 Asset Management Lecture Three
Asset Management Lecture Three
 Outline for today l Index model l Single-factor index model l Alpha and security analysis
Outline for today l Index model l Single-factor index model l Alpha and security analysis
 Drawbacks of Markowitz l The model requires a huge number of estimates l E. g. 50 stocks l 50 estimates of E(r) l 50 estimates of var(r) l 1225 estimates of cov(ri, rj) l The model does not provide guideline to the forecasting of E(r)-rf
Drawbacks of Markowitz l The model requires a huge number of estimates l E. g. 50 stocks l 50 estimates of E(r) l 50 estimates of var(r) l 1225 estimates of cov(ri, rj) l The model does not provide guideline to the forecasting of E(r)-rf
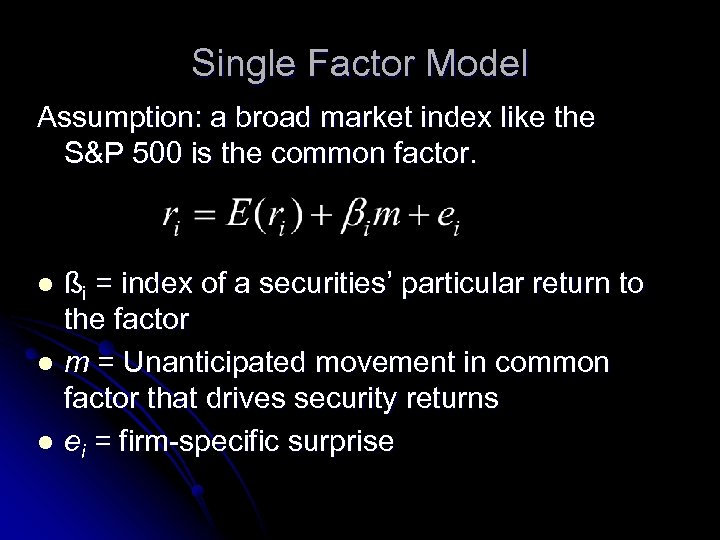 Single Factor Model Assumption: a broad market index like the S&P 500 is the common factor. ßi = index of a securities’ particular return to the factor l m = Unanticipated movement in common factor that drives security returns l ei = firm-specific surprise l
Single Factor Model Assumption: a broad market index like the S&P 500 is the common factor. ßi = index of a securities’ particular return to the factor l m = Unanticipated movement in common factor that drives security returns l ei = firm-specific surprise l
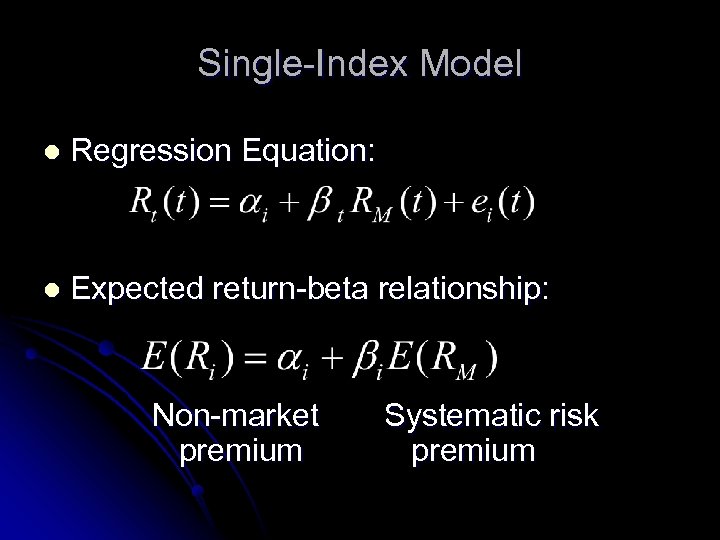 Single-Index Model l Regression Equation: l Expected return-beta relationship: Non-market premium Systematic risk premium
Single-Index Model l Regression Equation: l Expected return-beta relationship: Non-market premium Systematic risk premium
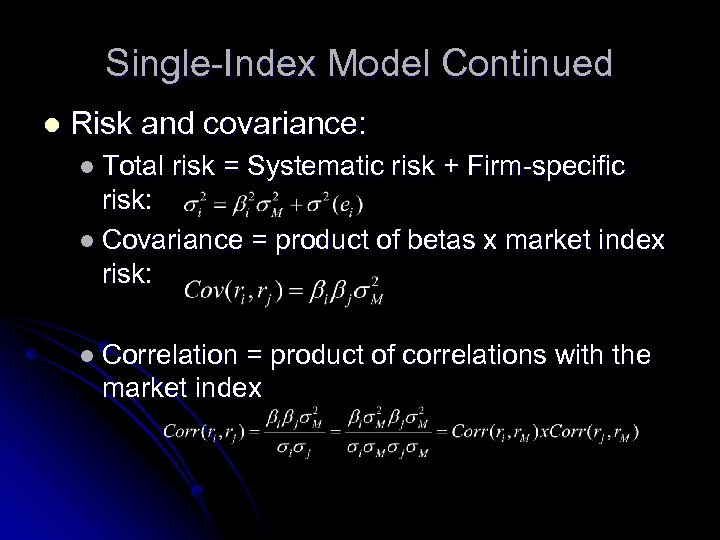 Single-Index Model Continued l Risk and covariance: l Total risk = Systematic risk + Firm-specific risk: l Covariance = product of betas x market index risk: l Correlation = product of correlations with the market index
Single-Index Model Continued l Risk and covariance: l Total risk = Systematic risk + Firm-specific risk: l Covariance = product of betas x market index risk: l Correlation = product of correlations with the market index
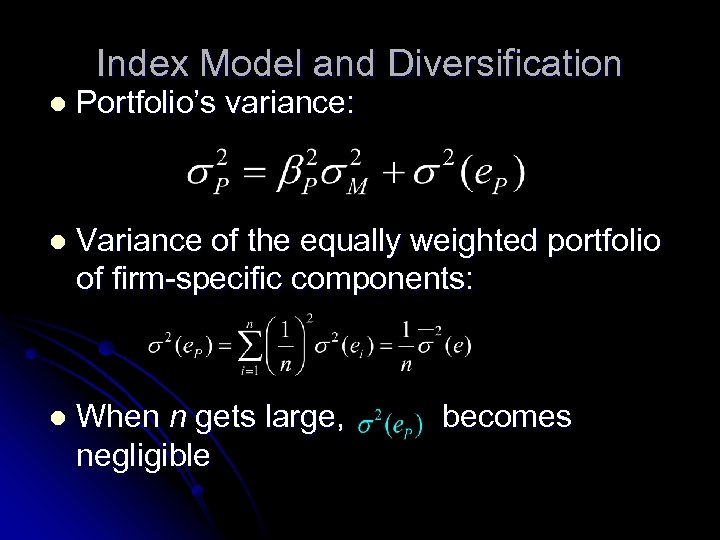 Index Model and Diversification l Portfolio’s variance: l Variance of the equally weighted portfolio of firm-specific components: l When n gets large, negligible becomes
Index Model and Diversification l Portfolio’s variance: l Variance of the equally weighted portfolio of firm-specific components: l When n gets large, negligible becomes
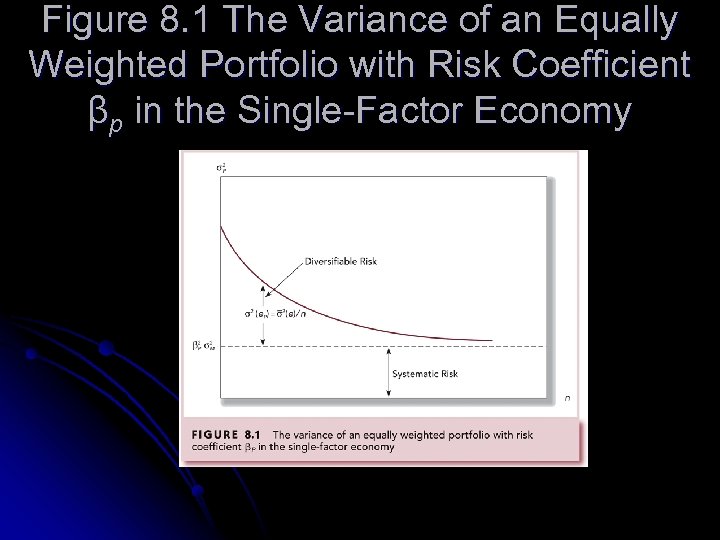 Figure 8. 1 The Variance of an Equally Weighted Portfolio with Risk Coefficient βp in the Single-Factor Economy
Figure 8. 1 The Variance of an Equally Weighted Portfolio with Risk Coefficient βp in the Single-Factor Economy
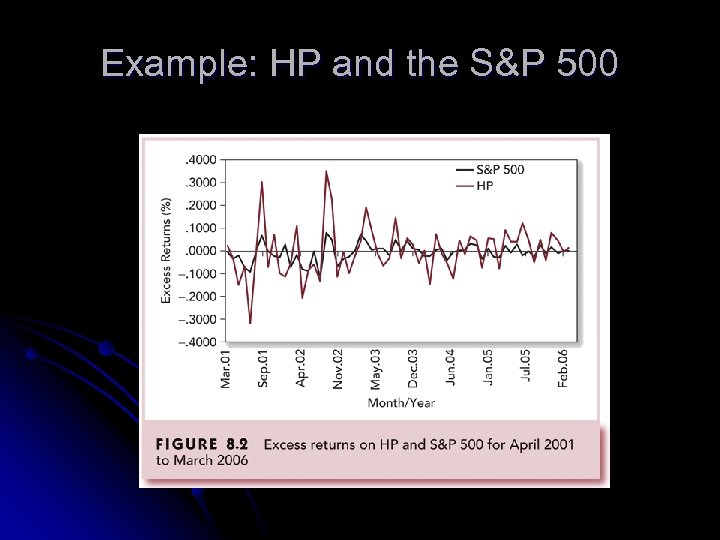 Example: HP and the S&P 500
Example: HP and the S&P 500
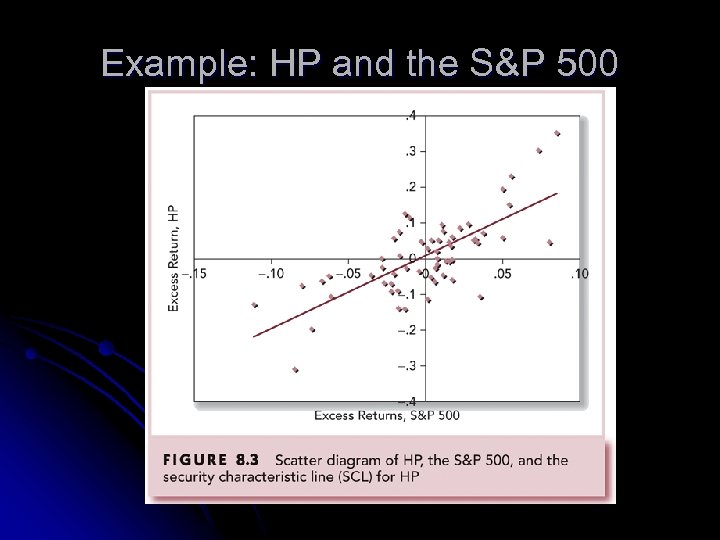 Example: HP and the S&P 500
Example: HP and the S&P 500
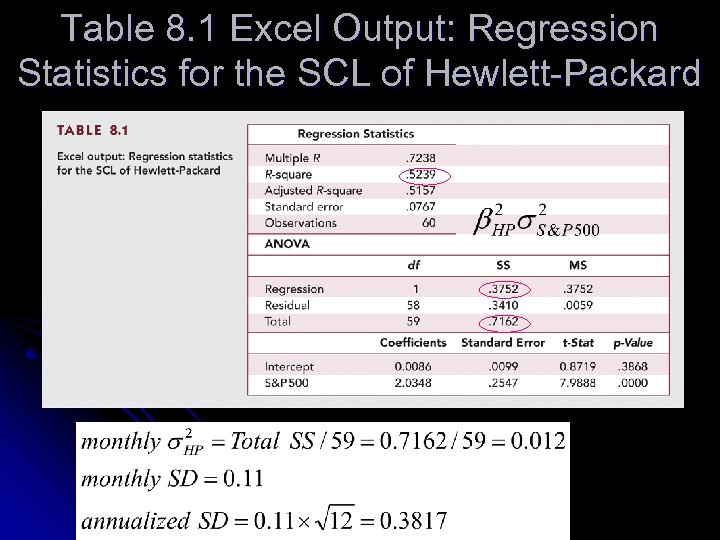 Table 8. 1 Excel Output: Regression Statistics for the SCL of Hewlett-Packard
Table 8. 1 Excel Output: Regression Statistics for the SCL of Hewlett-Packard
 Figure 8. 4 Excess Returns on Portfolio Assets
Figure 8. 4 Excess Returns on Portfolio Assets
 Alpha and Security Analysis Macroeconomic analysis is used to estimate the risk premium and risk of the market index l Statistical analysis is used to estimate the beta coefficients of all securities and their residual variances, σ2 ( e i ) l Developed from security analysis l
Alpha and Security Analysis Macroeconomic analysis is used to estimate the risk premium and risk of the market index l Statistical analysis is used to estimate the beta coefficients of all securities and their residual variances, σ2 ( e i ) l Developed from security analysis l
 Alpha and Security Analysis The market-driven expected return is conditional on information common to all securities l Security-specific expected return forecasts are derived from various security-valuation models l The alpha value distills the incremental risk premium attributable to private information l Helps determine whether security is a good or bad buy l
Alpha and Security Analysis The market-driven expected return is conditional on information common to all securities l Security-specific expected return forecasts are derived from various security-valuation models l The alpha value distills the incremental risk premium attributable to private information l Helps determine whether security is a good or bad buy l