2c6ce8392e4cdc04bc0f0b1228329e3e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans Exploring the High-Energy Frontier of Particle Physics Workshop on Cooperation in HEP between CERN and China, Beijing 14 -15 May 2005 (P. Jenni, CERN) 1 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans Exploring the High-Energy Frontier of Particle Physics Workshop on Cooperation in HEP between CERN and China, Beijing 14 -15 May 2005 (P. Jenni, CERN) 1 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 LHC pp • s = 14 Te. V (7 times higher than Tevatron/Fermilab) search for new massive particles up to m ~ 5 Te. V • Ldesign = 1034 cm-2 s-1 (>102 higher than Tevatron/Fermilab) search for rare processes with small (N = L ) ATLAS and CMS : pp, general purpose 27 km ring used for e+e- LEP machine in 1989 -2000 ALICE : heavy ions P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 Start : Summer 2007 LHCb : pp, B-physics ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans 2
LHC pp • s = 14 Te. V (7 times higher than Tevatron/Fermilab) search for new massive particles up to m ~ 5 Te. V • Ldesign = 1034 cm-2 s-1 (>102 higher than Tevatron/Fermilab) search for rare processes with small (N = L ) ATLAS and CMS : pp, general purpose 27 km ring used for e+e- LEP machine in 1989 -2000 ALICE : heavy ions P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 Start : Summer 2007 LHCb : pp, B-physics ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans 2
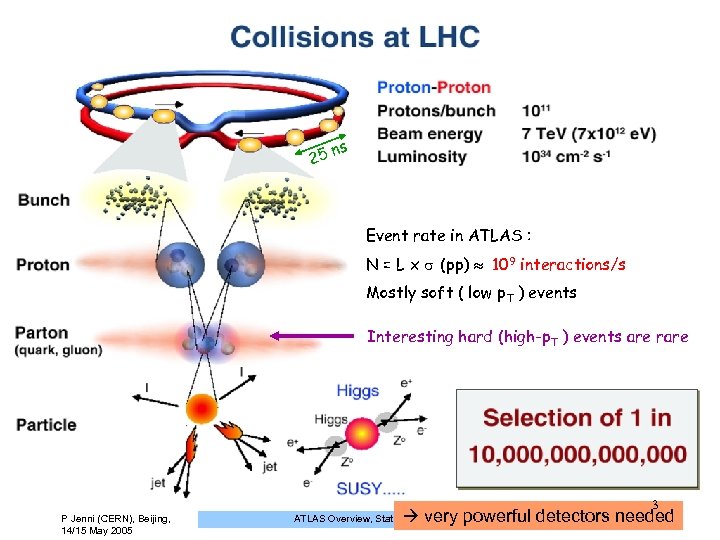 25 ns Event rate in ATLAS : N = L x (pp) 109 interactions/s Mostly soft ( low p. T ) events Interesting hard (high-p. T ) events are rare 3 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 very powerful detectors needed ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
25 ns Event rate in ATLAS : N = L x (pp) 109 interactions/s Mostly soft ( low p. T ) events Interesting hard (high-p. T ) events are rare 3 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 very powerful detectors needed ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 The ATLAS physics goals Search for the Standard Model Higgs boson over ~ 115 < m. H < 1000 Ge. V Search for physics beyond the SM (Supersymmetry, q/ compositeness, leptoquarks, W’/Z’, heavy q/ , Extra-dimensions, …. ) up to the Te. V-range Precise measurements : -- W mass -- top mass, couplings and decay properties -- Higgs mass, spin, couplings (if Higgs found) -- B-physics (complementing LHCb): CP violation, rare decays, B 0 oscillations -- QCD jet cross-section and as -- etc. …. Study of phase transition at high density from hadronic matter to plasma of deconfined quarks and gluons (complementing ALICE). Transition plasma hadronic matter happened in universe ~ 10 -5 s after Big Bang Etc. etc. …. . 4 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
The ATLAS physics goals Search for the Standard Model Higgs boson over ~ 115 < m. H < 1000 Ge. V Search for physics beyond the SM (Supersymmetry, q/ compositeness, leptoquarks, W’/Z’, heavy q/ , Extra-dimensions, …. ) up to the Te. V-range Precise measurements : -- W mass -- top mass, couplings and decay properties -- Higgs mass, spin, couplings (if Higgs found) -- B-physics (complementing LHCb): CP violation, rare decays, B 0 oscillations -- QCD jet cross-section and as -- etc. …. Study of phase transition at high density from hadronic matter to plasma of deconfined quarks and gluons (complementing ALICE). Transition plasma hadronic matter happened in universe ~ 10 -5 s after Big Bang Etc. etc. …. . 4 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
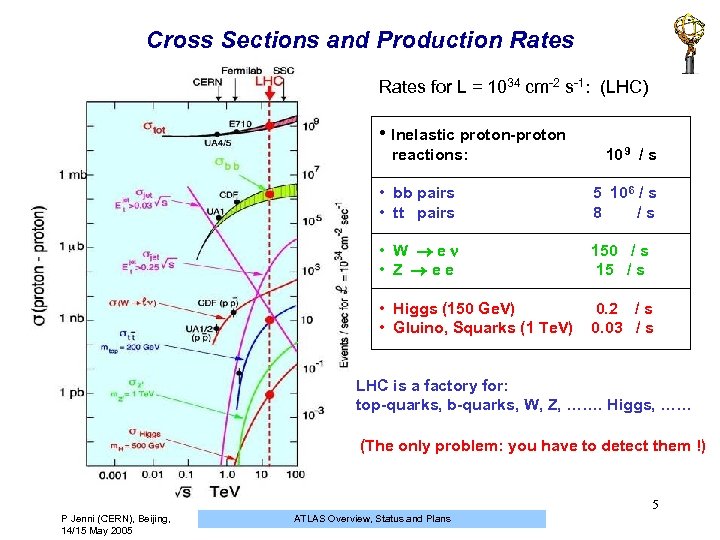 Cross Sections and Production Rates for L = 1034 cm-2 s-1: (LHC) • Inelastic proton-proton reactions: 10 9 / s • bb pairs 5 10 6 / s • tt pairs 8 / s • W e 150 / s • Z e e 15 / s • Higgs (150 Ge. V) 0. 2 / s • Gluino, Squarks (1 Te. V) 0. 03 / s LHC is a factory for: top-quarks, b-quarks, W, Z, ……. Higgs, …… (The only problem: you have to detect them !) 5 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Cross Sections and Production Rates for L = 1034 cm-2 s-1: (LHC) • Inelastic proton-proton reactions: 10 9 / s • bb pairs 5 10 6 / s • tt pairs 8 / s • W e 150 / s • Z e e 15 / s • Higgs (150 Ge. V) 0. 2 / s • Gluino, Squarks (1 Te. V) 0. 03 / s LHC is a factory for: top-quarks, b-quarks, W, Z, ……. Higgs, …… (The only problem: you have to detect them !) 5 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
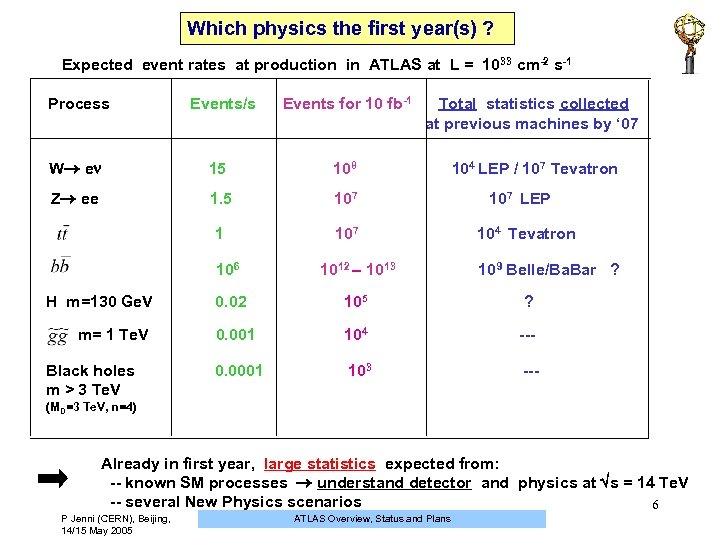 Which physics the first year(s) ? Expected event rates at production in ATLAS at L = 10 33 cm-2 s-1 Process Events/s Events for 10 fb-1 Total statistics collected at previous machines by ‘ 07 W e 15 108 104 LEP / 107 Tevatron Z ee 1. 5 107 LEP 107 104 Tevatron 106 1012 – 1013 109 Belle/Ba. Bar ? H m=130 Ge. V 0. 02 105 ? m= 1 Te. V 0. 001 104 --- Black holes 0. 0001 103 --m > 3 Te. V (MD=3 Te. V, n=4) Already in first year, large statistics expected from: -- known SM processes understand detector and physics at s = 14 Te. V -- several New Physics scenarios 6 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Which physics the first year(s) ? Expected event rates at production in ATLAS at L = 10 33 cm-2 s-1 Process Events/s Events for 10 fb-1 Total statistics collected at previous machines by ‘ 07 W e 15 108 104 LEP / 107 Tevatron Z ee 1. 5 107 LEP 107 104 Tevatron 106 1012 – 1013 109 Belle/Ba. Bar ? H m=130 Ge. V 0. 02 105 ? m= 1 Te. V 0. 001 104 --- Black holes 0. 0001 103 --m > 3 Te. V (MD=3 Te. V, n=4) Already in first year, large statistics expected from: -- known SM processes understand detector and physics at s = 14 Te. V -- several New Physics scenarios 6 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 ATLAS Collaboration 34 Countries 151 Institutions 1770 Scientific Authors Longstanding partnership with Chinese teams since the beginning (R&D started in 1990) Albany, Alberta, NIKHEF Amsterdam, Ankara, LAPP Annecy, Argonne NL, Arizona, UT Arlington, Athens, NTU Athens, Baku, IFAE Barcelona, Belgrade, Bergen, Berkeley LBL and UC, Bern, Birmingham, Bonn, Boston, Brandeis, Bratislava/SAS Kosice, Brookhaven NL, Bucharest, Cambridge, Carleton, Casablanca/Rabat, CERN, Chinese Cluster, Chicago, Clermont-Ferrand, Columbia, NBI Copenhagen, Cosenza, INP Cracow, FPNT Cracow, Dortmund, JINR Dubna, Duke, Frascati, Freiburg, Geneva, Genoa, Glasgow, LPSC Grenoble, Technion Haifa, Hampton, Harvard, Heidelberg, Hiroshima IT, Indiana, Innsbruck, Iowa SU, Irvine UC, Istanbul Bogazici, KEK, Kobe, Kyoto UE, Lancaster, Lecce, Lisbon LIP, Liverpool, Ljubljana, QMW London, RHBNC London, UC London, Lund, UA Madrid, Mainz, Manchester, Mannheim, CPPM Marseille, Massachusetts, MIT, Melbourne, Michigan SU, Milano, Minsk NAS, Minsk NCPHEP, Montreal, FIAN Moscow, ITEP Moscow, MEPh. I Moscow, MSU Moscow, Munich LMU, MPI Munich, Nagasaki IAS, Naples, Naruto UE, New Mexico, Nijmegen, BINP Novosibirsk, Ohio SU, Okayama, Oklahoma, LAL Orsay, Oslo, Oxford, Paris VI and VII, Pavia, Pennsylvania, Pisa, Pittsburgh, CAS Prague, CU Prague, TU Prague, IHEP Protvino, Ritsumeikan, UFRJ Rio de Janeiro, Rochester, Rome I, Rome III, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, DAPNIA Saclay, Santa Cruz UC, Sheffield, Shinshu, Siegen, Simon Fraser Burnaby, Southern Methodist Dallas, NPI Petersburg, Stockholm, KTH Stockholm, Stony Brook, Sydney, AS Taipei, Tbilisi, Tel Aviv, Thessaloniki, Tokyo ICEPP, Tokyo MU, Tokyo UAT, Toronto, TRIUMF, Tsukuba, Tufts, Udine, Uppsala, Urbana UI, Valencia, UBC Vancouver, Victoria, Washington, Weizmann Rehovot, Wisconsin, Wuppertal, Yale, Yerevan 7 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
ATLAS Collaboration 34 Countries 151 Institutions 1770 Scientific Authors Longstanding partnership with Chinese teams since the beginning (R&D started in 1990) Albany, Alberta, NIKHEF Amsterdam, Ankara, LAPP Annecy, Argonne NL, Arizona, UT Arlington, Athens, NTU Athens, Baku, IFAE Barcelona, Belgrade, Bergen, Berkeley LBL and UC, Bern, Birmingham, Bonn, Boston, Brandeis, Bratislava/SAS Kosice, Brookhaven NL, Bucharest, Cambridge, Carleton, Casablanca/Rabat, CERN, Chinese Cluster, Chicago, Clermont-Ferrand, Columbia, NBI Copenhagen, Cosenza, INP Cracow, FPNT Cracow, Dortmund, JINR Dubna, Duke, Frascati, Freiburg, Geneva, Genoa, Glasgow, LPSC Grenoble, Technion Haifa, Hampton, Harvard, Heidelberg, Hiroshima IT, Indiana, Innsbruck, Iowa SU, Irvine UC, Istanbul Bogazici, KEK, Kobe, Kyoto UE, Lancaster, Lecce, Lisbon LIP, Liverpool, Ljubljana, QMW London, RHBNC London, UC London, Lund, UA Madrid, Mainz, Manchester, Mannheim, CPPM Marseille, Massachusetts, MIT, Melbourne, Michigan SU, Milano, Minsk NAS, Minsk NCPHEP, Montreal, FIAN Moscow, ITEP Moscow, MEPh. I Moscow, MSU Moscow, Munich LMU, MPI Munich, Nagasaki IAS, Naples, Naruto UE, New Mexico, Nijmegen, BINP Novosibirsk, Ohio SU, Okayama, Oklahoma, LAL Orsay, Oslo, Oxford, Paris VI and VII, Pavia, Pennsylvania, Pisa, Pittsburgh, CAS Prague, CU Prague, TU Prague, IHEP Protvino, Ritsumeikan, UFRJ Rio de Janeiro, Rochester, Rome I, Rome III, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, DAPNIA Saclay, Santa Cruz UC, Sheffield, Shinshu, Siegen, Simon Fraser Burnaby, Southern Methodist Dallas, NPI Petersburg, Stockholm, KTH Stockholm, Stony Brook, Sydney, AS Taipei, Tbilisi, Tel Aviv, Thessaloniki, Tokyo ICEPP, Tokyo MU, Tokyo UAT, Toronto, TRIUMF, Tsukuba, Tufts, Udine, Uppsala, Urbana UI, Valencia, UBC Vancouver, Victoria, Washington, Weizmann Rehovot, Wisconsin, Wuppertal, Yale, Yerevan 7 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 The Chinese teams form jointly one Institution in the ATLAS Collaboration Institute of High Energy Physics, Beijing Nanjing University, Nanjing Shandong University, Jinan University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei The contributions are in the fields of - LAr hadronic end-cap and forward calorimeters - Muon spectrometer instrumentation (MDT and TGC) - Computing and preparation for physics 8 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
The Chinese teams form jointly one Institution in the ATLAS Collaboration Institute of High Energy Physics, Beijing Nanjing University, Nanjing Shandong University, Jinan University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei The contributions are in the fields of - LAr hadronic end-cap and forward calorimeters - Muon spectrometer instrumentation (MDT and TGC) - Computing and preparation for physics 8 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
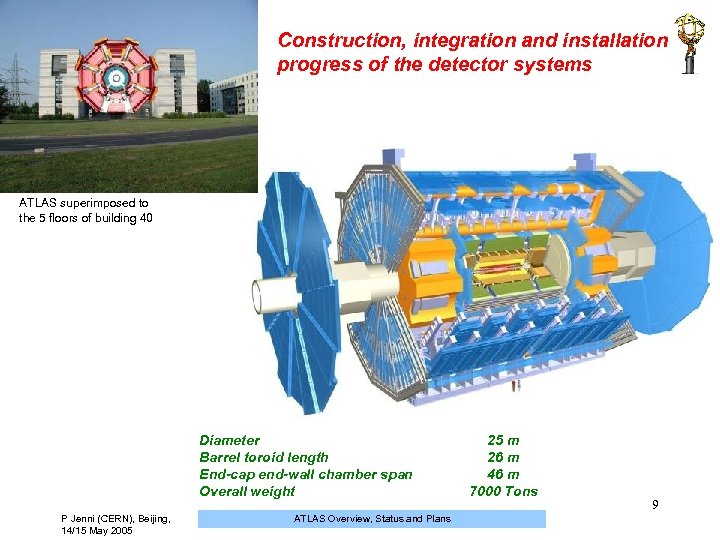 Construction, integration and installation progress of the detector systems ATLAS superimposed to the 5 floors of building 40 Diameter Barrel toroid length End-cap end-wall chamber span Overall weight P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans 25 m 26 m 46 m 7000 Tons 9
Construction, integration and installation progress of the detector systems ATLAS superimposed to the 5 floors of building 40 Diameter Barrel toroid length End-cap end-wall chamber span Overall weight P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans 25 m 26 m 46 m 7000 Tons 9
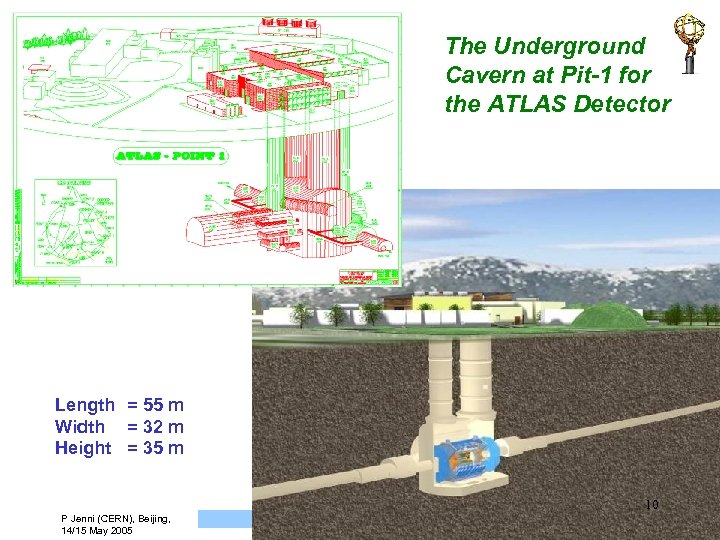 The Underground Cavern at Pit-1 for the ATLAS Detector Length = 55 m Width = 32 m Height = 35 m 10 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
The Underground Cavern at Pit-1 for the ATLAS Detector Length = 55 m Width = 32 m Height = 35 m 10 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Visit of HE Professor Chen Jiaer to the ATLAS experiment pit on 4 th April 2002 Visit of Deputy Minister Liu Yanhua to the ATLAS pit on 17 th February 2004 11 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Visit of HE Professor Chen Jiaer to the ATLAS experiment pit on 4 th April 2002 Visit of Deputy Minister Liu Yanhua to the ATLAS pit on 17 th February 2004 11 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
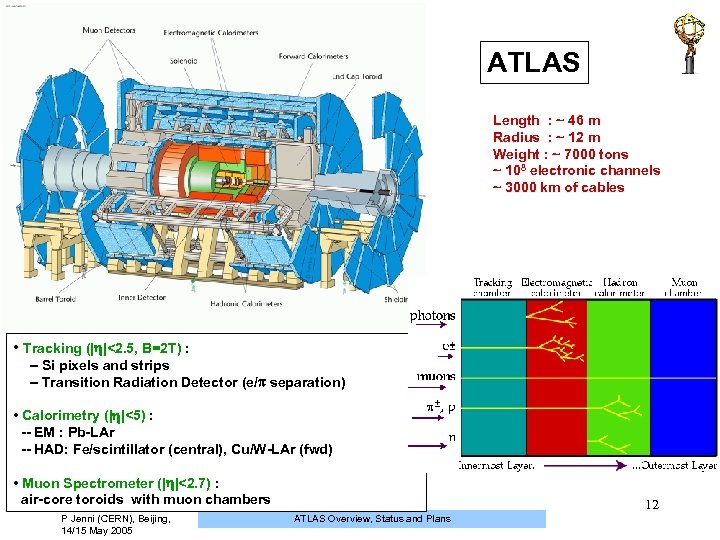 ATLAS Length : ~ 46 m Radius : ~ 12 m Weight : ~ 7000 tons ~ 108 electronic channels ~ 3000 km of cables • Tracking (| |<2. 5, B=2 T) : -- Si pixels and strips -- Transition Radiation Detector (e/ separation) • Calorimetry (| |<5) : -- EM : Pb-LAr -- HAD: Fe/scintillator (central), Cu/W-LAr (fwd) • Muon Spectrometer (| |<2. 7) : air-core toroids with muon chambers P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 12 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
ATLAS Length : ~ 46 m Radius : ~ 12 m Weight : ~ 7000 tons ~ 108 electronic channels ~ 3000 km of cables • Tracking (| |<2. 5, B=2 T) : -- Si pixels and strips -- Transition Radiation Detector (e/ separation) • Calorimetry (| |<5) : -- EM : Pb-LAr -- HAD: Fe/scintillator (central), Cu/W-LAr (fwd) • Muon Spectrometer (| |<2. 7) : air-core toroids with muon chambers P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 12 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Physics example H ZZ 4 e, g t H g “Gold-plated” channel for Higgs discovery at LHC Z(*) Z e, e, m. Z Signal expected in ATLAS after 1 year of LHC operation Simulation of a H ee event in ATLAS 13 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Physics example H ZZ 4 e, g t H g “Gold-plated” channel for Higgs discovery at LHC Z(*) Z e, e, m. Z Signal expected in ATLAS after 1 year of LHC operation Simulation of a H ee event in ATLAS 13 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
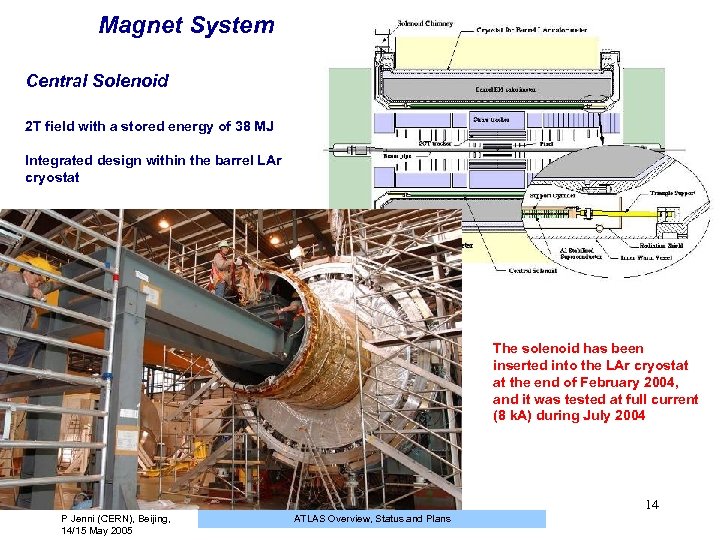 Magnet System Central Solenoid 2 T field with a stored energy of 38 MJ Integrated design within the barrel LAr cryostat The solenoid has been inserted into the LAr cryostat at the end of February 2004, and it was tested at full current (8 k. A) during July 2004 14 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Magnet System Central Solenoid 2 T field with a stored energy of 38 MJ Integrated design within the barrel LAr cryostat The solenoid has been inserted into the LAr cryostat at the end of February 2004, and it was tested at full current (8 k. A) during July 2004 14 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
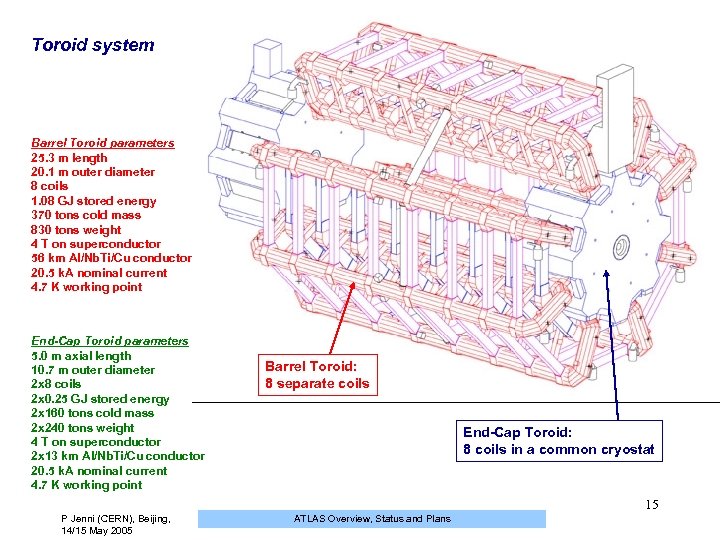 Toroid system Barrel Toroid parameters 25. 3 m length 20. 1 m outer diameter 8 coils 1. 08 GJ stored energy 370 tons cold mass 830 tons weight 4 T on superconductor 56 km Al/Nb. Ti/Cu conductor 20. 5 k. A nominal current 4. 7 K working point End-Cap Toroid parameters 5. 0 m axial length 10. 7 m outer diameter 2 x 8 coils 2 x 0. 25 GJ stored energy 2 x 160 tons cold mass 2 x 240 tons weight 4 T on superconductor 2 x 13 km Al/Nb. Ti/Cu conductor 20. 5 k. A nominal current 4. 7 K working point Barrel Toroid: 8 separate coils End-Cap Toroid: 8 coils in a common cryostat 15 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Toroid system Barrel Toroid parameters 25. 3 m length 20. 1 m outer diameter 8 coils 1. 08 GJ stored energy 370 tons cold mass 830 tons weight 4 T on superconductor 56 km Al/Nb. Ti/Cu conductor 20. 5 k. A nominal current 4. 7 K working point End-Cap Toroid parameters 5. 0 m axial length 10. 7 m outer diameter 2 x 8 coils 2 x 0. 25 GJ stored energy 2 x 160 tons cold mass 2 x 240 tons weight 4 T on superconductor 2 x 13 km Al/Nb. Ti/Cu conductor 20. 5 k. A nominal current 4. 7 K working point Barrel Toroid: 8 separate coils End-Cap Toroid: 8 coils in a common cryostat 15 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
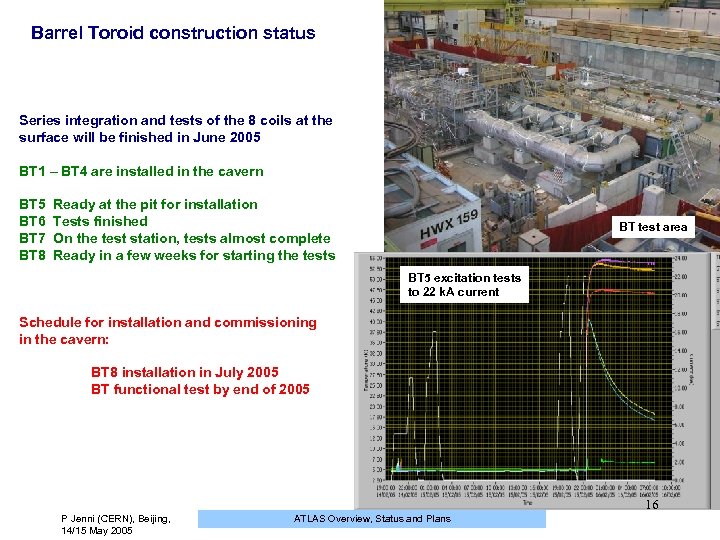 Barrel Toroid construction status Series integration and tests of the 8 coils at the surface will be finished in June 2005 BT 1 – BT 4 are installed in the cavern BT 5 Ready at the pit for installation BT 6 Tests finished BT 7 On the test station, tests almost complete BT 8 Ready in a few weeks for starting the tests BT test area BT 5 excitation tests to 22 k. A current Schedule for installation and commissioning in the cavern: BT 8 installation in July 2005 BT functional test by end of 2005 16 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Barrel Toroid construction status Series integration and tests of the 8 coils at the surface will be finished in June 2005 BT 1 – BT 4 are installed in the cavern BT 5 Ready at the pit for installation BT 6 Tests finished BT 7 On the test station, tests almost complete BT 8 Ready in a few weeks for starting the tests BT test area BT 5 excitation tests to 22 k. A current Schedule for installation and commissioning in the cavern: BT 8 installation in July 2005 BT functional test by end of 2005 16 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Barrel Toroid coil transport and installation 17 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Barrel Toroid coil transport and installation 17 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
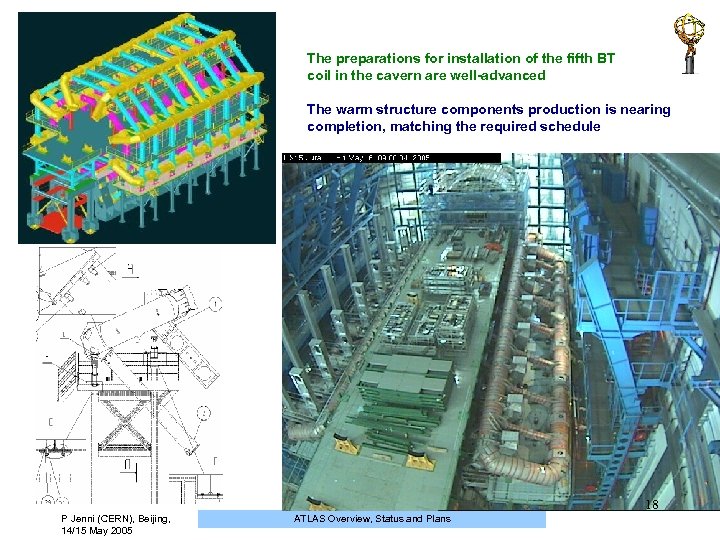 The preparations for installation of the fifth BT coil in the cavern are well-advanced The warm structure components production is nearing completion, matching the required schedule 18 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
The preparations for installation of the fifth BT coil in the cavern are well-advanced The warm structure components production is nearing completion, matching the required schedule 18 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 ATLAS End-Cap Toroids updates All 16 coils for both ECTs are now wound, impregnated, and delivered to CERN Both ECT vacuum vessels have been at CERN since long, including their thermal shields and superinsulations, as well as all components for the assembly of the first ECT The cold mass assembly for the first one (ECT-C) has started in Hall 191 (scheduled for cold mass completion in June, insertion into vacuum vessel in summer, and completion in November 2005) ECT integration work in Hall 191 19 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
ATLAS End-Cap Toroids updates All 16 coils for both ECTs are now wound, impregnated, and delivered to CERN Both ECT vacuum vessels have been at CERN since long, including their thermal shields and superinsulations, as well as all components for the assembly of the first ECT The cold mass assembly for the first one (ECT-C) has started in Hall 191 (scheduled for cold mass completion in June, insertion into vacuum vessel in summer, and completion in November 2005) ECT integration work in Hall 191 19 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
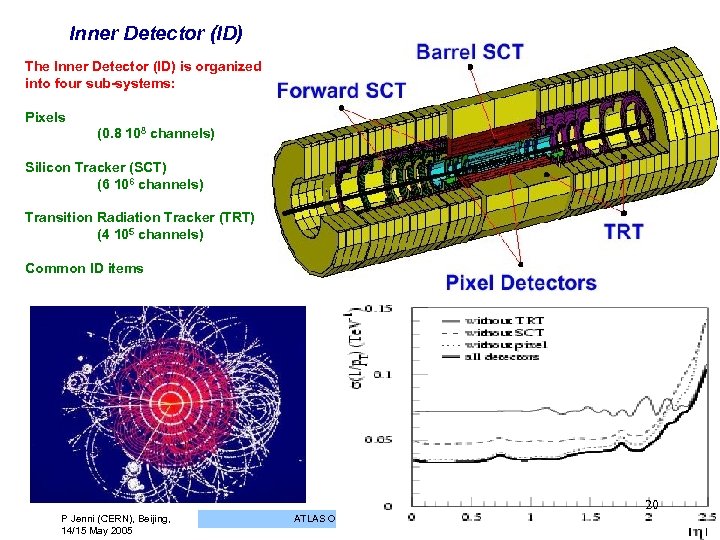 Inner Detector (ID) The Inner Detector (ID) is organized into four sub-systems: Pixels (0. 8 108 channels) Silicon Tracker (SCT) (6 106 channels) Transition Radiation Tracker (TRT) (4 105 channels) Common ID items 20 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Inner Detector (ID) The Inner Detector (ID) is organized into four sub-systems: Pixels (0. 8 108 channels) Silicon Tracker (SCT) (6 106 channels) Transition Radiation Tracker (TRT) (4 105 channels) Common ID items 20 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Inner Detector Progress Summary Pixels: Steady ‘on-schedule’ progress on all aspects of the sub-system for 3 layers SCT: Module mounting (‘macro-assembly’) on the 4 barrel cylinders ongoing (the first cylinder is finished and tested, and is now at CERN) The module mounting progressing on the forward disks (the first 4 disks are completed) TRT: First complete SCT barrel cylinder Barrel module mounting into support structure is completed End-cap wheel production is now also smooth, and the stacking at CERN into the end-cap structures has started The schedule for the Inner Detector remains very tight, without any float left (critical path: all SCT, and second TRT end-cap) P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans 21 TRT barrel support with all modules
Inner Detector Progress Summary Pixels: Steady ‘on-schedule’ progress on all aspects of the sub-system for 3 layers SCT: Module mounting (‘macro-assembly’) on the 4 barrel cylinders ongoing (the first cylinder is finished and tested, and is now at CERN) The module mounting progressing on the forward disks (the first 4 disks are completed) TRT: First complete SCT barrel cylinder Barrel module mounting into support structure is completed End-cap wheel production is now also smooth, and the stacking at CERN into the end-cap structures has started The schedule for the Inner Detector remains very tight, without any float left (critical path: all SCT, and second TRT end-cap) P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans 21 TRT barrel support with all modules
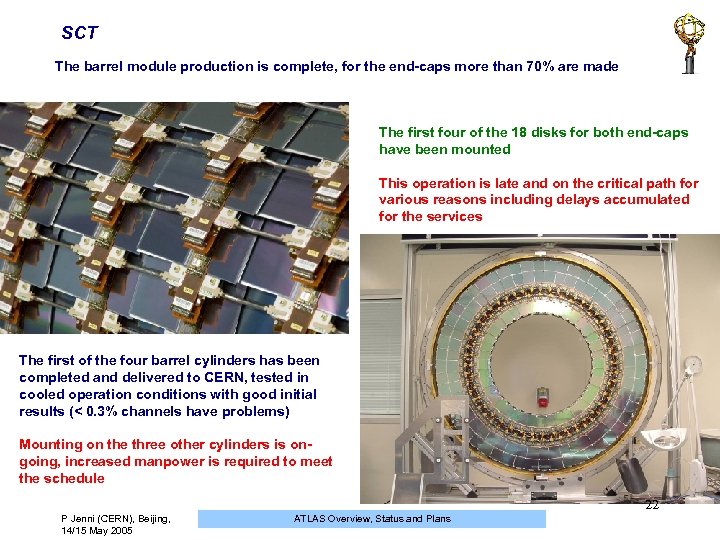 SCT The barrel module production is complete, for the end-caps more than 70% are made The first four of the 18 disks for both end-caps have been mounted This operation is late and on the critical path for various reasons including delays accumulated for the services The first of the four barrel cylinders has been completed and delivered to CERN, tested in cooled operation conditions with good initial results (< 0. 3% channels have problems) Mounting on the three other cylinders is ongoing, increased manpower is required to meet the schedule 22 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
SCT The barrel module production is complete, for the end-caps more than 70% are made The first four of the 18 disks for both end-caps have been mounted This operation is late and on the critical path for various reasons including delays accumulated for the services The first of the four barrel cylinders has been completed and delivered to CERN, tested in cooled operation conditions with good initial results (< 0. 3% channels have problems) Mounting on the three other cylinders is ongoing, increased manpower is required to meet the schedule 22 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Pixels All FE chips have been delivered (all tested, showing a yield of 82%) The sensor production is finished for 2 layers, and on time for 3 layers The module production rate (with bump-bonding in 2 industries) has improved, on track for 3 layers in time First completed disk (two layers of 24 modules each, with 2’ 200’ 000 channels of electronics The series production of final staves (barrel) and sectors (end-cap disks) has passed the 10% mark, this activity is now on the critical path of the Pixel project 23 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Pixels All FE chips have been delivered (all tested, showing a yield of 82%) The sensor production is finished for 2 layers, and on time for 3 layers The module production rate (with bump-bonding in 2 industries) has improved, on track for 3 layers in time First completed disk (two layers of 24 modules each, with 2’ 200’ 000 channels of electronics The series production of final staves (barrel) and sectors (end-cap disks) has passed the 10% mark, this activity is now on the critical path of the Pixel project 23 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 LAr and Tile Calorimeters Tile barrel Tile extended barrel LAr hadronic end-cap (HEC) LAr EM end-cap (EMEC) LAr EM barrel LAr forward calorimeter (FCAL) 24 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
LAr and Tile Calorimeters Tile barrel Tile extended barrel LAr hadronic end-cap (HEC) LAr EM end-cap (EMEC) LAr EM barrel LAr forward calorimeter (FCAL) 24 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 LAr EM Barrel Calorimeter and Solenoid Commissioning at the Surface The barrel EM calorimeter is installed in the cryostat, and after insertion of the solenoid, the cold vessel was closed and welded A successful complete cold test (with LAr) was made during summer 2004 on the surface End of October 2004 the cryostat was transported to the pit, and lowered into the cavern LAr barrel EM calorimeter after insertion into the cryostat P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 Solenoid just before insertion into the cryostat 25 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
LAr EM Barrel Calorimeter and Solenoid Commissioning at the Surface The barrel EM calorimeter is installed in the cryostat, and after insertion of the solenoid, the cold vessel was closed and welded A successful complete cold test (with LAr) was made during summer 2004 on the surface End of October 2004 the cryostat was transported to the pit, and lowered into the cavern LAr barrel EM calorimeter after insertion into the cryostat P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 Solenoid just before insertion into the cryostat 25 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 26 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
26 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 ATLAS Barrel Calorimeter The mechanical installation of the LAr and Tile Barrel Calorimeters in the pit has been completed end of 2004 on the support trucks below the access shaft on the C-side The installation of electronics and services is ongoing 27 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
ATLAS Barrel Calorimeter The mechanical installation of the LAr and Tile Barrel Calorimeters in the pit has been completed end of 2004 on the support trucks below the access shaft on the C-side The installation of electronics and services is ongoing 27 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
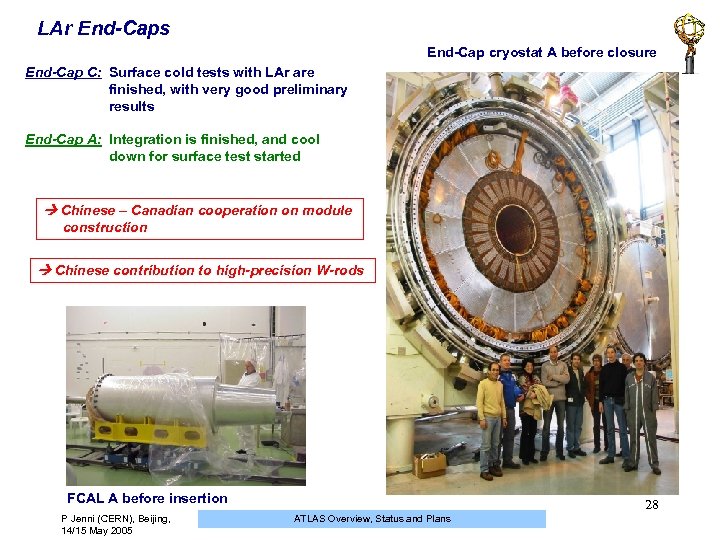 LAr End-Caps End-Cap cryostat A before closure End-Cap C: Surface cold tests with LAr are finished, with very good preliminary results End-Cap A: Integration is finished, and cool down for surface test started Chinese – Canadian cooperation on module construction Chinese contribution to high-precision W-rods FCAL A before insertion P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 28 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
LAr End-Caps End-Cap cryostat A before closure End-Cap C: Surface cold tests with LAr are finished, with very good preliminary results End-Cap A: Integration is finished, and cool down for surface test started Chinese – Canadian cooperation on module construction Chinese contribution to high-precision W-rods FCAL A before insertion P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 28 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
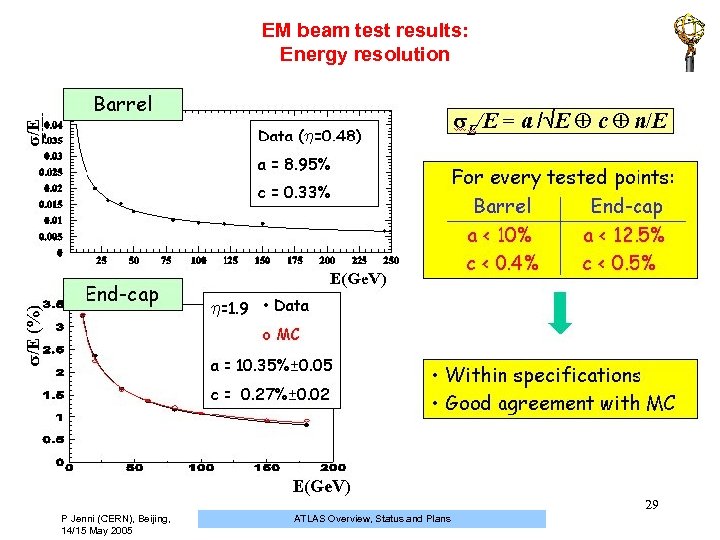 EM beam test results: Energy resolution 29 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
EM beam test results: Energy resolution 29 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
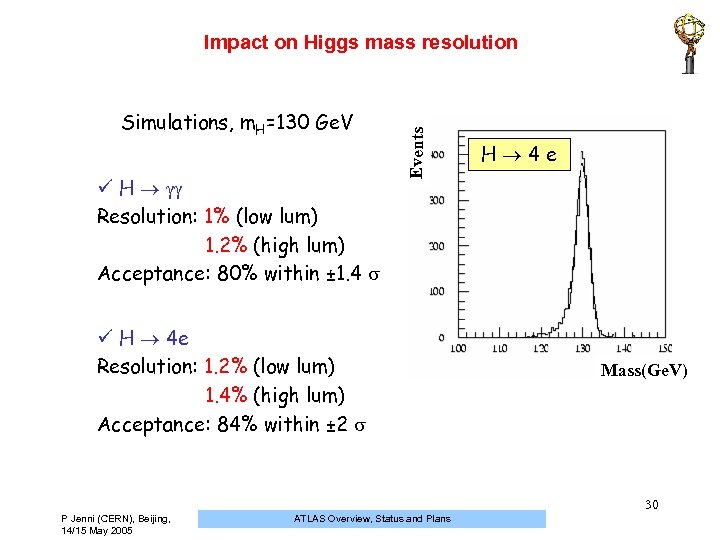 Simulations, m. H=130 Ge. V ü H Resolution: 1% (low lum) 1. 2% (high lum) Acceptance: 80% within ± 1. 4 Events Impact on Higgs mass resolution ü H 4 e Resolution: 1. 2% (low lum) 1. 4% (high lum) Acceptance: 84% within ± 2 H 4 e Mass(Ge. V) 30 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Simulations, m. H=130 Ge. V ü H Resolution: 1% (low lum) 1. 2% (high lum) Acceptance: 80% within ± 1. 4 Events Impact on Higgs mass resolution ü H 4 e Resolution: 1. 2% (low lum) 1. 4% (high lum) Acceptance: 84% within ± 2 H 4 e Mass(Ge. V) 30 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Muon Spectrometer Instrumentation The Muon Spectrometer is instrumented with precision chambers and fast trigger chambers A crucial component to reach the required accuracy is the sophisticated alignment measurement and monitoring system P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 Precision chambers: - MDTs in the barrel and end-caps - CSCs at large rapidity for the innermost end-cap stations Trigger chambers: - RPCs in the barrel - TGCs in the end-caps 31 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Muon Spectrometer Instrumentation The Muon Spectrometer is instrumented with precision chambers and fast trigger chambers A crucial component to reach the required accuracy is the sophisticated alignment measurement and monitoring system P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 Precision chambers: - MDTs in the barrel and end-caps - CSCs at large rapidity for the innermost end-cap stations Trigger chambers: - RPCs in the barrel - TGCs in the end-caps 31 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
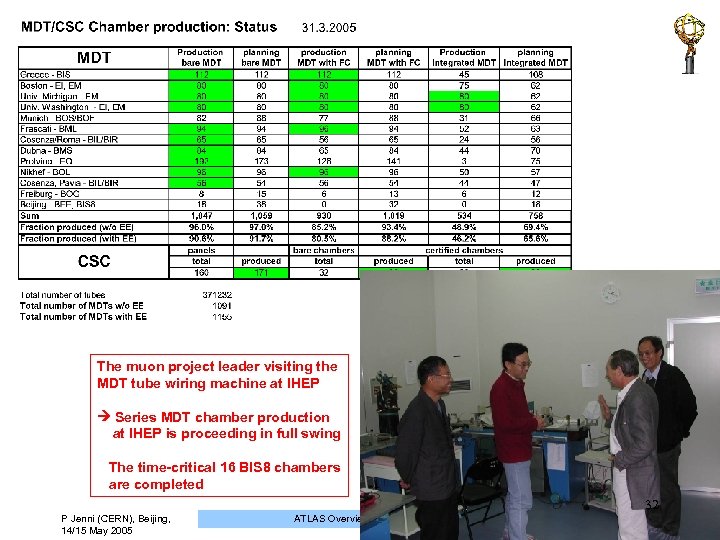 The muon project leader visiting the MDT tube wiring machine at IHEP Series MDT chamber production at IHEP is proceeding in full swing The time-critical 16 BIS 8 chambers are completed 32 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
The muon project leader visiting the MDT tube wiring machine at IHEP Series MDT chamber production at IHEP is proceeding in full swing The time-critical 16 BIS 8 chambers are completed 32 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 The IHEP ATLAS MDT clean room 33 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
The IHEP ATLAS MDT clean room 33 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 The installation of the barrel muon station has started in the feet region of the detector 34 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
The installation of the barrel muon station has started in the feet region of the detector 34 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
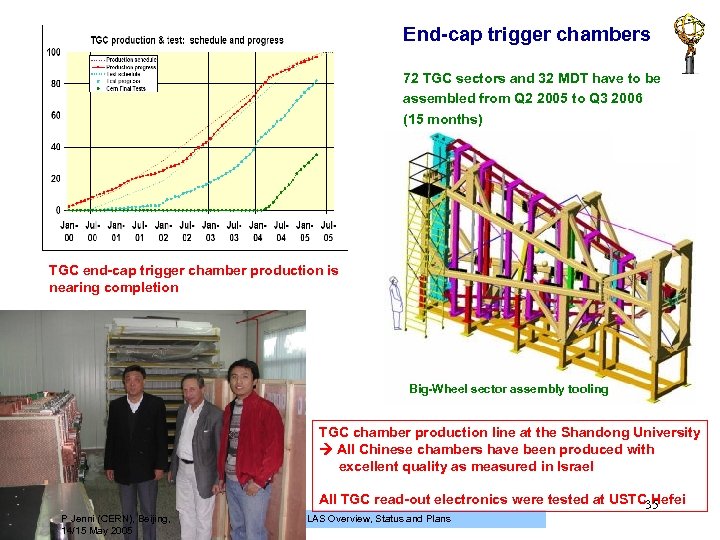 End-cap trigger chambers 72 TGC sectors and 32 MDT have to be assembled from Q 2 2005 to Q 3 2006 (15 months) TGC end-cap trigger chamber production is nearing completion Big-Wheel sector assembly tooling TGC chamber production line at the Shandong University All Chinese chambers have been produced with excellent quality as measured in Israel All TGC read-out electronics were tested at USTC Hefei 35 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
End-cap trigger chambers 72 TGC sectors and 32 MDT have to be assembled from Q 2 2005 to Q 3 2006 (15 months) TGC end-cap trigger chamber production is nearing completion Big-Wheel sector assembly tooling TGC chamber production line at the Shandong University All Chinese chambers have been produced with excellent quality as measured in Israel All TGC read-out electronics were tested at USTC Hefei 35 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
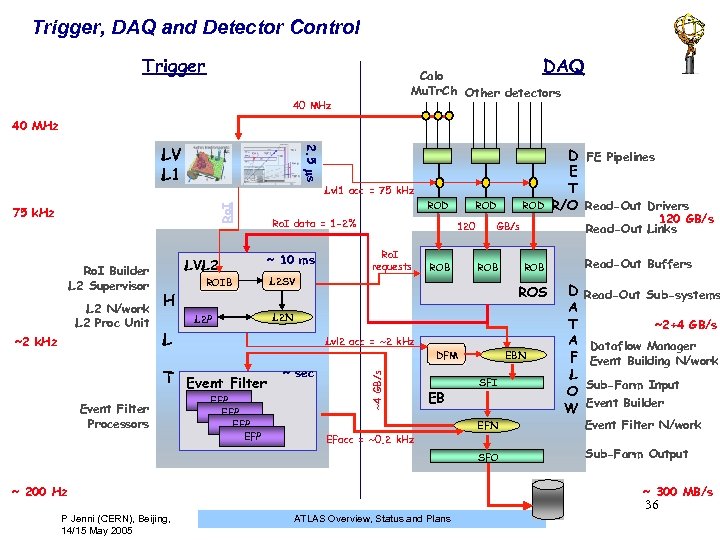 Trigger, DAQ and Detector Control Trigger DAQ Calo Mu. Tr. Ch Other detectors 40 MHz 2. 5 s LV L 1 Ro. I ~2 k. Hz LVL 2 ROIB H L 2 P ROD Ro. I data = 1 -2% ~ 10 ms Event Filter Processors Ro. I requests ROB Read-Out Buffers ROS L 2 N Lvl 2 acc = ~2 k. Hz EFP EFP ROB ~ sec DFM EB 120 GB/s Read-Out Links GB/s L 2 SV L T Event Filter ROD 120 ~4 GB/s L 2 N/work L 2 Proc Unit ROB Lvl 1 acc = 75 k. Hz Ro. I Builder L 2 Supervisor ROD D FE Pipelines E T R/O Read-Out Drivers EBN SFI D A T A F L O W Read-Out Sub-systems ~2+4 GB/s Dataflow Manager Event Building N/work Sub-Farm Input Event Builder EFN SFO ~ 200 Hz P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 Event Filter N/work Sub-Farm Output EFacc = ~0. 2 k. Hz ~ 300 MB/s 36 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Trigger, DAQ and Detector Control Trigger DAQ Calo Mu. Tr. Ch Other detectors 40 MHz 2. 5 s LV L 1 Ro. I ~2 k. Hz LVL 2 ROIB H L 2 P ROD Ro. I data = 1 -2% ~ 10 ms Event Filter Processors Ro. I requests ROB Read-Out Buffers ROS L 2 N Lvl 2 acc = ~2 k. Hz EFP EFP ROB ~ sec DFM EB 120 GB/s Read-Out Links GB/s L 2 SV L T Event Filter ROD 120 ~4 GB/s L 2 N/work L 2 Proc Unit ROB Lvl 1 acc = 75 k. Hz Ro. I Builder L 2 Supervisor ROD D FE Pipelines E T R/O Read-Out Drivers EBN SFI D A T A F L O W Read-Out Sub-systems ~2+4 GB/s Dataflow Manager Event Building N/work Sub-Farm Input Event Builder EFN SFO ~ 200 Hz P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 Event Filter N/work Sub-Farm Output EFacc = ~0. 2 k. Hz ~ 300 MB/s 36 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Inner detector Channels No. ROLs Fragment size - k. B Pixels 0. 8 x 108 120 0. 5 SCT 6. 2 x 106 92 1. 1 TRT 3. 7 x 105 232 1. 2 ATLAS total event size = 1. 5 MB Total no. ROLs = 1600 Calorimetry Channels No. ROLs Fragment size - k. B LAr 1. 8 x 105 764 0. 75 Tile 104 64 0. 75 Muon system Channels No. ROLs Fragment size - k. B MDT 3. 7 x 105 192 0. 8 CSC 6. 7 x 104 32 0. 2 RPC 3. 5 x 105 32 0. 38 TGC 4. 4 x 105 16 0. 38 Channels LVL 1 Trigger No. ROLs Fragment size - k. B 56 1. 2 37 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Inner detector Channels No. ROLs Fragment size - k. B Pixels 0. 8 x 108 120 0. 5 SCT 6. 2 x 106 92 1. 1 TRT 3. 7 x 105 232 1. 2 ATLAS total event size = 1. 5 MB Total no. ROLs = 1600 Calorimetry Channels No. ROLs Fragment size - k. B LAr 1. 8 x 105 764 0. 75 Tile 104 64 0. 75 Muon system Channels No. ROLs Fragment size - k. B MDT 3. 7 x 105 192 0. 8 CSC 6. 7 x 104 32 0. 2 RPC 3. 5 x 105 32 0. 38 TGC 4. 4 x 105 16 0. 38 Channels LVL 1 Trigger No. ROLs Fragment size - k. B 56 1. 2 37 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
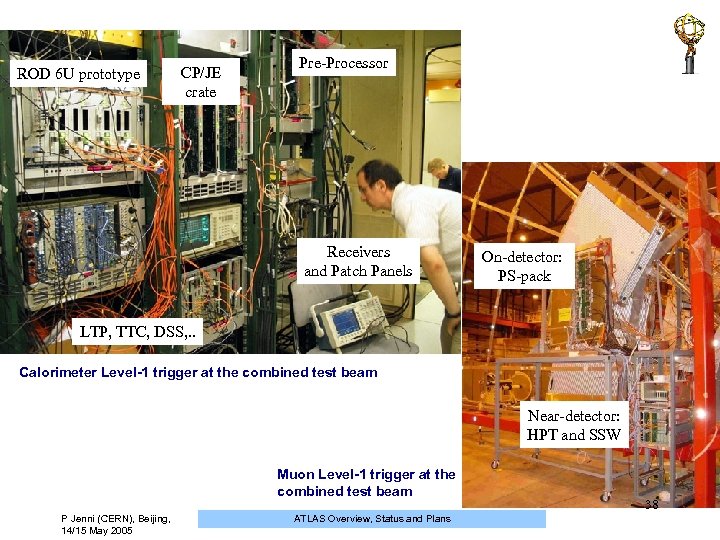 ROD 6 U prototype CP/JE crate Pre-Processor Receivers and Patch Panels On-detector: PS-pack LTP, TTC, DSS, . . Calorimeter Level-1 trigger at the combined test beam Near-detector: HPT and SSW Muon Level-1 trigger at the combined test beam P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans 38
ROD 6 U prototype CP/JE crate Pre-Processor Receivers and Patch Panels On-detector: PS-pack LTP, TTC, DSS, . . Calorimeter Level-1 trigger at the combined test beam Near-detector: HPT and SSW Muon Level-1 trigger at the combined test beam P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans 38
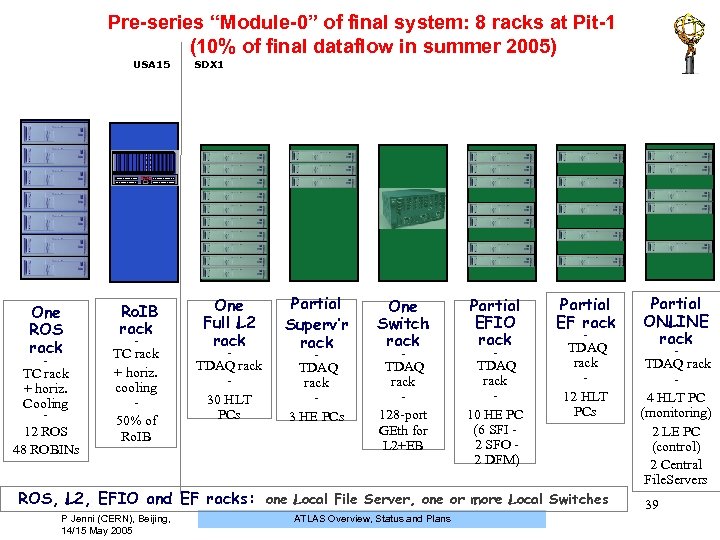 Pre-series “Module-0” of final system: 8 racks at Pit-1 (10% of final dataflow in summer 2005) USA 15 SDX 1 5. 5 One ROS rack - TC rack + horiz. Cooling - 12 ROS 48 ROBINs Ro. IB rack - TC rack + horiz. cooling 50% of Ro. IB One Full L 2 rack Partial Superv’r rack One Switch rack Partial EFIO rack TDAQ rack 30 HLT PCs TDAQ rack 3 HE PCs TDAQ rack 128 -port GEth for L 2+EB TDAQ rack 10 HE PC (6 SFI 2 SFO 2 DFM) - - Partial EF rack - TDAQ rack 12 HLT PCs ROS, L 2, EFIO and EF racks: one Local File Server, one or more Local Switches P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans Partial ONLINE rack - TDAQ rack 4 HLT PC (monitoring) 2 LE PC (control) 2 Central File. Servers 39
Pre-series “Module-0” of final system: 8 racks at Pit-1 (10% of final dataflow in summer 2005) USA 15 SDX 1 5. 5 One ROS rack - TC rack + horiz. Cooling - 12 ROS 48 ROBINs Ro. IB rack - TC rack + horiz. cooling 50% of Ro. IB One Full L 2 rack Partial Superv’r rack One Switch rack Partial EFIO rack TDAQ rack 30 HLT PCs TDAQ rack 3 HE PCs TDAQ rack 128 -port GEth for L 2+EB TDAQ rack 10 HE PC (6 SFI 2 SFO 2 DFM) - - Partial EF rack - TDAQ rack 12 HLT PCs ROS, L 2, EFIO and EF racks: one Local File Server, one or more Local Switches P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans Partial ONLINE rack - TDAQ rack 4 HLT PC (monitoring) 2 LE PC (control) 2 Central File. Servers 39
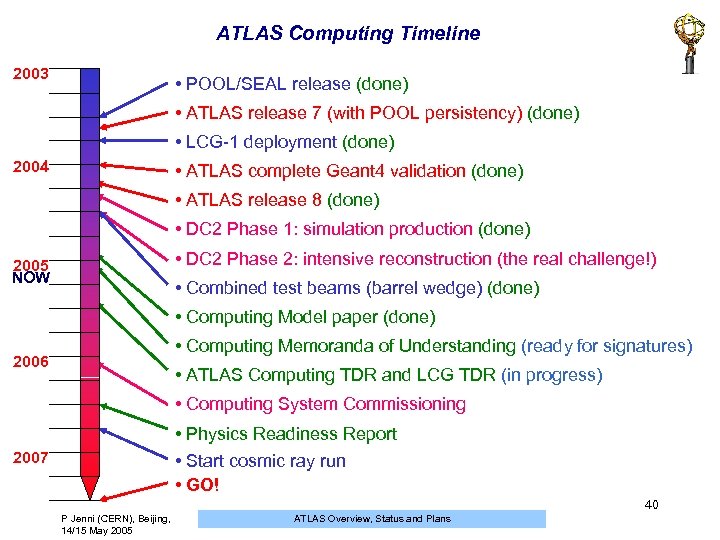 ATLAS Computing Timeline 2003 • POOL/SEAL release (done) • ATLAS release 7 (with POOL persistency) (done) • LCG-1 deployment (done) 2004 • ATLAS complete Geant 4 validation (done) • ATLAS release 8 (done) • DC 2 Phase 1: simulation production (done) • DC 2 Phase 2: intensive reconstruction (the real challenge!) 2005 NOW • Combined test beams (barrel wedge) (done) • Computing Model paper (done) • Computing Memoranda of Understanding (ready for signatures) 2006 • ATLAS Computing TDR and LCG TDR (in progress) • Computing System Commissioning • Physics Readiness Report • Start cosmic ray run • GO! 2007 40 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
ATLAS Computing Timeline 2003 • POOL/SEAL release (done) • ATLAS release 7 (with POOL persistency) (done) • LCG-1 deployment (done) 2004 • ATLAS complete Geant 4 validation (done) • ATLAS release 8 (done) • DC 2 Phase 1: simulation production (done) • DC 2 Phase 2: intensive reconstruction (the real challenge!) 2005 NOW • Combined test beams (barrel wedge) (done) • Computing Model paper (done) • Computing Memoranda of Understanding (ready for signatures) 2006 • ATLAS Computing TDR and LCG TDR (in progress) • Computing System Commissioning • Physics Readiness Report • Start cosmic ray run • GO! 2007 40 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Computing System Commissioning Goals • We have recently defined the high-level goals of the Computing System Commissioning operation during the first half of 2006 – Formerly called “DC 3” – More a running-in of continuous operation than a stand-alone challenge • Main aim of Computing System Commissioning will be to test the software and computing infrastructure that we will need at the beginning of 2007: – Calibration and alignment procedures and conditions DB – Full trigger chain – Tier-0 reconstruction and data distribution – Distributed access to the data for analysis • At the end (mid-2006) we will have a working and operational system, ready to take data with cosmic rays at increasing rates 41 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Computing System Commissioning Goals • We have recently defined the high-level goals of the Computing System Commissioning operation during the first half of 2006 – Formerly called “DC 3” – More a running-in of continuous operation than a stand-alone challenge • Main aim of Computing System Commissioning will be to test the software and computing infrastructure that we will need at the beginning of 2007: – Calibration and alignment procedures and conditions DB – Full trigger chain – Tier-0 reconstruction and data distribution – Distributed access to the data for analysis • At the end (mid-2006) we will have a working and operational system, ready to take data with cosmic rays at increasing rates 41 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
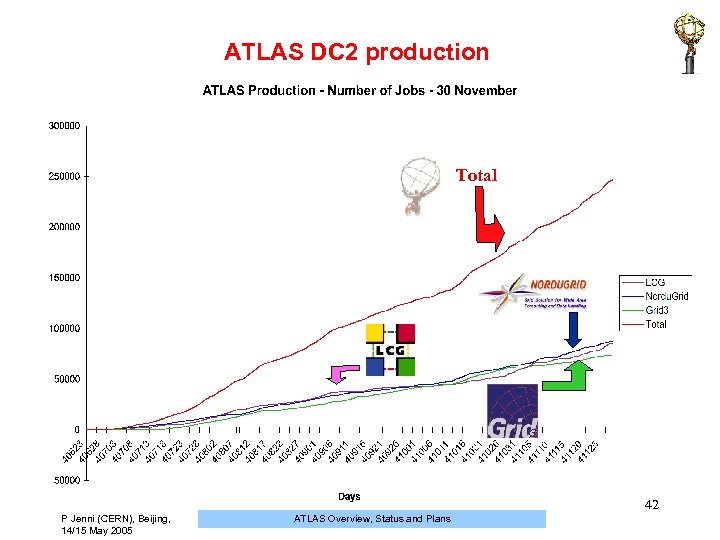 ATLAS DC 2 production Total 42 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
ATLAS DC 2 production Total 42 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Towards the complete experiment: ATLAS combined test beam in 2004 Full “vertical slice” of ATLAS tested on CERN H 8 beam line May-November 2004 Geant 4 simulation of test-beam set-up y x z For the first time, all ATLAS sub-detectors integrated and run together with common DAQ, “final” electronics, slow-control, etc. Gained lot of global operation experience during ~ 6 month run. Common ATLAS software used to analyze the data 43 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Towards the complete experiment: ATLAS combined test beam in 2004 Full “vertical slice” of ATLAS tested on CERN H 8 beam line May-November 2004 Geant 4 simulation of test-beam set-up y x z For the first time, all ATLAS sub-detectors integrated and run together with common DAQ, “final” electronics, slow-control, etc. Gained lot of global operation experience during ~ 6 month run. Common ATLAS software used to analyze the data 43 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
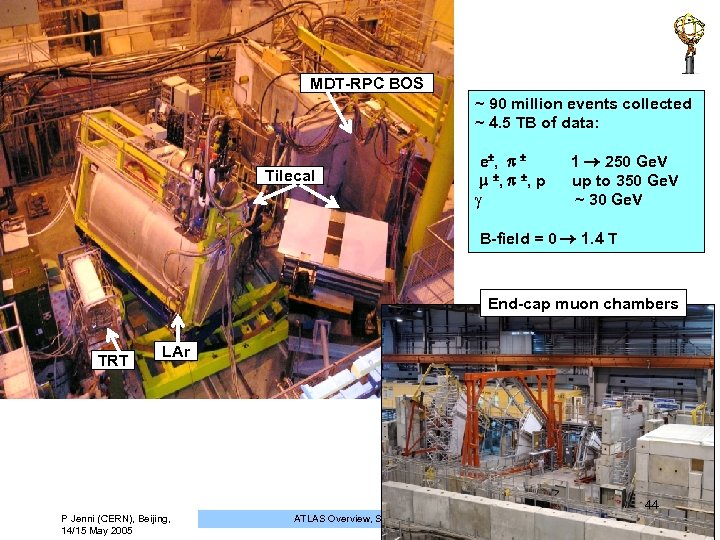 MDT-RPC BOS ~ 90 million events collected ~ 4. 5 TB of data: Tilecal e , 1 250 Ge. V , , p up to 350 Ge. V ~ 30 Ge. V B-field = 0 1. 4 T End-cap muon chambers TRT LAr 44 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
MDT-RPC BOS ~ 90 million events collected ~ 4. 5 TB of data: Tilecal e , 1 250 Ge. V , , p up to 350 Ge. V ~ 30 Ge. V B-field = 0 1. 4 T End-cap muon chambers TRT LAr 44 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
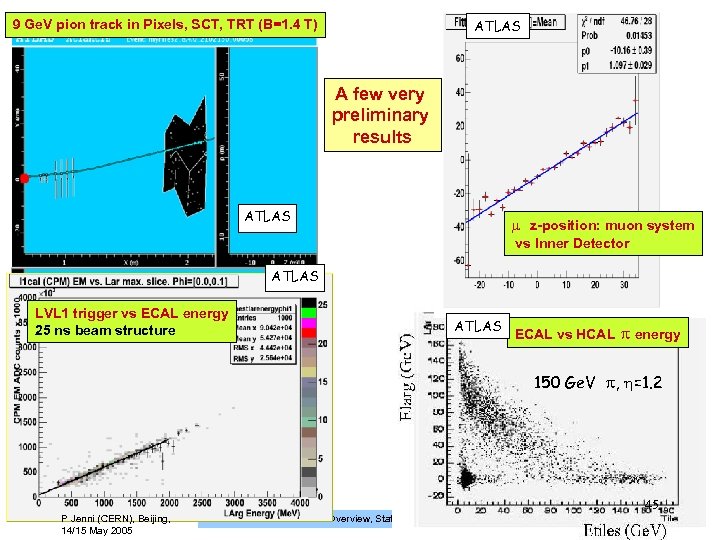 ATLAS 9 Ge. V pion track in Pixels, SCT, TRT (B=1. 4 T) A few very preliminary results ATLAS z-position: muon system vs Inner Detector ATLAS LVL 1 trigger vs ECAL energy 25 ns beam structure ATLAS ECAL vs HCAL energy 150 Ge. V , =1. 2 45 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
ATLAS 9 Ge. V pion track in Pixels, SCT, TRT (B=1. 4 T) A few very preliminary results ATLAS z-position: muon system vs Inner Detector ATLAS LVL 1 trigger vs ECAL energy 25 ns beam structure ATLAS ECAL vs HCAL energy 150 Ge. V , =1. 2 45 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
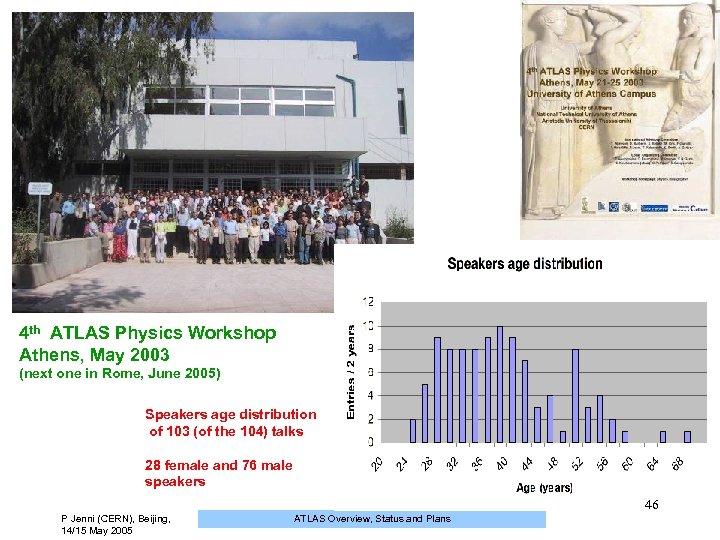 4 th ATLAS Physics Workshop Athens, May 2003 (next one in Rome, June 2005) Speakers age distribution of 103 (of the 104) talks 28 female and 76 male speakers 46 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
4 th ATLAS Physics Workshop Athens, May 2003 (next one in Rome, June 2005) Speakers age distribution of 103 (of the 104) talks 28 female and 76 male speakers 46 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Search for the Higgs boson H ZZ(*) 4 ATLAS ~ 4 years ~1 year ~3 years 5 discovery present limit 47 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Search for the Higgs boson H ZZ(*) 4 ATLAS ~ 4 years ~1 year ~3 years 5 discovery present limit 47 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
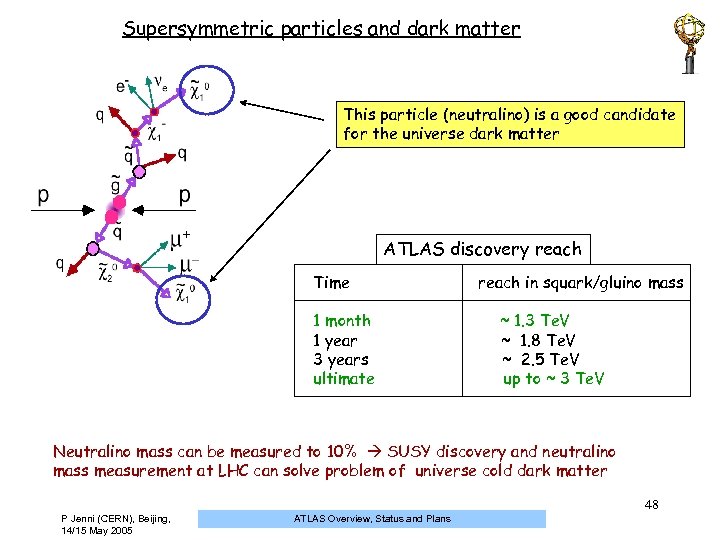 Supersymmetric particles and dark matter This particle (neutralino) is a good candidate for the universe dark matter ATLAS discovery reach Time 1 month 1 year 3 years ultimate reach in squark/gluino mass ~ 1. 3 Te. V ~ 1. 8 Te. V ~ 2. 5 Te. V up to ~ 3 Te. V Neutralino mass can be measured to 10% SUSY discovery and neutralino mass measurement at LHC can solve problem of universe cold dark matter 48 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Supersymmetric particles and dark matter This particle (neutralino) is a good candidate for the universe dark matter ATLAS discovery reach Time 1 month 1 year 3 years ultimate reach in squark/gluino mass ~ 1. 3 Te. V ~ 1. 8 Te. V ~ 2. 5 Te. V up to ~ 3 Te. V Neutralino mass can be measured to 10% SUSY discovery and neutralino mass measurement at LHC can solve problem of universe cold dark matter 48 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
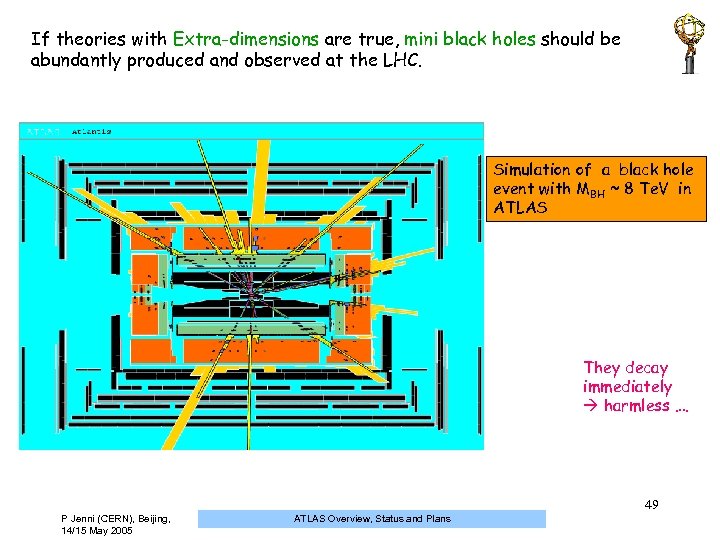 If theories with Extra-dimensions are true, mini black holes should be abundantly produced and observed at the LHC. Simulation of a black hole event with MBH ~ 8 Te. V in ATLAS They decay immediately harmless …. 49 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
If theories with Extra-dimensions are true, mini black holes should be abundantly produced and observed at the LHC. Simulation of a black hole event with MBH ~ 8 Te. V in ATLAS They decay immediately harmless …. 49 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Are there links with astrophysics and cosmology ? Yes, many …. s = 14 Te. V corresponds to E ~ 100 Pe. V fixed target proton beam The LHC will be the first machine able to explore the high-E part of the cosmic ray spectrum 50 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Are there links with astrophysics and cosmology ? Yes, many …. s = 14 Te. V corresponds to E ~ 100 Pe. V fixed target proton beam The LHC will be the first machine able to explore the high-E part of the cosmic ray spectrum 50 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 ATLAS potential for heavy ions Specific strengths of the detector can be exploited for HI - Best jet calorimetry at LHC detailed jet quenching - Tracking and muon spectrometer production/suppression of heavy quark states Pb-Pb collision b = 0, dy = 0. 5 5. 5 Te. V/coll. nucl. 1027 cm-2 s-1 Pb-Pb collision Upsilon production 51 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
ATLAS potential for heavy ions Specific strengths of the detector can be exploited for HI - Best jet calorimetry at LHC detailed jet quenching - Tracking and muon spectrometer production/suppression of heavy quark states Pb-Pb collision b = 0, dy = 0. 5 5. 5 Te. V/coll. nucl. 1027 cm-2 s-1 Pb-Pb collision Upsilon production 51 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Recent example: ATLAS potential for ‘Little Higgs Models’ LHM New approach to the hierarchy problem, predicting a rich phenomenology with many new particles (heavy top T, new Gauge Bosons WH, ZH, AH and Higgs triplet F 0, F++), WH and ZH search shown is defined by boson mass (M) and mixing angle (q) parameters (reach plot is for 300 fb-1) 52 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Recent example: ATLAS potential for ‘Little Higgs Models’ LHM New approach to the hierarchy problem, predicting a rich phenomenology with many new particles (heavy top T, new Gauge Bosons WH, ZH, AH and Higgs triplet F 0, F++), WH and ZH search shown is defined by boson mass (M) and mixing angle (q) parameters (reach plot is for 300 fb-1) 52 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Overall summary installation schedule version 7. 0 (New baseline approved in the February 2005 ATLAS EB) 53 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Overall summary installation schedule version 7. 0 (New baseline approved in the February 2005 ATLAS EB) 53 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Future Plans Obviously, the foremost priority is to get the ATLAS detector completed, installed and commissioned in time for the first LHC collisions in summer 2007 The initial detector will have some parts staged, for financial reasons, mainly processing power affecting the acceptable trigger level-1 data rate (50% of design capacity only), and some muon tracking redundancy (chambers to be built in the US) Also staged will be some shielding components for the design luminosity running (this could be an interesting opportunity for new short-term investments with engineering and fabrication) Internally, ATLAS has started a coherent, well-focused effort to plan and develop an R&D strategy towards changes to ATLAS which will be needed for some components for an upgraded high-luminosity LHC (beyond the present design, up to 10 35 cm-2 s-1) The main efforts will be needed in the tracking system (detectors, electronics and engineering), the LAr calorimeter electronics, and in shielding engineering It is too early to present specific plans, but it is not too early to get involved in the discussion and setting up of ATLAS R&D groups A next major event is the ATLAS Tracker High-Luminosity Workshop in Genoa 18 -20 July 2005 (http: //atu-2005. ge. infn. it/) 54 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
Future Plans Obviously, the foremost priority is to get the ATLAS detector completed, installed and commissioned in time for the first LHC collisions in summer 2007 The initial detector will have some parts staged, for financial reasons, mainly processing power affecting the acceptable trigger level-1 data rate (50% of design capacity only), and some muon tracking redundancy (chambers to be built in the US) Also staged will be some shielding components for the design luminosity running (this could be an interesting opportunity for new short-term investments with engineering and fabrication) Internally, ATLAS has started a coherent, well-focused effort to plan and develop an R&D strategy towards changes to ATLAS which will be needed for some components for an upgraded high-luminosity LHC (beyond the present design, up to 10 35 cm-2 s-1) The main efforts will be needed in the tracking system (detectors, electronics and engineering), the LAr calorimeter electronics, and in shielding engineering It is too early to present specific plans, but it is not too early to get involved in the discussion and setting up of ATLAS R&D groups A next major event is the ATLAS Tracker High-Luminosity Workshop in Genoa 18 -20 July 2005 (http: //atu-2005. ge. infn. it/) 54 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
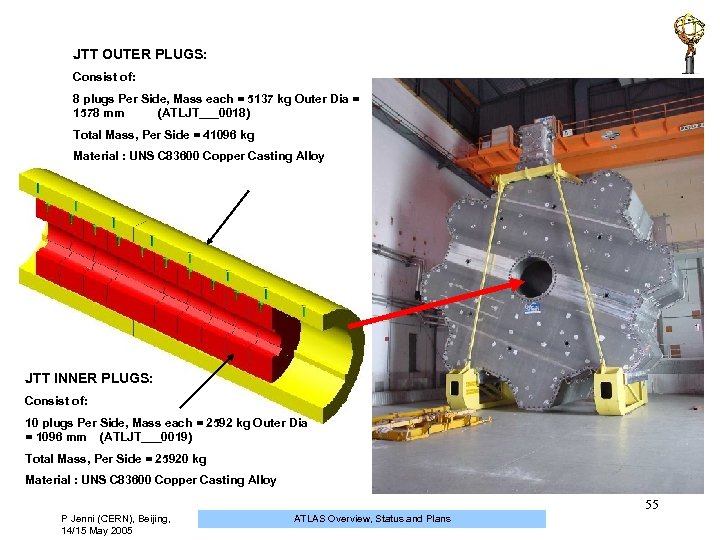 JTT OUTER PLUGS: Consist of: 8 plugs Per Side, Mass each = 5137 kg Outer Dia = 1578 mm (ATLJT___0018) Total Mass, Per Side = 41096 kg Material : UNS C 83600 Copper Casting Alloy JTT INNER PLUGS: Consist of: 10 plugs Per Side, Mass each = 2592 kg Outer Dia = 1096 mm (ATLJT___0019) Total Mass, Per Side = 25920 kg Material : UNS C 83600 Copper Casting Alloy 55 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
JTT OUTER PLUGS: Consist of: 8 plugs Per Side, Mass each = 5137 kg Outer Dia = 1578 mm (ATLJT___0018) Total Mass, Per Side = 41096 kg Material : UNS C 83600 Copper Casting Alloy JTT INNER PLUGS: Consist of: 10 plugs Per Side, Mass each = 2592 kg Outer Dia = 1096 mm (ATLJT___0019) Total Mass, Per Side = 25920 kg Material : UNS C 83600 Copper Casting Alloy 55 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
 Conclusions Many important milestones have been passed in the construction, pre-assembly, integration and installation of the ATLAS detector components Very major software and computing activities are underway as well, using the LHC Computing Grid for world-wide distributed computing resources Planning for the commissioning and the early physics phases has started The collaboration with the Chinese teams is a pleasure, and ATLAS values highly their scientific and technical contributions There will be exciting physics to be shared in the future, and an increased cooperation would be highly welcome The Chinese teams should not miss this great opportunity to train with LHC many Ph. D generations of young scientists! P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans 56
Conclusions Many important milestones have been passed in the construction, pre-assembly, integration and installation of the ATLAS detector components Very major software and computing activities are underway as well, using the LHC Computing Grid for world-wide distributed computing resources Planning for the commissioning and the early physics phases has started The collaboration with the Chinese teams is a pleasure, and ATLAS values highly their scientific and technical contributions There will be exciting physics to be shared in the future, and an increased cooperation would be highly welcome The Chinese teams should not miss this great opportunity to train with LHC many Ph. D generations of young scientists! P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans 56
 The ATLAS Collaboration is highly motivated and on track for LHC physics in 2007 57 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans
The ATLAS Collaboration is highly motivated and on track for LHC physics in 2007 57 P Jenni (CERN), Beijing, 14/15 May 2005 ATLAS Overview, Status and Plans


