Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. EARTH’S HISTORY























- Размер: 483 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 24
Описание презентации Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. EARTH’S HISTORY по слайдам
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. EARTH’S HISTORY
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. EARTH’S HISTORY
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. What is Geology ? Geo : earth logy : science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties.
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. What is Geology ? Geo : earth logy : science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties.
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. Geologists study: the origin and evolution of our planet; the chemical and physical properties of minerals, rocks, and fluids; the structure of our mobile crust — its newly forming ocean floors and its ancient drifting continents; the history of life ; and the human adaptation to earthquakes, volcanos, landslides and floods.
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. Geologists study: the origin and evolution of our planet; the chemical and physical properties of minerals, rocks, and fluids; the structure of our mobile crust — its newly forming ocean floors and its ancient drifting continents; the history of life ; and the human adaptation to earthquakes, volcanos, landslides and floods.
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs • Geophysics is the study of the Earth by quantitative physical methods. It is an applied science and includes the Earth’s interior, crust, oceans, and atmosphere. • Geochemistry is the study of the distribution of chemicals in the Earth and atmosphere. • Geomorphology is the study of landforms and underlying structures.
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs • Geophysics is the study of the Earth by quantitative physical methods. It is an applied science and includes the Earth’s interior, crust, oceans, and atmosphere. • Geochemistry is the study of the distribution of chemicals in the Earth and atmosphere. • Geomorphology is the study of landforms and underlying structures.
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. Paleontology is the study of past life observed in the geologic record (fossils). Tectonics deals with large scale Earth structures such as tectonic plates and its deep interior. Volcanology is the study of volcanoes and volcanic processes.
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. Paleontology is the study of past life observed in the geologic record (fossils). Tectonics deals with large scale Earth structures such as tectonic plates and its deep interior. Volcanology is the study of volcanoes and volcanic processes.
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs
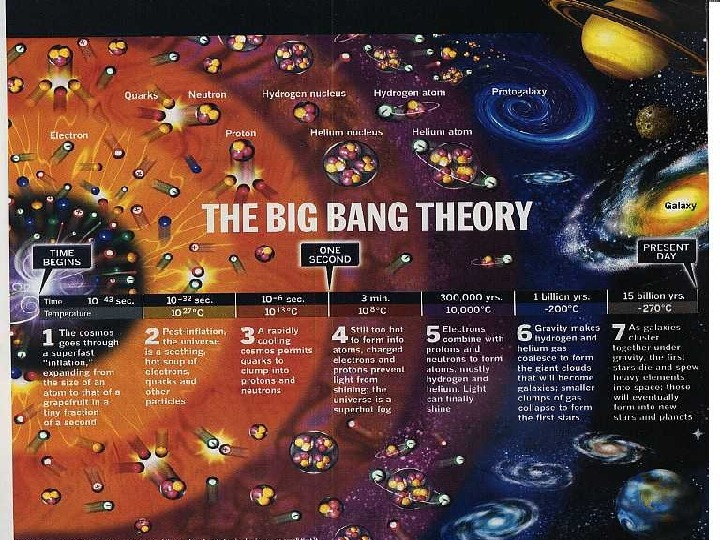
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. BIG BANG
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. BIG BANG
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balk ıs
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balk ıs
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. Earth’s History • 10 to 15 billion years for the age of the Universe (based on the recession of distant galaxies) (cosmic explosion) • 11 to 13 billion years for the age of the Milky Way Galaxy (based on the stage of evolution of globular cluster stars) and • 4. 54 billion years found for the Solar System and Earth.
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. Earth’s History • 10 to 15 billion years for the age of the Universe (based on the recession of distant galaxies) (cosmic explosion) • 11 to 13 billion years for the age of the Milky Way Galaxy (based on the stage of evolution of globular cluster stars) and • 4. 54 billion years found for the Solar System and Earth.
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. The Beginning of Earth • 4. 5 billion years ago the Earth is born from a cloud of dust and fire orbiting the sun. • There are no seas upon the barren Earth. The sun blisters down as poisonous gases swirl about. • Racked with volcanoes, bombarded by asteroids and comets, • Earth is incredibly hot with a sea of molten rock covering its surface. The early Earth is a world in slow turmoil for many, many thousands of years.
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. The Beginning of Earth • 4. 5 billion years ago the Earth is born from a cloud of dust and fire orbiting the sun. • There are no seas upon the barren Earth. The sun blisters down as poisonous gases swirl about. • Racked with volcanoes, bombarded by asteroids and comets, • Earth is incredibly hot with a sea of molten rock covering its surface. The early Earth is a world in slow turmoil for many, many thousands of years.
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balk ıs. Sea of molten rock
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balk ıs. Sea of molten rock
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. The cooling of this mass formed: • the «lithosphere» (land: the earth crust and interior mass), • «hydrosphere» (zone of water: oceans, lake), • «atmosphere» (air: gaseous envelope surrounding the hydrosphere and lithosphere).
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. The cooling of this mass formed: • the «lithosphere» (land: the earth crust and interior mass), • «hydrosphere» (zone of water: oceans, lake), • «atmosphere» (air: gaseous envelope surrounding the hydrosphere and lithosphere).
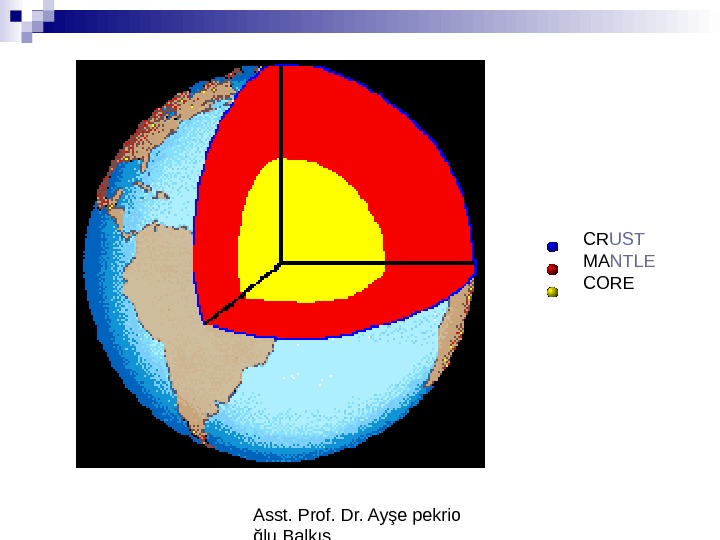
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. Layers of the Earth By analyzing the seismograms from many earthquakes, scientists have discovered that three main levels or shells exist within the Earth: • CRUST • MANTLE • COR
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. Layers of the Earth By analyzing the seismograms from many earthquakes, scientists have discovered that three main levels or shells exist within the Earth: • CRUST • MANTLE • COR
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrio ğlu Balkıs CR UST MA NTLE COR
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrio ğlu Balkıs CR UST MA NTLE COR
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrio ğlu Balkıs
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrio ğlu Balkıs
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. The Core is predominantly composed of iron and nickel. The matter with the highest density (mostly iron) sinks to form Earth’s solid inner core. Even after 4. 5 billion years of cooling, the Earth’s core remains very hot.
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. The Core is predominantly composed of iron and nickel. The matter with the highest density (mostly iron) sinks to form Earth’s solid inner core. Even after 4. 5 billion years of cooling, the Earth’s core remains very hot.
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. The Earth’s core is divided into two layers : • a solid inner core, and • a liquid outer core.
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. The Earth’s core is divided into two layers : • a solid inner core, and • a liquid outer core.
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. The Core • The Inner Core is solid nickle-iron alloy. • The Outer Core is a molten nickle-iron alloy.
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. The Core • The Inner Core is solid nickle-iron alloy. • The Outer Core is a molten nickle-iron alloy.
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. The mantle • Surrounding the inner and outer core is the mantle • The Mantle is approximately 2885 kilometers thick and is the middle layer of the Earth. The Mantle is made up of minerals rich in the elements: • iron, magnesium, • silica, and • oxygen. • The mantle is relatively flexible so it flows instead of fracturing. The Mantle makes up approximately ~85% of the Earth’s volume.
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. The mantle • Surrounding the inner and outer core is the mantle • The Mantle is approximately 2885 kilometers thick and is the middle layer of the Earth. The Mantle is made up of minerals rich in the elements: • iron, magnesium, • silica, and • oxygen. • The mantle is relatively flexible so it flows instead of fracturing. The Mantle makes up approximately ~85% of the Earth’s volume.
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. Earth’s crust The Earth’s outer layer, the Crust is 4 to 60 kilometers thick. The crust is: • relatively light, brittle and rocky material • rich in the elements oxygen and silica with lesser amounts of aluminum, iron, calcium, potassium, sodium, and magnesium.
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. Earth’s crust The Earth’s outer layer, the Crust is 4 to 60 kilometers thick. The crust is: • relatively light, brittle and rocky material • rich in the elements oxygen and silica with lesser amounts of aluminum, iron, calcium, potassium, sodium, and magnesium.
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrio ğlu Balkıs
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrio ğlu Balkıs
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. Most Common Chemical Elements in the Earth Element Weight Percent • Oxygen O, 46. 6 • Silicon Si, 27. 7 • Aluminum Al, 8. 1 • Iron Fe, 5. 0 • Calcium Ca, 3. 6 • Sodium Na, 2. 8 • Potassium K, 2. 6 • Magnesium Mg, 2. 1 • Others 1.
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs. Most Common Chemical Elements in the Earth Element Weight Percent • Oxygen O, 46. 6 • Silicon Si, 27. 7 • Aluminum Al, 8. 1 • Iron Fe, 5. 0 • Calcium Ca, 3. 6 • Sodium Na, 2. 8 • Potassium K, 2. 6 • Magnesium Mg, 2. 1 • Others 1.
 Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs • Most (74. 3%) of the minerals in the Earth’s crust contain Oxygen (O) and Silicon (Si). • This is why the Silicate mineral family (minerals having the ion Si. O 4 ) compose 90% of all rock forming minerals.
Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe pekrioğlu Balkıs • Most (74. 3%) of the minerals in the Earth’s crust contain Oxygen (O) and Silicon (Si). • This is why the Silicate mineral family (minerals having the ion Si. O 4 ) compose 90% of all rock forming minerals.

