are “paid holy place by. I it is the sin offering for the high priest as an offering don’t have to forgive my debtors until they are “paid in full” as well assembly. for sin, are burned outside the • When Jesus “bore” and “carried” thecamp. Therefore Jesus also, sorrows and infirmities of people, He. Romans 8: 3 and “carriedthat He those sorrows the “bore away” might sanctify and For what the Law could not do, infirmities, without becoming infected by them. Likewise, in His death, people through His own blood, weak as away” and “carried away” suffered outside the gate. He “bore it was through the flesh, our sins, as in John 1: 29: God did: sending His own Son in “Behold, the Lamb of God, who takes away the likeness of sinful flesh and as the sin of the an offering for sin, He condemned world!” sin in 5: 21 “He • 2 Cor. the flesh, made Him who knew no sin to be sin on our behalf” – Refers to the “sin offering” of the Law of Moses (compare Leviticus 4: 21 to Hebrews 13: 11 -12 and Romans 8: 3)
 Problems with Penal Substitution Theory • The penalty for sin is eternal destruction (2 Thess. 1: 9); Jesus did not experience this spiritual death…He went to Paradise & was resurrected on the 3 rd day • If physical death is the penalty for sin, and Jesus’ physical death satisfies the penalty, why do people still die? • Per 2 Corinthians 5: 14 -15, if Christ died as our substitute then He also was raised up as our substitute and we won’t be resurrected! • 2 Corinthians 10: 6 – Paul is still punishing disobedience • Hebrews 10: 29 – some deserve more severe punishment • Romans 1: 27 - people still receive their “due penalty” • Colossians 2: 14 - Jesus did not “pay” the debt… • If Jesus took our cross, why Matt. 10: 38?
Problems with Penal Substitution Theory • The penalty for sin is eternal destruction (2 Thess. 1: 9); Jesus did not experience this spiritual death…He went to Paradise & was resurrected on the 3 rd day • If physical death is the penalty for sin, and Jesus’ physical death satisfies the penalty, why do people still die? • Per 2 Corinthians 5: 14 -15, if Christ died as our substitute then He also was raised up as our substitute and we won’t be resurrected! • 2 Corinthians 10: 6 – Paul is still punishing disobedience • Hebrews 10: 29 – some deserve more severe punishment • Romans 1: 27 - people still receive their “due penalty” • Colossians 2: 14 - Jesus did not “pay” the debt… • If Jesus took our cross, why Matt. 10: 38?
 Problems with Penal Substitution Theory • If Jesus took all my sins on himself and paid the full penalty in my place already, why should I repent and what do I have to fear by sinful living? • If there is anything I have to do to be saved, whether it is recite a “sinner’s prayer” or be baptized, then substitution theory cannot hold. • This theory does not take into consideration the blood of Christ, only the death of His body. Yet the Scriptures show that all the power for our salvation is in the blood of Christ! • It also makes Christ’s resurrection and intercessory priesthood unnecessary • A substitute takes the place of another to do exactly what the original could have done. Jesus did God’s work, not man’s work!
Problems with Penal Substitution Theory • If Jesus took all my sins on himself and paid the full penalty in my place already, why should I repent and what do I have to fear by sinful living? • If there is anything I have to do to be saved, whether it is recite a “sinner’s prayer” or be baptized, then substitution theory cannot hold. • This theory does not take into consideration the blood of Christ, only the death of His body. Yet the Scriptures show that all the power for our salvation is in the blood of Christ! • It also makes Christ’s resurrection and intercessory priesthood unnecessary • A substitute takes the place of another to do exactly what the original could have done. Jesus did God’s work, not man’s work!
 Calvinist terminology…a dangerous problem! Indeed, even among brethren today, there are those who have been reading and absorbing denominational ideas and terminology from suspicious sources: periodicals, tracts, commentaries and books of avowed Calvinists. Bible subjects are phrased in Calvinistic terms. Positions which faithful Gospel preachers have opposed in debates with Baptist and other Calvinist preachers in the past are now advocated by preachers in the church of Christ. And these positions are being widely circulated in sermons and bulletins. - Tom Roberts, Neo-Calvinism In The Church Of Christ, 1980. Examples: Barnes’ Notes, Matthew Henry Commentary, Adam Clarke’s Commentary, Pulpit Commentary, A. T. Robertson’s Word Pictures Calvinists (Presbyterian, Southern Baptists, etc. ) vigorously defend Penal Substitution Theory today…it is the foundation of their doctrine…it is the hand inside the 3 -fingered glove of imputation!
Calvinist terminology…a dangerous problem! Indeed, even among brethren today, there are those who have been reading and absorbing denominational ideas and terminology from suspicious sources: periodicals, tracts, commentaries and books of avowed Calvinists. Bible subjects are phrased in Calvinistic terms. Positions which faithful Gospel preachers have opposed in debates with Baptist and other Calvinist preachers in the past are now advocated by preachers in the church of Christ. And these positions are being widely circulated in sermons and bulletins. - Tom Roberts, Neo-Calvinism In The Church Of Christ, 1980. Examples: Barnes’ Notes, Matthew Henry Commentary, Adam Clarke’s Commentary, Pulpit Commentary, A. T. Robertson’s Word Pictures Calvinists (Presbyterian, Southern Baptists, etc. ) vigorously defend Penal Substitution Theory today…it is the foundation of their doctrine…it is the hand inside the 3 -fingered glove of imputation!
 Calvinism and Arminiunism • Calvin’s salvation theory has 5 points: – Total hereditary depravity (inherited sin, totally evil nature) – Unconditional election (predestination of who will be saved) – Limited atonement (substitution theory, but only for the elect) – Irresistable grace (God is sovereign; you can’t resist salvation) – Perseverance of the saved (once saved, always saved) • Jacobus Arminius (1560 -1609) started off as a Calvinist • Decided to reject the “U” and the “I” of Calvin’s TULIP • Wrote his own “ 5 Articles of Remonstrance” based on Governmental Theory of Atonement • Later, John Wesley used Arminius’ views to found the Methodist denomination. • Church of the Nazarene, Seventh Day Adventists, Assembly of God, Pentecostals, & Salvation Army denominations teach Arminiunism & Governmental Theory
Calvinism and Arminiunism • Calvin’s salvation theory has 5 points: – Total hereditary depravity (inherited sin, totally evil nature) – Unconditional election (predestination of who will be saved) – Limited atonement (substitution theory, but only for the elect) – Irresistable grace (God is sovereign; you can’t resist salvation) – Perseverance of the saved (once saved, always saved) • Jacobus Arminius (1560 -1609) started off as a Calvinist • Decided to reject the “U” and the “I” of Calvin’s TULIP • Wrote his own “ 5 Articles of Remonstrance” based on Governmental Theory of Atonement • Later, John Wesley used Arminius’ views to found the Methodist denomination. • Church of the Nazarene, Seventh Day Adventists, Assembly of God, Pentecostals, & Salvation Army denominations teach Arminiunism & Governmental Theory
 Atonement Theories: What Do We Believe? • There is no “atonement theory” taught in the New Testament. There are only atonement facts. • The New Testament presents God’s reconciliatory work in many different manners, and all of them involve the blood of Jesus • Let us take comfort in knowing that God’s work is sufficient to make salvation possible • Let us concern ourselves with our own role in responding to God’s gracious offer and invitation (2 Cor. 5: 20)
Atonement Theories: What Do We Believe? • There is no “atonement theory” taught in the New Testament. There are only atonement facts. • The New Testament presents God’s reconciliatory work in many different manners, and all of them involve the blood of Jesus • Let us take comfort in knowing that God’s work is sufficient to make salvation possible • Let us concern ourselves with our own role in responding to God’s gracious offer and invitation (2 Cor. 5: 20)


