f391fd15684c6f7e7406a3734ce7f8e7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

ATHENS UNIVERSITY OF ECONOMICS & BUSINESS KTIMA SPYROPOYLOY Spyropoulou domain PART II II. ALTERNATIVE STRATEGIES Teacher: Prof. S. Lioukas 1

Part II: Alternative strategies • • Generating strategies - tools Preliminary evaluation of new strategies Qualitative evaluation (SFA) Synthesizing alternatives – new composite strategies • Financial evaluation of new strategies • Conclusions- Recommendation 2
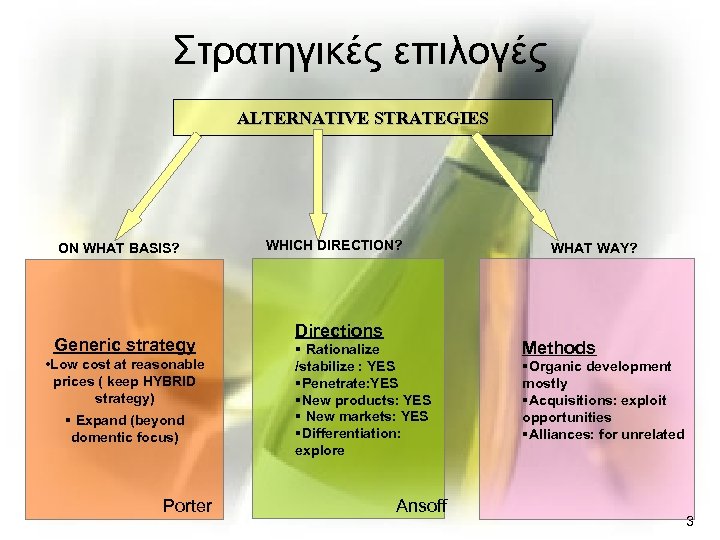
Στρατηγικές επιλογές ALTERNATIVE STRATEGIES ON WHAT BASIS? Generic strategy • Low cost at reasonable prices ( keep HYBRID strategy) § Expand (beyond domentic focus) Porter WHICH DIRECTION? Directions § Rationalize /stabilize : YES §Penetrate: YES §New products: YES § New markets: YES §Differentiation: explore Ansoff WHAT WAY? Methods §Organic development mostly §Acquisitions: exploit opportunities §Alliances: for unrelated 3
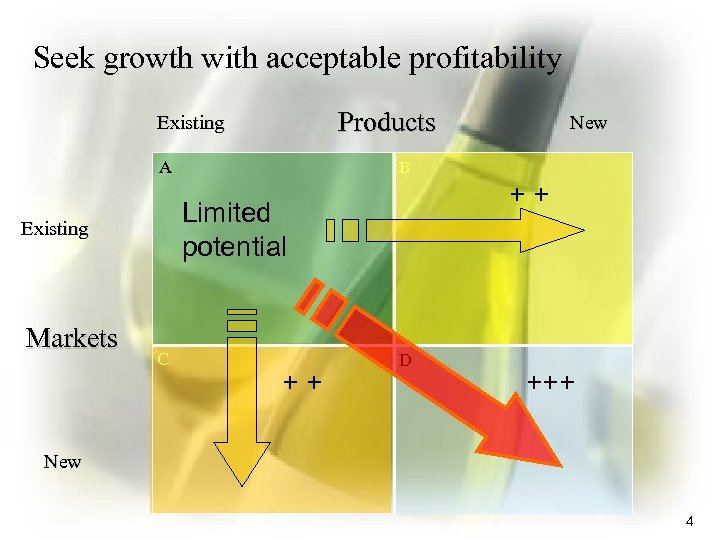
Seek growth with acceptable profitability Products Existing B A Markets ++ Limited potential Existing C New ++ D +++ New 4
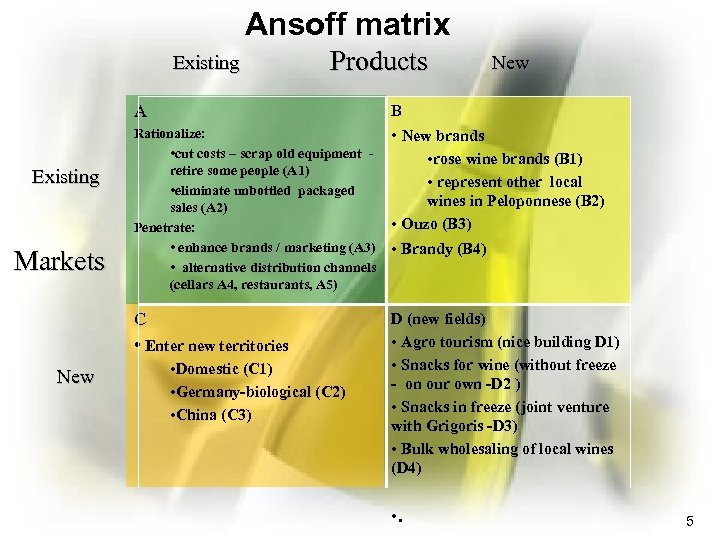
Ansoff matrix Existing Products A Existing Markets Rationalize: • cut costs – scrap old equipment retire some people (A 1) • eliminate unbottled packaged sales (A 2) Penetrate: • enhance brands / marketing (A 3) • alternative distribution channels (cellars A 4, restaurants, A 5) C • Enter new territories New • Domestic (C 1) • Germany-biological (C 2) • China (C 3) New B • New brands • rose wine brands (B 1) • represent other local wines in Peloponnese (B 2) • Ouzo (B 3) • Brandy (B 4) D (new fields) • Agro tourism (nice building D 1) • Snacks for wine (without freeze - on our own -D 2 ) • Snacks in freeze (joint venture with Grigoris -D 3) • Bulk wholesaling of local wines (D 4) • . 5

Preliminary evaluation • Keep the same generic strategy (Hybrid) across – Eliminate A 2: unbottled packaged sales as it damages the quality / brand name – Reject D 3: Grigoris low cost strategy does not fit; partnering with other quality food chains does not appropriate enough profits – Reject D 4: diverts attention from quality brands, impairs image • Strategies in existing products markets do not secure an acceptable future, rationalization – penetration has limited potential – We need alternatives from the other categories – But the company is over borrowed and cannot raise additional loans to finance growth – capital increase in the stock exchange is not feasible 6
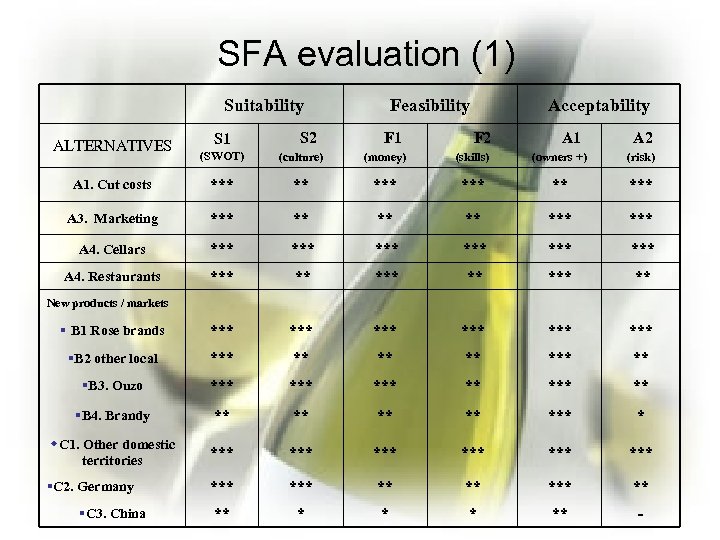
SFA evaluation (1) Suitability ALTERNATIVES S 1 S 2 Feasibility F 1 Acceptability F 2 A 1 A 2 (SWOT) (culture) (money) (skills) (owners +) (risk) A 1. Cut costs *** ** *** A 3. Marketing *** ** *** A 4. Cellars *** *** *** A 4. Restaurants *** ** § B 1 Rose brands *** *** *** §B 2 other local *** ** §B 3. Ouzo *** *** ** §B 4. Brandy ** ** *** * w. C 1. Other domestic territories *** *** *** §C 2. Germany *** ** * ** - New products / markets §C 3. China
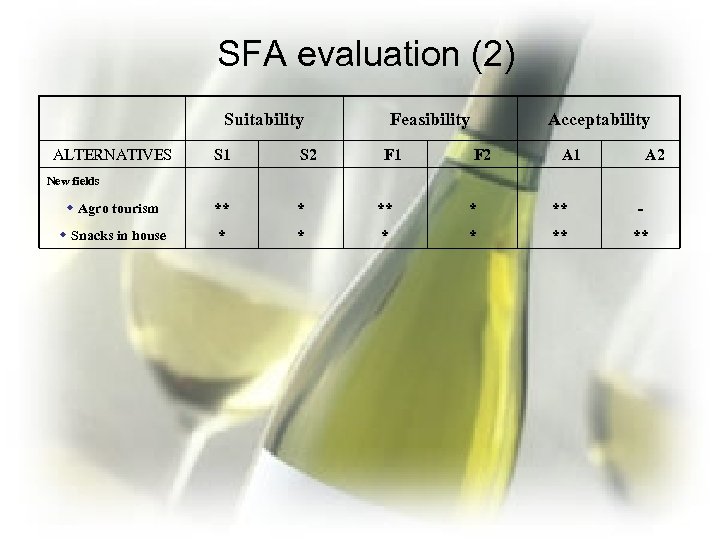
SFA evaluation (2) Suitability ALTERNATIVES Feasibility F 1 Acceptability S 1 S 2 F 2 A 1 A 2 w Agro tourism ** * ** - w Snacks in house * * ** ** New fields

Composite strategies • Strategy 1 (Α, and certain B&C): Moderate, low risk – – – Cut costs, scrap old equipment, reduce staff Penetrate / marketing Distribution through cellars and restaurants Rose brands Expand into other local territories Ouzo • Strategy 2( all of Strategy 1 plus B, C, D): – – Represent other local wines Introduce Brandy Enter Germany Snacks in house • Reject agro tourism and China (Low SFA evaluations)

An evaluation of Strategies 1 & 2 with more SFA criteria Strategy Suitability • Does it exploit opportunities arising in the environment • Does it exploit attractive market segments? • Does it contribute to the competitive position of the company ? • Does it utilize unique resources and capabilities which exist, or can be developed? • Does it fit with the culture and the prevailing philosophy of the company? • Does it provide possibilities for creating significant and viable competitive advantage? Feasibility. • Do we have the resources and capabilities to implement the strategy? • Can the resources and skills for its implementation be developed in the course of action? • Can the alternatives which compose this strategy be integrated in the current operations? • Are there synergies among alternatives and with the existing activities? • Does it contribute to the achievement of attractive growth rates? • Does it contribute to the profitability of the company? Acceptability. • Is the strategy attractive for the share holders? • Has it secured the commitment of the employees? • Is it supported by managers ? • Can it be supported by other stakeholders? Can it be resisted? • Υis there a good probability of success? • Can it stand under adverse conditions (pessimistic scenario)? TOTAL GRADE. . . . . . 10 1 & 2 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 2 3 5 5 4 3 3 3 4 4 5 5 3 4 5 5 4 5 4 4 66 69

Financial evaluation • Are cash flows positive? • Is NPV acceptable ? • We evaluate each composite strategy in total – As there are synergies, it is difficult to isolate each alternative, – With the exception of snacks / delicatessen which accompany the wine, which is evaluated as separate concern
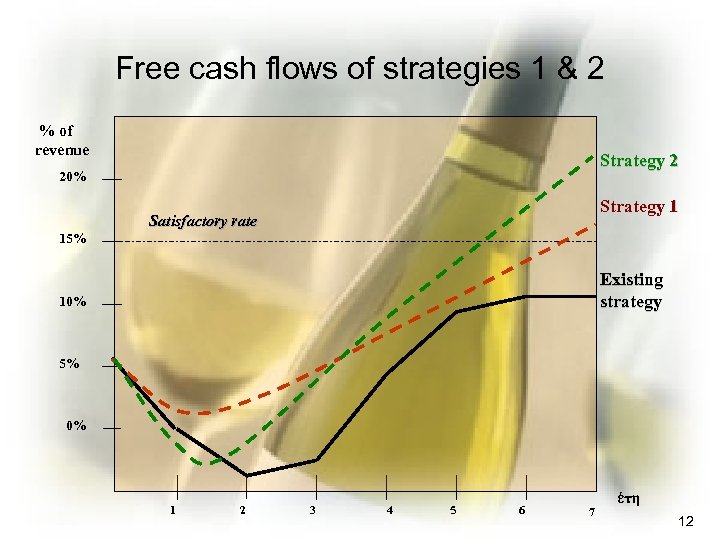
Free cash flows of strategies 1 & 2 % of revenue Strategy 2 20% Strategy 1 Satisfactory rate 15% Existing strategy 10% 5% 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 έτη 12
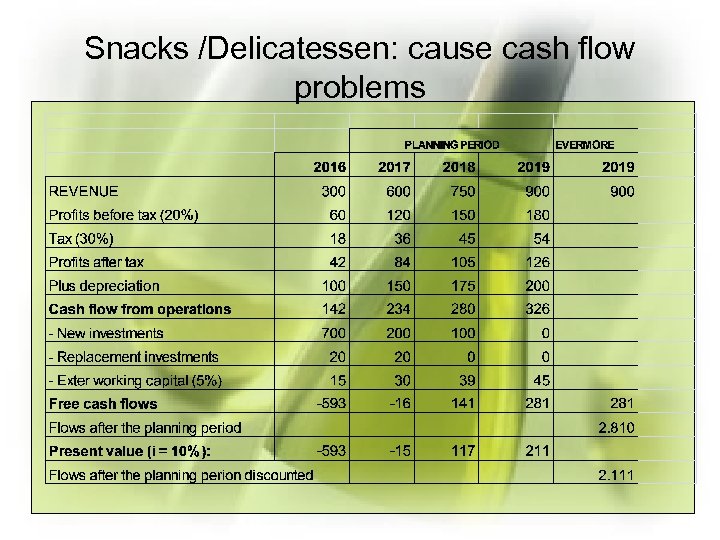
Snacks /Delicatessen: cause cash flow problems

Conclusions • Existing strategy is not acceptable. It gives 2 -3 years with negative cash flows, and future prospects are limited • Strategy 1: (cost cutting, marketing, alternative distribution networks, expansion into Greece and introduction of Ouzo): – there a possibility to reach satisfactory performance after 5 or 6 years, with no cash flow problems between. It is acceptable • The more aggressive strategy 2, (adding merchandizing of more Peloponnese wines, Brandy, entering Germany with biological wines and snacks development in house) – would produce better results than Strategy 1, after 5 -6 years – but we have to face negative cash flows for the first 2 -3 years. Can we finance this period? Negotiate with banks. – If not then drop snacks/delicatessen 14

ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΑΘΗΝΩΝ Spyropoulou Domain Part III: Implementing the new strategy 15
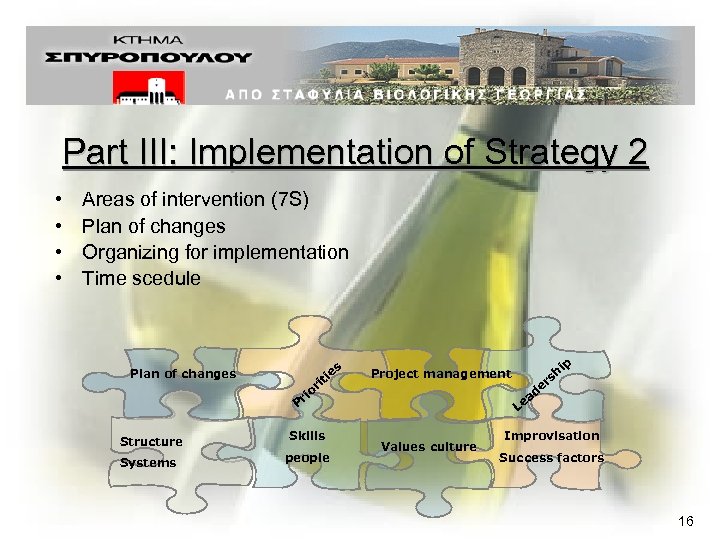
Part III: Implementation of Strategy 2 • • Areas of intervention (7 S) Plan of changes Organizing for implementation Time scedule s Plan of changes ie it or i Pr Structure Skills Systems people Project management e L Values culture d ea h rs ip Improvisation Success factors 16
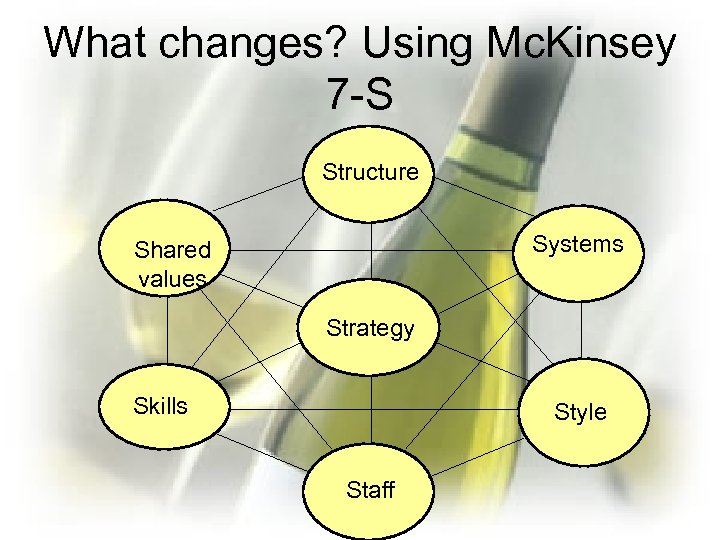
What changes? Using Mc. Kinsey 7 -S Structure Systems Shared values Strategy Skills Style Staff
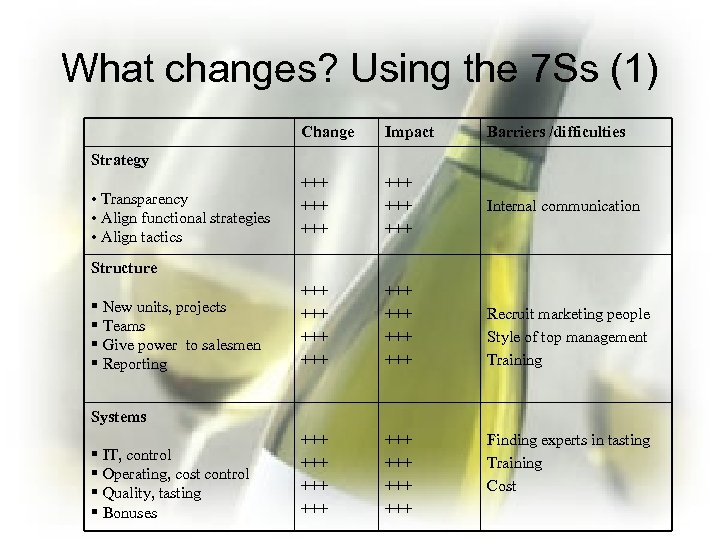
What changes? Using the 7 Ss (1) Change Impact Barriers /difficulties +++ +++ +++ Internal communication +++ +++ +++ +++ Strategy • Transparency • Align functional strategies • Align tactics Structure § New units, projects § Teams § Give power to salesmen § Reporting Recruit marketing people Style of top management Training Systems § IT, control § Operating, cost control § Quality, tasting § Bonuses Finding experts in tasting Training Cost
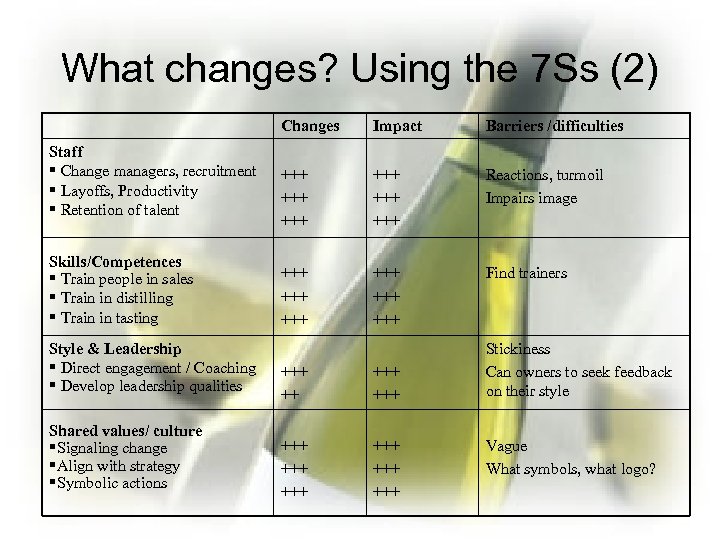
What changes? Using the 7 Ss (2) Changes Staff § Change managers, recruitment § Layoffs, Productivity § Retention of talent Skills/Competences § Train people in sales § Train in distilling § Train in tasting Style & Leadership § Direct engagement / Coaching § Develop leadership qualities Shared values/ culture §Signaling change §Align with strategy §Symbolic actions Impact Barriers /difficulties +++ +++ +++ Reactions, turmoil Impairs image +++ +++ +++ Find trainers +++ +++ +++ Stickiness Can owners to seek feedback on their style Vague What symbols, what logo?

Plan if changes From 7 S to specific actionable projects : • • • • Sell old equipment Formulate and apply an early retirement plan Recruit a Marketing Director Form a horizontal team for the introduction of Ouzo Buy distillers for ouzo Recruit specialist in distilling New department for snacks / delicatessen Strike agreements with cellars and restaurants Recruit an expert in wine tasting Train other people in wine tasting Train salesmen for restaurants, cellars Make agreements with local distributors in other areas Introduce rose wine brands with historical local names… 20

Plan if changes • Cost of changes: • About 250 000 Euro for two years • Return of “investment” in change • IRR with the changes – IRR without = IRR 8% • Financing: seek new loan • Execution: • Fast, in two years 21

Priorities • Cut costs to release resources to the plan • Staff the new Department of Marketing • Train salesmen • Investment in new equipment • Engage all managers &staff in the change. . . 22

Method of implementation • Select a project manager to coordinate all changes • From existing managers • Active engagement of top management: give the tone from the top • Select certain new managers • Marketing, ++ • Monitoring execution • Form horizontal project teams • for ouzo, agreements, delicatessen 23
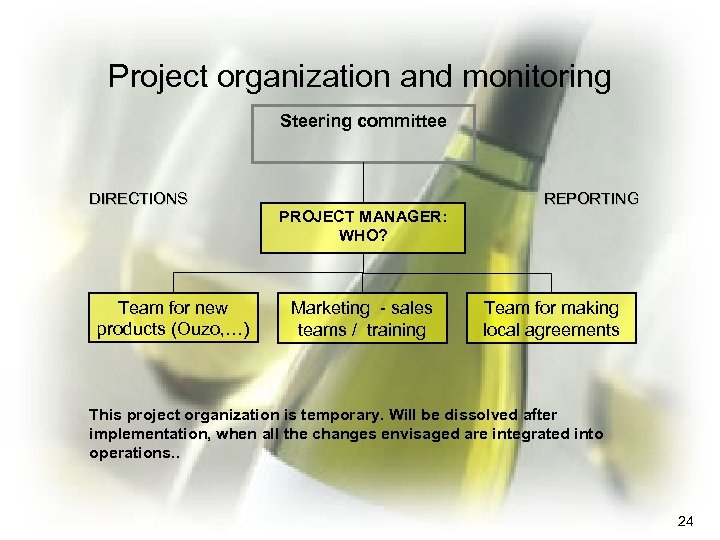
Project organization and monitoring Steering committee DIRECTIONS Team for new products (Ouzo, …) PROJECT MANAGER: WHO? Marketing - sales teams / training REPORTING Team for making local agreements Τhis project organization is temporary. Will be dissolved after implementation, when all the changes envisaged are integrated into operations. . 24
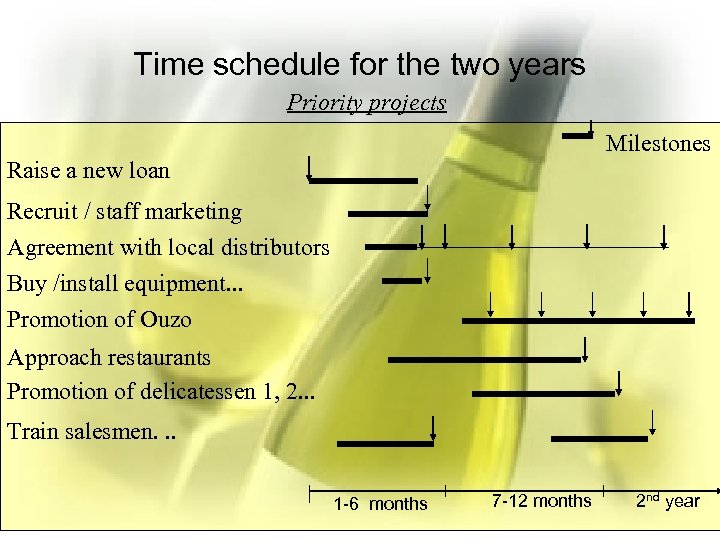
Time schedule for the two years Priority projects Milestones Raise a new loan Recruit / staff marketing Agreement with local distributors Buy /install equipment. . . Promotion of Ouzo Approach restaurants Promotion of delicatessen 1, 2. . . Train salesmen. . . 1 -6 months 7 -12 months 2 nd year
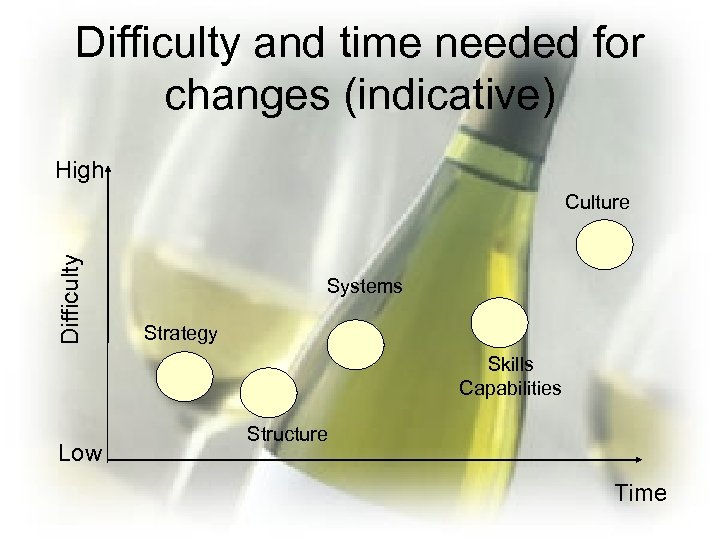
Difficulty and time needed for changes (indicative) High Difficulty Culture Systems Strategy Skills Capabilities Low Structure Time

«Ούτος (οίνος) θεοίσι σπένδεται θεός γεγώς» (Ευριπίδη, Βάκχαι, στ. 280 -285) [Μτφρ. : Θεός είναι (το κρασί) και χρησιμεύει για σπονδή (θυσία) στους θεούς]. THE END 27

«Ούτος (οίνος) θεοίσι σπένδεται θεός γεγώς» (Ευριπίδη, Βάκχαι, στ. 280 -285) [Μτφρ. : Θεός είναι (το κρασί) και χρησιμεύει για σπονδή (θυσία) στους θεούς]. THE END 28
f391fd15684c6f7e7406a3734ce7f8e7.ppt