2935c5850cee62767f3a03bcfaee36d7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 ATLAS Tier 2 Paths Within ESnet Mike O’Connor ESnet Network Engineering Group Lawrence Berkeley National Lab moc@es. net
ATLAS Tier 2 Paths Within ESnet Mike O’Connor ESnet Network Engineering Group Lawrence Berkeley National Lab moc@es. net
 ATLAS Tier 2 Connectivity • Typical ATLAS tier 2 site connectivity should be via Abilene and ESnet in order to reach Brookhaven Lab. • “ESnet’s Goal is that DOE Lab ↔ Univ. connectivity should be as good as Lab ↔ Lab and Univ. ↔ Univ. ” W. E. Johnston
ATLAS Tier 2 Connectivity • Typical ATLAS tier 2 site connectivity should be via Abilene and ESnet in order to reach Brookhaven Lab. • “ESnet’s Goal is that DOE Lab ↔ Univ. connectivity should be as good as Lab ↔ Lab and Univ. ↔ Univ. ” W. E. Johnston
 ATLAS Tier 2 Support • The role of ESnet is to provide networking that supports and anticipates the needs of the Office of Science Labs and their collaborators. • ESnet support for ATLAS tier 2 site connectivity makes high bandwidth and fault tolerant paths between BNL and Abilene an absolute priority. • Planning is underway to upgrade BNL’s ESnet OC 48 circuit to a multi 10 G lambda fault tolerant Metropolitan Area Network (MAN). (Targeted for Q 1 2006) • Today ESnet and Abilene peer in Atlanta, Chicago, New York and Sunnyvale with a combined bandwidth of 18. 2 Gbps. These four locations comprise a high bandwidth and fault tolerant interconnect between these two networks.
ATLAS Tier 2 Support • The role of ESnet is to provide networking that supports and anticipates the needs of the Office of Science Labs and their collaborators. • ESnet support for ATLAS tier 2 site connectivity makes high bandwidth and fault tolerant paths between BNL and Abilene an absolute priority. • Planning is underway to upgrade BNL’s ESnet OC 48 circuit to a multi 10 G lambda fault tolerant Metropolitan Area Network (MAN). (Targeted for Q 1 2006) • Today ESnet and Abilene peer in Atlanta, Chicago, New York and Sunnyvale with a combined bandwidth of 18. 2 Gbps. These four locations comprise a high bandwidth and fault tolerant interconnect between these two networks.
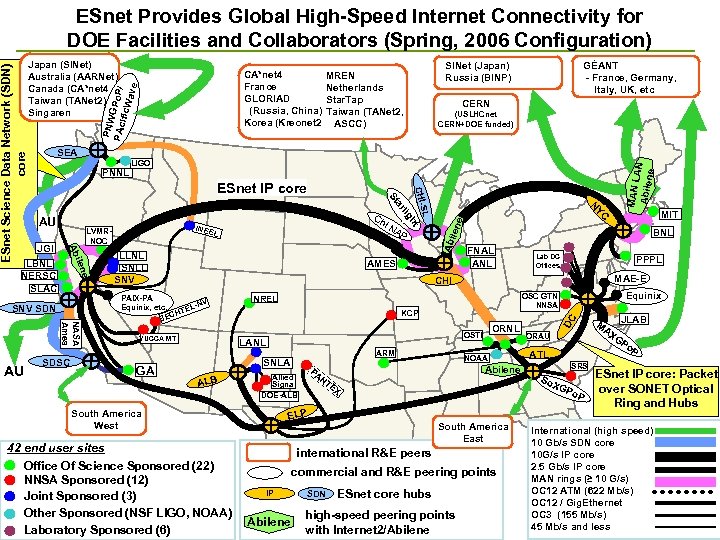 Japan (SINet) Australia (AARNet) Canada (CA*net 4 Taiwan (TANet 2) Singaren PNW PAc GPo. P/ ific. W ave GÉANT - France, Germany, Italy, UK, etc SINet (Japan) Russia (BINP) MREN Netherlands Star. Tap Taiwan (TANet 2, ASCC) CERN (USLHCnet CERN+DOE funded) N e len AMES YUCCA MT FNAL ANL Lab DC Offices PPPL MAE-E OSTI LANL ALB 42 end user sites Office Of Science Sponsored (22) NNSA Sponsored (12) Joint Sponsored (3) Other Sponsored (NSF LIGO, NOAA) Laboratory Sponsored (6) NOAA Abilene PA NT Allied Signal DOE-ALB South America East international R&E peers commercial and R&E peering points IP Abilene SDN ORAU JLAB MA XG Po P ATL SRS So ESnet IP core: Packet over SONET Optical Po P Ring and Hubs XG EX ELP South America West ORNL DC KCP SNLA Equinix OSC GTN NNSA NREL ARM GA BNL CHI PAIX-PA -NV Equinix, etc. TEL ECH B MIT YC t LLNL SNLL SNV AP SL e NASA Ames SDSC L gh ilen SNV SDN i. N INEE LVMRNOC CHI- JGI Ch rli AU a St ESnet IP core MAN L AN Abilen e LIGO Abi PNNL LBNL NERSC SLAC AU CA*net 4 France GLORIAD (Russia, China) Korea (Kreonet 2 SEA Ab ESnet Science Data Network (SDN) core ESnet Provides Global High-Speed Internet Connectivity for DOE Facilities and Collaborators (Spring, 2006 Configuration) ESnet core hubs high-speed peering points with Internet 2/Abilene International (high speed) 10 Gb/s SDN core 10 G/s IP core 2. 5 Gb/s IP core MAN rings (≥ 10 G/s) OC 12 ATM (622 Mb/s) OC 12 / Gig. Ethernet OC 3 (155 Mb/s) 45 Mb/s and less
Japan (SINet) Australia (AARNet) Canada (CA*net 4 Taiwan (TANet 2) Singaren PNW PAc GPo. P/ ific. W ave GÉANT - France, Germany, Italy, UK, etc SINet (Japan) Russia (BINP) MREN Netherlands Star. Tap Taiwan (TANet 2, ASCC) CERN (USLHCnet CERN+DOE funded) N e len AMES YUCCA MT FNAL ANL Lab DC Offices PPPL MAE-E OSTI LANL ALB 42 end user sites Office Of Science Sponsored (22) NNSA Sponsored (12) Joint Sponsored (3) Other Sponsored (NSF LIGO, NOAA) Laboratory Sponsored (6) NOAA Abilene PA NT Allied Signal DOE-ALB South America East international R&E peers commercial and R&E peering points IP Abilene SDN ORAU JLAB MA XG Po P ATL SRS So ESnet IP core: Packet over SONET Optical Po P Ring and Hubs XG EX ELP South America West ORNL DC KCP SNLA Equinix OSC GTN NNSA NREL ARM GA BNL CHI PAIX-PA -NV Equinix, etc. TEL ECH B MIT YC t LLNL SNLL SNV AP SL e NASA Ames SDSC L gh ilen SNV SDN i. N INEE LVMRNOC CHI- JGI Ch rli AU a St ESnet IP core MAN L AN Abilen e LIGO Abi PNNL LBNL NERSC SLAC AU CA*net 4 France GLORIAD (Russia, China) Korea (Kreonet 2 SEA Ab ESnet Science Data Network (SDN) core ESnet Provides Global High-Speed Internet Connectivity for DOE Facilities and Collaborators (Spring, 2006 Configuration) ESnet core hubs high-speed peering points with Internet 2/Abilene International (high speed) 10 Gb/s SDN core 10 G/s IP core 2. 5 Gb/s IP core MAN rings (≥ 10 G/s) OC 12 ATM (622 Mb/s) OC 12 / Gig. Ethernet OC 3 (155 Mb/s) 45 Mb/s and less
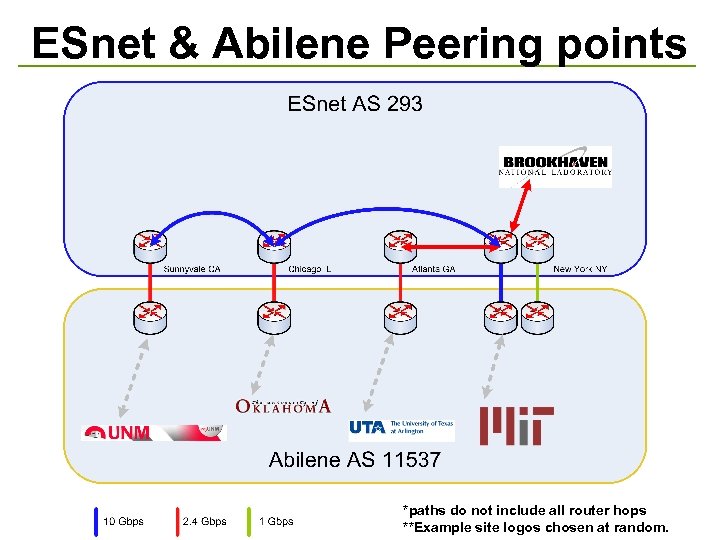 ESnet & Abilene Peering points *paths do not include all router hops **Example site logos chosen at random.
ESnet & Abilene Peering points *paths do not include all router hops **Example site logos chosen at random.
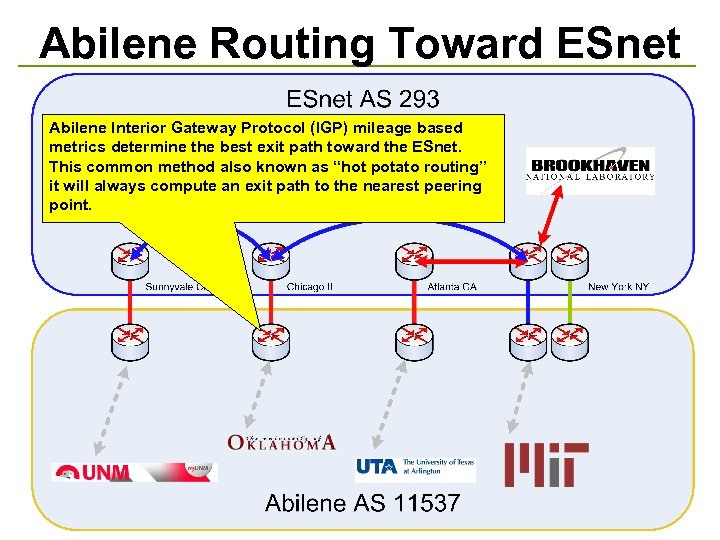 Abilene Routing Toward ESnet Abilene Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) mileage based metrics determine the best exit path toward the ESnet. This common method also known as “hot potato routing” it will always compute an exit path to the nearest peering point.
Abilene Routing Toward ESnet Abilene Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) mileage based metrics determine the best exit path toward the ESnet. This common method also known as “hot potato routing” it will always compute an exit path to the nearest peering point.
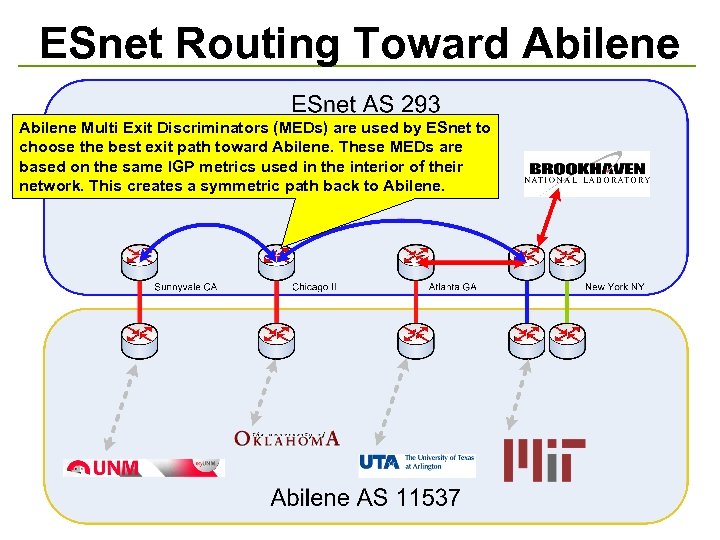 ESnet Routing Toward Abilene Multi Exit Discriminators (MEDs) are used by ESnet to choose the best exit path toward Abilene. These MEDs are based on the same IGP metrics used in the interior of their network. This creates a symmetric path back to Abilene.
ESnet Routing Toward Abilene Multi Exit Discriminators (MEDs) are used by ESnet to choose the best exit path toward Abilene. These MEDs are based on the same IGP metrics used in the interior of their network. This creates a symmetric path back to Abilene.
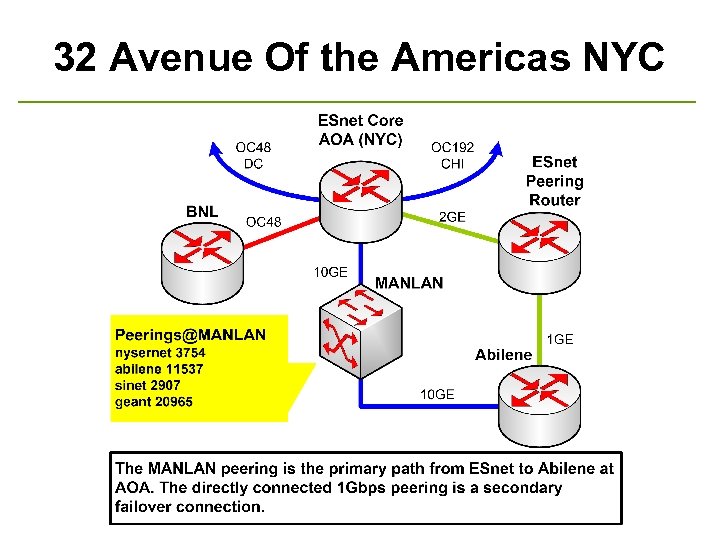 32 Avenue Of the Americas NYC
32 Avenue Of the Americas NYC
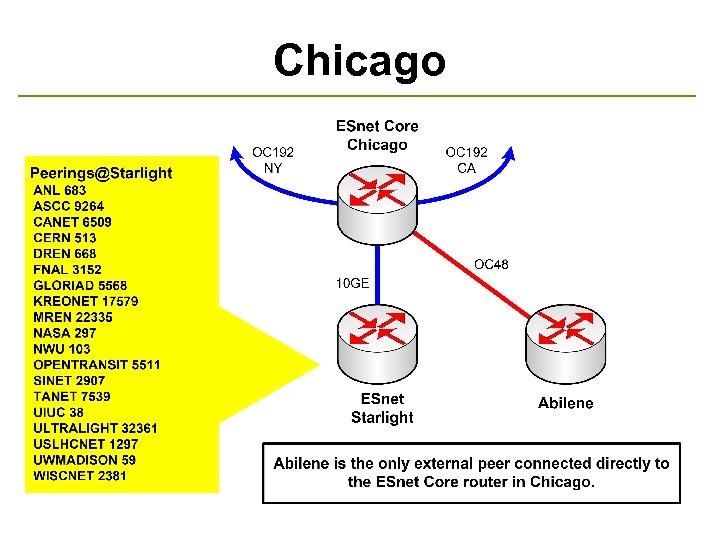 Chicago
Chicago
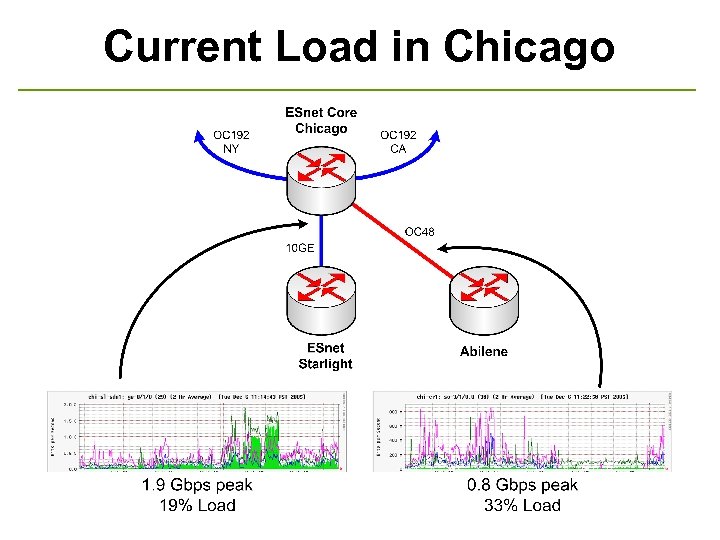 Current Load in Chicago
Current Load in Chicago
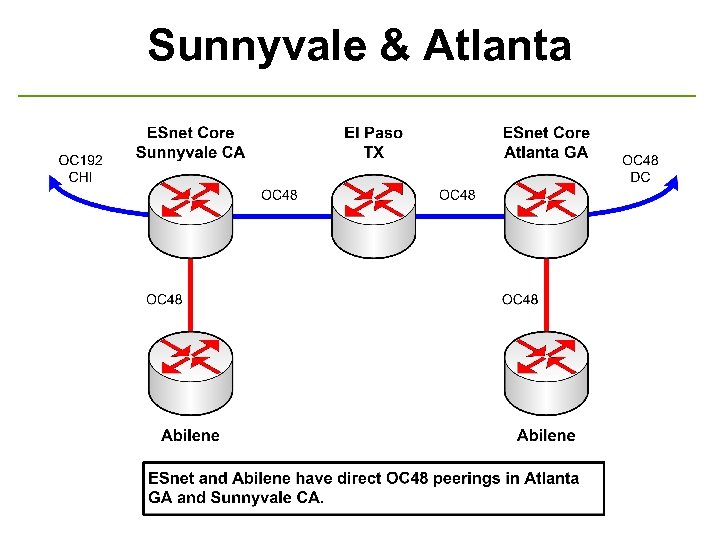 Sunnyvale & Atlanta
Sunnyvale & Atlanta
 Future Directions • Long Island MAN Ring • ESnet Lambda Infrastructure
Future Directions • Long Island MAN Ring • ESnet Lambda Infrastructure
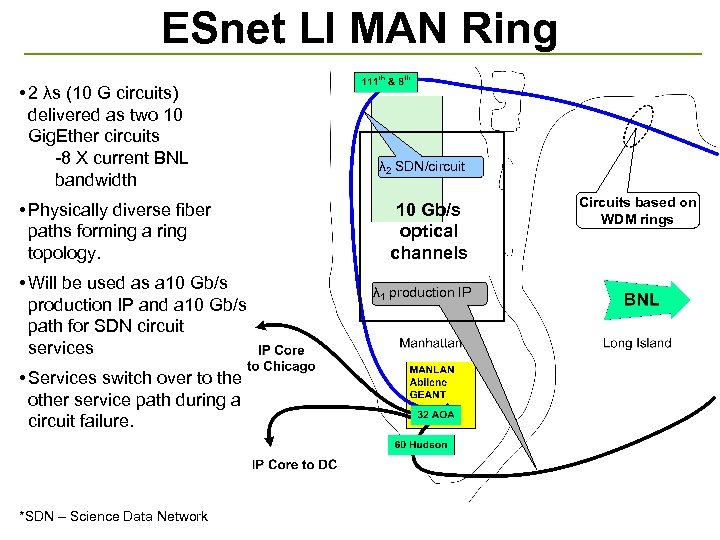 ESnet LI MAN Ring • 2 λs (10 G circuits) delivered as two 10 Gig. Ether circuits -8 X current BNL bandwidth • Physically diverse fiber paths forming a ring topology. • Will be used as a 10 Gb/s production IP and a 10 Gb/s path for SDN circuit services • Services switch over to the other service path during a circuit failure. *SDN – Science Data Network λ 2 SDN/circuit 10 Gb/s optical channels λ 1 production IP Circuits based on WDM rings
ESnet LI MAN Ring • 2 λs (10 G circuits) delivered as two 10 Gig. Ether circuits -8 X current BNL bandwidth • Physically diverse fiber paths forming a ring topology. • Will be used as a 10 Gb/s production IP and a 10 Gb/s path for SDN circuit services • Services switch over to the other service path during a circuit failure. *SDN – Science Data Network λ 2 SDN/circuit 10 Gb/s optical channels λ 1 production IP Circuits based on WDM rings
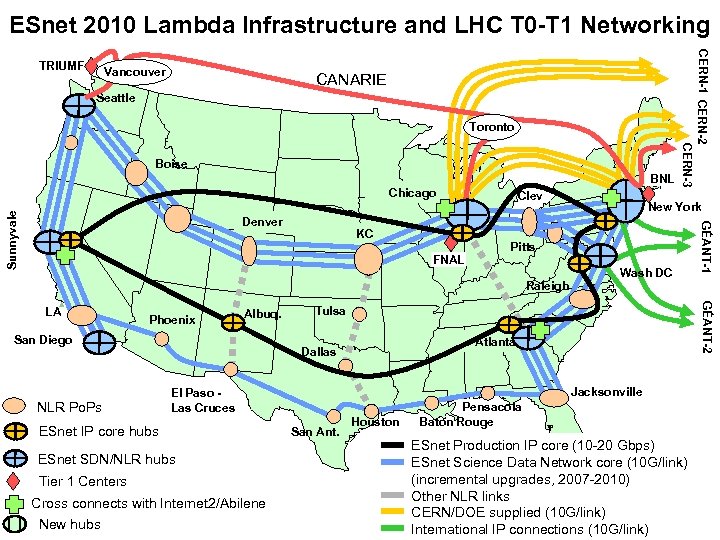 ESnet 2010 Lambda Infrastructure and LHC T 0 -T 1 Networking Vancouver CANARIE Seattle Toronto Boise BNL Denver KC FNAL Clev Pitts Raleigh Phoenix Albuq. San Diego NLR Po. Ps Tulsa Atlanta Dallas Jacksonville El Paso Las Cruces ESnet IP core hubs ESnet SDN/NLR hubs Tier 1 Centers Cross connects with Internet 2/Abilene New hubs Wash DC GÉANT-2 LA New York San Ant. Houston GÉANT-1 Sunnyvale Chicago CERN-1 CERN-2 CERN-3 TRIUMF Pensacola Baton Rouge ESnet Production IP core (10 -20 Gbps) ESnet Science Data Network core (10 G/link) (incremental upgrades, 2007 -2010) Other NLR links CERN/DOE supplied (10 G/link) International IP connections (10 G/link)
ESnet 2010 Lambda Infrastructure and LHC T 0 -T 1 Networking Vancouver CANARIE Seattle Toronto Boise BNL Denver KC FNAL Clev Pitts Raleigh Phoenix Albuq. San Diego NLR Po. Ps Tulsa Atlanta Dallas Jacksonville El Paso Las Cruces ESnet IP core hubs ESnet SDN/NLR hubs Tier 1 Centers Cross connects with Internet 2/Abilene New hubs Wash DC GÉANT-2 LA New York San Ant. Houston GÉANT-1 Sunnyvale Chicago CERN-1 CERN-2 CERN-3 TRIUMF Pensacola Baton Rouge ESnet Production IP core (10 -20 Gbps) ESnet Science Data Network core (10 G/link) (incremental upgrades, 2007 -2010) Other NLR links CERN/DOE supplied (10 G/link) International IP connections (10 G/link)
 Conclusions • ESnet provides an infrastructure and services that are critical to ATLAS science • ESnet is well positioned to provide essential network services to the LHC tier 2 community • ESnet is working on providing the DOE mission science networking requirements with several new initiatives and a new architecture
Conclusions • ESnet provides an infrastructure and services that are critical to ATLAS science • ESnet is well positioned to provide essential network services to the LHC tier 2 community • ESnet is working on providing the DOE mission science networking requirements with several new initiatives and a new architecture




