 at h W it? is s it ? y i ing h t W es ter in Wh at Th are imp e lica tio ns? Quantum Hamiltonian Complexity Dorit Aharonov School of Computer Science and Engineering The Hebrew University, Grou Jerusalem, nd s ent tate lem Israel s ng 1 nta E
at h W it? is s it ? y i ing h t W es ter in Wh at Th are imp e lica tio ns? Quantum Hamiltonian Complexity Dorit Aharonov School of Computer Science and Engineering The Hebrew University, Grou Jerusalem, nd s ent tate lem Israel s ng 1 nta E
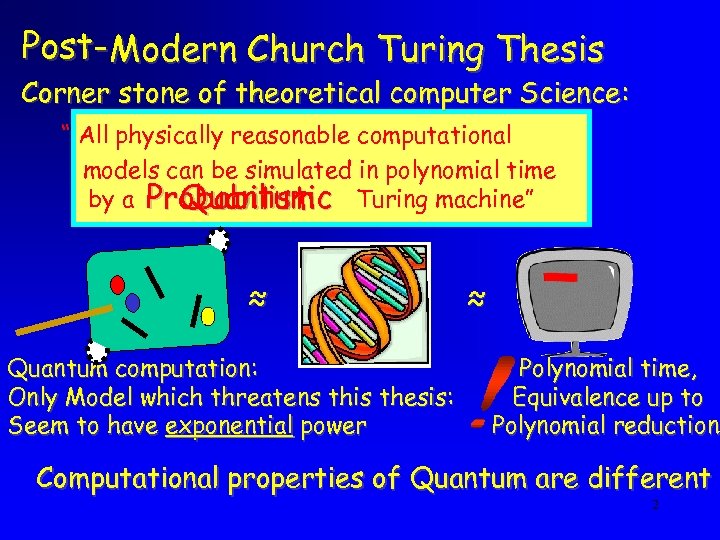 Post-Modern Church Turing Thesis Corner stone of theoretical computer Science: “ All physically reasonable computational models can be simulated in polynomial time by a Probabilistic Turing machine” Quantum ≈ Quantum computation: Only Model which threatens this thesis: Seem to have exponential power ≈ Polynomial time, Equivalence up to Polynomial reductions reduction Computational properties of Quantum are different 2
Post-Modern Church Turing Thesis Corner stone of theoretical computer Science: “ All physically reasonable computational models can be simulated in polynomial time by a Probabilistic Turing machine” Quantum ≈ Quantum computation: Only Model which threatens this thesis: Seem to have exponential power ≈ Polynomial time, Equivalence up to Polynomial reductions reduction Computational properties of Quantum are different 2
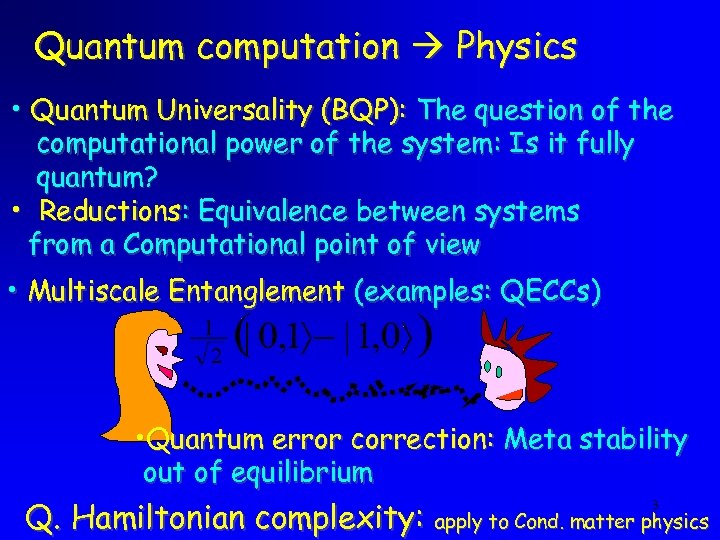 Quantum computation Physics • Quantum Universality (BQP): The question of the computational power of the system: Is it fully quantum? • Reductions: Equivalence between systems from a Computational point of view • Multiscale Entanglement (examples: QECCs) • Quantum error correction: Meta stability out of equilibrium Q. Hamiltonian complexity: apply to Cond. matter physics 3
Quantum computation Physics • Quantum Universality (BQP): The question of the computational power of the system: Is it fully quantum? • Reductions: Equivalence between systems from a Computational point of view • Multiscale Entanglement (examples: QECCs) • Quantum error correction: Meta stability out of equilibrium Q. Hamiltonian complexity: apply to Cond. matter physics 3
 Condensed Matter Physics Local Hamiltonian, (e. g. AKLT) Ground states: What are their properties? Expectation values of various observables? How do two-point correlations behave? And what about the spectral gap? 4
Condensed Matter Physics Local Hamiltonian, (e. g. AKLT) Ground states: What are their properties? Expectation values of various observables? How do two-point correlations behave? And what about the spectral gap? 4
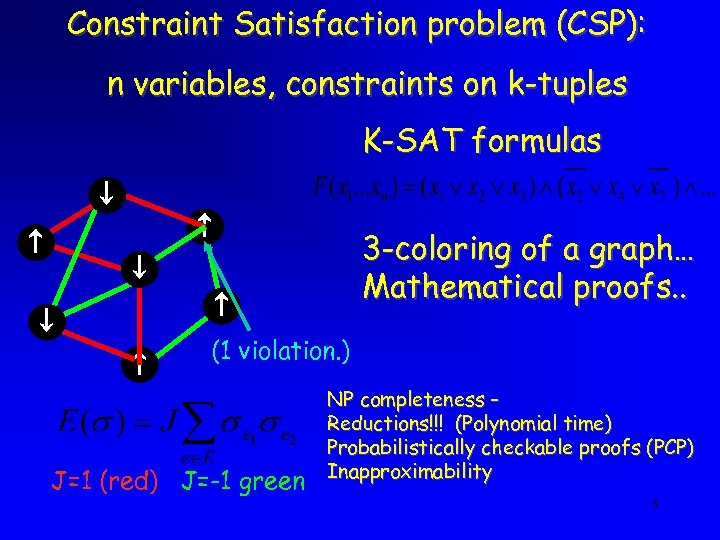 Constraint Satisfaction problem (CSP): n variables, constraints on k-tuples K-SAT formulas 3 -coloring of a graph… Mathematical proofs. . (1 violation. ) J=1 (red) J=-1 green NP completeness – Reductions!!! (Polynomial time) Probabilistically checkable proofs (PCP) Inapproximability 5
Constraint Satisfaction problem (CSP): n variables, constraints on k-tuples K-SAT formulas 3 -coloring of a graph… Mathematical proofs. . (1 violation. ) J=1 (red) J=-1 green NP completeness – Reductions!!! (Polynomial time) Probabilistically checkable proofs (PCP) Inapproximability 5
 Quantum Hamiltonian Complexity Deep connection between these two major Problems: Local Hamiltonians can be viewed as quantum CSPs Similar questions plus more complications: enter entanglement Power of various Hamiltonian classes… Entanglement properties of ground states… Provides a whole new lance through which to look at Quantum many body physics: The computational point of 6 view.
Quantum Hamiltonian Complexity Deep connection between these two major Problems: Local Hamiltonians can be viewed as quantum CSPs Similar questions plus more complications: enter entanglement Power of various Hamiltonian classes… Entanglement properties of ground states… Provides a whole new lance through which to look at Quantum many body physics: The computational point of 6 view.
 CSP & Hamiltonian Constraints Energy Penalties Solution Ground state CSP Is ground energy 0 or at least 1? CSP estimate the ground energy of H. [Cook-Levin[‘ 69 ish]: CSP is NP-complete Estimating the ground energy is at least as hard as NP 7
CSP & Hamiltonian Constraints Energy Penalties Solution Ground state CSP Is ground energy 0 or at least 1? CSP estimate the ground energy of H. [Cook-Levin[‘ 69 ish]: CSP is NP-complete Estimating the ground energy is at least as hard as NP 7
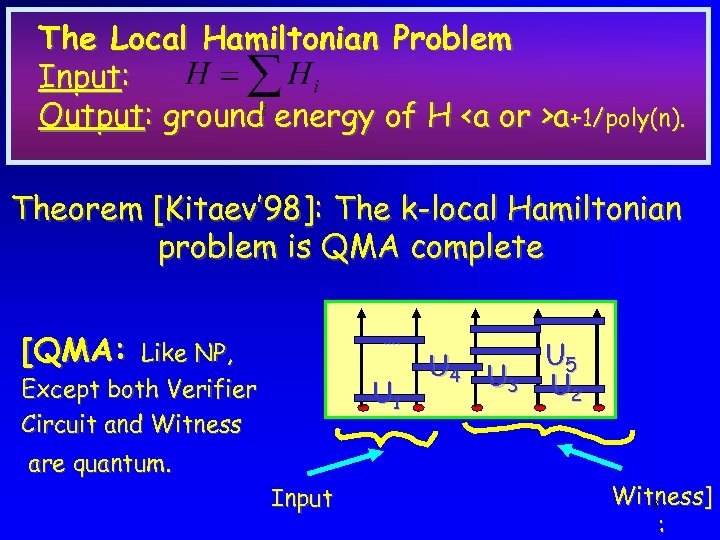 The Local Hamiltonian Problem Input: Output: ground energy of H a+1/poly(n). Theorem [Kitaev’ 98]: The k-local Hamiltonian problem is QMA complete …. [QMA: Like NP, Except both Verifier Circuit and Witness U 1 are quantum. Input U 4 U U 5 3 U 2 Witness] 8 :
The Local Hamiltonian Problem Input: Output: ground energy of H a+1/poly(n). Theorem [Kitaev’ 98]: The k-local Hamiltonian problem is QMA complete …. [QMA: Like NP, Except both Verifier Circuit and Witness U 1 are quantum. Input U 4 U U 5 3 U 2 Witness] 8 :
![The Cook-Levin Theorem: Computation is local [Cook-Levin’ 79] Time steps History of a computation The Cook-Levin Theorem: Computation is local [Cook-Levin’ 79] Time steps History of a computation](https://present5.com/presentation/c9602aa06d6fc1ae00ee59a907d756d8/image-9.jpg) The Cook-Levin Theorem: Computation is local [Cook-Levin’ 79] Time steps History of a computation can be checked locally can associate a CSP with the local dynamics The verifier is mapped to a SAT formula SAT is NP-complete 9
The Cook-Levin Theorem: Computation is local [Cook-Levin’ 79] Time steps History of a computation can be checked locally can associate a CSP with the local dynamics The verifier is mapped to a SAT formula SAT is NP-complete 9
![The Circuit-to-Hamiltonian construction [Kitaev 98, Following Feynman 82] Time steps : any line Feynman’s The Circuit-to-Hamiltonian construction [Kitaev 98, Following Feynman 82] Time steps : any line Feynman’s](https://present5.com/presentation/c9602aa06d6fc1ae00ee59a907d756d8/image-10.jpg) The Circuit-to-Hamiltonian construction [Kitaev 98, Following Feynman 82] Time steps : any line Feynman’s particle on a rom al on f a loc ucti to Red cuit L 0 k-1 kk+1 ty ir ian ali c Q ilton vers Ham Uni Hamiltonian whose ground m ntu state is the History. Qua 10
The Circuit-to-Hamiltonian construction [Kitaev 98, Following Feynman 82] Time steps : any line Feynman’s particle on a rom al on f a loc ucti to Red cuit L 0 k-1 kk+1 ty ir ian ali c Q ilton vers Ham Uni Hamiltonian whose ground m ntu state is the History. Qua 10
![Adiabatic Computation: [Farhi. Godstone. Gutman. Sipser’ 00] H(T) H(0) of H(0) Ground state ground Adiabatic Computation: [Farhi. Godstone. Gutman. Sipser’ 00] H(T) H(0) of H(0) Ground state ground](https://present5.com/presentation/c9602aa06d6fc1ae00ee59a907d756d8/image-11.jpg) Adiabatic Computation: [Farhi. Godstone. Gutman. Sipser’ 00] H(T) H(0) of H(0) Ground state ground state of H(T) Adiabatic Computation ≈ Quantum Computation [A’van. Dam. Kempe. Landau. Lloyd. Regev’ 04] …. U 1 U 4 U U 5 3 U 2 H(T) H(0) Want adiabatic computation with γ(t)>1/Lc from which to deduce answer. Instead of , use a local Hamiltonian H(T) tum uan whose ground state the History. is Q n ctio rsality Spectral gap: Redu ive ntime steps! H(t) ≈ random walk U on Markov chain techniques. 0 k-1 kk+1 11 L
Adiabatic Computation: [Farhi. Godstone. Gutman. Sipser’ 00] H(T) H(0) of H(0) Ground state ground state of H(T) Adiabatic Computation ≈ Quantum Computation [A’van. Dam. Kempe. Landau. Lloyd. Regev’ 04] …. U 1 U 4 U U 5 3 U 2 H(T) H(0) Want adiabatic computation with γ(t)>1/Lc from which to deduce answer. Instead of , use a local Hamiltonian H(T) tum uan whose ground state the History. is Q n ctio rsality Spectral gap: Redu ive ntime steps! H(t) ≈ random walk U on Markov chain techniques. 0 k-1 kk+1 11 L
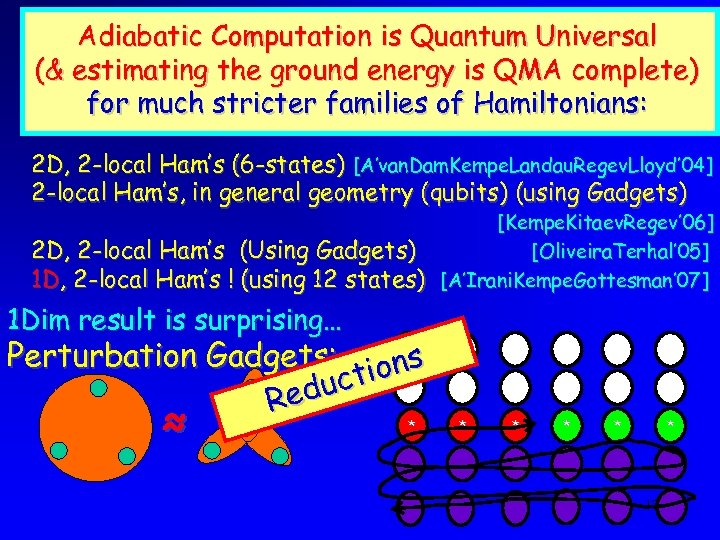 Adiabatic Computation is Quantum Universal (& estimating the ground energy is QMA complete) for much stricter families of Hamiltonians: 2 D, 2 -local Ham’s (6 -states) [A’van. Dam. Kempe. Landau. Regev. Lloyd’ 04] 2 -local Ham’s, in general geometry (qubits) (using Gadgets) 2 D, 2 -local Ham’s (Using Gadgets) 1 D, 2 -local Ham’s ! (using 12 states) [Kempe. Kitaev. Regev’ 06] [Oliveira. Terhal’ 05] [A’Irani. Kempe. Gottesman’ 07] 1 Dim result is surprising… Perturbation Gadgets: ions uct Red ≈ * * * 12
Adiabatic Computation is Quantum Universal (& estimating the ground energy is QMA complete) for much stricter families of Hamiltonians: 2 D, 2 -local Ham’s (6 -states) [A’van. Dam. Kempe. Landau. Regev. Lloyd’ 04] 2 -local Ham’s, in general geometry (qubits) (using Gadgets) 2 D, 2 -local Ham’s (Using Gadgets) 1 D, 2 -local Ham’s ! (using 12 states) [Kempe. Kitaev. Regev’ 06] [Oliveira. Terhal’ 05] [A’Irani. Kempe. Gottesman’ 07] 1 Dim result is surprising… Perturbation Gadgets: ions uct Red ≈ * * * 12
 Quantum Hamiltonian Complexity: Open: Correlations & entanglement? Easy: In P, gs is MPS Hard: BQP complete, QMA complete, NP hard, etc. Efficient simulation of 1 D gapped adiabatic [Hastings’ 09] Open: Can the ground state be found classically efficienlty? In 1 D: Limited entanglement too (area law). [Hastings’ 07]. MPS description of ground state of 1 D gapped systems Constant gap: Correlations decay exponentially for all D [Hastings’ 05]. Small correlations Little Entanglement! (data Hiding, Q expander states) 13
Quantum Hamiltonian Complexity: Open: Correlations & entanglement? Easy: In P, gs is MPS Hard: BQP complete, QMA complete, NP hard, etc. Efficient simulation of 1 D gapped adiabatic [Hastings’ 09] Open: Can the ground state be found classically efficienlty? In 1 D: Limited entanglement too (area law). [Hastings’ 07]. MPS description of ground state of 1 D gapped systems Constant gap: Correlations decay exponentially for all D [Hastings’ 05]. Small correlations Little Entanglement! (data Hiding, Q expander states) 13
 Back to the Hardness side… Some examples 1. Hardness for interesting physical systems: Approximating ground energy of Hubbard model: QMA complete Solving Schrodinger’s eq. for interacting electrons: QMA-hard [Schuch. Verstraete’ 07] 2. Ruling out various physical attempts: “Universal density functional” cannot be efficiently computable unless NP=QMA. [Schuch. Verstraete’ 07] 3. How hard is local Hamiltonians for restricted Hamiltonians? For a 1/poly(n) gapped 1 D system: QCMA hard [A’Ben-Or. Brandao. Sattath’ 08]. What if we know the ground state is an MPS? The classical analog (solving 1 D CSPs) is easy… Quantumly: NP-hard [Schuch. Cirac. Verstraete’ 08] 14
Back to the Hardness side… Some examples 1. Hardness for interesting physical systems: Approximating ground energy of Hubbard model: QMA complete Solving Schrodinger’s eq. for interacting electrons: QMA-hard [Schuch. Verstraete’ 07] 2. Ruling out various physical attempts: “Universal density functional” cannot be efficiently computable unless NP=QMA. [Schuch. Verstraete’ 07] 3. How hard is local Hamiltonians for restricted Hamiltonians? For a 1/poly(n) gapped 1 D system: QCMA hard [A’Ben-Or. Brandao. Sattath’ 08]. What if we know the ground state is an MPS? The classical analog (solving 1 D CSPs) is easy… Quantumly: NP-hard [Schuch. Cirac. Verstraete’ 08] 14
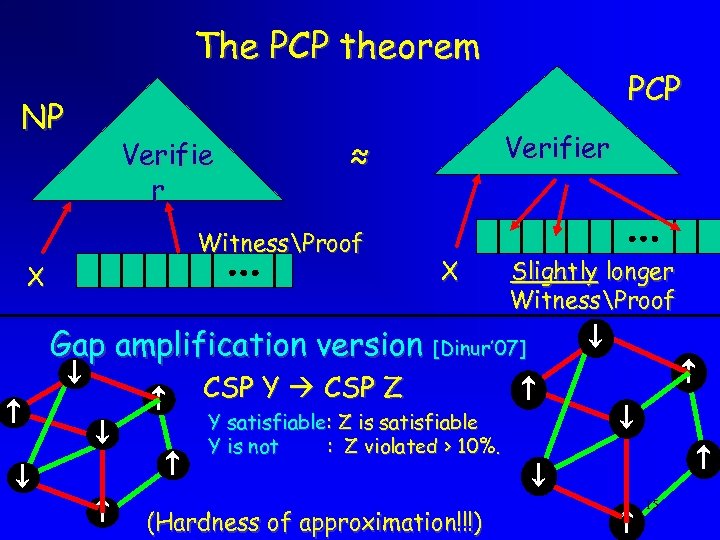 The PCP theorem NP Verifie r X Verifier ≈ WitnessProof PCP X Slightly longer WitnessProof Gap amplification version [Dinur’ 07] CSP Y CSP Z Y satisfiable: Z is satisfiable Y is not : Z violated > 10%. (Hardness of approximation!!!) 15
The PCP theorem NP Verifie r X Verifier ≈ WitnessProof PCP X Slightly longer WitnessProof Gap amplification version [Dinur’ 07] CSP Y CSP Z Y satisfiable: Z is satisfiable Y is not : Z violated > 10%. (Hardness of approximation!!!) 15
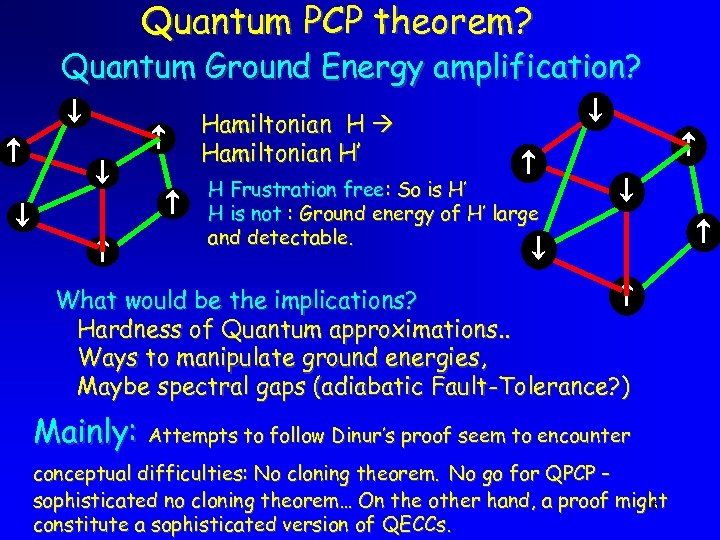 Quantum PCP theorem? Quantum Ground Energy amplification? Hamiltonian H’ H Frustration free: So is H’ H is not : Ground energy of H’ large and detectable. What would be the implications? Hardness of Quantum approximations. . Ways to manipulate ground energies, Maybe spectral gaps (adiabatic Fault-Tolerance? ) Mainly: Attempts to follow Dinur’s proof seem to encounter conceptual difficulties: No cloning theorem. No go for QPCP – sophisticated no cloning theorem… On the other hand, a proof might 16 constitute a sophisticated version of QECCs.
Quantum PCP theorem? Quantum Ground Energy amplification? Hamiltonian H’ H Frustration free: So is H’ H is not : Ground energy of H’ large and detectable. What would be the implications? Hardness of Quantum approximations. . Ways to manipulate ground energies, Maybe spectral gaps (adiabatic Fault-Tolerance? ) Mainly: Attempts to follow Dinur’s proof seem to encounter conceptual difficulties: No cloning theorem. No go for QPCP – sophisticated no cloning theorem… On the other hand, a proof might 16 constitute a sophisticated version of QECCs.
![Quantum Gap Amplification [A’Arad. Landau. Vazirani’ 09] (A proof of an important ingredient in Quantum Gap Amplification [A’Arad. Landau. Vazirani’ 09] (A proof of an important ingredient in](https://present5.com/presentation/c9602aa06d6fc1ae00ee59a907d756d8/image-17.jpg) Quantum Gap Amplification [A’Arad. Landau. Vazirani’ 09] (A proof of an important ingredient in Dinur’s proof, but without handling the no-cloning issue) Local terms Larger constraints, defined by walks on the graph Analyzing the ground energy of the new Hamiltonian H’: Requires a sophisticated reduction to a commuting case (The XY decomposition, pyramids, the detectability lemma) 17
Quantum Gap Amplification [A’Arad. Landau. Vazirani’ 09] (A proof of an important ingredient in Dinur’s proof, but without handling the no-cloning issue) Local terms Larger constraints, defined by walks on the graph Analyzing the ground energy of the new Hamiltonian H’: Requires a sophisticated reduction to a commuting case (The XY decomposition, pyramids, the detectability lemma) 17
 Open problems: Computational power of commuting Hamiltonians? Quantum PCP? Relations to adiabatic fault tolerance? or: Can we rule out quantum PCP (a sophisticated No-Cloning theorem? ) Extending other important classical results, e. g. : 1. Remove degeneracy? (Q Valiant-Vazirani) [see A’Ben. Or. Brandao. Sattath’ 09]? 2. Frustration freeness? (QMA 1 vs. QMA? )[see Aaronson’ 08] Rule out other physics programs similar to the universal density functional? Identify the complexity of other types of systems? (interacting electrons), Check the Post-Modern CT thesis for other known systems (field theory)? Much more on the computationally “easy” side: Area laws and entanglement vs. correlations in Dim>1? Finding the ground state for gapped 1 D Hamiltonians? 18
Open problems: Computational power of commuting Hamiltonians? Quantum PCP? Relations to adiabatic fault tolerance? or: Can we rule out quantum PCP (a sophisticated No-Cloning theorem? ) Extending other important classical results, e. g. : 1. Remove degeneracy? (Q Valiant-Vazirani) [see A’Ben. Or. Brandao. Sattath’ 09]? 2. Frustration freeness? (QMA 1 vs. QMA? )[see Aaronson’ 08] Rule out other physics programs similar to the universal density functional? Identify the complexity of other types of systems? (interacting electrons), Check the Post-Modern CT thesis for other known systems (field theory)? Much more on the computationally “easy” side: Area laws and entanglement vs. correlations in Dim>1? Finding the ground state for gapped 1 D Hamiltonians? 18
 Thanks! 19
Thanks! 19


