4663384f18ce4d51f9d0058dc72120dd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Association Studies, Haplotype Blocks and Tagging SNPs Prof. Sorin Istrail
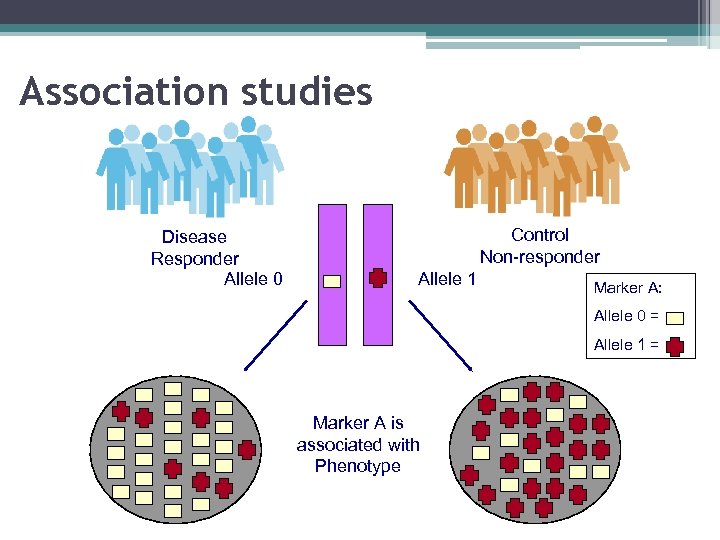
Association studies Disease Responder Allele 0 Control Non-responder Allele 1 Marker A: Allele 0 = Allele 1 = Marker A is associated with Phenotype
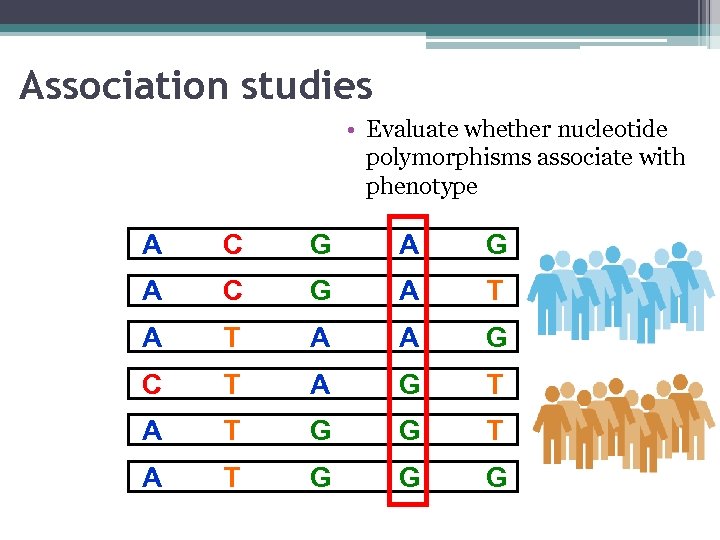
Association studies • Evaluate whether nucleotide polymorphisms associate with phenotype A C G A T A A G C T A G T A T G G G
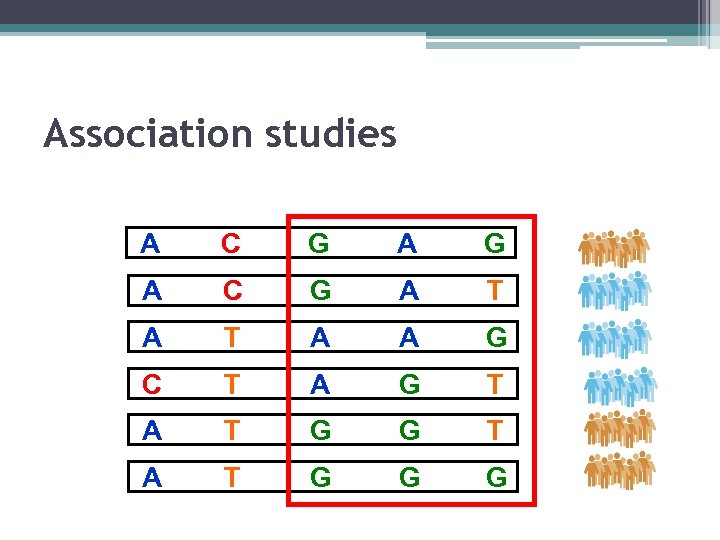
Association studies A C G A T A A G C T A G T A T G G G
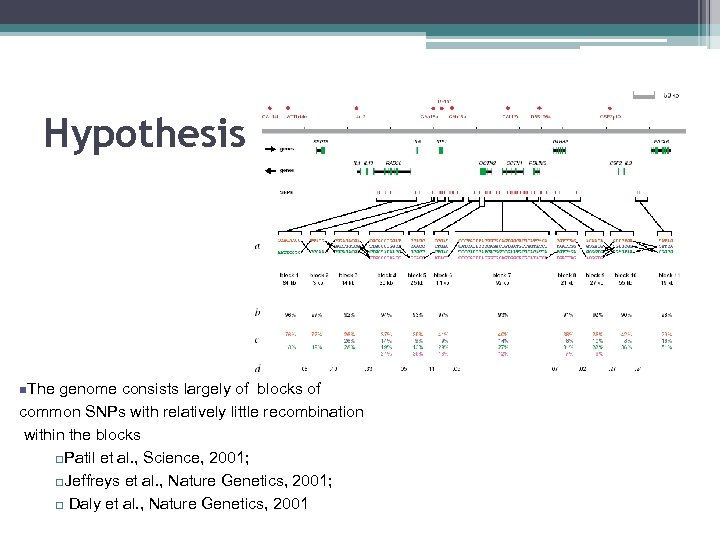
Hypothesis – Haplotype Blocks? n. The genome consists largely of blocks of common SNPs with relatively little recombination within the blocks q. Patil et al. , Science, 2001; q. Jeffreys et al. , Nature Genetics, 2001; q Daly et al. , Nature Genetics, 2001
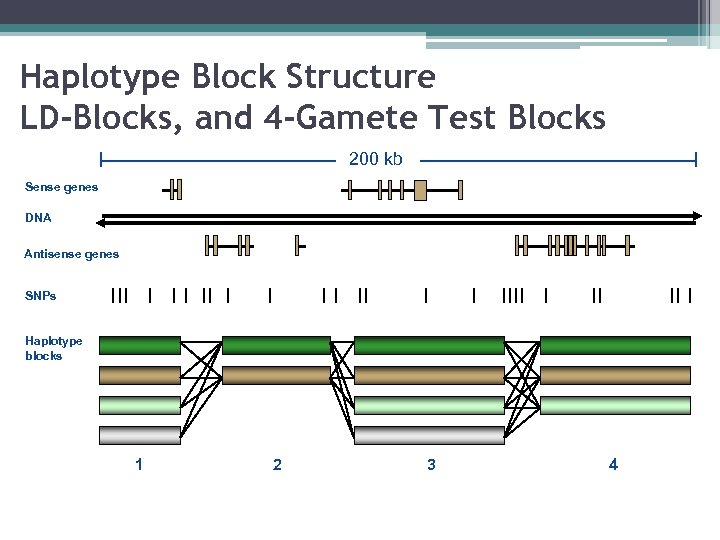
Haplotype Block Structure LD-Blocks, and 4 -Gamete Test Blocks 200 kb Sense genes DNA Antisense genes SNPs Haplotype blocks 1 2 3 4

One definition of block • Based on the Four Gamete test. • Intuition: when between two SNPs there all four gametes, there is a recombination point somewhere inbetween the two sites
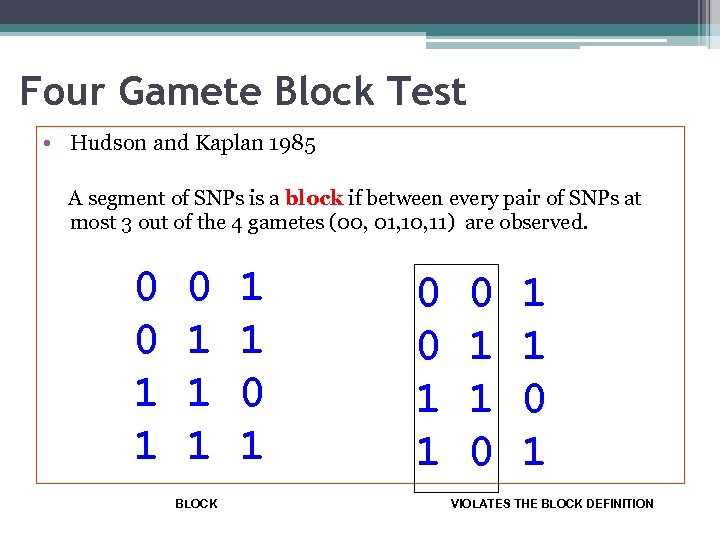
Four Gamete Block Test • Hudson and Kaplan 1985 A segment of SNPs is a block if between every pair of SNPs at most 3 out of the 4 gametes (00, 01, 10, 11) are observed. 0 0 1 1 1 BLOCK 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 VIOLATES THE BLOCK DEFINITION
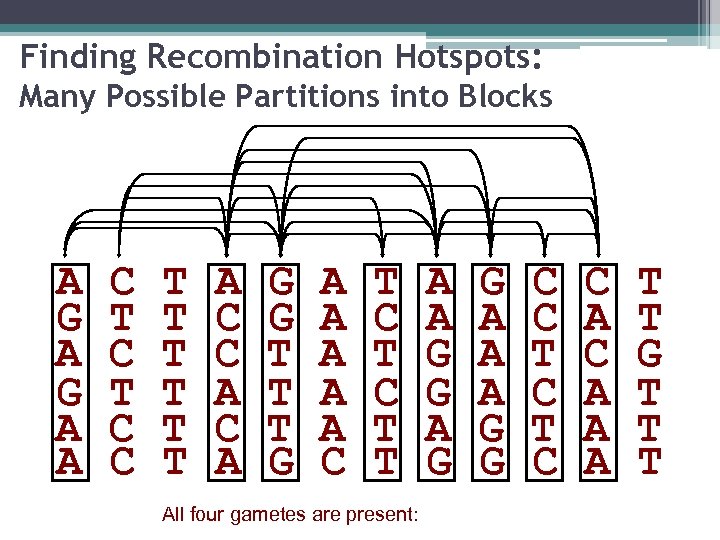
Finding Recombination Hotspots: Many Possible Partitions into Blocks A G A A C T C C T T T A C C A G G T T T G A A A C T C T T All four gametes are present: A A G G A A A G G C C T C C A A A T T G T T T

The final result is a minimum-size set of sites crossing all constraints. A C T A G A T A G C C T GFind the left-most right. A A C of T T T C G A C endpoint A AEliminate any constraints A T C G C T A Tmark crossing G the site any constraint and Repeat until all constraints A C A T G T T A a. T A site. G are gone. that C before it recombination site. A C T A T A G T A C T A G C T G G C A T
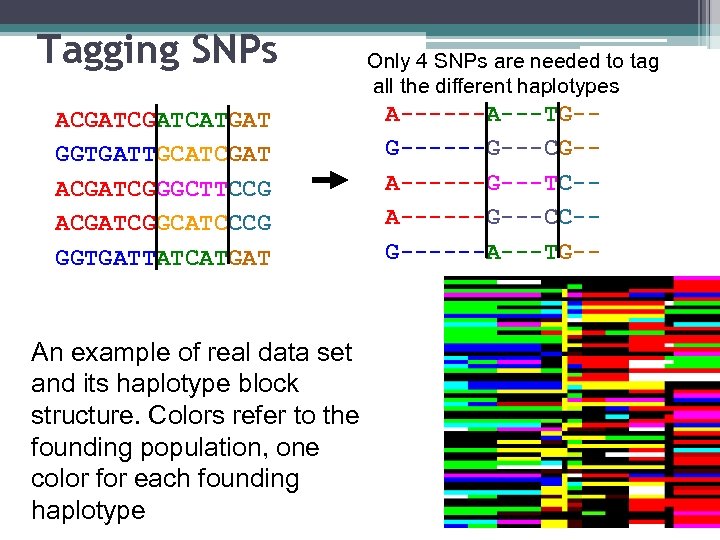
Tagging SNPs ACGATCATGAT GGTGATTGCATCGAT ACGATCGGGCTTCCG ACGATCGGCATCCCG GGTGATTATCATGAT An example of real data set and its haplotype block structure. Colors refer to the founding population, one color for each founding haplotype Only 4 SNPs are needed to tag all the different haplotypes A------A---TG-G------G---CG-A------G---TC-A------G---CC-G------A---TG--

Informativeness A measure for the “information” a SNP contains about another SNP. Useful for designing SNPs Arrays and Tagging SNPs selection. s h h 1 0 0 1 1 0 2 0 0 1
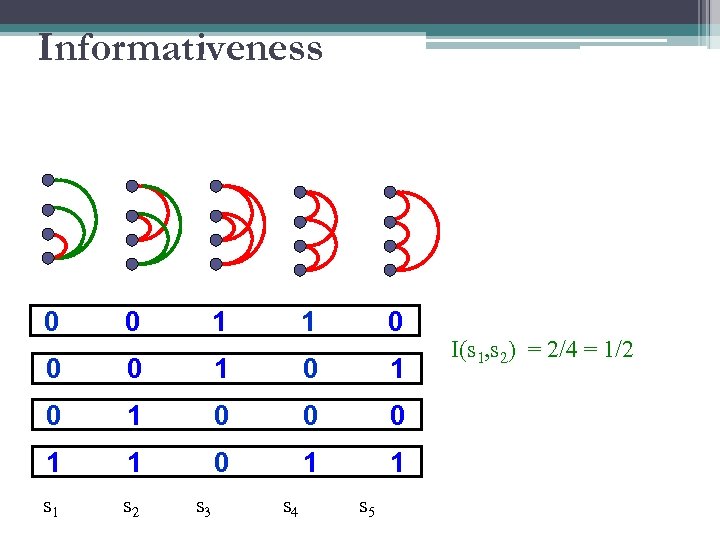
Informativeness 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 s 1 s 2 s 3 s 4 s 5 I(s 1, s 2) = 2/4 = 1/2
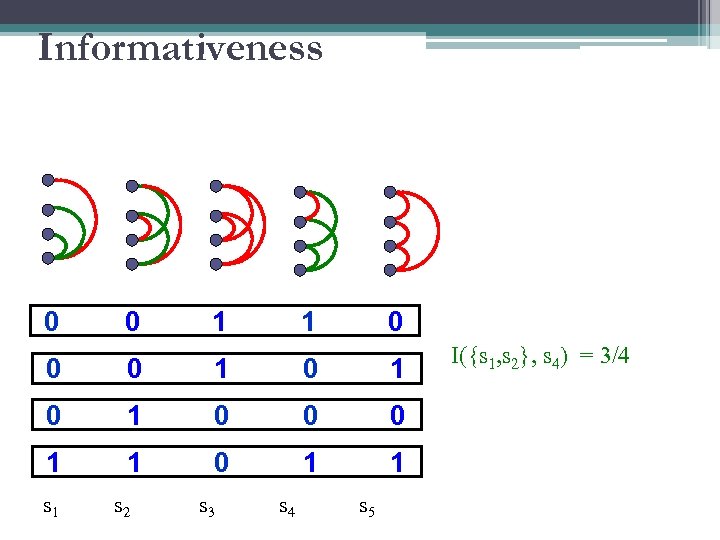
Informativeness 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 s 1 s 2 s 3 s 4 s 5 I({s 1, s 2}, s 4) = 3/4
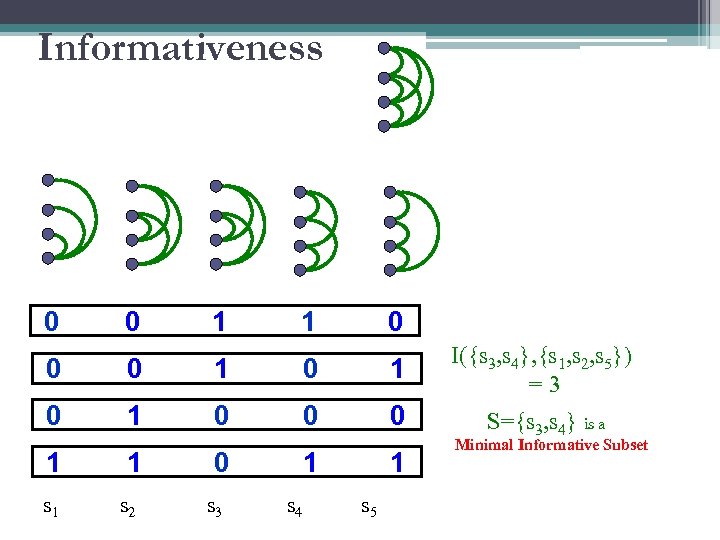
Informativeness 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 I({s 3, s 4}, {s 1, s 2, s 5}) =3 0 1 0 0 0 S={s 3, s 4} is a 1 s 1 1 s 2 0 s 3 1 s 4 1 s 5 Minimal Informative Subset
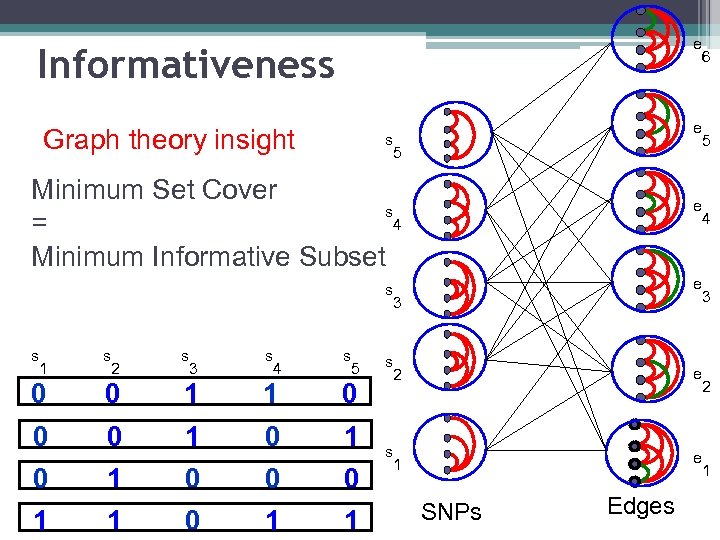
e Informativeness Graph theory insight e s 5 Minimum Set Cover s 4 = Minimum Informative Subset e e s 3 s 1 s 2 s 3 s 4 s 5 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 s 2 e s 1 e SNPs Edges 6 5 4 3 2 1
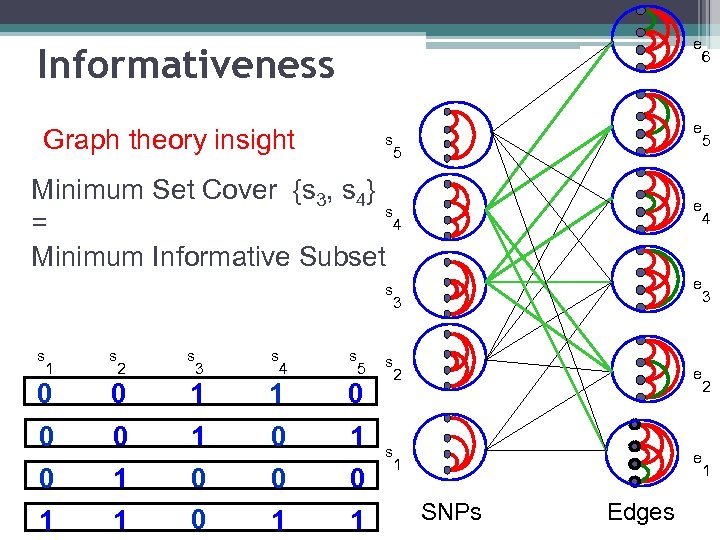
e Informativeness Graph theory insight e s 5 Minimum Set Cover {s 3, s 4} s 4 = Minimum Informative Subset e e s 3 s 1 s 2 s 3 s 4 s 5 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 s 2 e s 1 e SNPs Edges 6 5 4 3 2 1
4663384f18ce4d51f9d0058dc72120dd.ppt