2dff086d8258725fe8928fb72904d533.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review 27. -29. March 2007 Madeira, Portugal Project A 7 – Business Documents and Protocols Ulrike Greiner, SAP © ATHENA Consortium 2007 1
ATHENA M 36 Final Review 27. -29. March 2007 Madeira, Portugal Project A 7 – Business Documents and Protocols Ulrike Greiner, SAP © ATHENA Consortium 2007 1
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Presentation Outline ● ● ● Project Goals Building on ATHENA results Major Achievements Fulfilment of Work Plan Contributions to ATHENA Impact Made © ATHENA Consortium 2007 2
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Presentation Outline ● ● ● Project Goals Building on ATHENA results Major Achievements Fulfilment of Work Plan Contributions to ATHENA Impact Made © ATHENA Consortium 2007 2
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Project Goals ● ● Analyse business document and protocol standards and relate it to industry best practice Methods and tools for lifecycle management of business documents and protocols: ● Creation of business documents and protocols ● ● ● Ensuring consistency and reuse Different modelling layers (business – technical – execution) Support variants of business documents Storage and retrieval of business documents and protocols Mapping and transformation of business documents Creation of business content using ATHENA tools for selected industry best practice Methods and tools for efficient and easy management of Business Documents and Protocols © ATHENA Consortium 2007 3
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Project Goals ● ● Analyse business document and protocol standards and relate it to industry best practice Methods and tools for lifecycle management of business documents and protocols: ● Creation of business documents and protocols ● ● ● Ensuring consistency and reuse Different modelling layers (business – technical – execution) Support variants of business documents Storage and retrieval of business documents and protocols Mapping and transformation of business documents Creation of business content using ATHENA tools for selected industry best practice Methods and tools for efficient and easy management of Business Documents and Protocols © ATHENA Consortium 2007 3
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Building on ATHENA Results ● A 2: ● ● ● A 5: ● ● WSDL analyzer for mapping Agent platform as execution platform for business protocols Service execution infrastructure A 6: ● ● ● Modelling approach for cross-organisational business processes CBP modelling and execution infrastructure P 2 P infrastructure for repository services PIM 4 SOA as a basis for technical level business document and protocol models PIM->PSM transformations between modelling levels Semaphore transformation tool A 3: Tools and methods for semantic annotation ● Reconciliation rules specification and engine for business document reconciliation © ATHENA Consortium 2007 ● A 1: MPCE based repository interface ● 4
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Building on ATHENA Results ● A 2: ● ● ● A 5: ● ● WSDL analyzer for mapping Agent platform as execution platform for business protocols Service execution infrastructure A 6: ● ● ● Modelling approach for cross-organisational business processes CBP modelling and execution infrastructure P 2 P infrastructure for repository services PIM 4 SOA as a basis for technical level business document and protocol models PIM->PSM transformations between modelling levels Semaphore transformation tool A 3: Tools and methods for semantic annotation ● Reconciliation rules specification and engine for business document reconciliation © ATHENA Consortium 2007 ● A 1: MPCE based repository interface ● 4
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Definition of Basic Terms ● ● A business document is a set of information components that are interchanged as part of a business activity Possible components are: ● ● ● Information in business documents can be of different
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Definition of Basic Terms ● ● A business document is a set of information components that are interchanged as part of a business activity Possible components are: ● ● ● Information in business documents can be of different
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Major Achievements ● ● Analysis of industry requirements and standards Modelling of business documents on the technical level: ● ● Automated Mapping Support: ● ● P 2 P-based repository for flexibly storing and retrieving business documents and protocols Protocol support: ● ● ● Automated assistance to mapping business documents Repository: ● ● Supporting re-use and variant handling Support for business level stakeholders Implementation of DFDL standard for non-XML data Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to agent metamodel Transformation from business level CBPs to protocols Application of A 7 results to industry scenario © ATHENA Consortium 2007 7
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Major Achievements ● ● Analysis of industry requirements and standards Modelling of business documents on the technical level: ● ● Automated Mapping Support: ● ● P 2 P-based repository for flexibly storing and retrieving business documents and protocols Protocol support: ● ● ● Automated assistance to mapping business documents Repository: ● ● Supporting re-use and variant handling Support for business level stakeholders Implementation of DFDL standard for non-XML data Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to agent metamodel Transformation from business level CBPs to protocols Application of A 7 results to industry scenario © ATHENA Consortium 2007 7
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira As-is Situation in ATHENA Scenarios ● Questionnaires to gather information from ATHENA user partners about ● ● ● As-is situation in their company regarding business documents and protocols A 7 specific requirements Several shortcomings: ● ● ● Standards are very complex Implementation of standards is complicated, complex, and time-consuming Lots of interaction needed between the partners until integration is achieved ICT standards are difficult to use (no compliance certification) Rhythm of evolution is too fast for industrial needs ● ● ● robust and high quality standards are needed Overlapping and incoherency in coverage of different view points (engineering, ICT, organization, information) Framework to coherently compose standards to cover all necessary aspects is missing © ATHENA Consortium 2007 8
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira As-is Situation in ATHENA Scenarios ● Questionnaires to gather information from ATHENA user partners about ● ● ● As-is situation in their company regarding business documents and protocols A 7 specific requirements Several shortcomings: ● ● ● Standards are very complex Implementation of standards is complicated, complex, and time-consuming Lots of interaction needed between the partners until integration is achieved ICT standards are difficult to use (no compliance certification) Rhythm of evolution is too fast for industrial needs ● ● ● robust and high quality standards are needed Overlapping and incoherency in coverage of different view points (engineering, ICT, organization, information) Framework to coherently compose standards to cover all necessary aspects is missing © ATHENA Consortium 2007 8
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Requirements from DRDS ● A 7. 2 A 7. 4 A 7. 3 A 7. 4 A 7. 2 A 7. 5 Business document support should fulfil the following requirements: ● ● ● A 7. 4 A 2 ● A 7. 4 ● Coherent documents are needed instead of loosely connected messages Re-usability, Life cycle management Guidance for filling of document Support for multi-user access and multi-organization use of document Automated processing of exchanged documents Connection of business documents with Enterprise Modelling systems Easy implementation of business document related systems Business protocol support should fulfil the following requirements: ● ● Monitoring and controlling of protocols Enacting view processes, event notification, compliance with existing solution Technical features of the protocol system, e. g. support of © ATHENA Consortium 2007 ● 9
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Requirements from DRDS ● A 7. 2 A 7. 4 A 7. 3 A 7. 4 A 7. 2 A 7. 5 Business document support should fulfil the following requirements: ● ● ● A 7. 4 A 2 ● A 7. 4 ● Coherent documents are needed instead of loosely connected messages Re-usability, Life cycle management Guidance for filling of document Support for multi-user access and multi-organization use of document Automated processing of exchanged documents Connection of business documents with Enterprise Modelling systems Easy implementation of business document related systems Business protocol support should fulfil the following requirements: ● ● Monitoring and controlling of protocols Enacting view processes, event notification, compliance with existing solution Technical features of the protocol system, e. g. support of © ATHENA Consortium 2007 ● 9
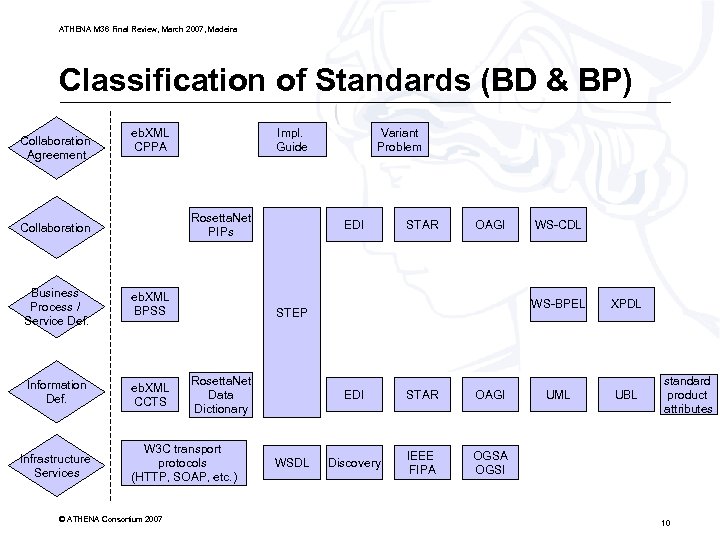 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Classification of Standards (BD & BP) Collaboration Agreement eb. XML CPPA Impl. Guide Rosetta. Net PIPs Collaboration Business Process / Service Def. eb. XML BPSS Information Def. eb. XML CCTS Infrastructure Services EDI STAR OAGI Rosetta. Net Data Dictionary EDI WSDL WS-CDL WS-BPEL STEP W 3 C transport protocols (HTTP, SOAP, etc. ) © ATHENA Consortium 2007 Variant Problem STAR OAGI Discovery IEEE FIPA XPDL UML UBL standard product attributes OGSA OGSI 10
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Classification of Standards (BD & BP) Collaboration Agreement eb. XML CPPA Impl. Guide Rosetta. Net PIPs Collaboration Business Process / Service Def. eb. XML BPSS Information Def. eb. XML CCTS Infrastructure Services EDI STAR OAGI Rosetta. Net Data Dictionary EDI WSDL WS-CDL WS-BPEL STEP W 3 C transport protocols (HTTP, SOAP, etc. ) © ATHENA Consortium 2007 Variant Problem STAR OAGI Discovery IEEE FIPA XPDL UML UBL standard product attributes OGSA OGSI 10
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Selected Standards • Detailed description and analysis of the following standards: • • • eb. XML CCTS and CPPA Rosetta. Net PIPs, data dictionary and schemas STEP Standard Product Attributes (DIN 4002) OAGI Schemas for non-XML documents: • DFDL / HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) • FIPA Agent Communication Language (ACL) • Further problems investigated in A 7: • Variant problem © ATHENA Consortium 2007 11
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Selected Standards • Detailed description and analysis of the following standards: • • • eb. XML CCTS and CPPA Rosetta. Net PIPs, data dictionary and schemas STEP Standard Product Attributes (DIN 4002) OAGI Schemas for non-XML documents: • DFDL / HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) • FIPA Agent Communication Language (ACL) • Further problems investigated in A 7: • Variant problem © ATHENA Consortium 2007 11
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Major Achievements ● ● Analysis of industry requirements and standards Modelling of business documents on the technical level: ● ● Automated Mapping Support: ● ● Automated assistance to mapping business documents Repository: ● ● Supporting re-use and variant handling Support for business level stakeholders Implementation of DFDL standard for non-XML data P 2 P-based repository for flexibly storing and retrieving business documents and protocols Protocol support: ● ● Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to agent metamodel Transformation from business level CBPs to protocols Application of A 7 results to industry scenario ● ATHENA Consortium 2007 © 12
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Major Achievements ● ● Analysis of industry requirements and standards Modelling of business documents on the technical level: ● ● Automated Mapping Support: ● ● Automated assistance to mapping business documents Repository: ● ● Supporting re-use and variant handling Support for business level stakeholders Implementation of DFDL standard for non-XML data P 2 P-based repository for flexibly storing and retrieving business documents and protocols Protocol support: ● ● Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to agent metamodel Transformation from business level CBPs to protocols Application of A 7 results to industry scenario ● ATHENA Consortium 2007 © 12
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Modeling Requirements and Approach ● ● Re-use of model types that are modeled once and can then be used in different document models Model representation targeted at business experts ● ● Semi-automatic transformation to technical specification ● ● Graphical modeling support needed e. g. through export functionality to create XML representations Support for handling variants of business documents: ● ● ● Share most of their data fields Differ in a limited number of data fields that depend on the context in which the document is used Example: a purchase order that differs slightly if used in different European countries Concept of business context defines specific ● © ATHENA Consortium 2007 13
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Modeling Requirements and Approach ● ● Re-use of model types that are modeled once and can then be used in different document models Model representation targeted at business experts ● ● Semi-automatic transformation to technical specification ● ● Graphical modeling support needed e. g. through export functionality to create XML representations Support for handling variants of business documents: ● ● ● Share most of their data fields Differ in a limited number of data fields that depend on the context in which the document is used Example: a purchase order that differs slightly if used in different European countries Concept of business context defines specific ● © ATHENA Consortium 2007 13
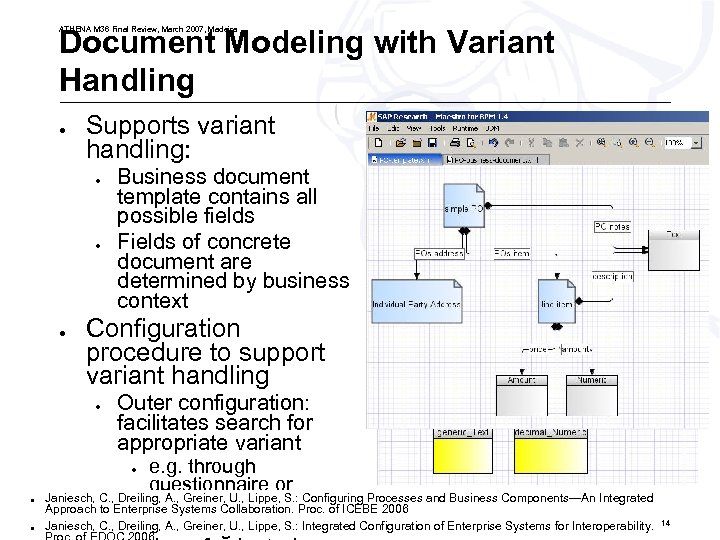 Document Modeling with Variant Handling ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira ● Supports variant handling: ● ● ● Business document template contains all possible fields Fields of concrete document are determined by business context Configuration procedure to support variant handling ● Outer configuration: facilitates search for appropriate variant e. g. through questionnaire or Janiesch, C. , Dreiling, A. , Greiner, U. , Lippe, S. : Configuring Processes and Business Components—An Integrated scenario-based Approach to Enterprise Systems Collaboration. Proc. of ICEBE 2006 ● ● Inner configuration: fine © ATHENA Consortium 2007 ● Janiesch, ● Dreiling, A. , Greiner, U. , Lippe, S. : Integrated Configuration of Enterprise Systems for Interoperability. C. , 14
Document Modeling with Variant Handling ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira ● Supports variant handling: ● ● ● Business document template contains all possible fields Fields of concrete document are determined by business context Configuration procedure to support variant handling ● Outer configuration: facilitates search for appropriate variant e. g. through questionnaire or Janiesch, C. , Dreiling, A. , Greiner, U. , Lippe, S. : Configuring Processes and Business Components—An Integrated scenario-based Approach to Enterprise Systems Collaboration. Proc. of ICEBE 2006 ● ● Inner configuration: fine © ATHENA Consortium 2007 ● Janiesch, ● Dreiling, A. , Greiner, U. , Lippe, S. : Integrated Configuration of Enterprise Systems for Interoperability. C. , 14
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Graphical Editor for PIM 4 SOA ● ● Built as a set of Eclipse plug-ins using Eclipse Graphical Modelling Framework (GMF) Based on updated version of PIM 4 SOA metamodel (A 6) ● ● Supports the graphical modelling of ● ● ● Services Processes Information (Business Documents) Creates models conform to PIM 4 SOA metamodel Developed general Eclipse plug-in for A 7 repository to allow ● ● Added support for extending documents Connection Browsing Import / Export Down-stream transformations ● ● Eclipse plug-ins: workbench integration with existing ATHENA MDE tools PIM 4 SOA editor stores natively in PIM 4 SOA format ● Existing A 6 transformations work with minor alterations © ATHENA Consortium 2007 15
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Graphical Editor for PIM 4 SOA ● ● Built as a set of Eclipse plug-ins using Eclipse Graphical Modelling Framework (GMF) Based on updated version of PIM 4 SOA metamodel (A 6) ● ● Supports the graphical modelling of ● ● ● Services Processes Information (Business Documents) Creates models conform to PIM 4 SOA metamodel Developed general Eclipse plug-in for A 7 repository to allow ● ● Added support for extending documents Connection Browsing Import / Export Down-stream transformations ● ● Eclipse plug-ins: workbench integration with existing ATHENA MDE tools PIM 4 SOA editor stores natively in PIM 4 SOA format ● Existing A 6 transformations work with minor alterations © ATHENA Consortium 2007 15
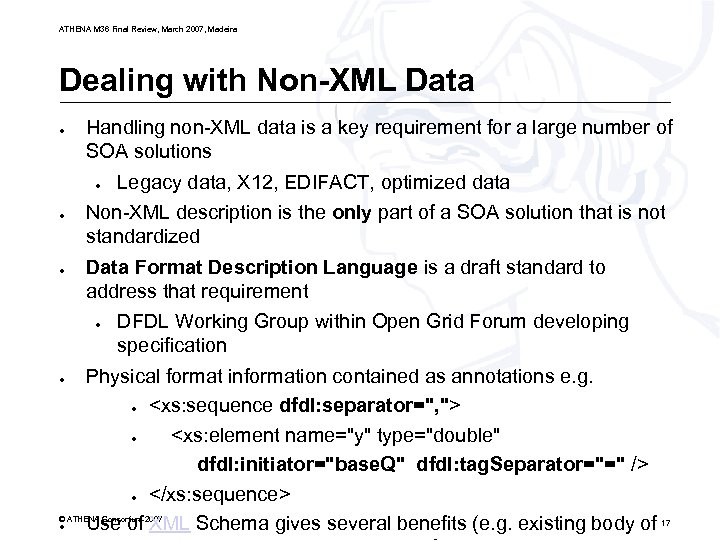 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Dealing with Non-XML Data ● Handling non-XML data is a key requirement for a large number of SOA solutions ● ● ● Non-XML description is the only part of a SOA solution that is not standardized Data Format Description Language is a draft standard to address that requirement ● ● Legacy data, X 12, EDIFACT, optimized data DFDL Working Group within Open Grid Forum developing specification Physical format information contained as annotations e. g. ●
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Dealing with Non-XML Data ● Handling non-XML data is a key requirement for a large number of SOA solutions ● ● ● Non-XML description is the only part of a SOA solution that is not standardized Data Format Description Language is a draft standard to address that requirement ● ● Legacy data, X 12, EDIFACT, optimized data DFDL Working Group within Open Grid Forum developing specification Physical format information contained as annotations e. g. ●
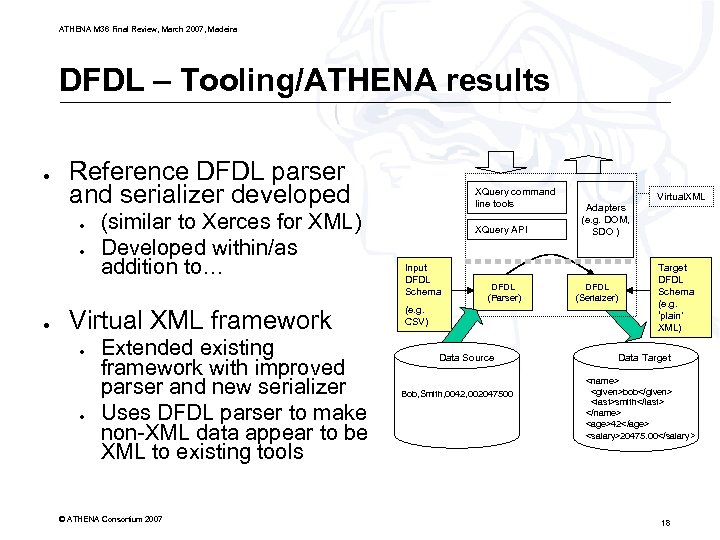 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira DFDL – Tooling/ATHENA results ● Reference DFDL parser and serializer developed ● ● ● (similar to Xerces for XML) Developed within/as addition to… Virtual XML framework ● ● Extended existing framework with improved parser and new serializer Uses DFDL parser to make non-XML data appear to be XML to existing tools © ATHENA Consortium 2007 XQuery command line tools XQuery API Input DFDL Schema DFDL (Parser) (e. g. CSV) Data Source Bob, Smith, 0042, 002047500 Adapters (e. g. DOM, SDO ) DFDL (Serialzer) Virtual. XML Target DFDL Schema (e. g. ‘plain’ XML) Data Target
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira DFDL – Tooling/ATHENA results ● Reference DFDL parser and serializer developed ● ● ● (similar to Xerces for XML) Developed within/as addition to… Virtual XML framework ● ● Extended existing framework with improved parser and new serializer Uses DFDL parser to make non-XML data appear to be XML to existing tools © ATHENA Consortium 2007 XQuery command line tools XQuery API Input DFDL Schema DFDL (Parser) (e. g. CSV) Data Source Bob, Smith, 0042, 002047500 Adapters (e. g. DOM, SDO ) DFDL (Serialzer) Virtual. XML Target DFDL Schema (e. g. ‘plain’ XML) Data Target
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Major Achievements ● ● Analysis of industry requirements and standards Modelling of business documents on the technical level: ● ● Automated Mapping Support: ● ● Automated assistance to mapping business documents Repository: ● ● Supporting re-use and variant handling Support for business level stakeholders Implementation of DFDL standard for non-XML data P 2 P-based repository for flexibly storing and retrieving business documents and protocols Protocol support: ● ● Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to agent metamodel Transformation from business level CBPs to protocols Application of A 7 results to industry scenario ● ATHENA Consortium 2007 © 19
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Major Achievements ● ● Analysis of industry requirements and standards Modelling of business documents on the technical level: ● ● Automated Mapping Support: ● ● Automated assistance to mapping business documents Repository: ● ● Supporting re-use and variant handling Support for business level stakeholders Implementation of DFDL standard for non-XML data P 2 P-based repository for flexibly storing and retrieving business documents and protocols Protocol support: ● ● Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to agent metamodel Transformation from business level CBPs to protocols Application of A 7 results to industry scenario ● ATHENA Consortium 2007 © 19
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Mapping Requirements, Problems, Goals ● Requirement for document mapping ● ● Current problems: ● ● ● Business processes and services are developed by different groups and use different interfaces. Standards (eb. XML, Rosetta. Net, etc. ) are too complicated for applications to implement Document mapping bridges between requester‘s service definition and provider‘s service definition Mapping is almost entirely manual Needs domain experts A 7 goal: ● Automate as much as possible ● ● Not expecting complete automation Build on existing mapping tools © ATHENA Consortium 2007 20
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Mapping Requirements, Problems, Goals ● Requirement for document mapping ● ● Current problems: ● ● ● Business processes and services are developed by different groups and use different interfaces. Standards (eb. XML, Rosetta. Net, etc. ) are too complicated for applications to implement Document mapping bridges between requester‘s service definition and provider‘s service definition Mapping is almost entirely manual Needs domain experts A 7 goal: ● Automate as much as possible ● ● Not expecting complete automation Build on existing mapping tools © ATHENA Consortium 2007 20
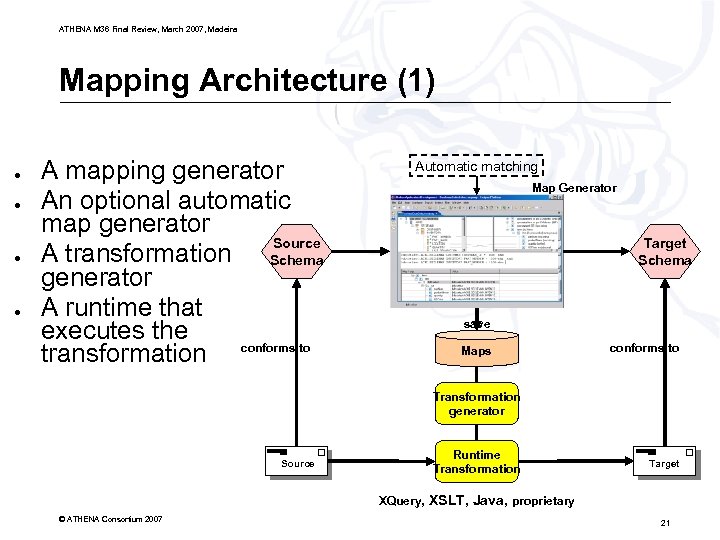 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Mapping Architecture (1) ● ● A mapping generator An optional automatic map generator Source A transformation Schema generator A runtime that executes the transformation conforms to Automatic matching Map Generator Target Schema save Maps conforms to Transformation generator Source Runtime Transformation Target XQuery, XSLT, Java, proprietary © ATHENA Consortium 2007 21
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Mapping Architecture (1) ● ● A mapping generator An optional automatic map generator Source A transformation Schema generator A runtime that executes the transformation conforms to Automatic matching Map Generator Target Schema save Maps conforms to Transformation generator Source Runtime Transformation Target XQuery, XSLT, Java, proprietary © ATHENA Consortium 2007 21
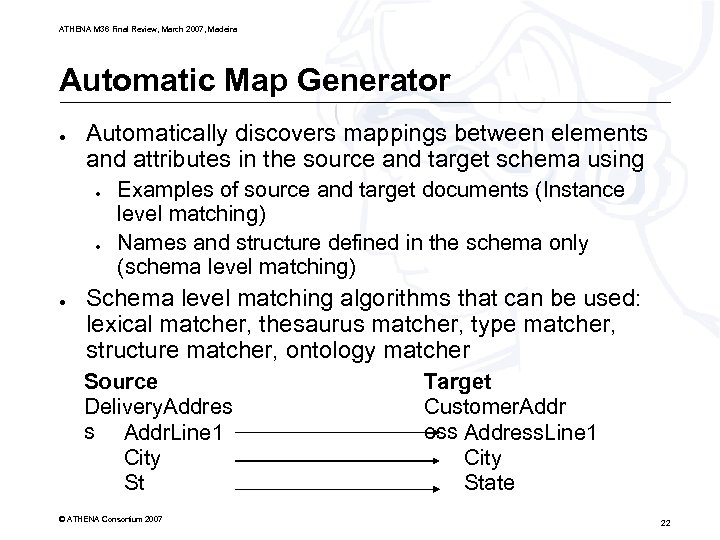 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Automatic Map Generator ● Automatically discovers mappings between elements and attributes in the source and target schema using ● ● ● Examples of source and target documents (Instance level matching) Names and structure defined in the schema only (schema level matching) Schema level matching algorithms that can be used: lexical matcher, thesaurus matcher, type matcher, structure matcher, ontology matcher Source Delivery. Addres s Addr. Line 1 City St © ATHENA Consortium 2007 Target Customer. Addr ess Address. Line 1 City State 22
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Automatic Map Generator ● Automatically discovers mappings between elements and attributes in the source and target schema using ● ● ● Examples of source and target documents (Instance level matching) Names and structure defined in the schema only (schema level matching) Schema level matching algorithms that can be used: lexical matcher, thesaurus matcher, type matcher, structure matcher, ontology matcher Source Delivery. Addres s Addr. Line 1 City St © ATHENA Consortium 2007 Target Customer. Addr ess Address. Line 1 City State 22
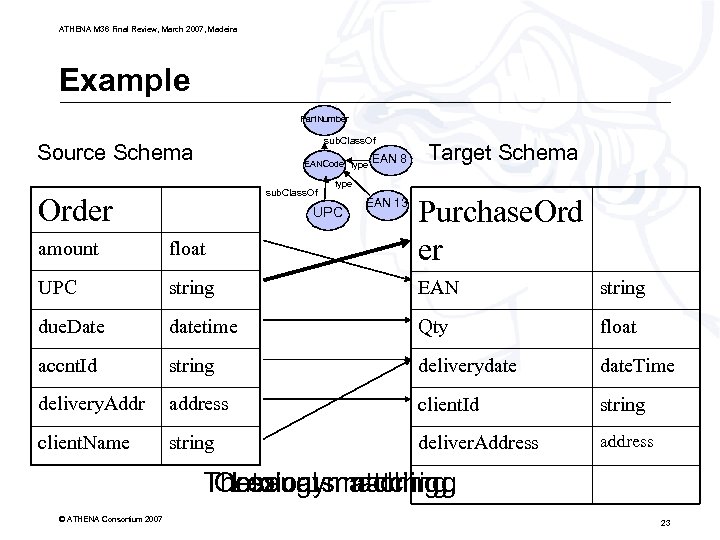 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Example Part. Number sub. Class. Of Source Schema EANCode type sub. Class. Of Order EAN 8 Target Schema type amount float Purchase. Ord er UPC string EAN string due. Date datetime Qty float accnt. Id string deliverydate. Time delivery. Addr address client. Id string client. Name string deliver. Address address UPC EAN 13 Thesaurusmatching Ontologymatching Lexical matching © ATHENA Consortium 2007 23
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Example Part. Number sub. Class. Of Source Schema EANCode type sub. Class. Of Order EAN 8 Target Schema type amount float Purchase. Ord er UPC string EAN string due. Date datetime Qty float accnt. Id string deliverydate. Time delivery. Addr address client. Id string client. Name string deliver. Address address UPC EAN 13 Thesaurusmatching Ontologymatching Lexical matching © ATHENA Consortium 2007 23
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Semaphore Extensions ● Integration with A 3 repository ● ● Connect to A 3 Repository Retrieve ontologies ● ● Integration with A 7 P 2 P repository ● Allows for storage and retrieval of relevant artifacts ● ● ● Automatic conversion to UML 2 models for mapping Schemas Models Mappings Uses same component (plug-in) as PIM 4 SOA Editor Extended support for complex mappings ● Valuable insight gained through work with CAS pilot © ATHENA Consortium 2007 24
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Semaphore Extensions ● Integration with A 3 repository ● ● Connect to A 3 Repository Retrieve ontologies ● ● Integration with A 7 P 2 P repository ● Allows for storage and retrieval of relevant artifacts ● ● ● Automatic conversion to UML 2 models for mapping Schemas Models Mappings Uses same component (plug-in) as PIM 4 SOA Editor Extended support for complex mappings ● Valuable insight gained through work with CAS pilot © ATHENA Consortium 2007 24
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Major Achievements ● ● Analysis of industry requirements and standards Modelling of business documents on the technical level: ● ● Automated Mapping Support: ● ● Automated assistance to mapping business documents Repository: ● ● Supporting re-use and variant handling Support for business level stakeholders Implementation of DFDL standard for non-XML data P 2 P-based repository for flexibly storing and retrieving business documents and protocols Protocol support: ● ● Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to agent metamodel Transformation from business level CBPs to protocols Application of A 7 results to industry scenario ● ATHENA Consortium 2007 © 25
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Major Achievements ● ● Analysis of industry requirements and standards Modelling of business documents on the technical level: ● ● Automated Mapping Support: ● ● Automated assistance to mapping business documents Repository: ● ● Supporting re-use and variant handling Support for business level stakeholders Implementation of DFDL standard for non-XML data P 2 P-based repository for flexibly storing and retrieving business documents and protocols Protocol support: ● ● Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to agent metamodel Transformation from business level CBPs to protocols Application of A 7 results to industry scenario ● ATHENA Consortium 2007 © 25
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Repository for Business Documents Specific requirements for business documents and protocols: ● ● A huge number of different formats Various origins: bodies (e. g. W³C, IEEE), companies (e. g. Scheer) Domain-specifics as from automotive Applicability at different business levels: ● ● ICT, content, process, … Size of the data objects ● Lots based on XML © ATHENA Consortium 2007 26
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Repository for Business Documents Specific requirements for business documents and protocols: ● ● A huge number of different formats Various origins: bodies (e. g. W³C, IEEE), companies (e. g. Scheer) Domain-specifics as from automotive Applicability at different business levels: ● ● ICT, content, process, … Size of the data objects ● Lots based on XML © ATHENA Consortium 2007 26
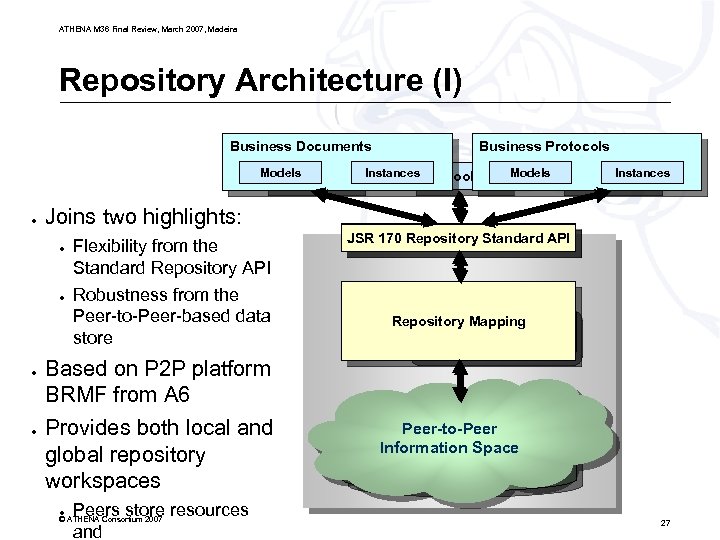 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Repository Architecture (I) Business Documents Models Application ● ● ● Instances Tool Models Instances GUI Joins two highlights: ● ● Business Protocols Flexibility from the Standard Repository API Robustness from the Peer-to-Peer-based data store Based on P 2 P platform BRMF from A 6 Provides both local and global repository workspaces ● Peers store resources and © ATHENA Consortium 2007 Repository API JSR 170 Repository Standard API Information Models Repository Engine Repository Mapping Peer-to-Peer Information Space Persistent Data Store 27
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Repository Architecture (I) Business Documents Models Application ● ● ● Instances Tool Models Instances GUI Joins two highlights: ● ● Business Protocols Flexibility from the Standard Repository API Robustness from the Peer-to-Peer-based data store Based on P 2 P platform BRMF from A 6 Provides both local and global repository workspaces ● Peers store resources and © ATHENA Consortium 2007 Repository API JSR 170 Repository Standard API Information Models Repository Engine Repository Mapping Peer-to-Peer Information Space Persistent Data Store 27
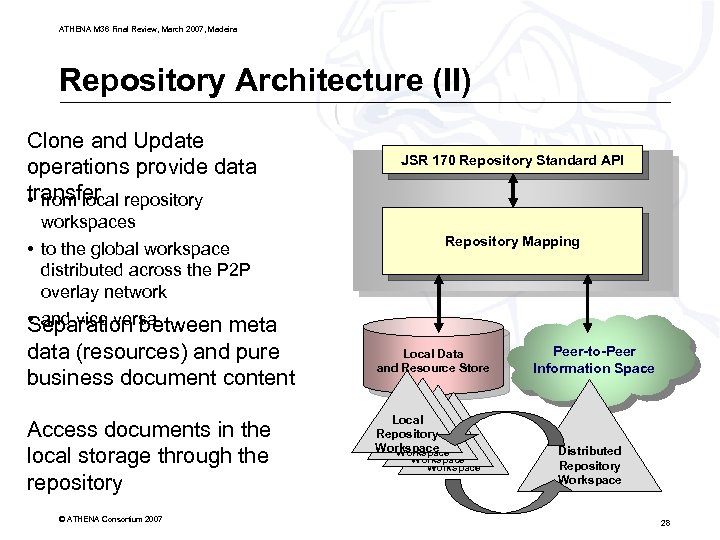 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Repository Architecture (II) Clone and Update operations provide data transfer repository • from local workspaces • to the global workspace distributed across the P 2 P overlay network • and vice versa Separation between meta data (resources) and pure business document content Access documents in the local storage through the repository © ATHENA Consortium 2007 JSR 170 Repository Standard API Repository Mapping Local Data and Resource Store Local local Repository Workspace local Workspace Repository Workspace Peer-to-Peer Information Space Distributed Repository Workspace 28
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Repository Architecture (II) Clone and Update operations provide data transfer repository • from local workspaces • to the global workspace distributed across the P 2 P overlay network • and vice versa Separation between meta data (resources) and pure business document content Access documents in the local storage through the repository © ATHENA Consortium 2007 JSR 170 Repository Standard API Repository Mapping Local Data and Resource Store Local local Repository Workspace local Workspace Repository Workspace Peer-to-Peer Information Space Distributed Repository Workspace 28
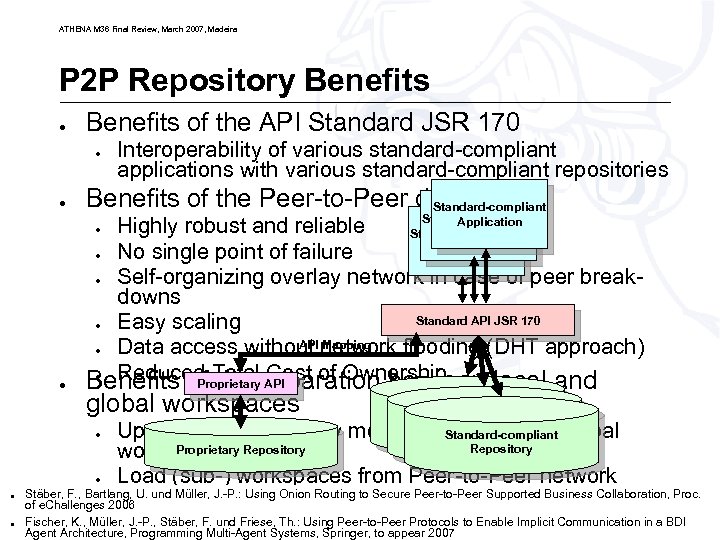 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira P 2 P Repository Benefits ● Benefits of the API Standard JSR 170 ● ● Interoperability of various standard-compliant applications with various standard-compliant repositories Benefits of the Peer-to-Peer data store Standard-compliant Application Highly robust and reliable Application Standard-compliant Application ● No single point of failure ● Self-organizing overlay network in case of peer breakdowns Standard API JSR 170 ● Easy scaling API Mapping ● Data access without network flooding (DHT approach) ● Reduced the API Cost of Ownership Proprietary Benefits of Totalseparation between local and ● ● global workspaces ● ● Standard-compliant Repository Update local repository modifications into the global Proprietary workspace Repository Load (sub-) workspaces from Peer-to-Peer network Stäber, F. , Bartlang, U. und Müller, J. -P. : Using Onion Routing to Secure Peer-to-Peer Supported Business Collaboration, Proc. of e. Challenges 2006 © Fischer, ATHENA Consortium 2007 K. , Müller, J. -P. , Stäber, F. und Friese, Th. : Using Peer-to-Peer Protocols to Enable Implicit Communication in a 29 BDI Agent Architecture, Programming Multi-Agent Systems, Springer, to appear 2007
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira P 2 P Repository Benefits ● Benefits of the API Standard JSR 170 ● ● Interoperability of various standard-compliant applications with various standard-compliant repositories Benefits of the Peer-to-Peer data store Standard-compliant Application Highly robust and reliable Application Standard-compliant Application ● No single point of failure ● Self-organizing overlay network in case of peer breakdowns Standard API JSR 170 ● Easy scaling API Mapping ● Data access without network flooding (DHT approach) ● Reduced the API Cost of Ownership Proprietary Benefits of Totalseparation between local and ● ● global workspaces ● ● Standard-compliant Repository Update local repository modifications into the global Proprietary workspace Repository Load (sub-) workspaces from Peer-to-Peer network Stäber, F. , Bartlang, U. und Müller, J. -P. : Using Onion Routing to Secure Peer-to-Peer Supported Business Collaboration, Proc. of e. Challenges 2006 © Fischer, ATHENA Consortium 2007 K. , Müller, J. -P. , Stäber, F. und Friese, Th. : Using Peer-to-Peer Protocols to Enable Implicit Communication in a 29 BDI Agent Architecture, Programming Multi-Agent Systems, Springer, to appear 2007
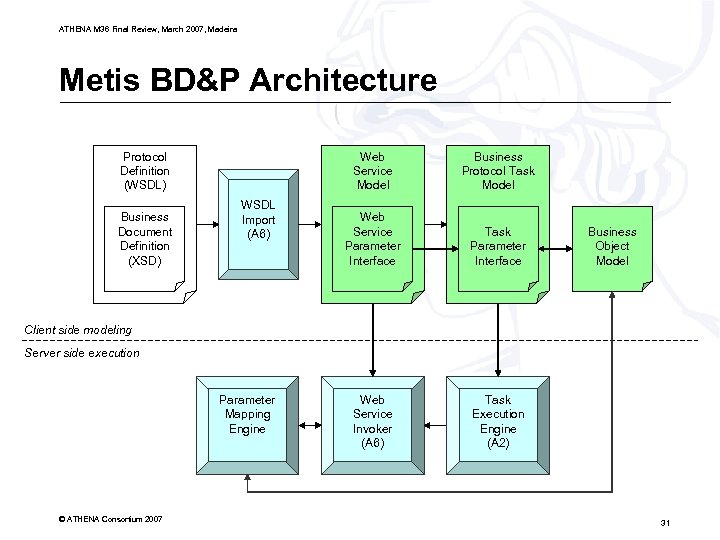 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Metis BD&P Architecture Protocol Definition (WSDL) Business Document Definition (XSD) Web Service Model WSDL Import (A 6) Business Protocol Task Model Web Service Parameter Interface Task Parameter Interface Web Service Invoker (A 6) Task Execution Engine (A 2) Business Object Model Client side modeling Server side execution Parameter Mapping Engine © ATHENA Consortium 2007 31
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Metis BD&P Architecture Protocol Definition (WSDL) Business Document Definition (XSD) Web Service Model WSDL Import (A 6) Business Protocol Task Model Web Service Parameter Interface Task Parameter Interface Web Service Invoker (A 6) Task Execution Engine (A 2) Business Object Model Client side modeling Server side execution Parameter Mapping Engine © ATHENA Consortium 2007 31
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Major Achievements ● ● Analysis of industry requirements and standards Modelling of business documents on the technical level: ● ● Automated Mapping Support: ● ● Automated assistance to mapping business documents Repository: ● ● Supporting re-use and variant handling Support for business level stakeholders Implementation of DFDL standard for non-XML data P 2 P-based repository for flexibly storing and retrieving business documents and protocols Protocol support: ● ● Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to agent metamodel Transformation from business level CBPs to protocols Application of A 7 results to industry scenario ● ATHENA Consortium 2007 © 33
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Major Achievements ● ● Analysis of industry requirements and standards Modelling of business documents on the technical level: ● ● Automated Mapping Support: ● ● Automated assistance to mapping business documents Repository: ● ● Supporting re-use and variant handling Support for business level stakeholders Implementation of DFDL standard for non-XML data P 2 P-based repository for flexibly storing and retrieving business documents and protocols Protocol support: ● ● Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to agent metamodel Transformation from business level CBPs to protocols Application of A 7 results to industry scenario ● ATHENA Consortium 2007 © 33
 Model-driven generation of executable protocols ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira ● Problem: ● ● ● Extend PIM 4 SOA to model service interaction patterns ● ● PIM 4 SOA ‚as is‘ concentrates on simple request/response patterns E. g. patterns that deal with multiple partners cannot be modelled ‚Conservative‘ extension Existing transformations should still work Enrich PIM 4 SOA with agent-related concepts Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to Agent Metamodel © ATHENA Consortium 2007 34
Model-driven generation of executable protocols ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira ● Problem: ● ● ● Extend PIM 4 SOA to model service interaction patterns ● ● PIM 4 SOA ‚as is‘ concentrates on simple request/response patterns E. g. patterns that deal with multiple partners cannot be modelled ‚Conservative‘ extension Existing transformations should still work Enrich PIM 4 SOA with agent-related concepts Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to Agent Metamodel © ATHENA Consortium 2007 34
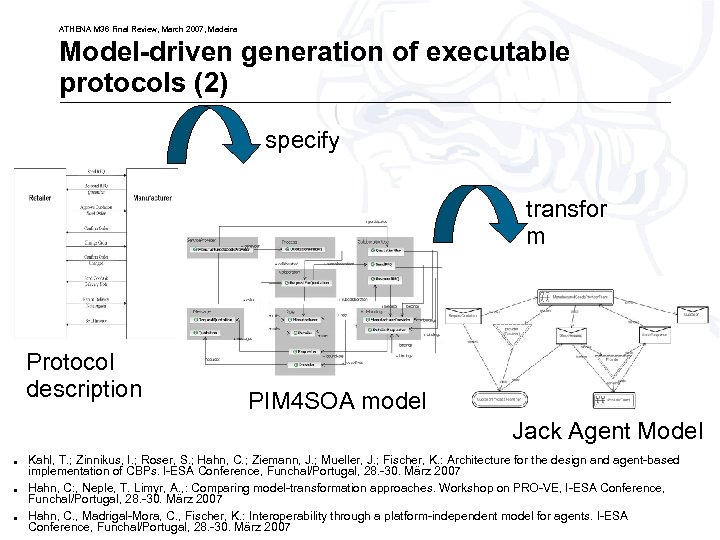 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Model-driven generation of executable protocols (2) specify transfor m Protocol description PIM 4 SOA model Jack Agent Model ● ● ● Kahl, T. ; Zinnikus, I. ; Roser, S. ; Hahn, C. ; Ziemann, J. ; Mueller, J. ; Fischer, K. : Architecture for the design and agent-based implementation of CBPs. I-ESA Conference, Funchal/Portugal, 28. -30. März 2007 Hahn, C: , Neple, T. Limyr, A. , : Comparing model-transformation approaches. Workshop on PRO-VE, I-ESA Conference, Funchal/Portugal, 28. -30. März 2007 Hahn, ©C. , Madrigal-Mora, C. , Fischer, K. : Interoperability through a platform-independent model for agents. I-ESA ATHENA Consortium 2007 35 Conference, Funchal/Portugal, 28. -30. März 2007
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Model-driven generation of executable protocols (2) specify transfor m Protocol description PIM 4 SOA model Jack Agent Model ● ● ● Kahl, T. ; Zinnikus, I. ; Roser, S. ; Hahn, C. ; Ziemann, J. ; Mueller, J. ; Fischer, K. : Architecture for the design and agent-based implementation of CBPs. I-ESA Conference, Funchal/Portugal, 28. -30. März 2007 Hahn, C: , Neple, T. Limyr, A. , : Comparing model-transformation approaches. Workshop on PRO-VE, I-ESA Conference, Funchal/Portugal, 28. -30. März 2007 Hahn, ©C. , Madrigal-Mora, C. , Fischer, K. : Interoperability through a platform-independent model for agents. I-ESA ATHENA Consortium 2007 35 Conference, Funchal/Portugal, 28. -30. März 2007
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Protocol Extensions ● ● Enhancements for transformations from business level CBP models to executable process models Steps for Transforming Event-driven Process Chain (EPC) to WS-BPEL model: 1) Complex semi-formal private processes are available 2) Business analyst describes interactions activities with EPC View Processes ● No technical knowledge is needed, EPC is well known 3) System Designer enriches EPC with technical details ● ● ● Names of involved Web Services, ports, types of XML messages Structure of the EPC stays the same! Formalized model to derive technical level models 4) Use transformations from A 2 and A 6 to convert technical EPC to PIM 4 SOA and then to BPEL ●© Kahl, Consortium 2007 ATHENAT. , Ziemann, J. , Greiner, U. , Lippe, S. : Enterprise Model Driven Creation of Business Protocols. Proc. of e. Challenges 2006 36
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Protocol Extensions ● ● Enhancements for transformations from business level CBP models to executable process models Steps for Transforming Event-driven Process Chain (EPC) to WS-BPEL model: 1) Complex semi-formal private processes are available 2) Business analyst describes interactions activities with EPC View Processes ● No technical knowledge is needed, EPC is well known 3) System Designer enriches EPC with technical details ● ● ● Names of involved Web Services, ports, types of XML messages Structure of the EPC stays the same! Formalized model to derive technical level models 4) Use transformations from A 2 and A 6 to convert technical EPC to PIM 4 SOA and then to BPEL ●© Kahl, Consortium 2007 ATHENAT. , Ziemann, J. , Greiner, U. , Lippe, S. : Enterprise Model Driven Creation of Business Protocols. Proc. of e. Challenges 2006 36
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Major Achievements ● ● Analysis of industry requirements and standards Modelling of business documents on the technical level: ● ● Automated Mapping Support: ● ● Automated assistance to mapping business documents Repository: ● ● Supporting re-use and variant handling Support for business level stakeholders Implementation of DFDL standard for non-XML data P 2 P-based repository for flexibly storing and retrieving business documents and protocols Protocol support: ● ● Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to agent metamodel Transformation from business level CBPs to protocols Application of A 7 results to industry scenario ● ATHENA Consortium 2007 © 38
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Major Achievements ● ● Analysis of industry requirements and standards Modelling of business documents on the technical level: ● ● Automated Mapping Support: ● ● Automated assistance to mapping business documents Repository: ● ● Supporting re-use and variant handling Support for business level stakeholders Implementation of DFDL standard for non-XML data P 2 P-based repository for flexibly storing and retrieving business documents and protocols Protocol support: ● ● Transformation from PIM 4 SOA to agent metamodel Transformation from business level CBPs to protocols Application of A 7 results to industry scenario ● ATHENA Consortium 2007 © 38
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Application of A 7 Results ● A 7 results have been applied in the following scenarios: ● ● ● e. Procurement scenario from the furniture pilot car configuration scenario from the outbound logistics pilot strategic sourcing scenario from the automotive pilot process for ordering a new vehicle from the manufacturer based on the STAR standard Main findings: ● ● results are well suited to handle industry scenarios and standards results made a significant contribution to the outbound logistics pilot A 7 complements A 2 results on modeling and enactment of CBPs provide means to also involve business users in the modelling effort thus abstracting from the purely technical representation provided e. g. by XML messages protocol extensions target different execution platforms thus considering different infrastructures already existing ● © ATHENA Consortium 2007 39
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Application of A 7 Results ● A 7 results have been applied in the following scenarios: ● ● ● e. Procurement scenario from the furniture pilot car configuration scenario from the outbound logistics pilot strategic sourcing scenario from the automotive pilot process for ordering a new vehicle from the manufacturer based on the STAR standard Main findings: ● ● results are well suited to handle industry scenarios and standards results made a significant contribution to the outbound logistics pilot A 7 complements A 2 results on modeling and enactment of CBPs provide means to also involve business users in the modelling effort thus abstracting from the purely technical representation provided e. g. by XML messages protocol extensions target different execution platforms thus considering different infrastructures already existing ● © ATHENA Consortium 2007 39
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Summary of Achievements ● ● Many standards and specifications of business documents and protocols are available Users need guidance and support for implementation through modeling guidelines and tools: ● ● ● Different stakeholders with different information needs have to be supported Transformation mechanisms are needed to cover different pre -existing system landscapes To reduce modeling effort users need means to re-use document models and handle variants Just dealing with the process level is insufficient: Business protocols have to be considered as a representation for more detailed interactions Prototype: Graphical modeling support for business users is combined with semi-automatic transformations to create executable representations ● processes, protocols and documents cover the most important aspects of modeling B 2 B collaborations © ATHENA Consortium 2007 40
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Summary of Achievements ● ● Many standards and specifications of business documents and protocols are available Users need guidance and support for implementation through modeling guidelines and tools: ● ● ● Different stakeholders with different information needs have to be supported Transformation mechanisms are needed to cover different pre -existing system landscapes To reduce modeling effort users need means to re-use document models and handle variants Just dealing with the process level is insufficient: Business protocols have to be considered as a representation for more detailed interactions Prototype: Graphical modeling support for business users is combined with semi-automatic transformations to create executable representations ● processes, protocols and documents cover the most important aspects of modeling B 2 B collaborations © ATHENA Consortium 2007 40
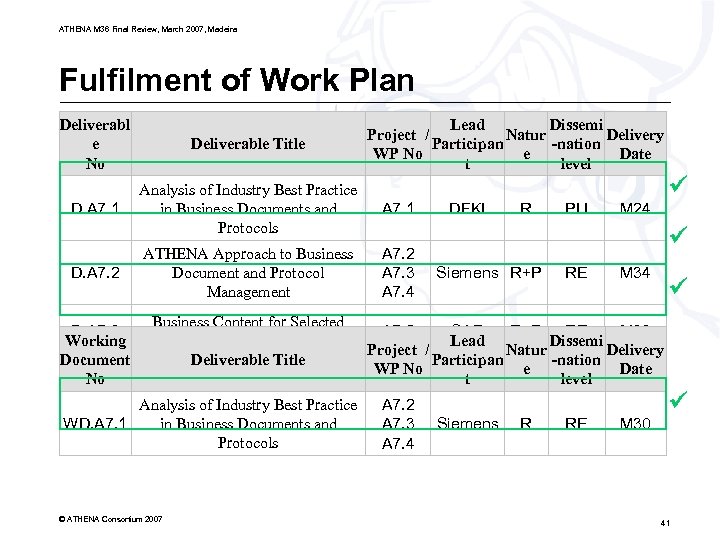 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Fulfilment of Work Plan Deliverabl e No Deliverable Title D. A 7. 1 Analysis of Industry Best Practice in Business Documents and Protocols A 7. 1 D. A 7. 2 ATHENA Approach to Business Document and Protocol Management A 7. 2 A 7. 3 A 7. 4 D. A 7. 3 Working Document No Business Content for Selected Industry Best Practice Deliverable Title Analysis of Industry Best Practice in Business Documents and WD. A 7. 1 Protocols © ATHENA Consortium 2007 Lead Dissemi Project / Natur Delivery Participan -nation WP No e Date t level DFKI R PU M 24 Siemens R+P RE M 34 A 7. 5 SAP R+P RE M 36 Lead Dissemi Project / Natur Delivery Participan -nation WP No e Date t level A 7. 2 A 7. 3 A 7. 4 Siemens R RE M 30 41
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Fulfilment of Work Plan Deliverabl e No Deliverable Title D. A 7. 1 Analysis of Industry Best Practice in Business Documents and Protocols A 7. 1 D. A 7. 2 ATHENA Approach to Business Document and Protocol Management A 7. 2 A 7. 3 A 7. 4 D. A 7. 3 Working Document No Business Content for Selected Industry Best Practice Deliverable Title Analysis of Industry Best Practice in Business Documents and WD. A 7. 1 Protocols © ATHENA Consortium 2007 Lead Dissemi Project / Natur Delivery Participan -nation WP No e Date t level DFKI R PU M 24 Siemens R+P RE M 34 A 7. 5 SAP R+P RE M 36 Lead Dissemi Project / Natur Delivery Participan -nation WP No e Date t level A 7. 2 A 7. 3 A 7. 4 Siemens R RE M 30 41
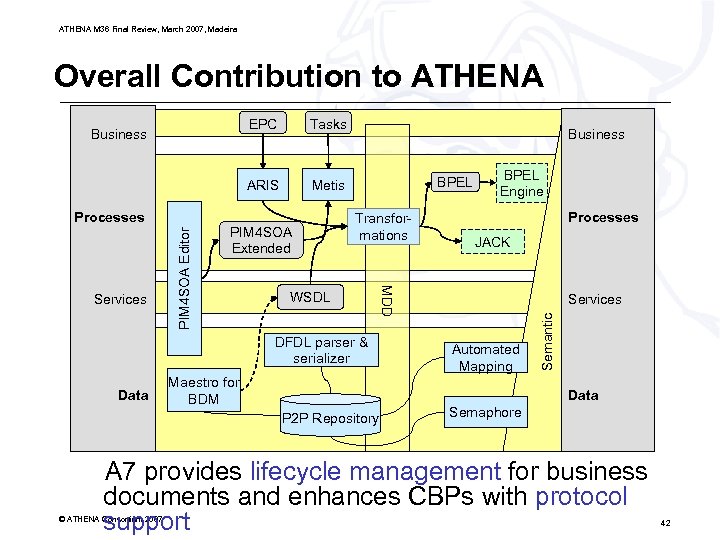 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Overall Contribution to ATHENA ARIS Metis PIM 4 SOA Extended Business BPEL Transformations WSDL DFDL parser & serializer Data Maestro for BDM BPEL Engine Processes JACK MDD Services PIM 4 SOA Editor Processes Tasks Services Automated Mapping Semantic EPC Business Data P 2 P Repository Semaphore A 7 provides lifecycle management for business documents and enhances CBPs with protocol support © ATHENA Consortium 2007 42
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Overall Contribution to ATHENA ARIS Metis PIM 4 SOA Extended Business BPEL Transformations WSDL DFDL parser & serializer Data Maestro for BDM BPEL Engine Processes JACK MDD Services PIM 4 SOA Editor Processes Tasks Services Automated Mapping Semantic EPC Business Data P 2 P Repository Semaphore A 7 provides lifecycle management for business documents and enhances CBPs with protocol support © ATHENA Consortium 2007 42
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Impact Made ● ● Extension and completion of ATHENA results on CBPs Contribution to outbound logistics pilot DFDL - Implementation and status: ● Parsers and Serializers can make use of physical annotations to read and write data in the described format ● Prototype making use of the current version of specification available (within Virtual XML Framework from IBM, http: //www. ibm. com/alphaworks) Metis A 7 implementation applied in two pilots in another EU project, and for demonstrations on ISO 15926 reference model import for the oil&gas © ATHENA Consortium 2007 43
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Impact Made ● ● Extension and completion of ATHENA results on CBPs Contribution to outbound logistics pilot DFDL - Implementation and status: ● Parsers and Serializers can make use of physical annotations to read and write data in the described format ● Prototype making use of the current version of specification available (within Virtual XML Framework from IBM, http: //www. ibm. com/alphaworks) Metis A 7 implementation applied in two pilots in another EU project, and for demonstrations on ISO 15926 reference model import for the oil&gas © ATHENA Consortium 2007 43
 ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Q&A © ATHENA Consortium 2007 44
ATHENA M 36 Final Review, March 2007, Madeira Q&A © ATHENA Consortium 2007 44


