NIS Atomic Theory.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Atomic Theory Atoms and their Makeup
Atomic Theory Atoms and their Makeup
 Atomic Theory Modern atomic theory is a result of more than 2000 years of empirical data, hypotheses, theories and the development of laws to explain the data! • ATOM: From Greece (400 BC) – Matter is made from ATOMS • an ATOM is a small indivisible unit
Atomic Theory Modern atomic theory is a result of more than 2000 years of empirical data, hypotheses, theories and the development of laws to explain the data! • ATOM: From Greece (400 BC) – Matter is made from ATOMS • an ATOM is a small indivisible unit
 John Dalton’s Model of the Atom (Billiard Ball Model) c. 1803 1) Elements are made of extremely small particles called atoms. 2) Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. 3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form chemical compounds. 5) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged.
John Dalton’s Model of the Atom (Billiard Ball Model) c. 1803 1) Elements are made of extremely small particles called atoms. 2) Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. 3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form chemical compounds. 5) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged.
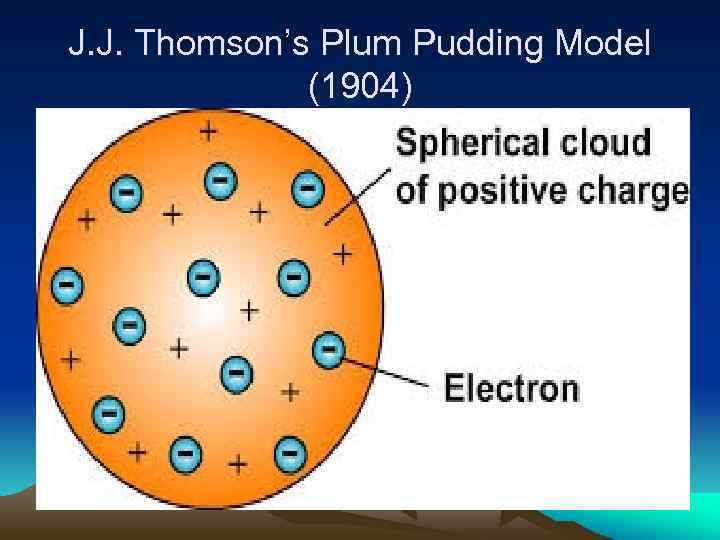 J. J. Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model (1904)
J. J. Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model (1904)
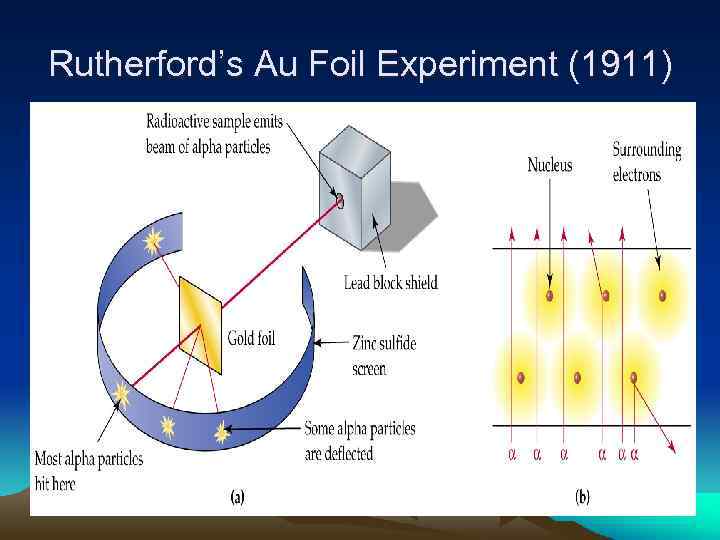 Rutherford’s Au Foil Experiment (1911)
Rutherford’s Au Foil Experiment (1911)
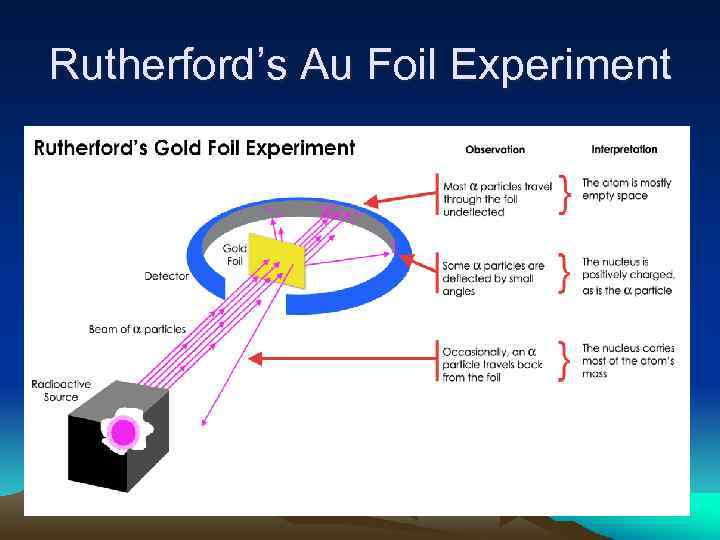 Rutherford’s Au Foil Experiment
Rutherford’s Au Foil Experiment
 Enter the Nucleus… But the biggest discovery was made when 1 in 20, 000 particles would deflect approximately 90 degrees or more from the parent beam. In fact, an occasional particle even fired right back at the experimenter. Perhaps Rutherford described the awe inspiring nature of the discovery best when he said: "It was as if you fired a 15 -inch shell at a sheet of tissue paper and it came back to hit you. "
Enter the Nucleus… But the biggest discovery was made when 1 in 20, 000 particles would deflect approximately 90 degrees or more from the parent beam. In fact, an occasional particle even fired right back at the experimenter. Perhaps Rutherford described the awe inspiring nature of the discovery best when he said: "It was as if you fired a 15 -inch shell at a sheet of tissue paper and it came back to hit you. "
 Alpha Particle? ? ? What is an alpha (α) Particle? ? ? An alpha particle is a bare Helium Nuclei… To understand this idea we need to know about Nuclide symbols, and isotopes…
Alpha Particle? ? ? What is an alpha (α) Particle? ? ? An alpha particle is a bare Helium Nuclei… To understand this idea we need to know about Nuclide symbols, and isotopes…
 Modern Atomic Theory Empirical data and 2000 plus years have given us the following model of the ATOM: 1. Atoms are electrically neutral: • charge (0) 2. Atoms are made from: • protons • neutrons • Electrons
Modern Atomic Theory Empirical data and 2000 plus years have given us the following model of the ATOM: 1. Atoms are electrically neutral: • charge (0) 2. Atoms are made from: • protons • neutrons • Electrons
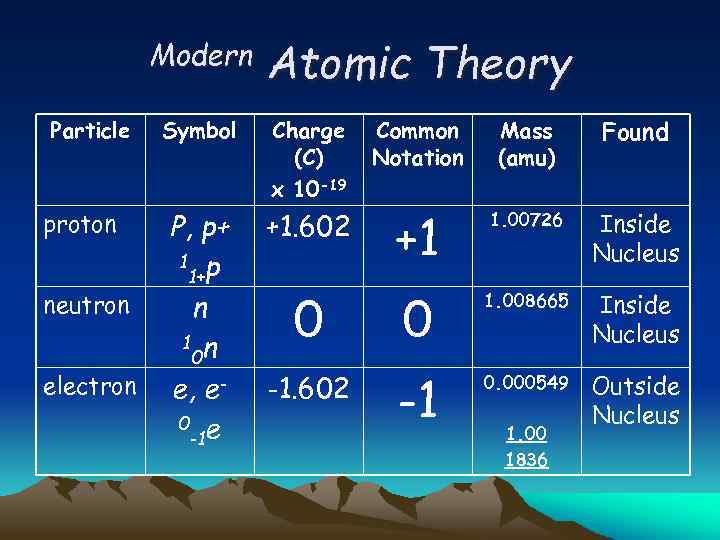 Modern Particle proton neutron electron Atomic Theory Common Notation Mass (amu) Found +1. 602 +1 1. 00726 Inside Nucleus 0 0 1. 008665 Inside Nucleus -1. 602 -1 0. 000549 Outside Nucleus Symbol Charge (C) x 10 -19 P, p+ 1 p 1+ n 1 n 0 e, e 0 e -1 1. 00 1836
Modern Particle proton neutron electron Atomic Theory Common Notation Mass (amu) Found +1. 602 +1 1. 00726 Inside Nucleus 0 0 1. 008665 Inside Nucleus -1. 602 -1 0. 000549 Outside Nucleus Symbol Charge (C) x 10 -19 P, p+ 1 p 1+ n 1 n 0 e, e 0 e -1 1. 00 1836
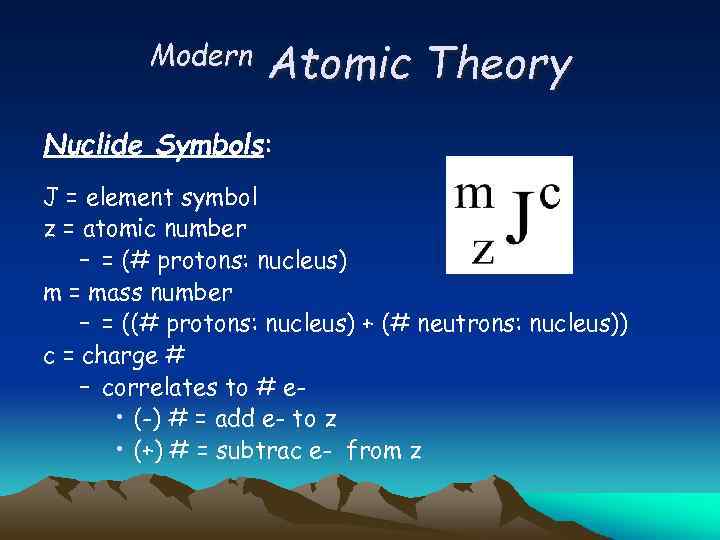 Modern Atomic Theory Nuclide Symbols: J = element symbol z = atomic number – = (# protons: nucleus) m = mass number – = ((# protons: nucleus) + (# neutrons: nucleus)) c = charge # – correlates to # e • (-) # = add e- to z • (+) # = subtrac e- from z
Modern Atomic Theory Nuclide Symbols: J = element symbol z = atomic number – = (# protons: nucleus) m = mass number – = ((# protons: nucleus) + (# neutrons: nucleus)) c = charge # – correlates to # e • (-) # = add e- to z • (+) # = subtrac e- from z
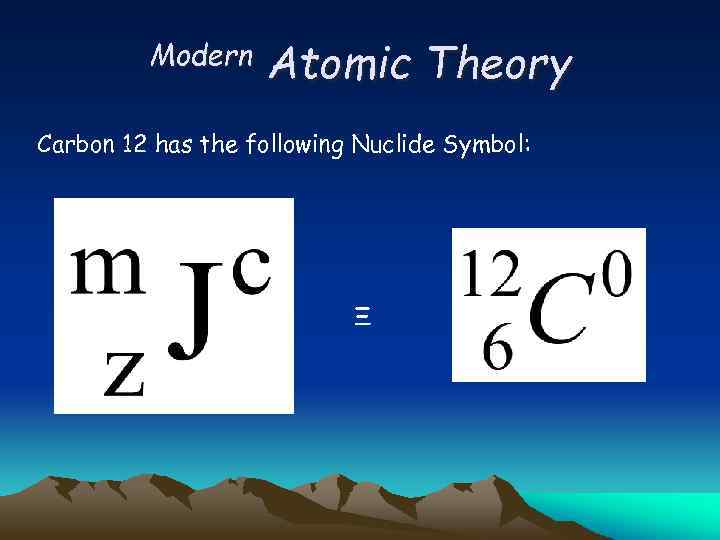 Modern Atomic Theory Carbon 12 has the following Nuclide Symbol: Ξ
Modern Atomic Theory Carbon 12 has the following Nuclide Symbol: Ξ
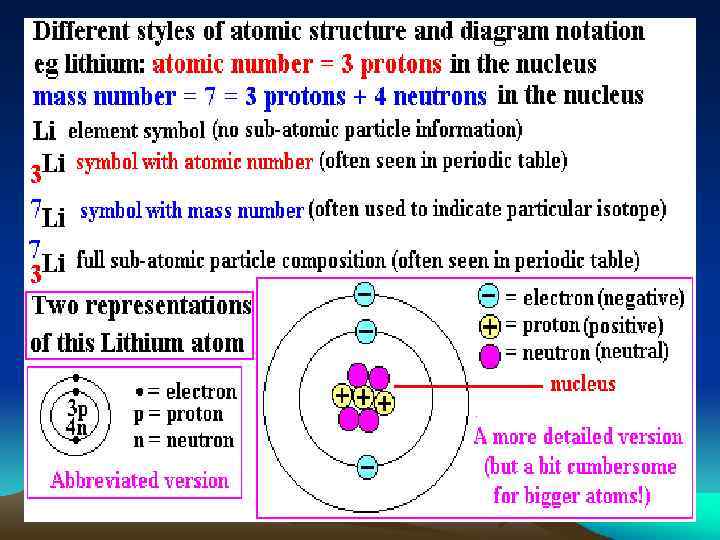
 Modern Atomic Theory Given a Nuclide Symbol: 1. Identify the element • cation or anion ? 2. provide the number of: – – – protons neutrons electrons
Modern Atomic Theory Given a Nuclide Symbol: 1. Identify the element • cation or anion ? 2. provide the number of: – – – protons neutrons electrons
 Modern Atomic Theory
Modern Atomic Theory
 Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in an iron (III) cation ? z= m= c=
Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in an iron (III) cation ? z= m= c=
 Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? z = Atomic Number (from Periodic Table) = 26 = Gives # protons = Element ID
Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? z = Atomic Number (from Periodic Table) = 26 = Gives # protons = Element ID
 Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? z = 26 m = Mass Number = 58 = Total number of protons and neutrons = Gives # neutrons
Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? z = 26 m = Mass Number = 58 = Total number of protons and neutrons = Gives # neutrons
 Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? z = 26 m = 58 (from nuclide symbol) c = charge number = +3 = Charge on the ion = Gives total number of electrons
Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? z = 26 m = 58 (from nuclide symbol) c = charge number = +3 = Charge on the ion = Gives total number of electrons
 Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? # protons # neutrons # electrons =? =? =?
Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? # protons # neutrons # electrons =? =? =?
 Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? # protons: =z 26
Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? # protons: =z 26
 Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? # neutrons: =m-z = 58 – 26 = 32
Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? # neutrons: =m-z = 58 – 26 = 32
 Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? # electrons: = z (+/-) (c): if +c: subtract c from z = if –c: add c to z = 26 – 3 = 23 (z – c = # e-) = (z + c = # e-)
Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? # electrons: = z (+/-) (c): if +c: subtract c from z = if –c: add c to z = 26 – 3 = 23 (z – c = # e-) = (z + c = # e-)
 Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? # protons # neutrons # electrons = 26 = 32 = 23
Modern Atomic Theory How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a cation of Fe+3? # protons # neutrons # electrons = 26 = 32 = 23
 Modern Atomic Theory For atoms of any given element, the atomic number (“z”) NEVER changes If “m” changes, you have “ISOTOPES” Isotopes: – One of two or more atoms of the same element with the same number of protons, but with different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei
Modern Atomic Theory For atoms of any given element, the atomic number (“z”) NEVER changes If “m” changes, you have “ISOTOPES” Isotopes: – One of two or more atoms of the same element with the same number of protons, but with different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei
 Modern Atomic Theory What are the 3 isotopes of hydrogen?
Modern Atomic Theory What are the 3 isotopes of hydrogen?
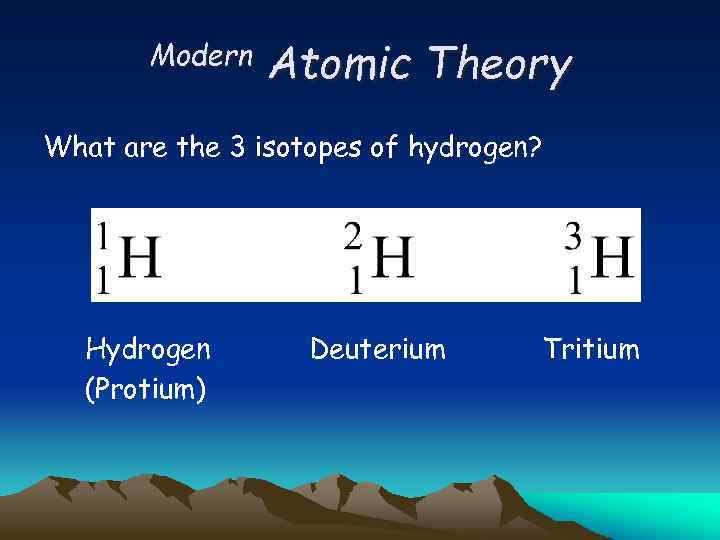 Modern Atomic Theory What are the 3 isotopes of hydrogen? Hydrogen (Protium) Deuterium Tritium
Modern Atomic Theory What are the 3 isotopes of hydrogen? Hydrogen (Protium) Deuterium Tritium
 Modern Atomic Theory The masses given on the periodic table are WEIGHTED AVERAGES of all known isotopes of a given element
Modern Atomic Theory The masses given on the periodic table are WEIGHTED AVERAGES of all known isotopes of a given element
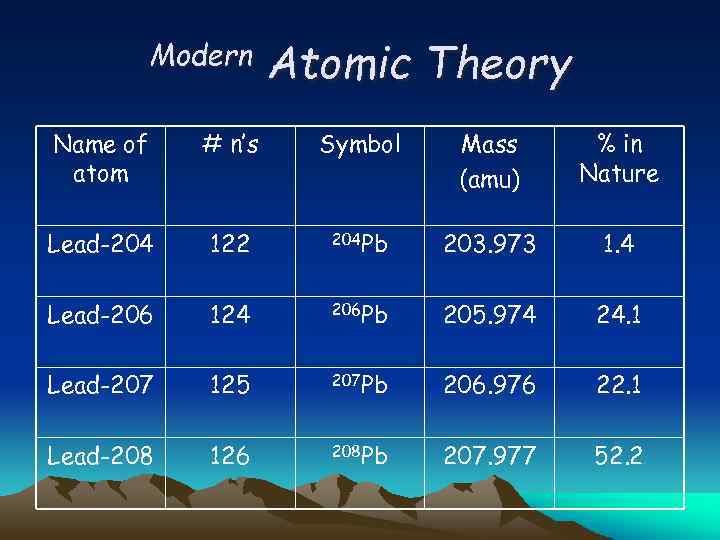 Modern Atomic Theory Name of atom # n’s Symbol Mass (amu) % in Nature Lead-204 122 204 Pb 203. 973 1. 4 Lead-206 124 206 Pb 205. 974 24. 1 Lead-207 125 207 Pb 206. 976 22. 1 Lead-208 126 208 Pb 207. 977 52. 2
Modern Atomic Theory Name of atom # n’s Symbol Mass (amu) % in Nature Lead-204 122 204 Pb 203. 973 1. 4 Lead-206 124 206 Pb 205. 974 24. 1 Lead-207 125 207 Pb 206. 976 22. 1 Lead-208 126 208 Pb 207. 977 52. 2
 Modern Atomic Theory What is the average atomic mass for Pb? Given: 0. 014 (203. 973) = 2. 8556 amu 0. 241 (205. 974) = 46. 639 amu 0. 221 (206. 976) = 45. 742 amu 0. 522 (207. 977) = 108. 56 amu Average mass = 206. 80 amu Why might this result differ from 207. 2?
Modern Atomic Theory What is the average atomic mass for Pb? Given: 0. 014 (203. 973) = 2. 8556 amu 0. 241 (205. 974) = 46. 639 amu 0. 221 (206. 976) = 45. 742 amu 0. 522 (207. 977) = 108. 56 amu Average mass = 206. 80 amu Why might this result differ from 207. 2?
 Modern Atomic Theory Radioactive decay, also known as nuclear decay or radioactivity, is the process by which a nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing radiation. A material that spontaneously emits this kind of radiation—which includes the emission of alpha particles (α), beta particles (β), and gamma rays (γ) —is considered radioactive.
Modern Atomic Theory Radioactive decay, also known as nuclear decay or radioactivity, is the process by which a nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing radiation. A material that spontaneously emits this kind of radiation—which includes the emission of alpha particles (α), beta particles (β), and gamma rays (γ) —is considered radioactive.
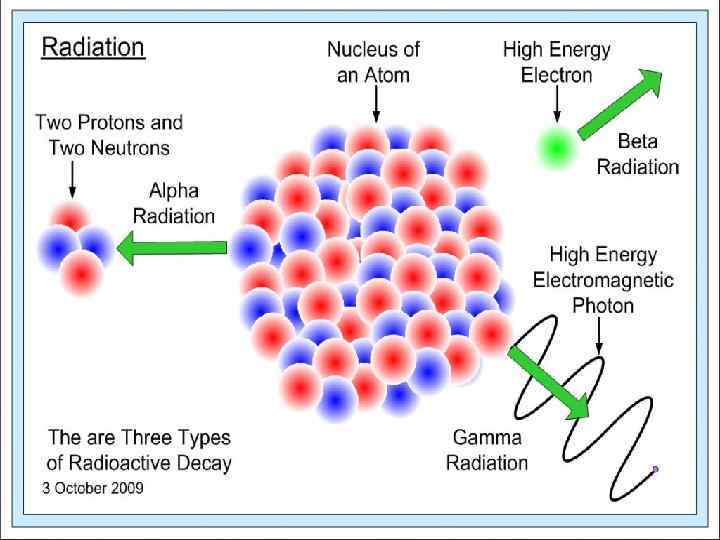
 Uranium-238 Decay
Uranium-238 Decay
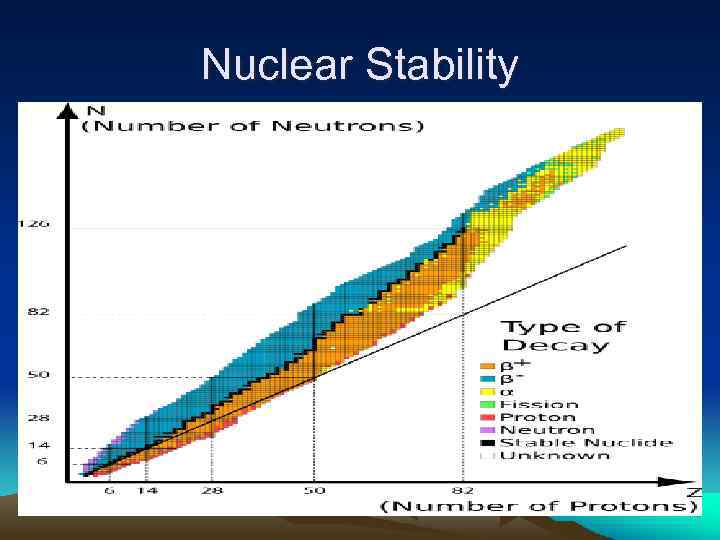 Nuclear Stability
Nuclear Stability
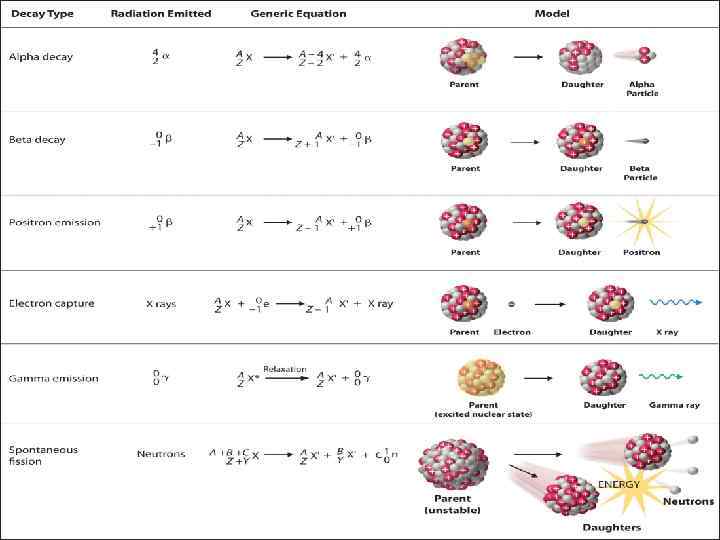
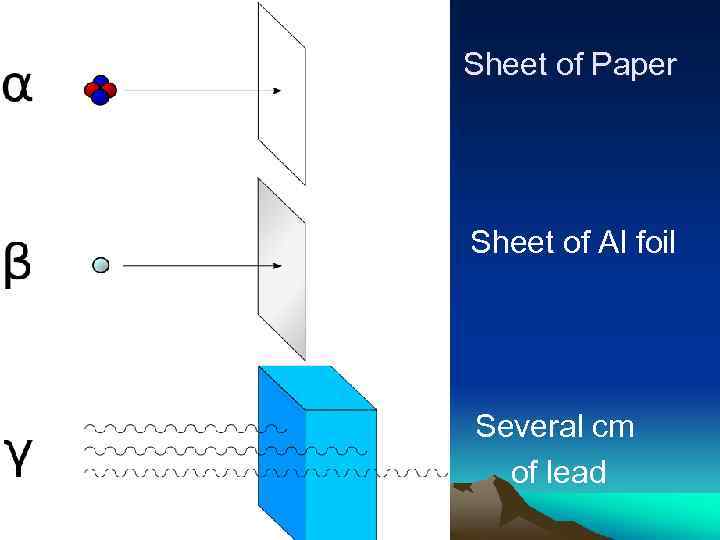 Sheet of Paper Sheet of Al foil Several cm of lead
Sheet of Paper Sheet of Al foil Several cm of lead


